
AFTER MID
TOTAL LEC: 31
Gynaecology
Dr. Nadjma
Lec 30 - Family Planning
DR. NADJMA - LEC 3
مكتب املدينة


FAMILY PLANNING
There are several methods available for contraception and are
classified as follows:
1) Hormonal contraception
v
COCP
v
Progesterone only preparation as:
o Progesterone only pills (POP)
o Injectable progesterone
o Subdermal implants
v
Intrauterine devices (IUDs)
o Conventional IUDs
o Hormone releasing intrauterine system
2) Barrier methods
v
Condoms
v
Female barriers
v
Coitus interruptus
v
Natural Family planning
v
Emergency contraception
3) Sterilization:
v
Female sterilization
v
Vasectomy
The most commonly used contraceptive methods in UK in
sequential order are COCP, condom, vasectomy then IUCD. Failure rate
of Contraception is due to failure of use rather than the product itself &
the failure rate is expressed per HWY (hundred women per year),
meaning the no. of pregnancies one would expect to occur if 100 women
were to use the method for one year.
The characteristics of ideal contraceptive:
1. Highly effective
2. No side effects
3. Independent of intercourse
4. Rapidly reversible
5. cheap, widespread availability
6. Acceptable to all cultures & religions
7. Easily distributed
8. Administration by health care personnel not required
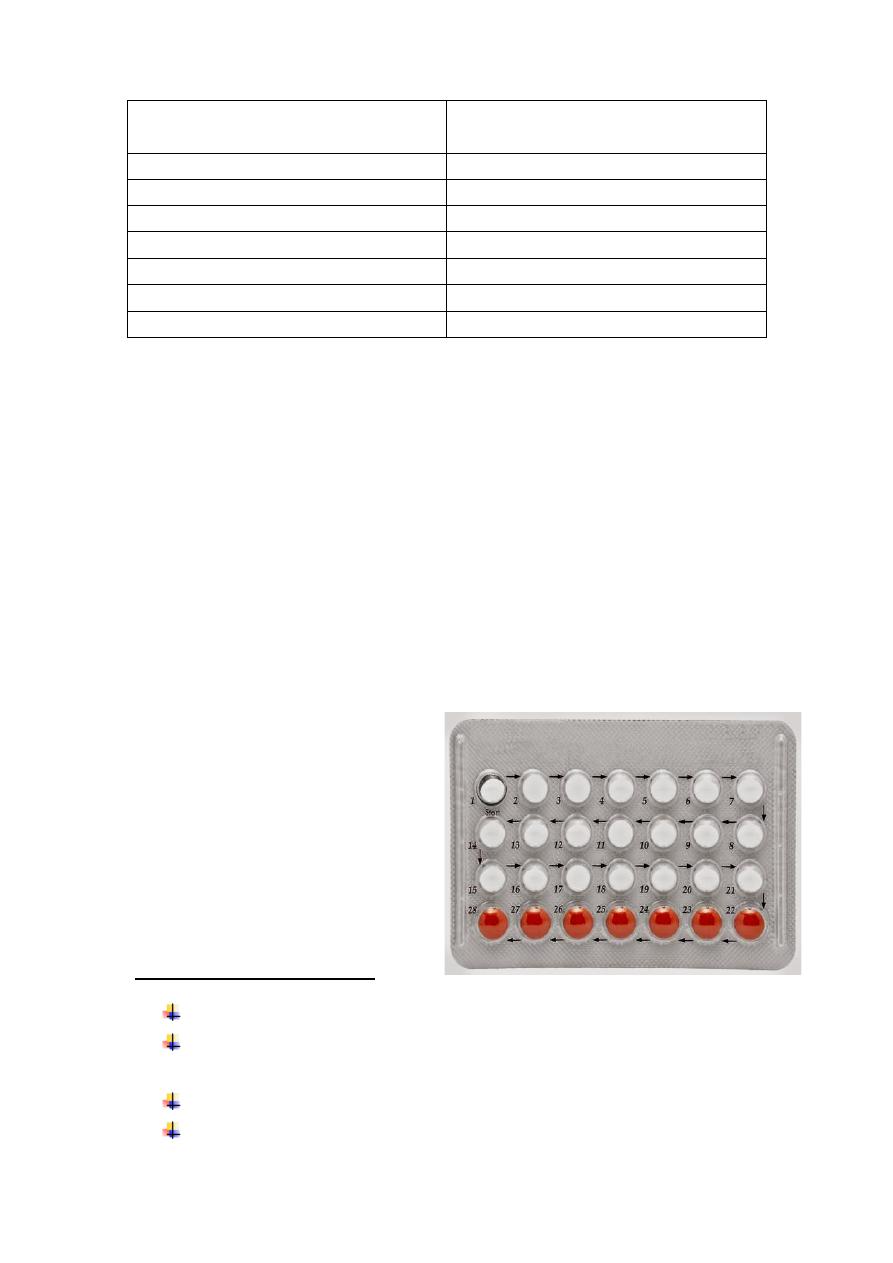
Combined Oral
Contraceptive Pills (COCP)
These pills contain both
estrogen & progesterone and are
taken for 21 days with 7 days pill
free interval.
