Antibiotic
Lecture ThreeCephalosporin
• Chemical structure.• Mechanism of action .
• Toxicity.
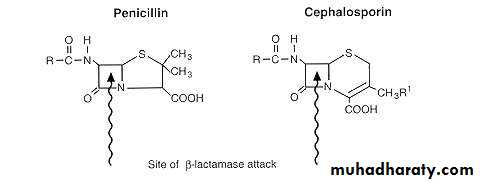
They are more stable than penicillin to many bacterial β- Lactamase, so they have broader spectrum of activity. It more susceptibility to B- lactamases .
β
Cephalosporin
Mechanism of action:Inhibition of cell wall synthesis.
Bactericidal
types of Cephalosporin
Classified according to bacterial susceptibility and resistance to β- Lactamase into :
a
First generation
cephalexin (Keflex)
Cefadroxil
cefazolin
Second generation
cefaclor (Ceclor)cefoxitin (Mefoxin)
cefotetan
cefuroxime
Third generation
-cefdinir
ceafixime (Suprax)
ceftriaxone (Rocephin)
cefotaxime(claforan)
Fourth generation
cefepime (Maxipime)First generation
BactericidalGood activity against gm+ve bacteria
Modest activity against gm-ve bacteria
Most mouth anaerobes are sensetive
cephalexin (Keflex)
Cefadroxil
cephalothin
Cefazolin( IV)
First generation
.Cephalexin(oral)500mg every 6hoursCefadroxil(oral) 500mg-1gm twise dialy.
,Cephalothin(oral), Cefazolin(parentral)0.5-2gm every 8 hours
used as a single prophylaxis dose prior to surgery because of its 1.8-hour half-life and its active against most PnG sensitive microorganisms and penicillinase-producing S. aureus.However, additional intraoperative cefazolin doses may be required if the surgicalprocedures, including orthopedic surgery because of its ability to penetrate bone..
Cephalexin
Similar in spectrum to cefazolin but less active against H.influenza.t1/2 60 min.
Use in dentistry as an alternative to amoxicillin.
250-500 cap.orally every 6 hour.
Cefadroxil
Activity and indication similar to cephalexin has good tissue penetration in alveolar bone
Can be given 12 hourly
Excreted unchanged
Can be use in density.
USES OF first generation
TonsillitisPhyringitis
Urinary tract infection
skin infection (Cellulites).
soft tissue abscess
Cephalosporins
Second generation-e.g cefaclor(oral),cefuroxime and cefoxitin(im.iv)
-have grater activity against gm-ve microorganism : H . Influenza ,meningococci Enterobacter aerogenosa some Neisseria Sp
Bactericidal (gram(+) & and more active against gram (-) with some anaerobic
Second generation
Cefaclor more active against gram -ve and anaerobic found in oral cavity and giving orally but diminshed use bec.of hydrolysis by B-Lactamase.Cefoxitin used in treatment of obstetric/surgical infection, lung abscess giving i.m,i.v. every 6-8 hours.
Second generation
Cefuroxime its more active against gram –ve B-lactamase organism and H.influenzae also has activity on gram +ve cocci and certain anaerobic
Giving i.m and used in meningitis and gonorrhoea..
Cephalosporins
Third generationCefixime
Cefdinir
Ceftriaxone
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Cefoperazone
Increase activity against gram (-)
more activity against beta-lactamase-producing microbial strains and some inhibit psedumonas.
Third generation
Cefixime 400 mg(orally once daily)or 200mg twise dialy(suprax)Cefdinir 300 mg cap twice daily
Ceftriaxone ,1gm once daily(IM,IV)longer t1/2(8hour)
Cefotaxime 1gm once dialy(IM,IV)
Ceftazidim(pseu.aer) injection every 8-12 hours
Cefoperazone(pseu.aeru+S.typhi and B.fragilis)
Third genaration
Third genaration used in serious infections including
Pneumonia
Immunocompramised patient for sepsis
UTI infection
ENTand skin infection
Uses of Third generation
Respiratory tract infection(chronic bronchitis)septicaemias.
Gonorrhoea
Typhoid
ceftriaxone or cefotaxime are effective in the treatment of neonatal and childhood meningitis caused by H. influenzae(high CSF level).
