
AFTER MID
Medicine
DR.محمد حنون
Nephrology
UTI
LEC: 3

MEDICINE
LEC.3
RENAL
حنون
محمد.د
UTI definition :
Multiplication of organisms in the urinary tract. It is usually associated
with the presence of neutrophils and > 100 000 organisms/ml in a
midstream sample of urine
Introduction:
-It is the most common bacterial infection in medical practice
- Incidence 50 000 / million persons / year
1-2 % of patients in primary care
- It is common in women (50%), the prevalence is about 3% at the age of 20,
Uncommon in males, except in the first year of life & over 60
- Common source of life-threatening G - ve septicemia
- Recurrent infection causes considerable morbidity;
- If complicated, it can cause ESRD (end stage renal disease)
UTI
Risk
Factors
- Incomplete bladder emptying;-
- Bladder outflow obstruction (e.g. benign prostatic hyperplasia, urethral
stricture)
- Neurological problems (e.g. multiple sclerosis, diabetic neuropathy)
- Gynecological abnormalities (e.g. uterine prolapse)

- Vesico-ureteric reflux
-
Foreign bodies
-Urethral catheter
-Ureteric stent
-After cystoscopy
-Loss of host defenses
- Atrophic urethritis & vaginitis in post-menopausal women
-Diabetes Mellitus
UTI Etiology and
pathogenesis
when the urinary tract is anatomically and physiologically normal and local and
systemic defense mechanisms are intact, bacteria are confined to the lower end of
the urethra.
Protective mechanisms
Neutrophil Activation
is essential for bacterial killing.
Urine osmolality and pH > 800 mOsm/kg and low or high pH reduce bacterial
survival.
Complement activation with IgA production from the uroepithelium.
Commensal organisms – (lactobacilli, bacteroides) Eradication by antibiotics or
by spermicidal jelly results in overgrowth of E. coli.
Urine flow and normal micturition wash out bacteria. While Urine stasis promotes
UTI.
Uroepithelium –Tamm-Horsfall proteins (in the mucus) covering uroepithelium,
have antibacterial properties. Disruption of this uroepithelium by trauma (e.g.
sexual intercourse or catheterization) predisposes to UTI
-UTI is most often due to bacteria from the patient's own bowel flora,
Transfer to Urinary Tract:

o Bloodstream & Lymphatics
o Direct extension (e.g. vesicocolic fistula),
o Ascending transurethral route (the most common)
o Colonization of the periurethral zone with pathogenic organisms.
o Urine is an excellent culture medium for bacteria;
o Uroepithelium of susceptible person may have more receptors to which
virulent strains of E. coli become adherent.
o In women > men
o relatively short urethra and
o absence of bactericidal prostatic secretions.
o Sexual intercourse may cause minor urethral trauma and transfer bacteria
from the perineum into the bladder.
o Instrumentation of the bladder may also introduce organisms. Multiplication of
organisms then depends on a number of factors, including the size of the
inoculum and virulence of the bacteria
Organisms causing UTI
Organism
Approximate frequency (%)
E.
coli and other 'coliforms‘’ from GIT
75 %
Proteus mirabilis
12%
Pseudomonous
Klebsiella aerogenes
*
Enterococcus faecalis *
Staphylococcus
10%
In hospital, E. coli still predominates; Klebsiella or streptococci are
more common than in the
community

Natural history
o Commonly it is an isolated
o In normal UTI, a persistent or recurrent infection seldom results in
serious kidney damage (uncomplicated UTI).
o Abnormal UT (with stones) & associated diseases such as DM made worse
with infection (complicated UTI).
o UTI, particularly (Proteus), may predispose to stone formation.
o The combination of infection and obstruction results in severe, rapid kidney
damage (obstructive pyonephrosis) and is a major cause of Gram-negative
septicemia
UTI the Spectrum of Presentations
- Asymptomatic bacteriuria
- Acute urethritis and cystitis
- Acute pyelonephritis
- Acute prostatitis
-Septicemia (usually Gram-negative bacteria)

Acute
urethritis
and
cystitis
Clinical Presentation
o Frequency Abrupt onset
o Dysuria (burning pain)
Scalding pain in the urethra during micturition
o Suprapubic pain during and after voiding.
o Urgency intense desire to pass more urine after micturition (due to spasm
of the inflamed bladder wall)
o Urine cloudy (milk like ) and have an unpleasant odor
o Hematuria microscopic or visible.
o Systemic symptoms are usually slight or absent. However, infection in
the lower urinary tract can spread up. With prominent systemic symptoms
with fever and loin pain suggest the presence of acute pyelonephritis and
in this case the patient becomes febrile and toxic.
UTI may also be present with
- (1) Minimal or no symptoms
- (2) Atypical symptoms such as
- abdominal pain,
-
Fever or