Mode of action of COCP:
Inhibition of ovulation
Change in Cervical mucus characteristics, interfering with sperm
transport
Alteration in tubal motility
Endometrial atrophy &impaired uterine receptivity.
Contraception method
Failure rate per HWY
COCP
0.1 - 1
POP
1-3
Depo Provera
0.1 - 2
Norplant
0.2 - 1
Cupper bearing IUD
1 - 2
Levonorgestrel releasing IUD
0.5
Male condom
2 - 5
Advantages of COCP:
1. Menstrual cycle becomes more regular & menstrual bleeding is
lighter & of shorter period.
2. Less dysmenorrhea & less PMS.
3. Decrease incidence of Iron Deficiency Anemia.
4. Decrease incidence of benign breast lumps.
5. Decrease rate of functional ovarian cysts, endometriosis, acne and
PID.
6. protect against endometrial & ovarian cancer.
Contraindications of COCP:
Absolute Contraindication are:
1.
Ischemic heart disease
2.
CVA
3.
Significant HPT
4.
Arterial or venous thrombosis
5.
Acute or severe liver disease
6.
Pulmonary HPT
7.
Hyperlipidemia
8.
Pregnancy
9.
Focal migraine
10.
Estrogen dependant neoplasm as breast cancer
11.
Undiagnosed genital tract bleeding
Relative contraindication:
1. Generalized migraine
2. Long term immobilization
3. D.M, obesity, heavy smoking.
Side effects of COCP:
A.
Minor S.E:-
o
Weight gain, fluid retention & leg cramps
o
Headache, Nausea & vomiting.
o
Chloasma (Melasma) & greasy skin.
o
Mood changes, depression.
o
Loss of libido.
o
Mastalgia & breast enlargement.
o
Vaginal discharge, irregular bleeding
o
Growth of fibroid.
B.
Serious S.E:
o Venous thromboembolism
o Arterial disease
o Malignant disease
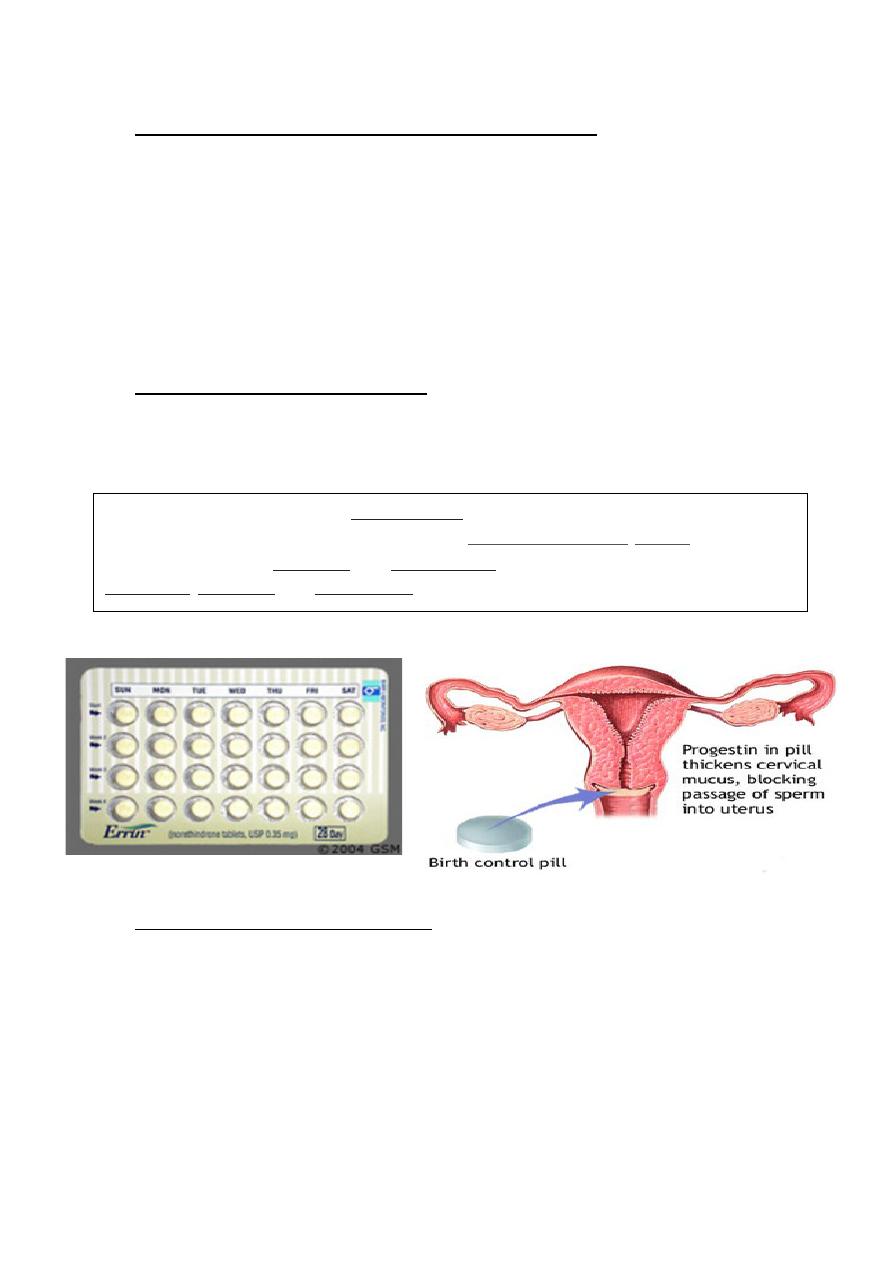
Progesterone only contraception
These include:
1. POP
2. Injectable progestogen.
3. Subdermal implant.
4. Hormone releasing Intrauterine system
