
AFTER MID
TOTAL LEC: 34
Gynaecology
Dr. Shaima’a Kadhim Al-Khafaji
Lec 34 - Assisted Reproduction
DR. SHAIMA’A - LEC 3
مكتب املدينة


1
Assisted Reproduction
It is the facilitation of natural conception by some form of scientific
intervention. They include many forms.
Assisted conception techniques abbreviations:
• (IVF) - In Vitro Fertilization
• (IUI) - Intrauterine Insemination
• (ICSI) - Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
• (PGD) - Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis
• (PGS) - Preimplantation Genetic Screening
• (DOT) - Direct Oocyte Transfer
• (PROST) - Pronuclear Stage Transfer
• (DIPT) - Direct Intraperitoneal Insemination
• (MESA) - Microepididymal Sperm Aspiration
• (TESE) - Testicular Sperm Extraction
• (PESA) - Percutaneous Epedidymal Sperm
• (GIFT) - Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer
Investigations prior to assisted conception:
They are done to ensure best results when assisted conception is
performed and to reduce the chance of any diagnosis being missed
before multiple cycles are embarked upon, which if they were
unsuccessful, will result in subsequent emotional and financial cost to
the patient. These include:
1. Hormonal profile:
AMH, FSH, E2 assess ovarian reserve
Progesterone (check of ovulation)
2. Semen analysis.
3. Pelvic ultrasound.
4. Evaluation of uterine cavity and fallopian tubes: HSG,
laparoscopy and hysteroscopy.
2
5. For the male: not only to assess for normal WHO sperm criteria,
but most units perform sperm function test to choose the best
techniques. Assessment of other problems is also important like
the presence of antisperm antibodies.
Notes:
ü
Patients should be advised to stop smoking as this significantly
