Objectives
1- Describe the clinical features and investigations of discoid lupus, subacute lupus , Systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic sclerosis, morphea and dermatomyositis2- list the lines of treatment of the above diseases.
C.T. diseases
The cardinal feature of these conditions is inflammation in the connective tissue which leads to dermal atrophy or sclerosis.ranging from benign cutaneous to severe multisystemic diseases.
Lupus erythematosusSkin skin and some int. problems multisystem dis.
(Discoid) (subacute cut. Lupus) (systemic lupus)
SLE
Aetioology and pathogenesis: Multifactorial
●Disturbance of the immune regulation
uncontrolled production of autoantibodies and immune complexes
●Genetic: monozygotic twins, family history of CT, compliment deficiency.
●Environmental factors: sunlight, drugs, estrogens and pregnancyClinical features
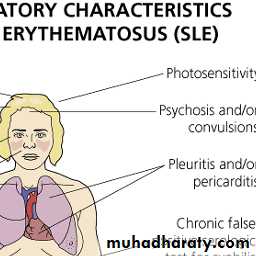
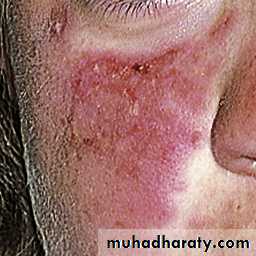
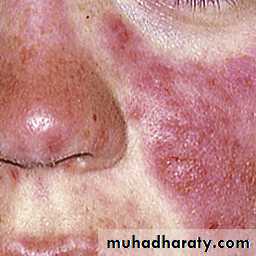
Criteria for the diagnosis: at least 41- butterfly rash
2- photosensitive rash3- discoid lesions
4- oral ulcers
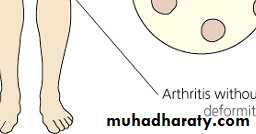
5- arthritis
6- serositis
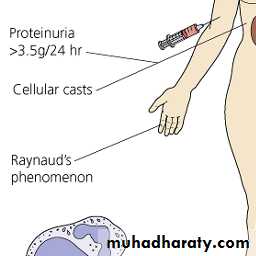
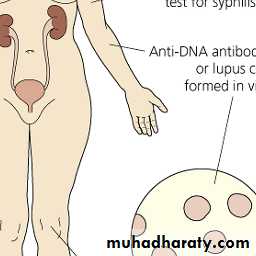
7-nephropathy
8- CNS
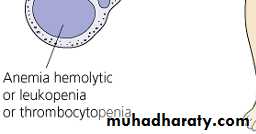
9- Hematologic: hemolytic an. or leukopenia or lymphopenia
10- Immunologic: anti DNA or false + VDRL
11- + ANA
• ‹ My LibraryX
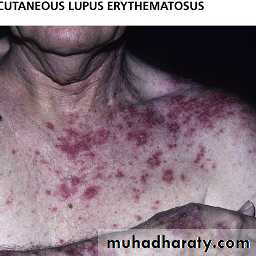
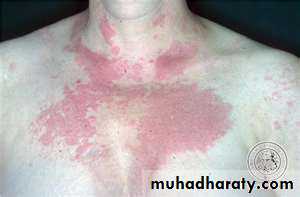
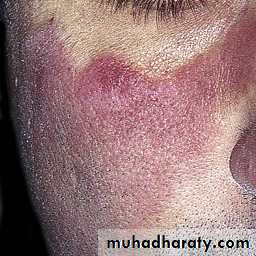
Clinical featuresYoung to middle age women. F/M: 9/1
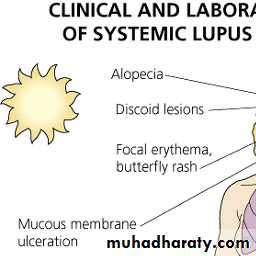
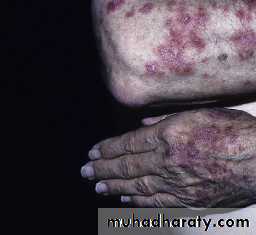
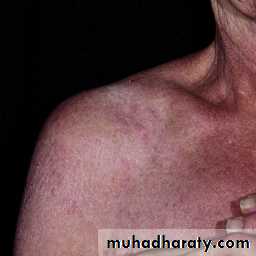