Mechanism of action:
It inhibits ovulation in high dose
Affect Cervical mucus & reduce sperm penetration
Affect endometrium making it thin & atrophic thereby prevent
implantation
Side effects of progestogen only contraception:
1.
I
rregular Vaginal bleeding or amenorrhea.
2. Premenstrual like syndrome.
3. Acne and breast tenderness
4. Functional ovarian cyst.
5. Osteoporosis.
6. Risk of ectopic pregnancy.
Progesterone Only Pills (POP)
It is taken continuously every day without a free interval, they
contain the 2
nd
generation progesterone.
Particular indications for POP :
§
Breastfeeding
§
Older women
§
Presence of CVS risk factors
§
D.M.
Failure rate of POP is greater than that of COCP
NOTE ADDED BY A STUDENT: Norethisterone was the first active progestin used in oral
contraceptive pills and is classified
along with medroxyprogesterone acetate,
as a first -
generation progestin. Norgestrel and levonorgestrel are second - generation progestin, and
desogestrel, gestodene, and norgestimate are the newer, third - generation progestin

Injectable progestogen
These include medroxyprogesterone acetate 150 mg (Depo
Provera) given every 3 months & Norethisterone enanthate 200mg
given every 2 months. Depo Provera is given by deep IM injection, it
inhibits ovulation causes infrequent or scanty bleeding or amenorrhea.
Particular side effect of Depo Provera:
§
Delayed fertility
§
Weight gain
§
Osteoporosis
§
Persistent menstrual irregularity.
Progestogen implants
Norplant which consist of six silastic rods is inserted Subdermally
in the inner aspect of upper arm under local anesthesia by a special
trained person, it release levonorgestrel & last for 5 years. It is expensive
and cause menstrual irregularity.