- Hematuria in the absence of frequency or dysuria
In small children, who cannot complain of dysuria, symptoms are often 'atypical'.
The possibility of UTI must always be considered in the fretful, febrile sick child who
fails to thrive.
UTI
Diagnosis
Definitive diagnosis (clinical features with findings in the urine).
- Urine dipstick
* Tests for nitrite-most urinary pathogens reduce nitrate to nitrite.
* Leucocyte esterase, suggesting the presence of neutrophils.
- Neutrophils present in the urine in symptomatic infections. (Urine taken
by suprapubic aspiration should be sterile, so the Presence of any
organisms is significant.)
If either test is positive, UTI is probable; if they are both negative, UTI is unlikely
Dipstick tests positive for both nitrite and leucocyte esterase are highly predictive of
acute infection (sensitivity of 75% and specificity of 82%).
UTI
Investigations
Urine C/S
is necessary, in patients with:-
- recurrent infection or
- after failure of initial treatment,
- during pregnancy, or
- susceptible to serious infection ( DM, immunocompromised with an indwelling
catheter)
In an otherwise healthy woman with a single lower UTI and no indications of a
complicated infection, urine culture prior to treatment is not mandatory.
Investigation•Culture of MSU/ suprapubic aspiration
•Micro ex, of urine for white and red cell

•Dipstick ex. for nitrite and leucocyte esterase •May substitute for micro,
C/S in uncomplicated infection.
•Dipstick ex. of urine for blood, protein and glucose . Full blood count •RFT
•RBG
•Blood culture•Pelvic examination Women with recurrent UTI
•Rectal examination Men to examine prostate
Renal ultrasound or CTto identify obstruction, cysts, calculi, indications are:
Infants, children, men after single
UTI Women who have
(1) Acute pyelonephritis;
(2) Recurrent UTI after antibiotic treatment;
(3) UTI or asymptomatic bacteriuria in pregnancy
Intravenous urogram (IVU):- Alternative to ultrasound, particularly to image the
collecting system after voiding
Micturating cysto-urethrogram (MCU) or radioisotope study to identify and
assess severity of vesico-ureteric reflux or impaired bladder emptying
Selected infants and children; to look for reflux and renal scars
Cystoscopy;-
Patients with hematuria or a suspected bladder lesion
May substitute for microscopy and culture in uncomplicated infection.
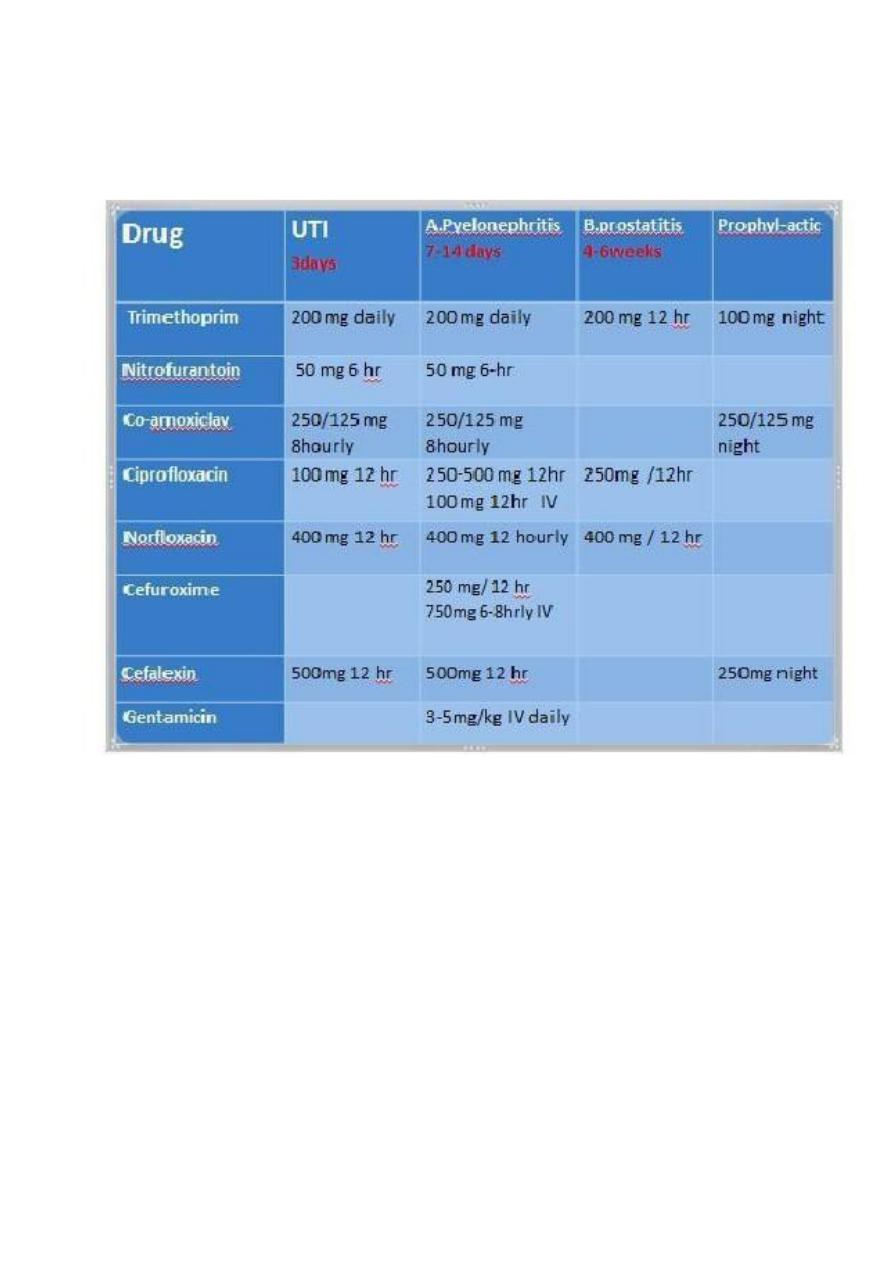
UTI
Treatment
-Antibiotics are recommended in all cases of proven UTI
-treatment to be started while awaiting the result of c/s.
-treatment for 3 days is the norm and is less likely to induce
antibiotic resistance than more prolonged therapy.
-Trimethoprim is the usual choice for initial treatment. 200 mg daily,
-Nitrofurantoin, 50mg 6 hourly.
(it is only used in UTI as it is completely excreted in urine and
it is so called urine antiseptic. Contraindicated in renal failure). Mentioned by the doctor
- Quinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin, and cefalexin are
also generally effective.