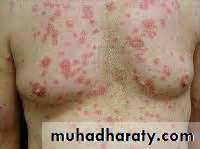
Skin involvement : + in 80%
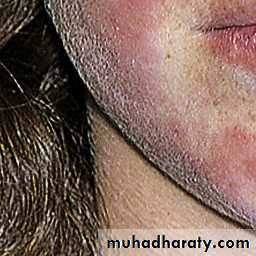
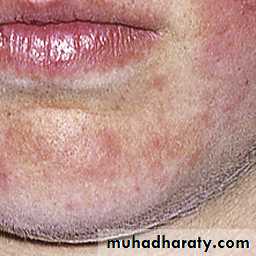
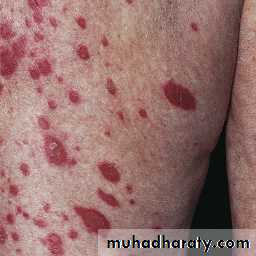
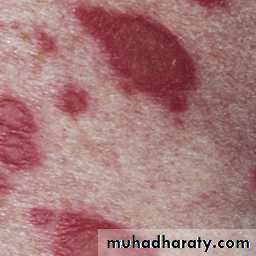
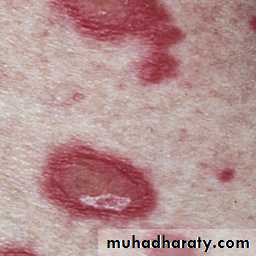
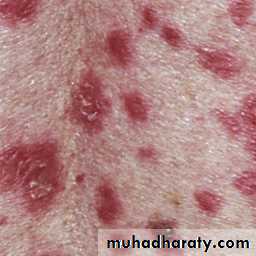
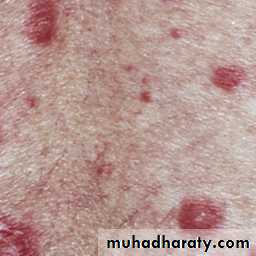
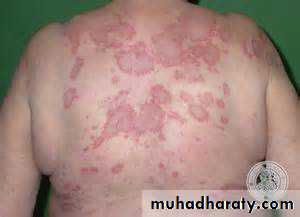
Butterfly rash: superficial or indurated plaques lasting for days to months. Non scarring.
Discoid lesions
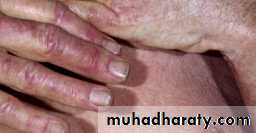
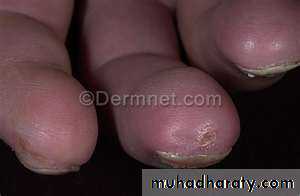
Erythema and puffiness of finger tips
Alopecia: diffuse non scarring
Leg ulcers due to vasculitis or thrombosis.
Petechi and livedo reticularis
Raynaud's phenomenon.
• ‹ My LibraryX
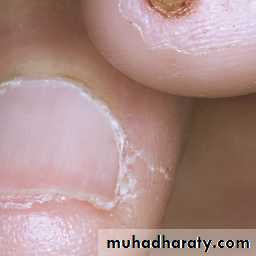
Butterfly rash: superficial or indurated plaques lasting for days to months. Non scarring.Repeated and increasingly severe attacks of Raynaud’s phenomenon lead to fingertip ulcerations that leave pitted or star-shaped scars.
Investigations
CBC: normochromic normocytic anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia.ESR, CRP
Serological test:
*ANA: + in 95% sensitive but not specific
* Anti DNA: + in 60 %. specific but not sensitive.
* Anti sm: + 15%, highly specific
* Serum compliment: low level indicates active dis.
Treatment
AntimalarialsSteroids
Immunosuppresive therapy.
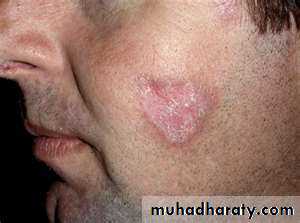
Discoid lupus erythematosus
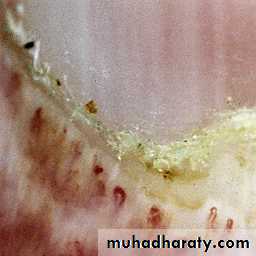
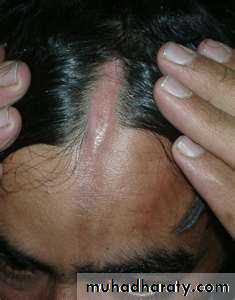
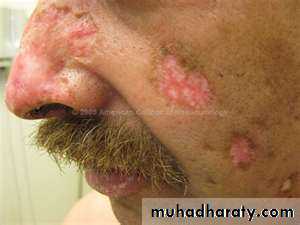
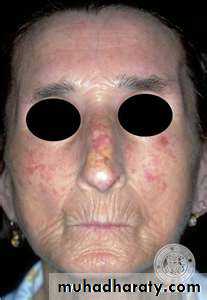
Discoid erythematous plaques with adherent scales with follicular plugging and telangiectasia affecting the face, ears, scalp, rarely below the neck.