reduces effectiveness of all forms of ART.
ü
It is recommended that the patient should have a BMI between
(19 - 30). Outside this range, success rates of ART are reduced. If
BMI > 30 then miscarriage rates are also higher and incidence of
complications as OHSS (ovarian hyper stimulation syndrome) is
also increased.
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF):
Involves surgical removal of the mature oocyte from the ovary and its
fertilization by sperm in the laboratory. (The world’s first successful IVF
baby was delivered in 1978).
Indications:
1. Severe tubal disease – tubal blockage.
2. Severe endometriosis.
3. Moderate male factor
4. Unexplained infertility
5. Unsuccessful IUI.
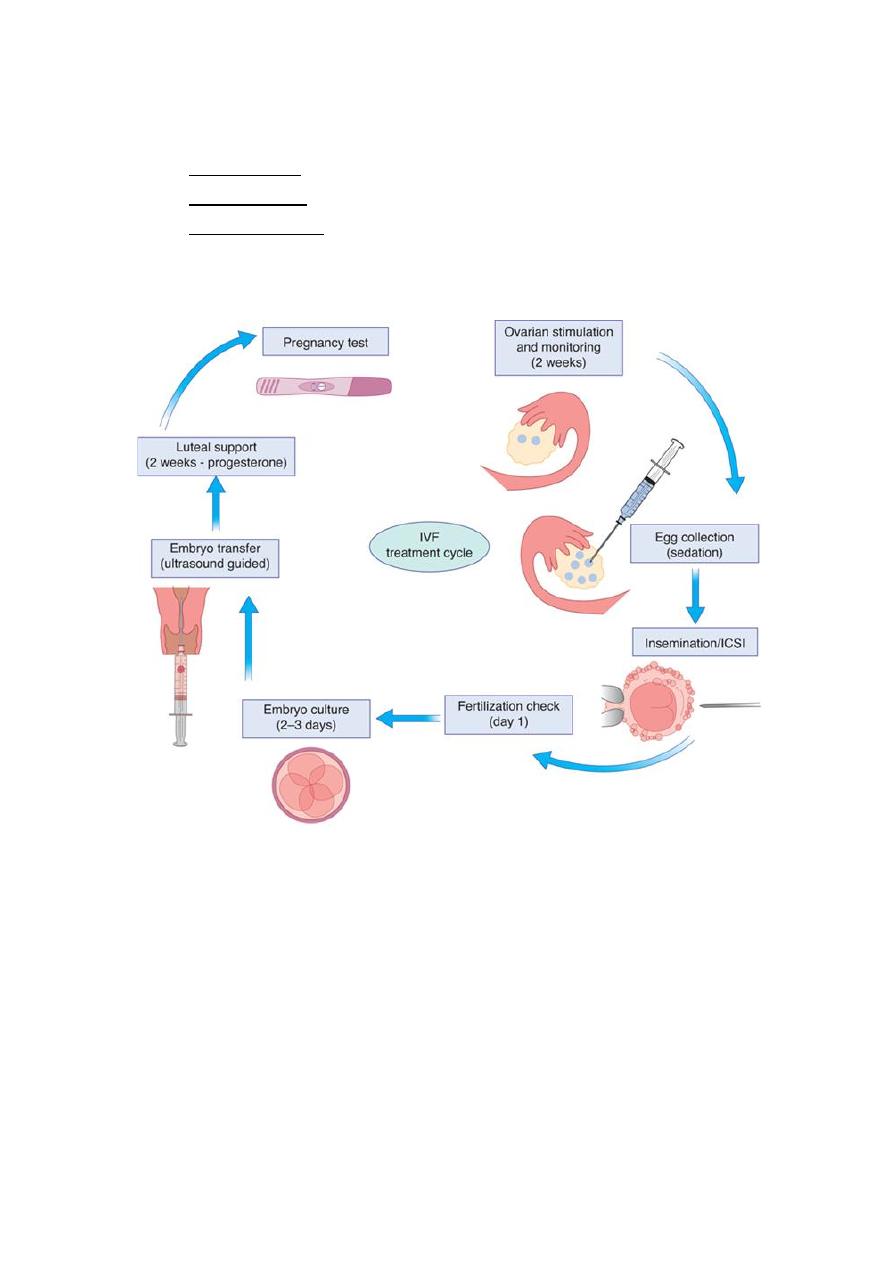
Stages of IVF:
1) Pituitary down regulation.
2) Ovarian stimulation.
3) hCG trigger.
4) Oocyte retrieval.
5) Fertilization (insemination or ICSI).
6) Embryo culture.
7) Embryo transfer.
8) Luteal support.
3
IVF protocols are now categorized to 3 main groups:
o Natural cycle.
o Long protocol: using GnRH agonist.
o Short protocol: using GnRH antagonist. Monitoring is used by
serial transvaginal ultrasound scan to assess the follicular growth.
- HCG trigger: is used to induce final maturation of the oocyte prior to
oocyte retrieval. It is given when either 1 or 2 follicles reach 18 mm. The
injection is given so that oocyte retrieval is done approximately 34 hours
later (before the occurrence of physiological ovulation).
- Oocyte retrieval: Usually done by ultrasound directed needling of the
ovaries. local anesthesia with some form of intravenous sedation enable
transvaginal egg retrieval, but it can also be done under GA. Oocyte can
also be retrieved Laparoscopically.