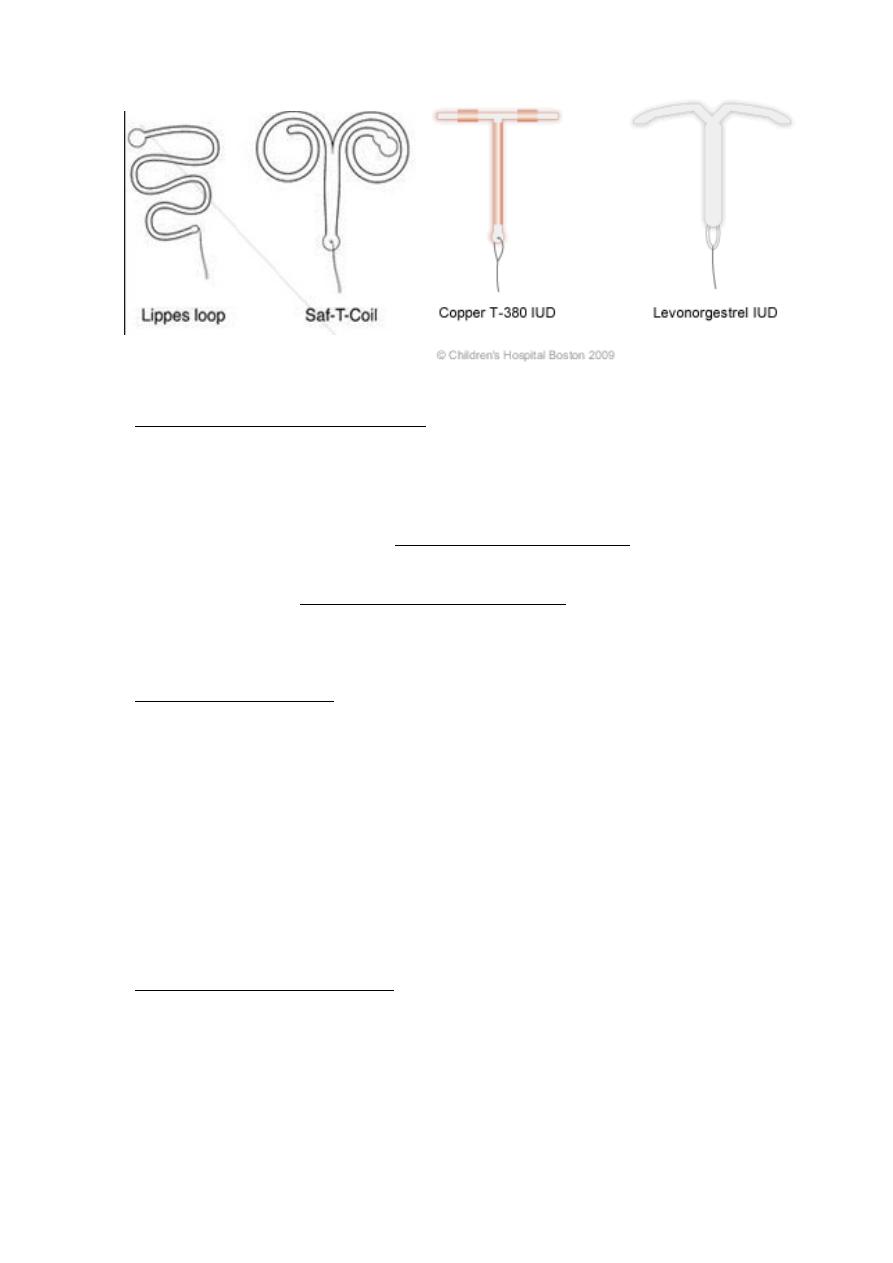
Intrauterine contraceptive device
There are several types:
A. inert plastic device as lippes loop or saf - T coil, and Dalkon shield.
They cause heavy & painful menstrual periods, they could be left
in place until menopause. (not much used anymore)
B. Newer copper beering IUD they cause less menstrual disruption
than the older plastic device, they licensed for 3-5 years of use,
but many will last longer possibly for up to 10 years.
C. Hormone-releasing IUDs as Levonorgestrel IUS (marina), it is
associated with dramatic reduction in menstrual blood loss.
Mechanism of action of IUCD:
All IUCDs induce an inflammatory response in the endometrium
that prevents implantation.
Cu-bearing IUCD has a toxic effect on sperms that prevent
fertilization while Hormone releasing IUS prevent pregnancy by a local
hormone effect on Cervical mucus & endometrium.
Side effects of IUCD:
§
Increase menstrual blood loss
§
Increase dysmenorrhea
§
Increase risk of pelvic infection following insertion
§
Perforation
§
Expulsion
§
Ectopic pregnancy
Contraindications to IUCD:
§
Previous PID.
§
Previous ectopic pregnancy.
§
Known malformations of uterus.