- Co-amoxiclav or amoxicillin should only be used when organism is known to be
sensitive.
- Penicillin and cephalosporins and aminoglyosides are safe to use in
pregnancy but trimethoprim, sulphonamides, quinolones and tetracycline
should be avoided.
- The treatment is modified after urine C/S, and/or the clinical response
- A fluid intake of at least 2 liters /day during treatment & for few /wk.
- Urinary alkalinizing (potassium citrate) may help symptomatically.
(except in proteus
infection as it causes alkaline media so do not give alkalinizing agents.(mentioned by the doctor)

Acute Pyelonephritis
-Classical Triad of - loin pain
*
, fever with tenderness over kidneys.
- Pathology –etiology;-
- Pelvis; Inflamed, parenchyma. Small abscesses, PMN infiltration.
- Route; - Ascending form lower UT (almost always)
- Bacteremia (rarely) - renal / perinephric abscesses
- mostly caused by Staphylococci
- Preexisting renal damage by cyst or stone
or scar.
- Medulla> cortex – low O2 tension, high osmolality, high H+
&ammonia
, impaired WBC function
-
Rarely, CT scanning can show wedge-shaped areas of inflammation in the
renal cortex and hence damage to renal function. (Rare with antibiotics, with
normal urinary tracts)
*
Tip:
most of the loin pain is of non renal origin , and if it is renal it should be associated
with nausea and vomiting and not change with movement. (mentioned by the doctor)
Clinical features;-
- Acute loin(s) pain, radiated to Iliac fossa or Suprapubic area /tender lumbar region
- Accompanied by cystitis
- Fever, rigor, vomiting &hypotension.
Rarely, complicated by papillary necrosis; - Fragments of renal papillary tissue
(small piece ) are passed per urethra and can be identified histologically.
They may cause ureteric obstruction, and if this occurs bilaterally or in a
single kidney, may cause acute renal failure.
Predisposing factors include: DM, Chronic urinary obstruction, Analgesic
nephropathy and Sickle-cell disease.
In perinephric abscess, there is marked pain and tenderness and often bulging of
the loin on the affected side. Patients are extremely ill, with fever, leucocytosis and
positive blood cultures. Urinary symptoms are absent, and urine contains neither
pus cells nor organisms.

