
SUPPURATIVE AND ASPIRATION PNEUMONIA
&PULMONARY ABSCESS

Upon completion of this lecture the students will
be able to :
Define suppurative and aspiration pneumonia
&pulmonary abscess and bronchiectasis
To know their etiological causes
Describe their clinical features
Illustrate ways of diagnosis
Management of suppurative and aspiration
pneumonia &pulmonary abscess and
bronchiectasis
Objectives:

DEFINITION
suppurative pneumonia:destruction of the lung
parenchyma by inflammatory processµ
abscesses formation
lung abscess is localized large collection of pus or
cavity usually morethan 2cm lined by chronic
inflammatory tissue from which pus has escaped
by rupture into a bronchus.
inhalation of septic material,tend to localize in
dependent areas of lung in 50%(apical segment
of lower lobe&posterior segment of upper lobe).

AETIOLOGY
1-aspiration:
A-reduced level of consciousness due to
CVA,alcoholism,drug abuse,general anesthesia.
B-dysphagia,achalasia,foreign body,nasogastric
tube,endotracheal tube.
2-gingivitis,sinusitis,bronchiectasis may result in
lung abscess
3-infection in lung infarction.
4-infection with virulent microorganism like
klebsiella&staph.aureus

CLINICAL FEATURES
symptoms
Acute:fever,cough,malaise,pleurisy
Chronic:Cough productive of large amounts of sputum
which is sometimes fetid and blood-stained,low grade
fever,malaise,anemia,weight loss, Sudden
expectoration of copious amounts of foul sputum
occurs if abscess ruptures into a bronchus .
signs
High remittent pyrexia
Profound systemic upset
Digital clubbing may develop quickly (10-14 days)
Chest examination usually reveals signs of consolidation;
signs of cavitation are rarely found
Pleural rub is common

DIAGNOSIS
Clinical features
sputum& blood for culture&sensitivity.
Sputum for AFB.
CXR: A large, dense opacity, which may later cavitate
and show a fluid level, is the characteristic finding
when a frank lung abscess is present.
CT scan also show acavity&fluid level
Bronchoscopy to exclude obstruction by foreign
body,tumor or lymph node.