§
Copper allergy
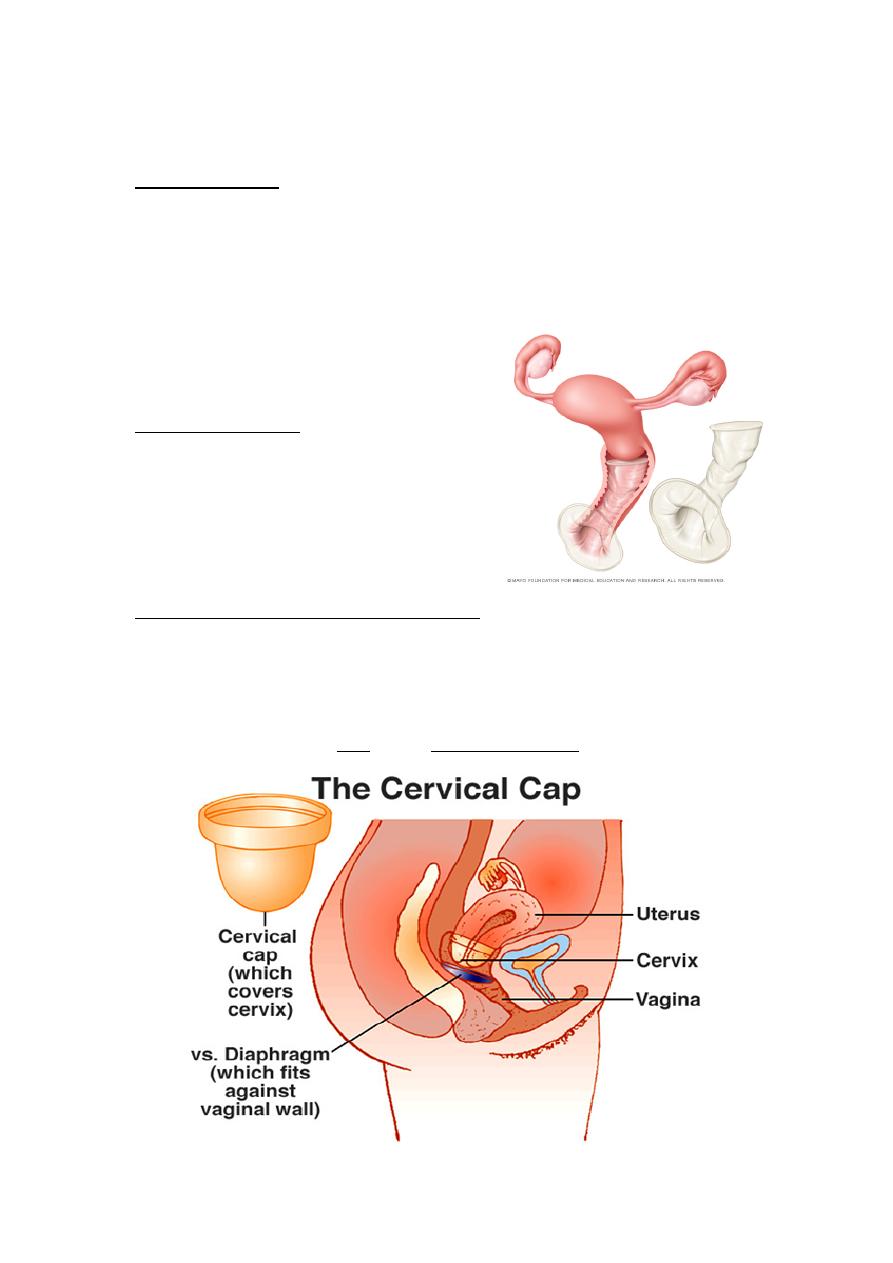
Barrier Methods of contraception
Male condom:
It is one of the most popular method of contraception. It is cheap,
widely available and free of side effects except for allergic reaction. It is
made of latex rubber and protects against STD. Most condoms are
lubricated with spermicidal cream or
jelly.
Female condom:
It is made of plastic & thus less
likely to burst. It protects against
infection but is expensive.
