
Sarcoidosis
Dr.Kassim.sultan
F.R.C.P

Definition:
•Multi systemic inflammatory disease characterized by the
presence of non caseating granulomas , of unknown cause.
•occurs in young, otherwise healthy adults.
•Women appear to be slightly more susceptible than men.
•At least 5% of patients with sarcoidosis will have a family
member with sarcoidosis.

Pathology:
•noncaseating granulomas are caused by increased local
fibroblast stimulation and hence fibrosis
•Mediastinal & superficial lymphadenopathy.
•lung is most commonly affected. Other organs commonly
affected are the liver, skin, and eye.
•recent studies show higher incidence of mycobacterial
catalase-peroxidase protien in granuloma.

Clinical Manifestations:
•1/3 of patients are asymptomatic(discovered on
screening CXR).
•Respiratory complaints including cough and dyspnea
are the most common presenting symptoms.
•Nonspecific constitutional symptoms include fatigue,
fever, night sweats, and weight loss.

Skin manifestations:
•Skin involvement is eventually identified in over a third of
patients with sarcoidosis.
•The classic lesions include Erythema nodosum,
maculopapular lesions, hyper-& hypopigmentation, keloid
formation& subcutaneous nodules.
•specific complex of involvement of the bridge of the nose,
the area beneath the eyes, and the cheeks is referred to as
lupus pernio(chronic sarcoidosis).

Eye manifestations:
•Anterior uveitis, over 1\4 of patients.
•Red eye.
•photophobia, blurred vision.
•Posterior uveitis, choroidal nodule, papilledema.

Neurologic manifestations:
•is reported in 5–10% of patients(Any part of the
Central Nervous System or Peripheral Nervous System
can be affected).
•Optic neuritis ,peripheral neuropathy,bilateral facial
palsy,parkinsonism&meningeal involvement.

Other manifestations:
•20–30% of patients will have liver involvement(portal
hypertension)
•myalgias and arthralgias.
•Hypercalcemia &/or hypercalciuria occurs in 10% of
patients leading to nephrocalcinosis & bone cyst.