The D.DX includes;-
Acute appendicitis,
Diverticulitis,
Cholecystitis
Salpingitis
Investigations
Appropriate investigations as in cystitis
Bacteria and neutrophils in the urine of a patient with typical clinical
features confirm the diagnosis.
Renal tract ultrasound should be performed as soon as possible, to
exclude a perinephric collection and obstruction as a predisposing factor.
Management
o Adequate fluid intake must be ensured, oral / intravenous.
o Antibiotics are continued for 7-14 days.
o Severe cases require intravenous therapy, with a cephalosporin, quinolone or
gentamicin), later switching to an oral agent. In less severe cases, oral
antibiotics can be used throughout. Penicillins and cephalosporins are safe in
pregnancy; other antibiotics should usually be avoided.
o Urine should be cultured during and after treatment.
o If obstruction is present, drainage by a percutaneous nephrostomy should
be considered
-Common in middle & young age males
- > 90 % of febrile UTI have asymptomatic prostatitis (high PSA & increased
prostate volume)
- Acute - UTI symptoms plus fever, rigor, constitutional symptoms
- Perianal & low back pain,
- Per Rectal examination - ?? Sepsis
- Tenderness, hot, swollen prostate
- Pus in expressed prostatic secretion.

-GUE, C/S as in UTI
-Treatment
; - 4-6 weeks - trimethoprim or ciprofloxacin
- Chronic – associated with Relapsing UTI, perianal & low back pain,
- No fever or constitutional symptoms
- PR non remarkable
Relapse:-
- Recurrence of bacteriuria with the same organism within 7
days of completion of antibacterial treatment
-Implies failure to eradicate infection,
- Usually in conditions such as stones, scarred kidneys, polycystic disease or
bacterial prostatitis.
-
It requires to increase the dose of antibiotics(this point was mentioned by
the doctor).
Reinfection;-
- When bacteriuria is absent after treatment for at least 14 days,
- Followed by recurrence of infection with the same or different organisms.
- This is not due to failure to eradicate infection, but is the result of reinvasion of a
susceptible tract with new organisms.
Both relapse and reinfection indicate underlying pathology.
Prophylactic measures to be adopted by women with recurrent urinary
infections:
o Fluid intake of at least 2 liters/day
o Regular complete emptying of bladder
o If vesico-ureteric reflux is present, practice double micturition (empty the
bladder then attempt micturition 10-15 minutes later
o Good personal hygiene
o Emptying of the bladder before / after sexual
intercourse Cranberry juice may be effective
The end of the lecture

Appendix
added by the students
Case1
A 25yearold woman comes to the physician complaining of a threeday history of
burning micturition and increased
urinary frequency. She has suprapubic discomfort but denies having unusual vaginal discharge. She has been
sexually active and monogamous with her husband for the past four years. She has never been pregnant and uses
condoms for contraception. Her periods are regular (every 28 days), last five days, and require 4 or 5 pads a day. Her
last menstrual period was two weeks ago, and her last sexual encounter was 2 days ago. She takes no medications and
has no known drug allergies. Her temperature is
37 .1•c (98 .9.F), blood pressure is 11 0/70 mm Hg, pulse is 68/min,
and respirations are 15/min. Examination shows suprapubic tenderness
without flank tenderness. The rest of the
examination is normal. Her urine pregnancy test is negative.
Urinalysis:
Leukocyte esterase : positive, Nitrites : positive, WBC:4050/hpf, RBC:610/hpf, Bacteria :50+
Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
A. Urine culture
B. Oral trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole
C. Oral fosfomycin
D. Oral ampicillin
E. Oral amoxicillin clavulanate
Explanation: This patient's clinical presentation and urinalysis support the diagnosis of acute, uncomplicated cystitis.
Uncomplicated cystitis refers to infections that occur in otherwise healthy, young, nonpregnant women. Complicated
cystitis refers to infections in women who are pregnant, very young, very old, diabetic, immunocompromised, or have
abnormal anatomy of the genitourinary tract. Both can present with dysuria, increased urinary frequency, suprapubic
pain, and/or hematuria (usually indicates hemorrhagic cystitis). Routine urine cultures are not indicated in uncomplicated
cystitis. Urine culture is indicated only if the patient has complicated cystitis, urinary symptoms not characteristic of
cystitis, persistent symptoms of cystitis despite treatment, or repeat symptoms of cystitis less than one month after
treatment for previous cystitis without a urine culture. Oral trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole and nitrofurantoin are the
preferred firstline agents for empiric treatment of uncomplicated cystitis, while a fluoroquinolone (levofloxacin or
ciprofloxacin) is the recommended firstline agent for complicated cystitis.
So the answer is B
Case 2
A 25yearold woman presents to the clinic complaining of several days of worsening burning and pain with urination.
She describes an increase in urinary frequency and suprapubic tenderness but no fever or back pain. She has no past
medical history with the exception of two prior episodes similar to this in the past 2 years. Urinalysis shows moderate
white blood cells. Which of the following is the most likely causative agent of her current symptoms?
A. Candida spp.
B. Escherichia coli
C. Enterobacter spp.
D. Klebsiella spp.
E. Proteus spp.
The answer is B.
Explanation: E. coli is the etiologic agent in most cases of uncomplicated urinary tract infections (UTIs)
