Substance – Related Disorders2
Dr Nesif Al-HemiaryDescription: Alcohol or ethylalcohol (ethanol) is present in varying amounts in beer, wine, and liquors
Route of administration: Oral
Acute Effects: Sedation, euphoria, lower heart rate and respiration, slowed reaction time, impaired coordination, coma, death
Alcohol: Basic facts (1)
Withdrawal Symptoms:
Tremors, chillsCramps
Hallucinations
Convulsions
Delirium tremens
Death
Alcohol: Basic facts (2)
• Decrease in blood cells leading to anemia, slow-healing wounds and other diseases
• Brain damage, loss of memory, blackouts, poor vision, slurred speech, and decreased motor control• Increased risk of high blood pressure, hardening of arteries, and heart disease
• Liver cirrhosis, jaundice, and diabetes
• Immune system dysfunction
• Stomach ulcers, hemorrhaging, and gastritis
• Thiamine (and other) deficiencies
• Testicular and ovarian atrophy
• Harm to a fetus during pregnancy
Long-term effects of alcohol use
Cannabinoids
Hashish
MarijuanaDescription: The active ingredient in cannabis is delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC)
• Marijuana: tops and leaves of the plant Cannabis sativa• Hashish: more concentrated resinous form of the plant
Route of administration:
• Smoked as a cigarette or in a pipe
• Oral, brewed as a tea or mixed with food
Cannabis: Basic facts (1)
Acute Effects:
Relaxation
Increased appetite
Dry mouth
Altered time sense
Mood changes
Bloodshot eyes
Impaired memory
Cannabis: Basic facts (2)
• Reduced nausea• Increased blood pressure
• Reduced cognitive capacity
• Paranoid ideation
Cannabis: Basic facts (3)
• Withdrawal Symptoms:• Insomnia
• Restlessness
• Loss of appetite
• Irritability
• Sweating
• Tremors
• Nausea
• Diarrhea
• Increase in activation of stress-response system
• Amotivational syndrome• Changes in neurotransmitter levels
• Psychosis in vulnerable individuals
• Increased risk for cancer, especially lung, head, and neck
• Respiratory illnesses (cough, phlegm) and lung infections
• Immune system dysfunction
• Harm to a fetus during pregnancy
Long-term effects of cannabis use
Stimulants
CRACK
METHAMPHETAMINE
COCAINEAmphetamine Type Stimulants (ATS)
MethamphetamineSpeed, crystal, ice, yaba, shabu
Amphetamine
Pharmaceutical products used for ADD and ADHD
Methamphetamine half-life: 8-10 hours
Types of stimulants (1)
Cocaine
Powder cocaine(Hydrochloride salt)
Smokeable cocaine
(crack, rock, freebase)
Cocaine half-life: 1-2 hours
Types of stimulants (2)Description:
Stimulants include: (1) a group of synthetic drugs (ATS) and (2) plant-derived compounds (cocaine) that increase alertness and arousal by stimulating the central nervous systemRoute of administration:
Smoked, injected, snorted, or administered by mouth or rectum
Stimulants: Basic facts (1)
Acute effects:Euphoria, rush, or flash
Wakefulness, insomnia
Increased physical activity
Decreased appetite
Increased respiration
Hyperthermia
Irritability
Tremors, convulsions
Anxiety
Paranoia
Aggressiveness
Stimulants: Basic facts (2)
Stimulants: Basic facts (3)
• Withdrawal symptoms:• Dysphoric mood (sadness, anhedonia)
• Fatigue
• Insomnia or hypersomnia
• Psychomotor agitation or retardation
• Craving
• Increased appetite
• Vivid, unpleasant dreams
• Strokes, seizures, headaches
• Depression, anxiety, irritability, anger• Memory loss, confusion, attention problems
• Insomnia, hypersomnia, fatigue
• Paranoia, hallucinations, panic reactions
• Suicidal ideation
• Nosebleeds, chronic runny nose, hoarseness, sinus infection
• Dry mouth, burned lips, worn teeth
• Chest pain, cough, respiratory failure
• Disturbances in heart rhythm and heart attack
• Loss of libido
• Weight loss, anorexia, malnourishment,
• Skin problems
Long-term effects of stimulants
Opioids
Opium
HeroinMorphine
Codeine
Hydrocodone
Oxycodone
Methadone
Buprenorphine
Thebaine
Opioids
Description:
Opium-derived or synthetic compounds that relieve pain, produce morphine-like addiction, or relieve symptoms during withdrawal from morphine addiction.Route of administration:
Intravenous, smoked, intranasal, oral, and intrarectal
Opioids: Basic facts (1)
Acute effects:
EuphoriaPain relief
Suppresses cough reflex
Histamine release
Warm flushing of the skin
Dry mouth
Drowsiness and lethargy
Sense of well-being
Depression of the central nervous system (mental functioning clouded)
Opioids: Basic facts (2)
Withdrawal symptoms:Intensity of withdrawal varies with level and chronicity of use
Cessation of opioids causes a rebound in functions depressed by chronic use
First signs occur shortly before next scheduled dose
For short-acting opioids (e.g., heroin), peak of withdrawal occurs 36 to 72 hours after last dose