recently MRSA are isolated which produce the toxin
panton-valentine lukocidin,which cause rapidly
progressive severe necrotizing pneumonia.
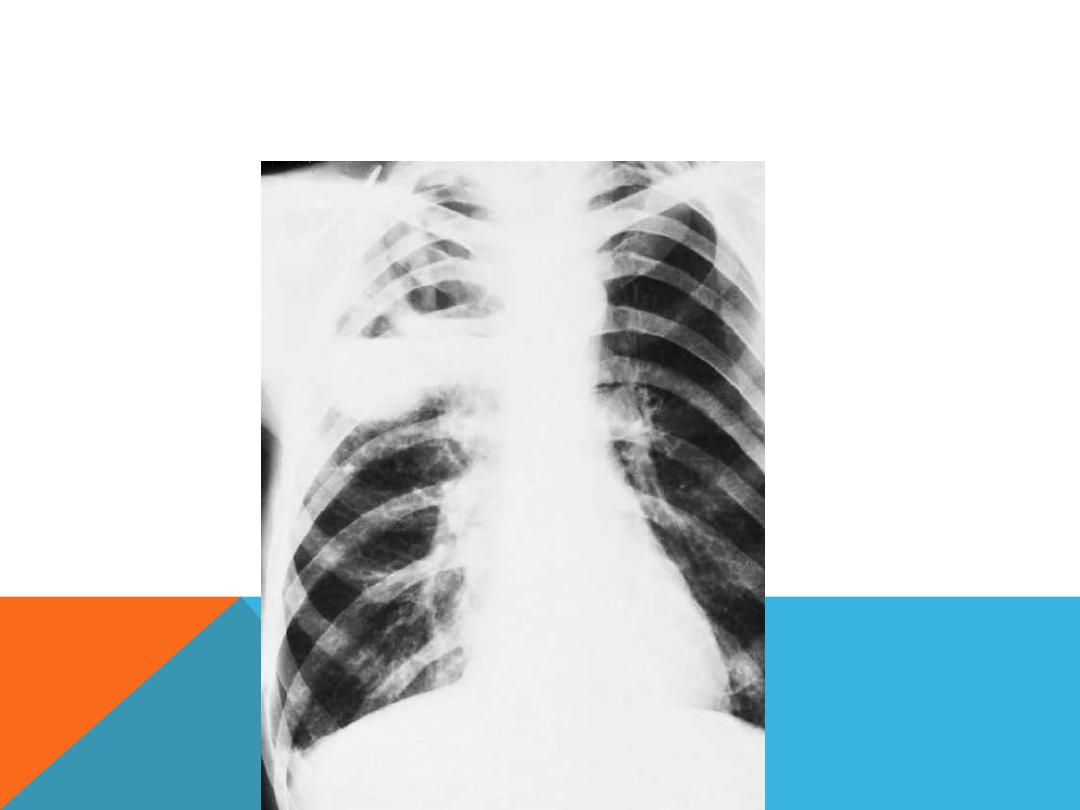
anaerobic pneumonia with abscess formation in a 48-year-old
alcoholic man. the abscesses are located in the posterior segment
of right upper lobe,pa view
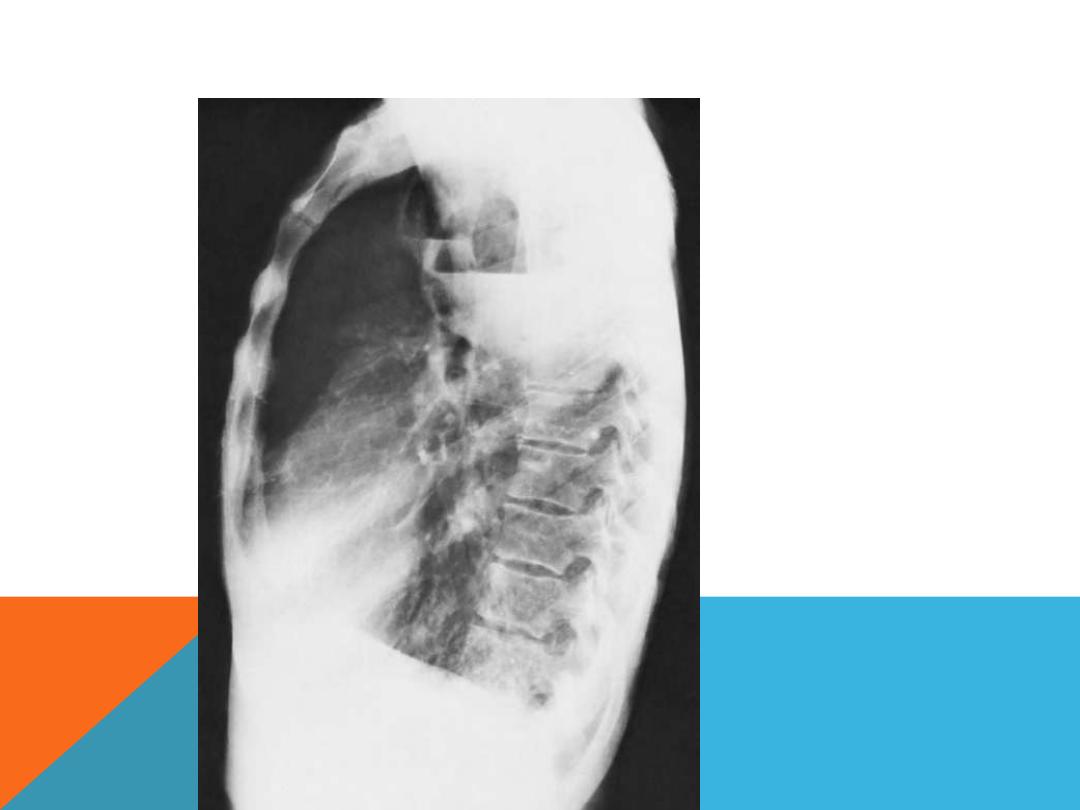
the same patient,lat.view

TREATMENT
1-antibiotics:according to culture & sensitivity
co-amoxiclav 1.2g 8hrly i.v.
If an anaerobic bacterial infection is suspected (e.g.
from fetor of the sputum),metronidazole 400 mg
8-hourly i.v should be added.
MRSA is treated by clindamycin 600mg 6hrly i.v
prolonged Rx for 4-6 wk(2 weeks via i.v route,then
continue on oral route) is required for lung
abscess or even longer.
2- physio Rx especially in large
abscesses&abscesses of upper lobes.

TREATMENT/CONTINUE
3-surgery should be considered in treatment failure
or complication like bronchiectasis.
4-bronchoscopic removal of materials obstructing
bronchi.

PROGNOSIS
Mortality rate is 5-10%
Poor prognostic criteria:
1-larg abscess more than 6cm.
2-underlying obstructive tumor.
3-immunocomporomised patients.

COMPLICATIONS
Empyema&pyopneumothorax.
Amyloidosis.
Brain&systemic abscesses.

Thanks for your listening