Cephalosporin
Fourth generationCefepime useful for treatment of serious infection in hospitalized infection.
have extended activity
Administered parentally .
Affected against streptococci , staphylococci,
gram (-)E.Coli, p.aeruginsa.
Cross CSF
Pharmacokinetics
Administration: Many of the cephalosporins must be administered IV or IM of their poor oral.Distribution: All cephalosporins distribute very well into body fluids. However, adequate therapeutic levels in the CSF..
All cephalosporins cross the placenta.
. Elimination occurs through tubular secretion and/or glomerular filtration .Therefore doses must be adjusted in cases of severe renal failure to guard against accumulation and toxicity.
Ceftriaxone and Cefoperazone is excreted through the bile
into the feces and, therefore, is frequently employed in patients withrenal insufficiency.
Cephalosporins side effects:
1- Allergic : patient have anaphylactic shock to P should not received cephalosporin ( Cross sensitivity between cephalosporin's and penicillin) because are chemically similar penicillin.2- Disulfiram – like effects , if taken with alcohol it block alcohol oxidation and lead to accumulation of acetaldehyde
3- bleeding (hypoprothrombinaemia)overcome by giving vit K 10mg twice weekly.(some of third generation)
4-IM painful, IV cause thrombophilibitis.
.
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
Carbapenems e.g (imipenem):
Broad spectrum, it is effect against Penicillinase producing
gram-positive and gram-negative, anaerobes and Pseudomonas aeruginosa, (Bactericidal ) used
In serious hospital acquired infections.
it administer I.V, penetration of CSF therefore used to treat Meningitis when inflamed .
UTI
Lower respiratory tract infection
Abdominal and gynecological infection
Skin, soft tissue, bone, joints infections
• Mechanism of action
– Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesisSide effect
Nausea , vomiting , diarrhea , , some time Cause seizers , Allergy,
Antibiotic-associated colitis
Other β-lactam Antibiotics
MonobactamAztreonam (Azactam)
Mechanism of action
Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
Bactericidal : against Enterobacteria and also against gram –ve rods but lack activity against gram +ve and anaerobic MO .
it administer I.V or IM, it may cause skin rash , some time abnormal liver function test ,
, it use as alternative to P and C in patient allergic to them .
Other β-lactam antibiotics
β-lactamase inhibitors
those are certain molecules that can inactivate β-lactamases due to hydrolysis of the ring either by enzyme cleavage with β-lactamase or by acid destroy the antimicrobial activity of β-lactam antibiotic..
They include :
1-clavulanic acid:
-irreversibly bind to β-lactamase of gm+ and gm- microorganisms-it is combined with amoxicillina for oral administration (Augmenten)dose,375,625,1000mg.
-it is combined with ticarcillin for parentral administration (timentin)
2- sulbactam: which is combined with ampicillin for i.v and i.m use (unasyn)
3-Tazobactam which is combined with piperacillin for parenteral preparation(Zosyn)
Other agents effect on cell wall glycopeptide
1- Vancomycin:Mechanism:inhibits synthesis of bacterial cell wall phospholipids as well as peptidoglycan thus weakening the cell wall and damaging the underlying cell membrane.
It effective primarily against gram-positive organisms It has been lifesaving in the treatment of MRSA and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis (MRSE) infections as well as enterococcal infections.
uses
severe infections with resistant gram + organisms
Vancomycin + Gentamycin shows synergy against mixed infectionsin
Used individual with prosthetic heart valve
Inflammation allowed penetration into meanings
Patient who have allergy to the B.lactam.in enterococcal endocarditis.
Diphtheria.
pkarmacokinetic
Slow IV infusion is employed for treatment of systemic infections or for prophylaxis. Because vancomycin is not absorbed after oral administration,Orally employed only for the treatment of antibiotic-induced colitis due to C. difficile when metronidazole has proven to be ineffective..
It often combine vancomycin with other antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone for synergistic effects when treating meningits.
. The normal half-life of vancomycin is 6 to 10 hours,
Adverse effect
1- fever , chills, phlebitis at infusion site , flushing (red mansyndrome ) and shock due to histamine release
2-Dose relating hearing loss occur in patient with renal failure
3- Ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity are common when vancomycin
and aminoglycoside administer together .
Antibiotic
Lecture Four