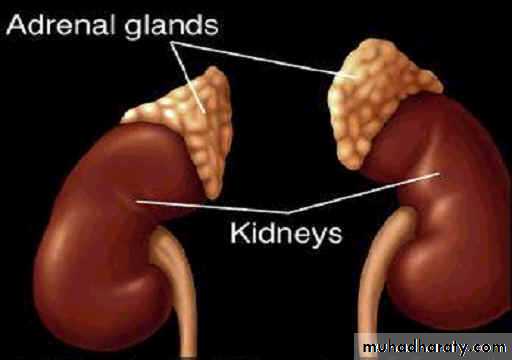
ADRENAL GLANDS
• Objectives• At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to:
• Describe the anatomy of adrenal glands.
• State the synthesis and secretion of adrenal hormones.
• Explain the functions of the adrenal hormones.
• Identify the pharmacological actions and therapeutic principles of corticosteroids.
• List the side effects of steroid abuse.
• Recognize the importance of steroid tapering after prolonged use.
Anatomy and Function
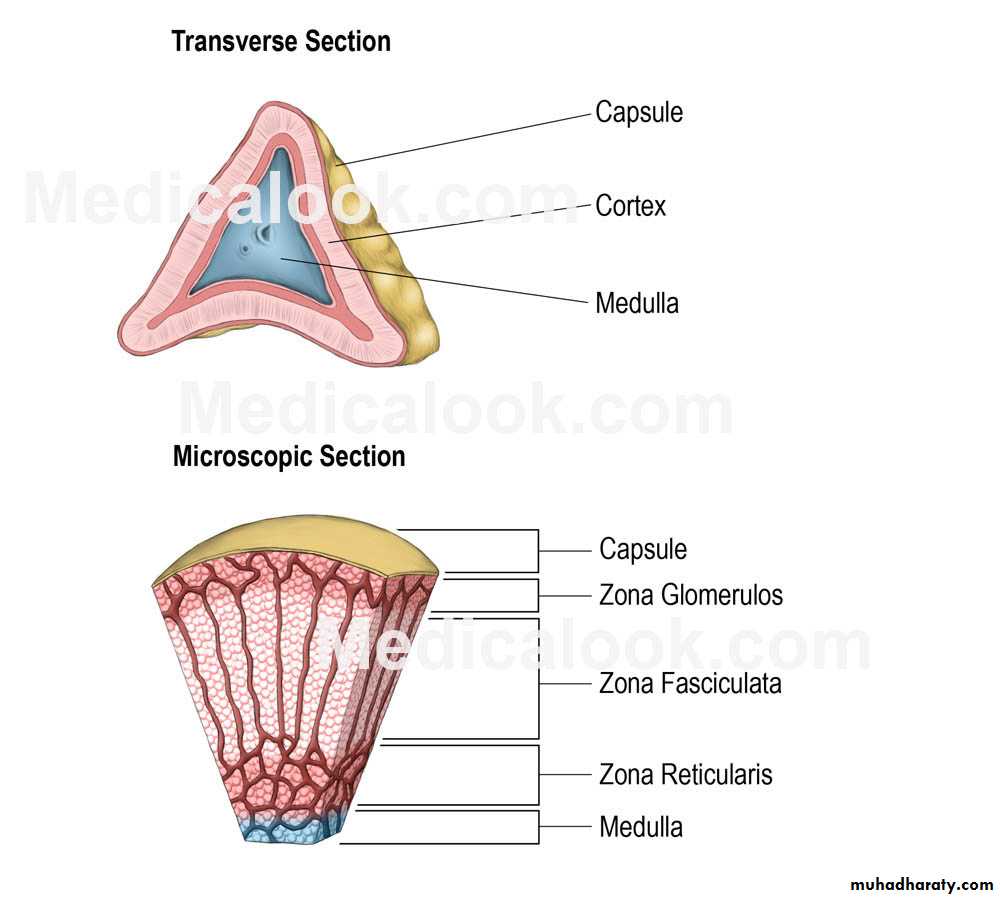
CapsuleCortex (outer) has 3 zones:
1- Zona glomerulosa : mineralocorticoids, mainly aldosteron, responsible for the regulation of BP. It affects the distal convoluted tubule and collecting duct of the kidney (increased reabsorption of Na + and excretion of both K + and H + ions.
2- Zona fasciculata: glucocorticoids, such as
11-deoxycorticosterone, corticosterone, and cortisol in humans.
3- Zona reticularis: produces androgens, mainly dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), DHEA sulfate (DHEA-S), and androstenedione (the precursor to testosterone) in humans.
Medulla (core of the gland)
It secretes norepinephrine and epinephrine. Catecholamines (aa tyrosine ), water-soluble, the major hormones underlying the fight-or-flight response.Receives input from the sympathetic nervous system through preganglionic fibers originating in the thoracic spinal cord from T5–T11.
Cortisol also promotes epinephrine synthesis.