Photosensitivity.
On the scalp causes scarring alopecia
ANA + in up to 35%
Female / male : 2/1
Prominent follicular plugging in a plaque of discoid LE located in the scalp.
DLEDiff. diagnosis
Psoriasis and seborrheic derm.: non scarringPolymorphous light eruption: seasonal variation
Tinea faciei: active boarder
Treatment
Steroids: topical / intralesionalSunscreens
Antimalarials
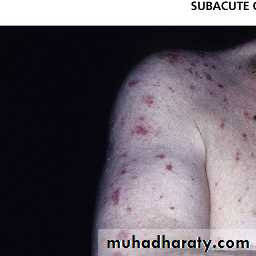
Subacute cut. lupus
Psoriasiform plaques affecting the face, hands , arms and chest.Photosensitivity.
Usually middle age women.
No scarring.
75% of patients have arthralgia or arthritis.
ANA + in 60%.
Anti Ro + in 60%
Treatment: steroids, antimalarials, immunosupp.
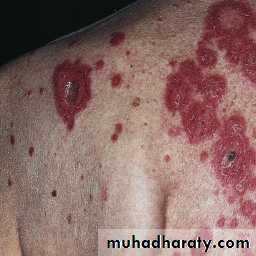
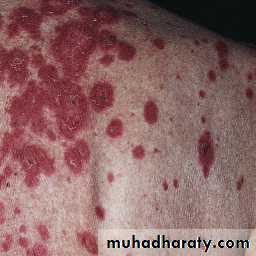
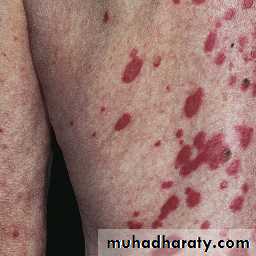
Papulosquamous pattern. Lesions are confined to exposed areas on the upper half of the body.
Annular-polycyclic pattern.
The annular plaques have an erythematous scaly border, the central area is hypopigmented
Systemic sclerosis and morpheaDisorders characterised by degeneration and fibrosis in the skin and many internal organs.
*Systemic sclerosis diffuse scleroderma
CREST syndrome
*Morphea (local or wide spread)
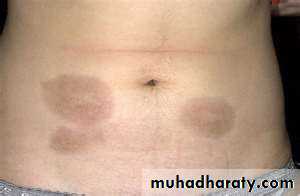
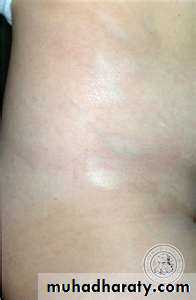
Morphea
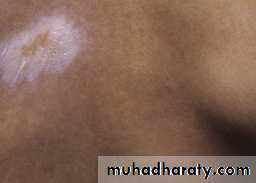
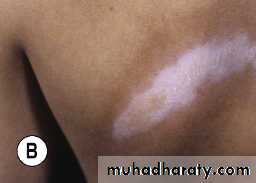
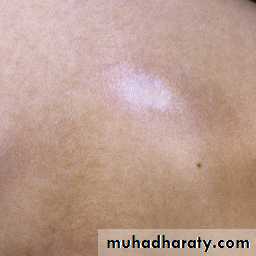
Pale or hyperpigmented indurated macules ,patches or plaques affecting the skin and / or the subcut. Often depressedRare systemic features.
Children and adults
Any body area
Treatment: spontaneous recovery may occur, topical steroids
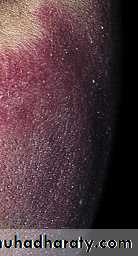
A single or few oval areas of nonpitting erythema and edema typically appear on the trunk. A violaceous border (lilac ring) surrounds the indurated area. The center of the lesion then develops smooth, ivory-colored hairless or hyperpigmented plaques
Morphea
Scleroderma
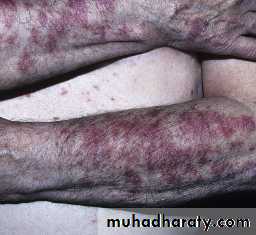
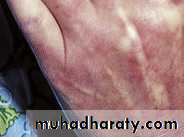
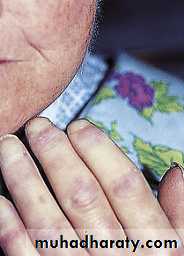
Raynaud’s phenomenon is usually the presenting complaint.Female/male: 3/1
Initially non pitting edema and sausage like swelling of fingers.