Acute symptoms subside over 3 to 7 days
Ongoing symptoms may linger for weeks or months
Opioids: Basic facts (3)
• Fatal overdose
• Collapsed veins
• Infectious diseases
• Higher risk of HIV/AIDS and hepatitis
• Infection of the heart lining and valves
• Pulmonary complications & pneumonia
• Respiratory problems
• Abscesses
• Liver disease
• Low birth weight and developmental delay
• Spontaneous abortion
• Cellulitis
Long-term effects of opioids
Other drugs
InhalantsPetroleum products, glue, paint, paint removers
Aerosols, sprays, gases, amyl nitrite
Club drugs (MDMA-ecstasy, GHB)
Hallucinogens (LSD, mushrooms, PCP, ketamine)
Hypnotics (quaaludes, mandrax)
Benzodiazepines (diazepam / valium)
Barbiturates
Steroids
Khat (Catha edulis)
Complicated
Costly
Relapses are common
Treatment of substance abuse
25
Stages of Change
Contemplation
ActionPrecontemplation
Preparation
Maintenance
Permanent Exit
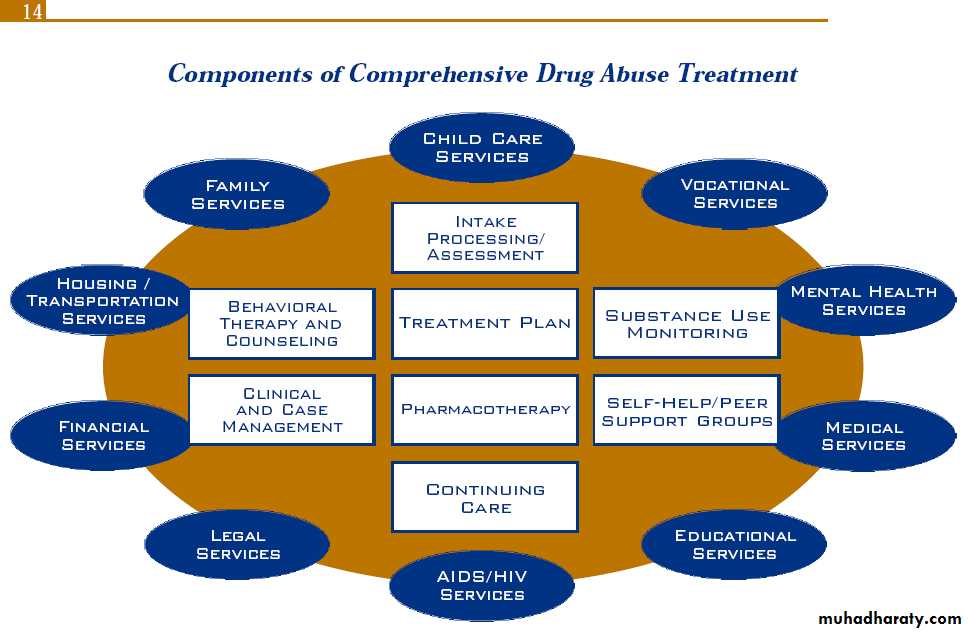
Interventions depend on the complexity of the problem.When the person has mild substance abuse problem, education might be enough. Some people might need short cognitive behavioral therapy.
When the patient is complaining of dependence then a more sophisticated help is needed which might include hospital admission to treat withdrawal syndrome that might appear after abstinence, in addition to many other psychosocial interventions and a long period of continuous care to prevent relapse which is very common.
The first stage of treatment after abstinence is called detoxification.
Treatment of substance abuse
Treatment of withdrawal syndrome can be done as an outpatient treatment , but many times it is preferred to put the patient under direct supervision in an addiction treatment facility.
Withdrawal symptoms can be severe and sometimes dangerous.
Treatment can be accomplished by many ways depending on the type of the addictive substance; it might be done by gradually decreasing the substance like in addiction on benzodiazepines, or by giving a medication that has similar pharmacological effects and then decreasing it gradually like giving chlordiazepoxide to treat withdrawal of alcohol.
Some substances can be treated by giving a medication that blocks the withdrawal by an effect on the receptors like naltrexone which is given to treat withdrawal of opiates and alcohol.
Some withdrawal symptoms are treated according to type of distress caused like antispasmodics for abdominal pain and diarrhea of opiate withdrawal, analgesics for pain , hypnotics for sleep problems ,and so on.
Detoxification
Treatment of substance abuse in not an easy task
Quitting the use of a substance needs lots of changes in life style, relationships, and behavior. This cannot be accomplished without a professional help. This help can be done by counseling , self-help groups, family and social support.Recovery of the brain might take a year or so during which the possibility of relapse is high.
Relapses are common and do not mean failure of treatment.
Family is very important part of treatment.
Counseling includes individual and group therapy sessions.
Interventions include: relapse prevention, CBT, life skills, etc.
Medications for maintenance are also available for some types of addiction like disulphiram and acamprostate for alcohol, and methadone for opiates.
Treatment of co-morbid psychiatric problems like depression and anxiety disorders is important.
Psychosocial intervention
Comprehensive treatments
Primary : dealing with causes: improvement of life circumstances, education, employment, good parenting, legislations ( limit the use and decrease availability of substances)
Secondary : treatment of substance abuse problems
Tertiary : decrease complications
Harm reduction : when people are unable to quit the use of substances. What to do?
Prevention
Some patients are unable or unwilling to abstain from the use of substances.
Those patients can be helped by many ways:• Education about safe sex
• Encouragement to use a safe way of injecting drugs which will decrease possibility of acquiring infections like hepatitis and HIV ,through needle exchange programs
• Opiate substitution therapy(OST): in which heroin is substituted by much less harmful opiates like methadone and piprenorphine.
Harm reduction
Substance abuse problems are very common
They have a great impact on the individuals, families, and community.Etiology is multi-factorial
Substance abuse problems should be considered in the differential diagnosis of any psychiatric disorder
Treatment is complicated and associated with high rates of relapse
We should deal with these problems as mental health problems (illnesses )
Conclusions