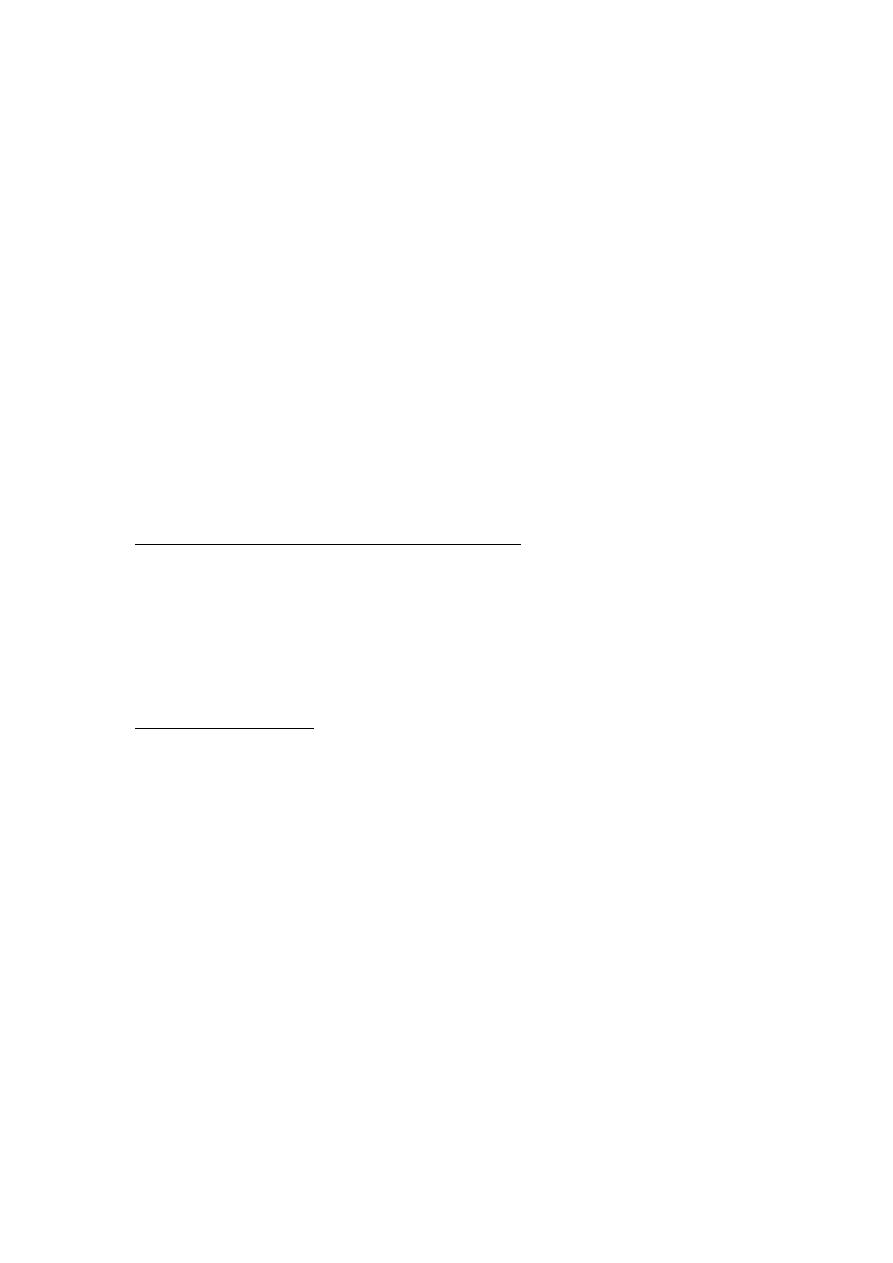
Vaginal diaphragm & Cervical cup:
Female condom
They are all used with spermicidal cream or gel. The diaphragm is
inserted prior to intercourse & should be removed no earlier than six
hours later. Female barrier offers protection against ascending infection
but can increase risk of UTI & may Vaginal irritation.
Natural family planning
This involves avoidance of intercourse during the fertile period of
the cycle. The fertile period is calculated by various techniques such as:
1. changes in basal body temperature (Increases by 0.5 C due to the
thermogenic progesterone hormone).
2. Changes in Cervical mucus (thin and cupious).
3. Changes in cervix.
4. Multiple indices., persona kits (It works by monitoring the changes
in luteinizing and estrogen hormones in patient's urine, when they
become elevated near ovulation time (LH surge) the couple should
abstain from intercourse).
Lactational Amenorrhea Method (LAM
)
For this method to be effective the mother should be fully a
breast feeder, amenorrhic & the age of her child less than 6 months.
Failure rate is 2%.
Coitus interruptus
This is widely practiced & does not require any medical
supervision, this involves removal of penis from the vagina immediately
before ejaculation takes place, it is not reliable as pre - ejaculatory
secretion may contain millions of sperms thus emergency contraception
should be available.
Emergency contraception
Defined as any drug or device used after intercourse to prevent
pregnancy, EC should be considered if unprotected intercourse has
occurred, if there has been failure of a barrier method e.g. a burst
condom or if COCP has been forgotten.
Types of EC:
a. Hormonal EC
A combination of 100mg of ethinyl estradiol & 500 mg of
levonorgestrel is taken twice, the two doses being 12 hours apart &
started within 72h of unprotected intercourse.
Mechanism of action
is believed to be prevention Of
implantation due to endometrial shedding
Side Effects
Nausea & Vomiting. Failure rate is 20 – 25 %.
b. IUD for EC
A Cu bearing IUD can be inserted. It is effective for 5 days
following the anticipated day of ovulation, the IUD prevents
implantation & the Cu ions exert an embryo toxic effect.