Later the skin become shiny with atrophy and ulceration of the finger tips.
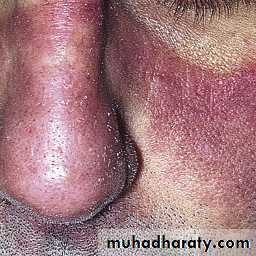
The face become taut and mask like with beaking of the nose.
Telangiectasia
Scleroderma. The hands may be edematous and swollen early in the disease. These changes progress to other areas including the face. This edematous stage precedes the sclerotic stage.
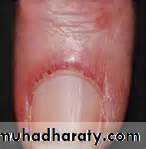
Dilated, irregular, nail fold capillary loops
Widespread calicifications of the skin can be seen by x- ray.Hyperpigmentation or depigmentation.
Nailfold capillary microscopy
Investigations
ANA + in 90 %Anti Scl-70 + in 20 %
Anticentromer + in 50-90% in CREST syndrome.
Treatment
SteroidsPenicillamine interfere with collagen cross linking.
nifedipine
Dermatomyositis
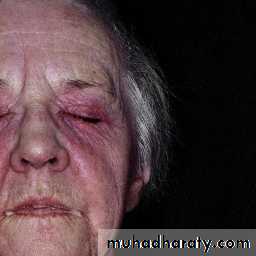
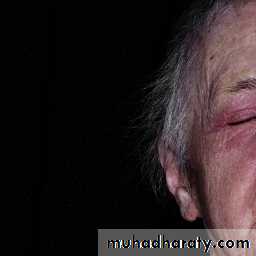
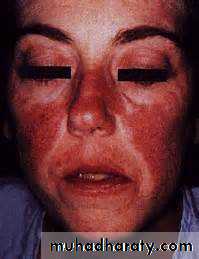
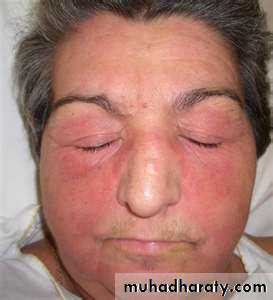
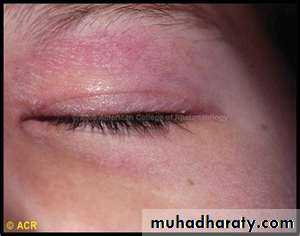
Starts with erythema and swelling of the face and eyelids which become violet (heliotrope).Photosensitivity.
months years
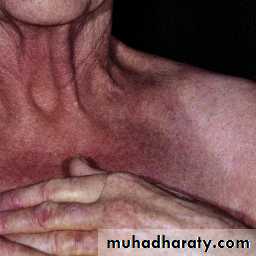
Edema and erythema of the neck, shoulder and arms
Nail fold telagiectasia
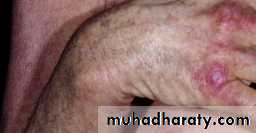
Gottron's papules: flat violaceous papules over the knuckles.
Violaceous scaling patches on the face and dorsal interphalangeal joints. The knuckles are involved.
Calcification occurs on the shoulder, elbows and hands.
Muscle changes: mostly involving the shoulder girdle and sometimes the pelvic region.Usually skin eruption precedes muscle weakness by 3 months.
Diagnostic criteria
1- Symmetrical weakness of limb girdle muscles and ant. Flexors of the neck.
2- muscle enzymes: CPK, TA, LDH, and aldolase.
3- abnormal EMG
4- myositis on muscle biopsy.
5- dermatologic features
3 diagnosis
Dermatomyositis and malignancy
5th and 6th decadesMore in women
Ovarian cancer
Investigations
CBC: anemia, WBCESR
Muscle enzymes: correlate with dis. Activity.
Antisynthetase Ab. Ex. Anti jo-1.
ANA
X ray.
EMG.
Skin or muscle biopsy.
Treatment
Systemic steroids.
Immunosuppressive therapy
Sunscreens
Topical steroids
Summary
DLE: scarring lesions affecting the face, butterfly, ears.Subacute cut. Lupus: psoriasiform lesions and photosensitivity.
SLE: young female, butterfly rash, multisystemic.
Morphea: hypo or hperpigmented sclerotic patches