Karyotype and Molecular Features
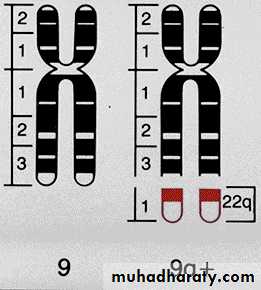
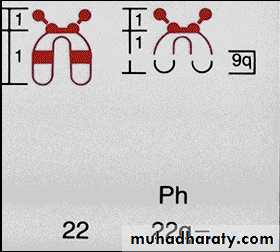
• The vast majority of CML show the Philadelphia (Ph+) chromosome* in (90-95%) and M-BCR-ABL p210 in (99% of patients), these two discoveries in 1960 & 1986 respectively are important landmarks.• *Ph chromosome is a minute chromosome 22 from which the long arms are deleted (22q-). It is part of reciprocal translocation between chromosome 9 & 22 t(9; 22)(q34; q11) in which part of 22 is clearly visible on 9 but the part of 9 on 22 is too small to be distinguished cytogenetically. This translocation is detected by PCR or FISH techniques
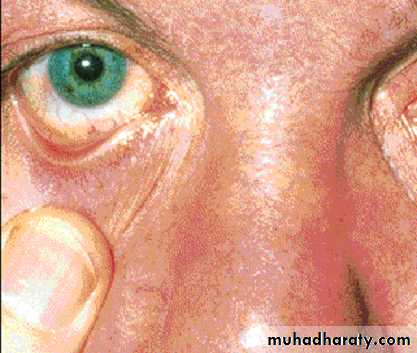
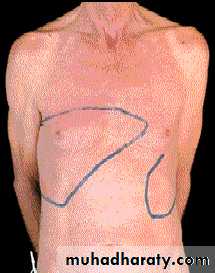
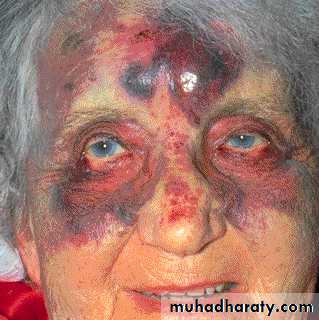
Conjunctival suffusion Hepatosplenomegaly
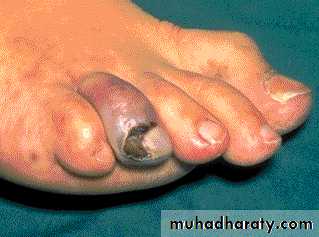
Essential Thrombocythemia Hemorrhage after minor trauma due to platelet dysfunction Gangrene of the toe