Sterilization
This is permanent method of contraception, they are chosen by
older individuals who are sure that they have completed their family & a
previous consent should be taken from the patient.
Female sterilization:
A.
Mechanical blockage of both fallopian tubes to prevent sperms
reaching & fertilizing the oocyte.
B.
Hysterectomy
C.
Bilateral salpingectomy
Female sterilization can be done by:
1. Laparoscopically
2. Minilaparatomy
3. Colpotomy through posterior vaginal fornix
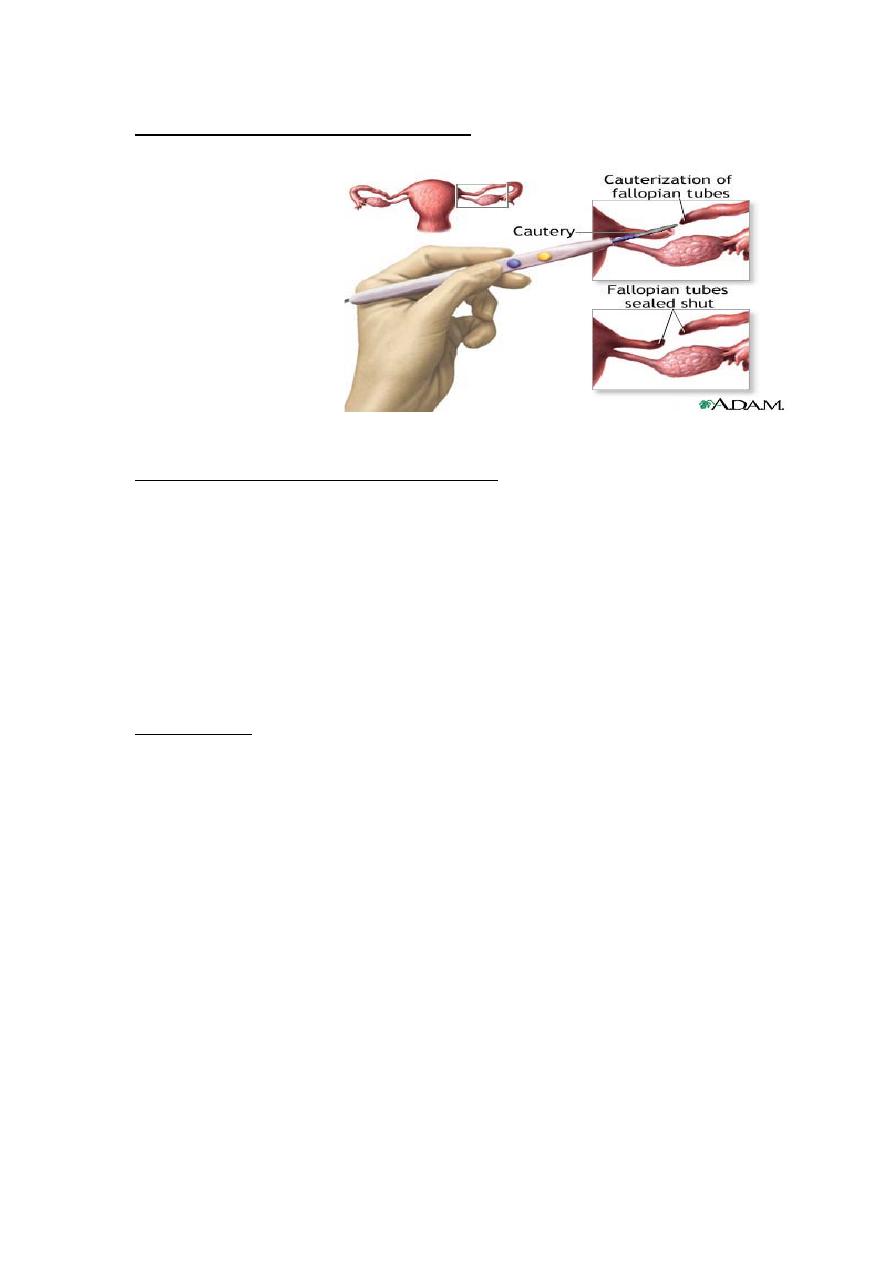
Techniques of female sterilization:
1. Ligation
2. Electrocautery \
diathermy
3. Falope ring
4. Clips
5. Laser
Complications of female sterilization:
•
Anesthetic complications
• Damage to intra-abdominal organs
• Ectopic pregnancy
• wound infection
• Menstrual disorder
• Failure
Vasectomy:
This involves division of vas deferens on each side to prevent
release of sperms during ejaculation, it is technically an easier, quicker
& performed under local anesthesia, vasectomy is not effective
immediately so men should do SFA 12 wk & then 16 wk later to check for
the presence of sperms.
