
Nephrology
Dr. Mohamad hanoon
Medicine
“ UTI ”
Dr.Mohamad
Lecture
#4
Total Lec: 41

LEC.4
MEDICINE
د
.
محمد
حنون
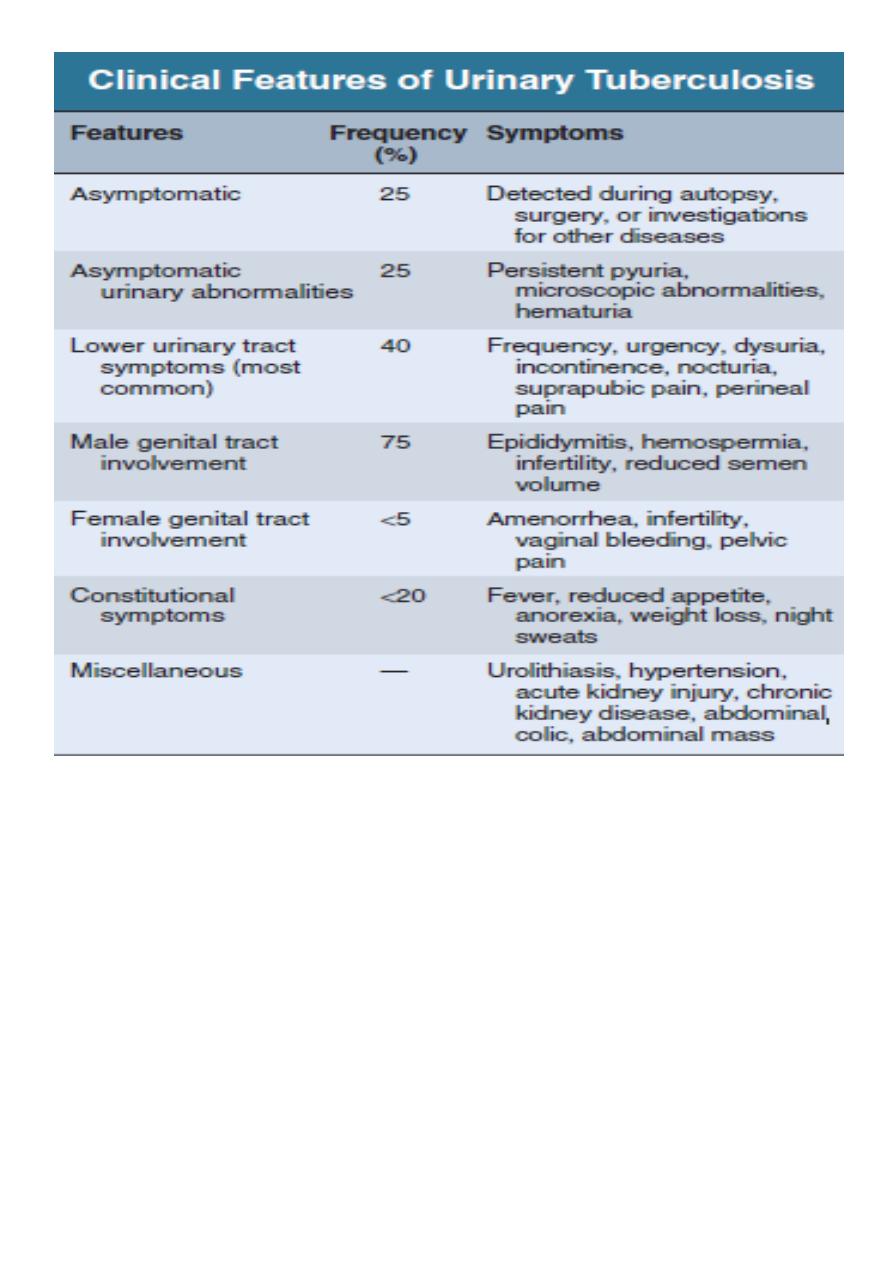
UTI in the presence of an indwelling catheter
After urinary catheterization > few days
colonization of the bladder by a
urinary pathogen, an increases the risk of Gram-negative bacteremia fivefold.
Treatment
is usually avoided in asymptomatic patients. and ABC indicated only if ;-
-
Symptoms or evidence of
infection,
-
Immunocompromised patients
-
Removal or replacement of the catheter.