History
1855 – Addison's disease
1856 – Adrenal glands essential for life
1930 – Cortex > medulla
1932 – Cushing’s syndrome
1949 – Steroids in rheumatoid arthritis
1952 – Aldosterone
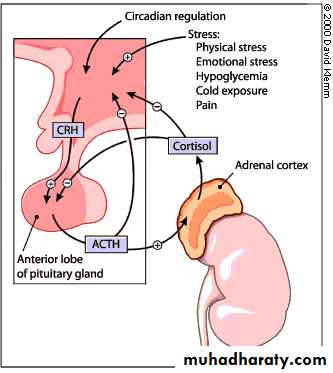
• Basal secretions
• Group• Hormone
• Daily secretions
• Glucocorticoids
• Cortisol
• Corticosterone
• 5 – 30 mg
• 2 – 5 mg
• Mineralocorticoids
• Aldosterone
• 11- deoxycorticosterone
• 5 – 150 mcg
• Trace
• Sex Hormones
• Androgen
• Progestogen
• Oestrogen
• DHEA
• Progesterone
• Oestradiol
• 15 – 30 mg
• 0.4 – 0.8 mg
• Trace
Cholesterol
PregnenoloneProgesterone
Corticosterone
11-Desoxy-corticosterone18-Hydroxy- corticosterone
ALDOSTERONE
17-α- Hydroxy pregnenolone
11- Desoxy- cortisol17- Hydroxy progesterone
21,β hydroxylase
CORTISOL
11,β hydroxylaseDehydro-epi androsterone
Andro-stenedione
Oestrone
OestriolTESTOSTERONE
OESTRADIOLACTH
Pharmacological Actions• Carbohydrate
• Protein
• Lipid
• Electrolyte & water
• CVS
• Sk. Muscle
• CNS
• Stomach
• Blood
• Anti-inflammatory
• Immunosuppressant
• Respiratory system
• Growth & Cell Division
• Calcium metabolism
Actions: Carbohydrate and protein metabolism
Gluconeogenesis ( in early fasting)
Peripheral actions (from AA, glycerol, lactate)
Hepatic actions ( glycogenolysis by passive influence on glucagon and activation of glycogen phosphorylase)
Peripheral utilization of glucose
Glycogenesis ( increase glycogen deposition in liver from unused glucose in late fasting) by activation of hepatic glycogen synthase.
Proteolysis and muscle wasting.
Negative nitrogen balance & hyperglycemiaRedistribution of Fat
Buffalo humpSupraclavicular fat
Moon face
Stimulation of fat breakdown in adipose tissue
Actions: Lipid metabolism
Cortisol sodium and water absorption and potassium excretion in the intestines.
Aldosterone is more important, acts on D.T. & C.D. of kidney
Na+ reabsorption
Urinary excretion of K+ and H+
Actions: Electrolyte and water balance
Actions: Cardiovascular systemRestrict capillary permeability
Maintain tone of arterioles
Enhance myocardial contractility
Hypertension
Addison's disease: weakness & fatigue is due to
Prolonged use:Actions: Skeletal Muscles
Needed for maintaining the normal function of Sk. muscleinadequacy of circulatory system
Steroid myopathy
Direct:
Mood
Cortisol works with epinephrine to create memories of short-term emotional events; this is the proposed mechanism for storage of flash bulb memories.
Actions: CNS
ICP (pseudotumor cerebri) - RareAggravate peptic ulcer. May be due to
Acid & pepsin secretionImmune response to H.Pylori
Actions: StomachRBC: Hb & RBC content
(erythrophagocytosis )WBC: Lymphocytes, eosinophils, monocytes,
basophilsActions: Blood
Recruitment of WBC & monocyte- macrophageinto affected area & elaboration of chemotactic
substances
Lipocortin
Production of IL12, (INF)- gamma and alpha, (TNF)- alpha from phagocytic cells and (Th)1 cells.
Upregulate IL4, 10, 13 by Th 2 cells.
Response of T cell to IL1 so unable to produce IL2.
Formation of Plasminogen Activator
Fibroblastic activity
Expression of cyclooxygenase II
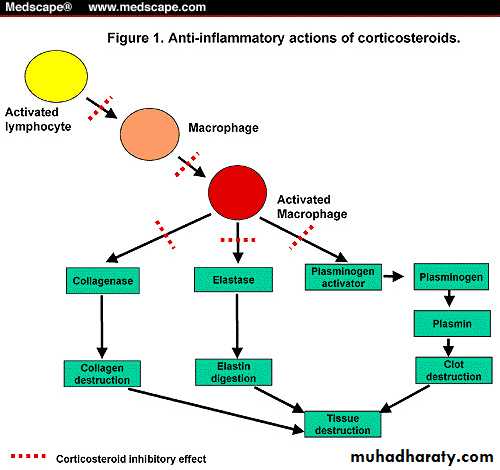
Actions: Anti-inflammatory
PhospholipidsArachidonic acids
lipoxygenase
Cycylooxygenase
Leukotriene
Prostaglandins,
Thromboxane
Prostacyclins
Phospholipase A2
Lipocortin (it supresses Phospholipase A2)
Corticosteroids
Anti-inflammatory actions of corticosteroids
Corticosteroid inhibitory effectImmunosuppressive & anti-allergic actions
Suppresses all types of hypersensitivity & allergic phenomenon.At High dose: Interfere with all steps of immunological response.
Causes greater suppression of CMI (graft rejection & delayed hypersensitivity).
Transplant rejection: antigen expression from grafted tissues, delay revascularization, sensitization of T lymphocytes.
Inhibit cell division or synthesis of DNA.
Delay the process of healing.Retard the growth of children.
Actions: Growth & Cell division
Intestinal absorption
Renal excretion
Excessive loss of calcium from spongy bones (e.g., vertebrae, ribs )
Actions: Calcium metabolismNot bronchodilators
Most potent and most effective anti-inflammatory.Effects not seen immediately (delay 6 or more hrs).
Inhaled corticosteroids are used for long term control.