4
- Embryo transfer: Eggs are fertilized by routine insemination with a
concentration of approximately 100 000 normally motile sperm per ml
or by ICSI, they are incubated in special media with careful control of pH,
temperature, humidity and gas content.
Traditionally, most embryos are transferred at day 2 after egg
collection, but now there is evidence that transfer on day 5 achieve
higher pregnancy rate. Regulations in UK for example: to transfer 2
embryos for those < 40 years of age and if > 40 years of age, 3 embryos
can be transferred.
The other normal embryos are frozen and can be transferred in
subsequent cycle.
- Luteal phase support: It is used because superovulation may impair
normal corpus luteal function.
It is broadly divided to two groups:
a. Use of luteotropic preparations such as hCG.
b. Use of progestogens or progesterone.
hCG is given as S.C. injection, and it increases the risk of OHSS, while
progesterone can be given as tablets, injection, vaginal gel or pessaries.
LPS is given minimally for 2 weeks, but some centers use it for up to 12
weeks.
Pregnancy test:
Pregnancy test is generally done 12 days after the embryo transfer and
can be performed either at home with urinary PT or at clinic with a
serum PT.
If PT is +ve then U/S is offered 2-3 weeks later to ensure it is an
intrauterine pregnancy and to assess viability.

5
Intrauterine Insemination: (IUI)
A prepared sample of sperm is placed into the uterine cavity using a
cannula at the appropriate time of the patient's menstrual cycle. 2
weeks later a pregnancy test is performed to see if the cycle has been
successful.
IUI can be done in natural cycle or after stimulation with clomid or FSH.
When stimulation is used, monitoring by U/S is essential to ensure
having the desired effect of induction (i.e. one or at most two
developing follicles over 18mm).
if more than 2 follicles are found, then the cycle should be cancelled.
Otherwise HCG injection is given approximately 36 hours prior to the
insemination to ensure optimal timing with ovulation.
Advantages:
1) Relatively simple technique that is cost effective.
2) It is not invasive as IVF.
3) Allows fertilization to occur at the fallopian tubes, therefore it is
generally acceptable to most religious groups.
Disadvantage:
1) Success rate is lower than in IVF: 5% for natural cycle, 8-10% with
clomid, 12-18% if FSH is used.
2) Requires at least one healthy fallopian tube and reasonable
sperm parameters.
3) If failure occurs, then less information can be obtained than if it
was with IVF cycle, particularly about egg or embryo quality.
4) If monitoring is suboptimal then there is increased risk of higher
order multiple, OHSS. The patient should also be warned about
the possibility of ectopic pregnancy and an early scan at 6-7
weeks should be offered after a positive Pregnancy test.

6
Indications:
1. Unexplained infertility.
2. Mild male factor.
3. Ejaculatory problem.
4. Cervical problem.
5. Ovulatory disorders.
6. Mild endometriosis.
7. To optimize the use of donor sperm.
Intra Cytoplasmic Sperm Injection: (ICSI)
It is done when individual morphologically normal sperm is immobilized
by striking the tail and then injected into a mature oocyte.
Indications:
1. Severe male factor infertility including azoospermia and
subsequent surgical sperm retrieval by for ex: MESA, TESE, PESA.
2. Severe oligo-astheno-teratozoospermia.
3. Poor or total non fertilization from previous IVF cycles.
4. Preimplantation genetic diagnosis cycles.
- Most IVF centers use ICSI in 40-50% of their total IVF cycles.
- Before ICSI, Karyotype is offered for the male partner. In some centers,
Y chromosome micro-deletion screening is also performed.
- With ICSI there is slight increase in genetic abnormalities of the
offspring. Most of them are minor, the major congenital malformation
rate is thought to be similar to that of general population.

7
Egg donation:
Indications:
1. Ovarian failure either premature or physiological.
2. Patients with very poor ovarian function in whom IVF has failed
previously.
3. Patients over the age of 45 years and with severe male factor
disease necessitating ICSI.
4. Patients with hereditary genetic disease, using the patient’s own
gametes in such individuals is not advisable.
Sperm donation:
Indications:
1. Azoospermia.
2. Carriers of severe genetic disease.
Surrogacy
: used when the patient’s uterus is either absent or unable
to maintain a pregnancy so a surrogate or host uterus is used to carry
the pregnancy.
Generally used in young patient who has lost her uterus due to cancer or
uncontrollable bleeding as PPH or difficult myomectomy.
Preimplantation Genetic Diagnosis: (PGD)
It is a form of very early prenatal diagnosis. It combines ART with
molecular and cytogenetics to detect genetic disease in embryos at the
preimplantation stage.
Indications:
1. Single gene defects such as cystic fibrosis, thalassemia or sickle
cell disease.
2. Chromosomal rearrangement such as translocation.
3. HLA matching for donor sibling stem cell transplantation.

8
Complications of ART:
1)
Multiple pregnancy: 24% of patients will have twin when 2-3
embryos are transferred.
2)
Ectopic pregnancy: The risk is increased not only in patients with
tubal disease but it is also thought to be due to post-embryo
transfer uterine contraction that forces the embryo into the
fallopian tubes.
3)
Transvaginal oocyte retrieval complications which include
infection of the ovaries causing ovarian abscess and damage to
the bowel. Its incidence is about 1% or less.
4)
Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: Characterized by an
excessive ovarian response resulting in multiple follicular growth.
Usually it is mild-moderate, but severe cases can be life
threatening and is associated with intravascular fluid depletion,
thrombosis, ascites, pleural effusion.
Risk factors:
•
Young patient.
•
High estradiol level.
•
Polycystic ovaries.
Management:
•
Hospital admission with careful monitoring of fluid balance.
•
Human albumin solution may be given if hypoproteinemia
develops.
•
If ascites is present → drainage.
•
Thromboprophylaxis by antithrombotic stockings and heparin.
•
Subsequent pregnancy is usually uneventful. Rarely when the
patient’s condition is deteriorating or her life is at risk, then
pregnancy may need to be terminated.