Prevention
Catheters should not be used unnecessarily
Sterile insertion, to be removed as soon as it is not required
Closed drainage systems
Bladder stones may form with long-term indwelling catheters,
Infection by Candida
Is a frequent complication of prolonged bladder catheterization Especially in DM
.Treatment for patients with evidence of invasive infection or those who are
immunosuppressed:
removal or replacement of the catheter,
urinary alkalinazation and
in severe infections intra vesical amphotericin
Asymptomatic bacteriuria
•
This is defined as > 100 000/ml organisms in the urine of apparently healthy
asymptomatic patients.
•
Approximately 1% of children < 1yr,
•
1% of schoolgirls, 0.03% of schoolboys and men,
•
3% of non-pregnant adult women and 5% of pregnant
•
more > 65 yr
•
30%
---- symptomatic infection within 1 year. n.
•
There is no evidence that this condition causes renal scarring in adults who are not
pregnant and have a normal urinary tract,
•
In general, treatment is not indicated only In :-
Infants
Pregnant women
Abnormal urinary tract.
Bacteriuria in pregnancy
•
Urine C/S is a must in pregnancy
•
2- 6% asymptomatic bacteriuria.
•
Risk of
- severe symptomatic pyelonephritis
-
Premature labour.
-
previous renal disease
-
Pre-eclamptic toxemia,
-
Anemia of pregnancy,
-
Small or premature babies.
•
Therefore bacteriuria must always be treated and be should to be eradicated.
•
Reinfection may require prophylactic therapy.
•
Amoxicillin and ampicillin, Nitrofurantoin & Cephalosporin may be safely be used in
pregnancy
•
WHILE Tetracycline, trimethoprim, sulphonamides and 4-quinolones must be avoided in
pregnancy
Urethral Syndrome
Abacteriuric frequency or dysuria
Usually female,
Symptoms of urethritis and cystitis
No bacteria are cultured from the urine. "sterile pyuria"
Causes include:-
postcoital bladder trauma,
post-menopausal atrophic vaginitis or urethritis in the elderly,
interstitial cystitis

infection with organisms not cultured by ordinary methods (e.g.
Chlamydia,
certain anaerobes ,TB),
intermittent or very low-count bacteriuria,
Reaction to toilet preparations or disinfectants.
0ther causes;-
Incomplete treatment by ABC.
Malignancy
Stones
Vasculitis
Antibiotics are not indicated
Tuberculosis of the urinary tract
TB Increase world-wide, in low socioeconomic group, reservoir of infection in HIV-
infected individuals and by the emergence of drug-resistant strains. .
Pathology
Cortical lesions from haematogenous spread in the primary phase. – Either
-
Heals (most) or
persists
- spreads to the papillae, cavitating lesions
-
Discharge of mycobacteria into the urine.
-
Infection of the ureters and bladder, (ureteral
stricture, a contracted bladder)
-
Rarely, cold abscesses may form in the loin.
-
In males the disease may present with testicular or epididymal discomfort and thickening
-
A high index of suspicion
-
Age 20 and 40 years,
-
Male to female ratio of 2:1.
•
High risk ;-
close contact with sputum smear–positive patients,
social deprivation, neglect,
Immunosuppression, HIV infection or (AIDS), DM and CRF.
Transplanted kidneys may also transmit TB to their recipients.
Diagnosis
;-
Constant awareness? Sterile pyuria.
Active infection: AFB with culture of mycobacteria from early-morning urine samples
Excretion urography may show;-
Cavitating lesions in the renal papillary areas, commonly with
calcification.
Evidence of ureteral obstruction with hydronephrosis.
may be normal in diffuse interstitial renal TB
Renal biopsy: Some patients present with small
unobstructed kidneys, when the
diagnosis is easy to miss.
Renal ultrasonography or excretion urography: should be carried out 2-3 months after
initiation of treatment as ureteric strictures may first develop in the healing phase.