If 2 consecutive samples are free of sperms then the vasectomy
can be considered complete & alternative methods of contraception
must be used until that time.
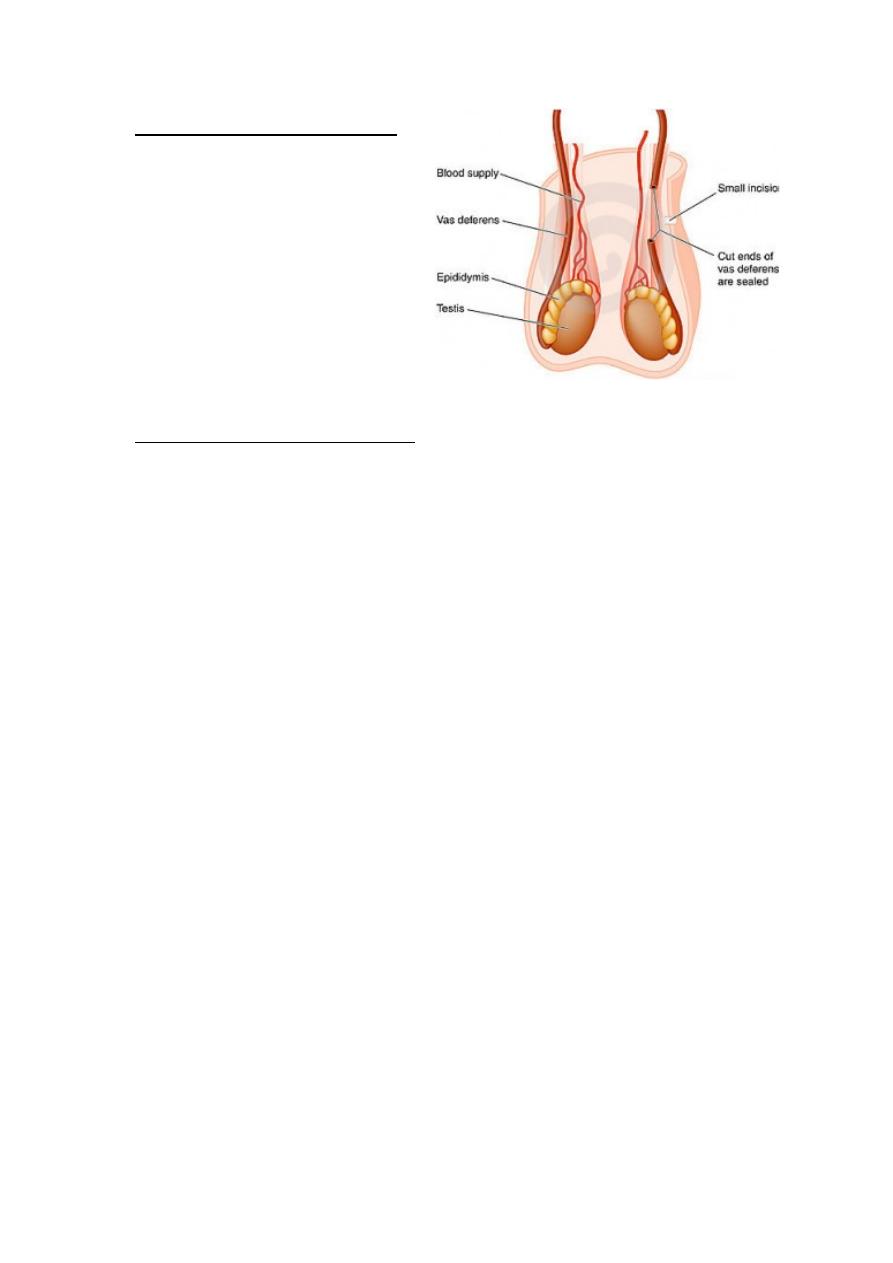
Techniques for vasectomy:
1. Ligation or clips
2. Unipolar diathermy
3. Excision
4. Non scalpel vasectomy
5. Silicone plugs, sclerosing
agents
Complications of vasectomy:
1.
Wound infection
2.
Heamatoma
3.
Sperm granuloma
4.
Antisperm AB
5.
Some suggest a linkage between vasectomy & testicular &
prostatic tumor