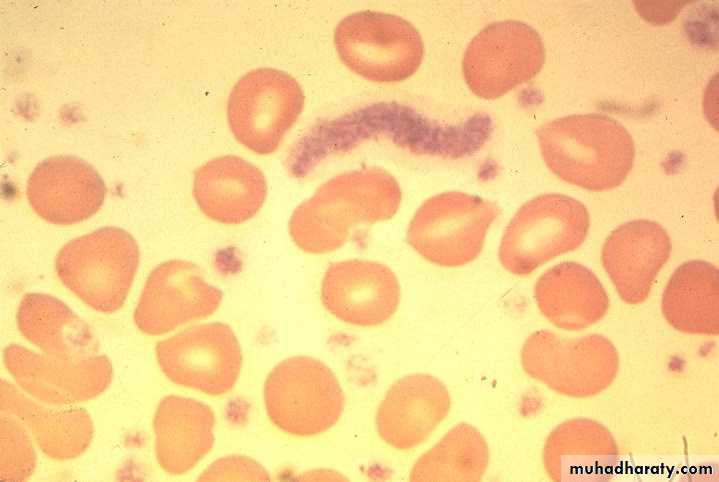
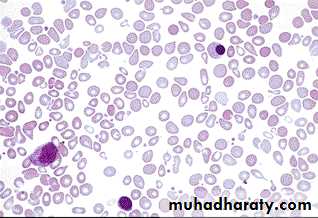
Essential thrombocythemia blood film
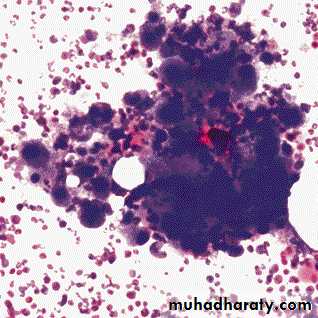
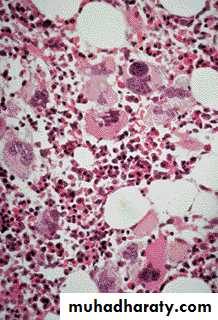
Essential thrombocythemia BMA (Left), BMB (Right)
Laboratory Findings: MF BF: Tear drop cells with leukoerythroblastic blood picture
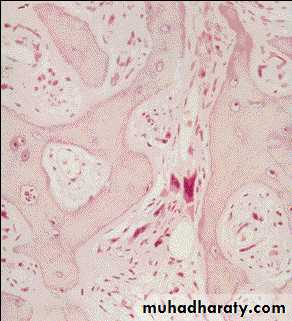
Myelofibrosis BM biopsy in advanced disease
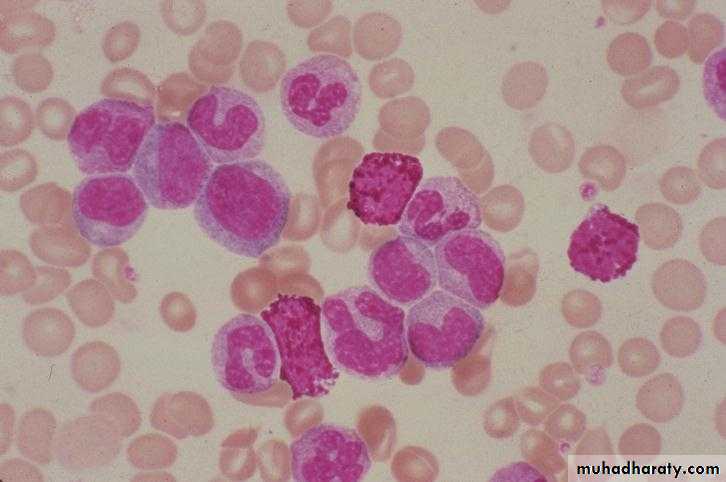
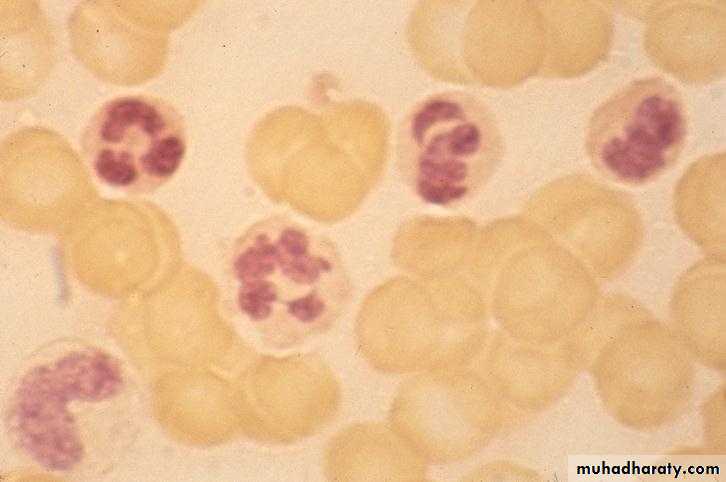
OsteoMF, replacement by fibrous connective tissue with thick bone trabeculaeBlood Film in CML - CP showing broad spectrum of granulocytic cells in various stages of maturation (Promyelocytes, myelocytes, metamyelocytes, neutrophils basophils and a monocyte)
Laboratory Findings:
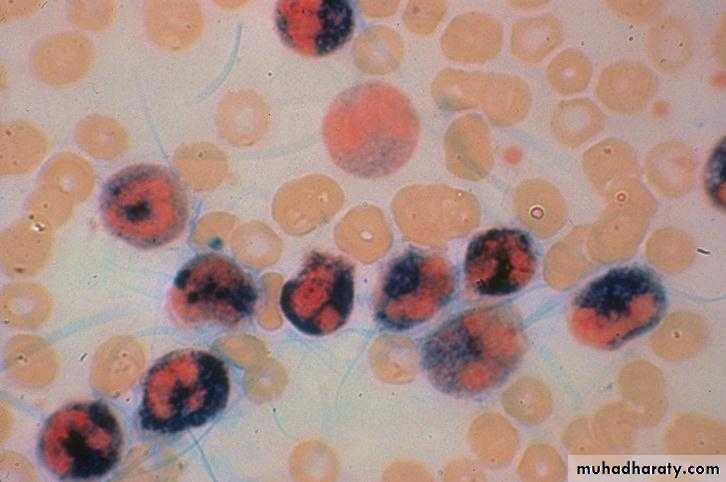
Absent NAP score (it is low or absent in about 95% of CML cases)Increased NAP score, as is seen by the dark staining reaction product in the neutrophils