Prenatal diagnosis
Dr.Maysarah M. AL-BadranM.B.ch.B,C.A.B.O.G,F.I.C.M
Prenatal diagnosis
Identification of a disease before birth.Usually preceded by screening test,women with risk factor identified during screening may undergo diagnostic test.
Screening test
Include:history:family hx,past obstetric hxmaternal biochemistry:Down syndrom
U/S:anomaly scan at 18-22wk
Diagnostic tests
High risk pregnanciesInvasive and non invasive
Invasive:amniocentesis,CVS, cordocentesis.
Risk of miscarrige
Non invasive prenatal diagnostic tests
US for structural abnormalities
Viral serology
free fetal DNA extracted from maternal blood to determine fetal blood group or the sex of fetus by PCR.
Fetal RNA from maternal to detect aneuploidy.
Pre-test counselling
IndicationThe procedure
Risk,limitations
Management options:continue or terminate pregnancy
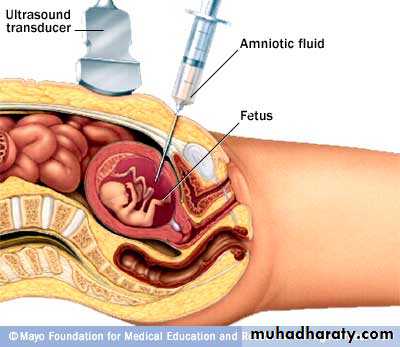
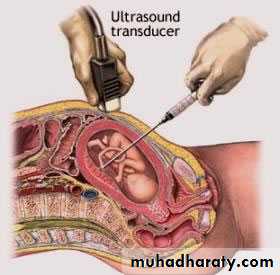
Amniocentesis
At or after 15 wkAdditional risk of miscarrige 1%
Earlier amniocentesis is more risk
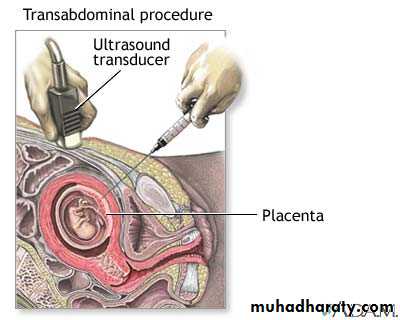
Chorionic villus sampling
At or after 11 wk
Additional risk of miscarrige 2%
If performed before 10 wk:limb distruption and oromandibular hypoplasia
Transabdominal 0r transcervical
Confined placental mosaicim
Laboratory analysis
Full culture for karyotyping:7-10 daysResult for common aneuploidy(trisomy21,18,13) take 48 hours by Fluorescence in situ hybridization(FISH)or Polymerase chain reaction(PCR)
Tests for genetic disorders take varying time
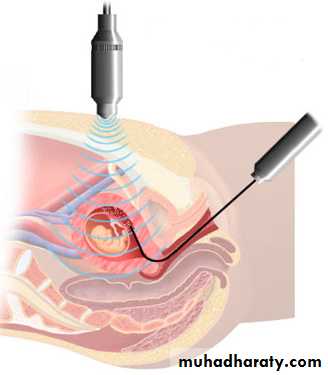
Cordocentesis
Around 20 wkGreater risk of miscarrige than amniocentesis and CVS(2-5%)
When fetal blood is needed as in alloimmune thrombocytopenia or when a rapid full culture for karyotype is needed
Screening for Down’s syndrom
Risk increases with age.Quadriple test(14-20wk):B-hCG,α-fetoprotein,unconjugated estriol,inhibin A
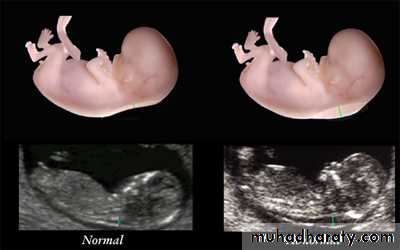
Nuchal transulency:11-14 weeks
Combined test(11-14wk): NT,B-hCG,pregnancy associated plasma protein A(PAPP-A)
Structural abnormality
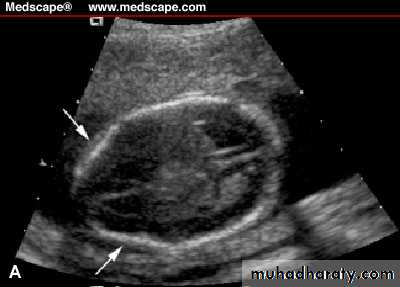
Neural tube defects:Anencephaly&encephalocele can be detected on first trimester U/S
Spina bifida:’lemon’&’banana’sign
Can be prevented by folic acid 400Mg-----high risk 5mg
Congenital heart defects
Genetic,maternal DM,viral inf.,lithiumScreening by U/S &fetal echo.
Diagnosis of GIT Structural abnormalities
Gastroschisis: US detect 90% of cases,not associated with other abn. or chrom. abn.Follow up is required—>risk of IUGR & oligohydramnios.
exomphalos:US detect 90% of cases,associated with chrom. Abn.& other structural abn.
Other methods of AN diagnosis
3D & 4D ultrasoundFetal MRI:CNS abnormalities