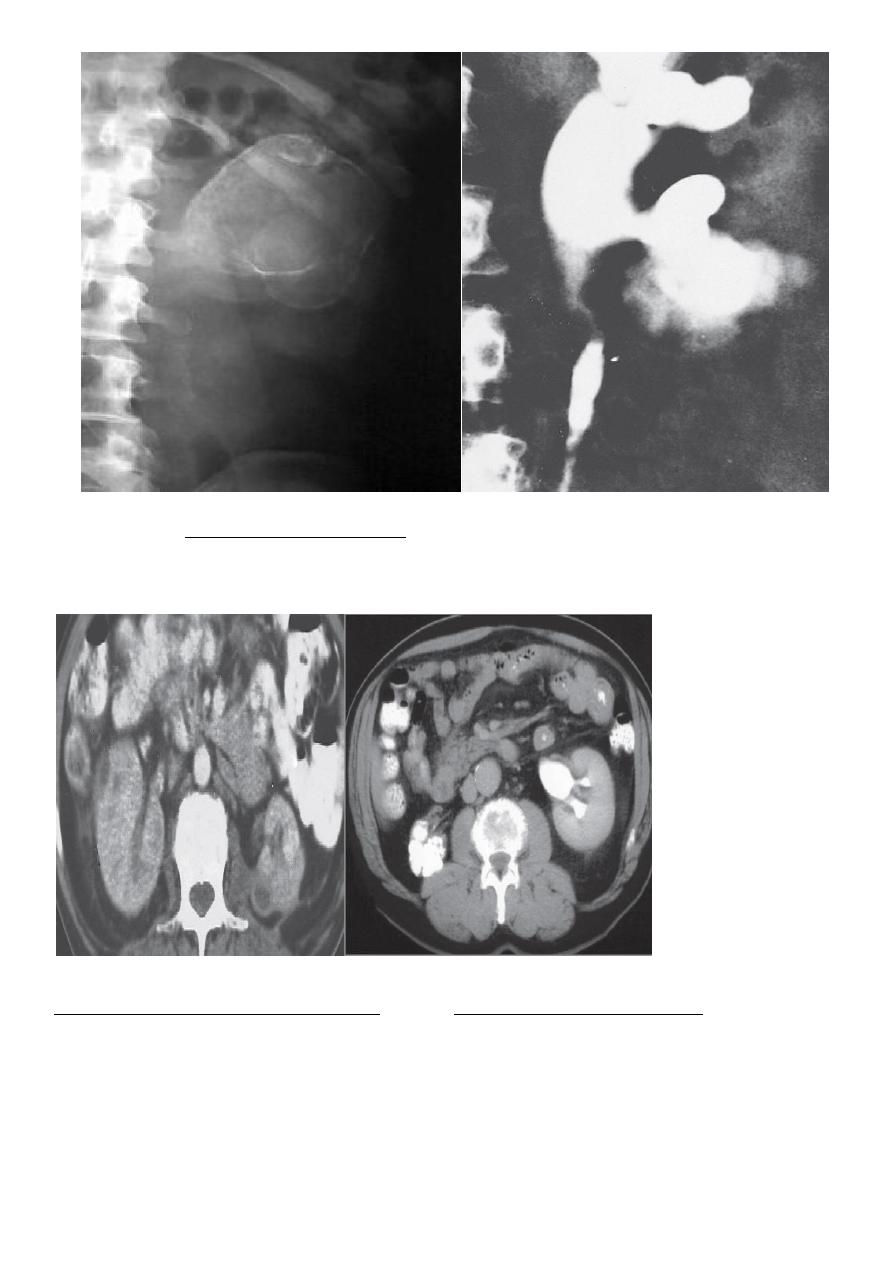
Plain x-ray (calcified kidney)
Multiple ureteral strictures.
Strictures associated with dilated ureter,
Infundibular stenosis and caliectasis
Renal tuberculosis CT scan shows an
Contrast-enhanced CT image showing
enlarged left kidney with multiple cavities
contracted calcified right kidney
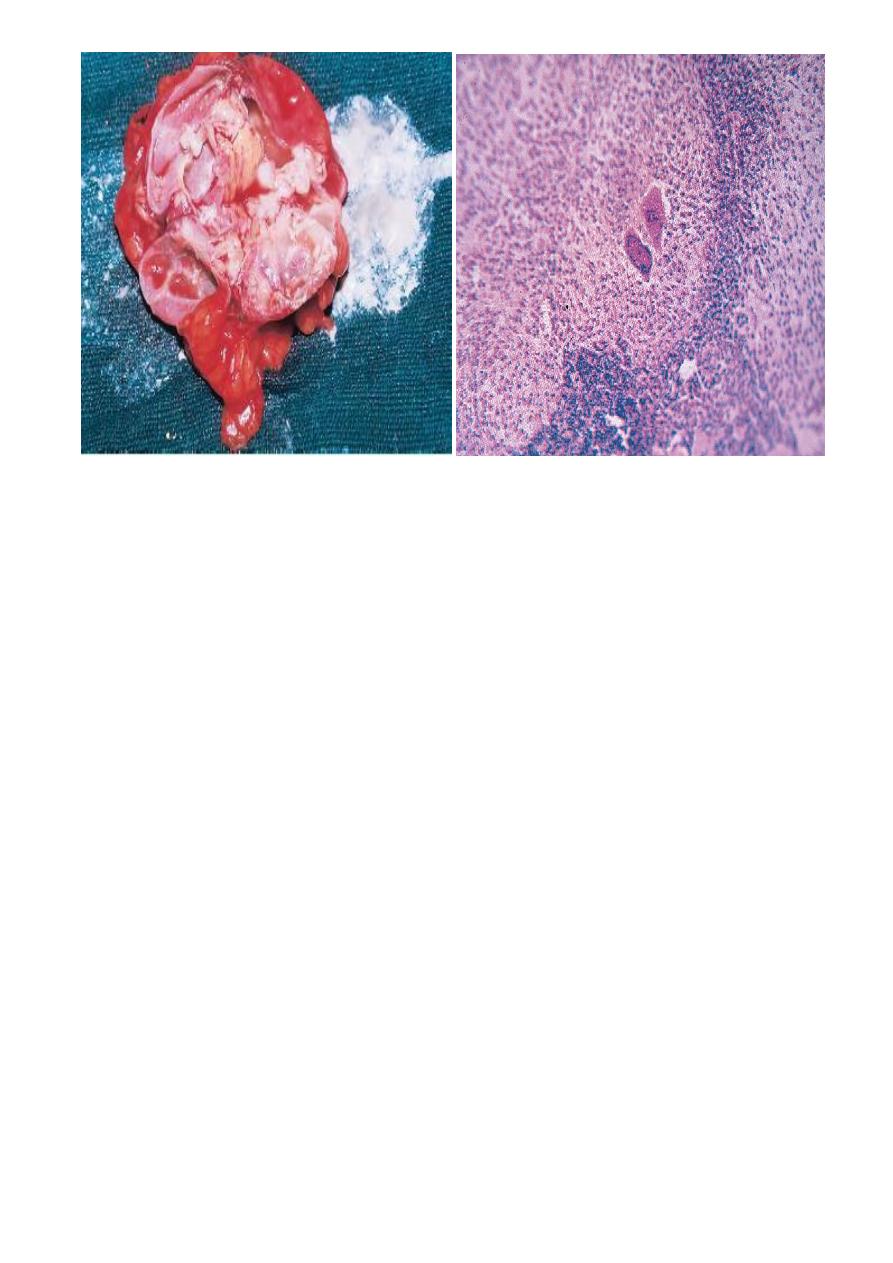
A cut section of kidney showing
Tuberculous granuloma. The areas of
cavitation and caseation necrosis
granuloma comprises Langherhans
giant cells (two large cells in the center),
surrounding epithelioid cells, and a rim of
lymphocytes
Treatment
Usually amenable to medical treatment.
Many anti-TB drugs reach kidneys, urinary tract, urine and cavitary lesions in high
concentration, and there are fewer organisms compared with cavitary lung lesions.
A short-course regimen is recommended.
The treatment is as for pulmonary TB
Daily rifampin (600 mg), isoniazid (300 mg), pyrazinamide (1500mg)
in the
morning. Pyrazinamide is discontinued after 2 months, and isoniazid and rifampin are
continued for another 4months.
If the patient is very sick with irritative bladder symptoms, streptomycin in daily doses
of 1 g may be added during the first 2 months
Longer courses of anti TB treatment 9 months to 2 years are useful in patients
who do not tolerate pyrazinamide,
those responding slowly to a standard regimen,
those with miliary or CNS disease,
children with multiple-site involvement

Surgical treatment. For:
ureteral strictures,
Stents across the narrow segment.
Reconstructive surgery involves the correction of obstruction to the ureter
pyeloplasty,
Removal of a unilateral nonfunctioning
kidney is controversial.
End of the lecture
MCQs
added by the students
1-pyuria in the absence of bacteriuria (sterile pyuria ) indicates infection with
A.C.trachomatis
B.U.urealyticum
C.Mycobacterium Tuberculosis
D.all of the above
The answer is D
2-acute cystitis in pregnancy can be treated with
A.Amoxicillin
B.Nitrofurantoin
C.cephalosporin
D.all of the above
The answer is D
3-patient with acute urinary tract infection (UTI) usually presents with:
A. Chills and fever.
B. Flank pain.
C. Nausea and vomiting.
D. 5 to 10 white blood cells per high-power field (hpf) in the uncentrifuged urine specimen.
E. Painful urination.
The answer is E