Diagnosis:
•FBC&ESR( anemia, lymphopenia, pancytopenia)
•Chest x-ray: staging:
Stage 0
Normal
Stage I Hilar lymphadenopathy
Stage II
Hilar lymphadenopathy and parenchymal infiltrate
Stage III
Parenchymal infiltrate
Stage IV
Fibrosis
•Increase serum ca++& urine ca++.
•Elevated levels of ACE,but not specific.
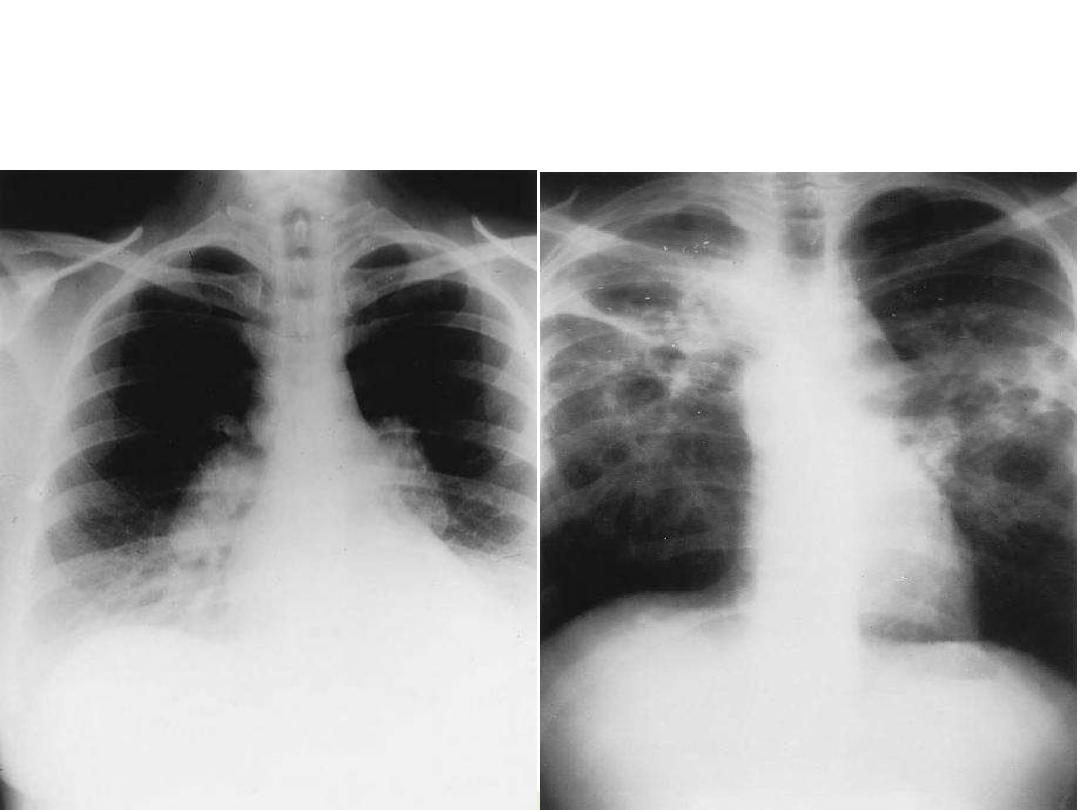
Chest radiographs of pulmonary sarcoidosis. A. Stage II sarcoidosis pattern with
prominent, discrete ‘‘standaway” hilar nodes, right paratracheal adenopathy, and fine
reticulonodular infiltrates.
B
. Fibrocystic sarcoidosis with extensive scarring, bullous
and cystic changes, hilar retraction, and parenchymal infiltrates.
A

Diagnosis :
•Tuberculin test,almost always –ve.
•PFT show restrictive defect.
•CT scan show mediastinal lymphadenopathy.
•Kviem-Siltzbach procedure is a specific Diagnostic test for
sarcoidosis. An intradermal injection of specially prepared
tissue derived from the spleen of a known sarcoidosis patient
is biopsied 4–6 weeks after injection. If noncaseating
granulomas are seen, this is highly specific for the diagnosis of
sarcoidosis.
•Bronchoscopy &BAL: show lymphocytosis).
•Biopsy OF the affected organ.

Management:
•Acute disease:observation,if no to minimal symptoms
without cardiac,neurological,ocular,calcium abnormality.
•Chronic disease: systemic treatment with glucocorticoid e.g
prednisone 20-40mg,taper dose within 6months to 7.5-
10mg&continue.
•If steroid toxicity or no response use methotrexate or
azathioprine as steroid sparing agents
•Hydroxychloroquine 200-400mg for skin&musculoskeletal
manifestations.
•ifliximab,thalidomide,cyclophosphamide if other treatments
fail to cure the disease.
•Topical steroids for eye manifestations only.

Differential diagnosis:
•Pulmonary Tuberculosis(caseating granuloma,+ve
AFB).
•Lymphoma
•Berylliosis
•Fungal infecation e.g:histoplasmosis
•Hypogammaglobulinaemia and recurrent infections.

Complications:
•blindness, paraplegia, or renal failure.
•Heart failure& ventricular arrhythmia from diffuse
cardiac muscle involvement.
•Mycetoma with massive hemoptysis.
•Pulmonary arterial hypertension is reported in at
least 5% of sarcoidosis patients.

Infiltrative interstitial lung disease include a wide variety of
different rare disease that cause fibrotic inflammatory
changes in parenchymal and interstitium of the lung.
Usually restrictive defect in pulmonary function test and
type 1 respiratory failure.
For diagnosis open lung biopsy may be needed.
Treatment according to the cause and lung transplant may be
needed.

Thanks for your listening
