
CLINICAL
SIGNIFICANCE
of
Proteins
in
Blood
and
Urine
Basil OM Saleh

Objective
1. Type of proteins in blood
2. Clinical Diagnostic & Utility
of Proteins Measurements in
blood
3. Causes of Proteinuria

Proteins are Polypeptide group of
nutrients in human body. All enzymes,
receptors, membrane channels such as
those of Na-K, Ca channels, Ags,
Abs(Igs), coagulation factors and peptide
hormones (GH, prolactin,… ),…, etc are
proteins in nature. All proteins are
synthesized in the liver, with exception

of complement systems ( C1-C9 these
are components of immune system
synthesized by liver and macrophages),
and Immunoglobulins (Igs) (by plasma
cells of immune system).
Proteins may
be linear structural (such as collagen
component of connective tissue) or
globular functional such as enzymes &
peptide hormones.

Amounts of proteins in blood depend on
balance:
rate of synthesis
↔
(rate of catabolism+
rate of clearance).
However, protein
distribution between the Intravascular
(IV) and Extra vascular compartments is
also important and therefore blood
protein concentrations are affected by
dehydration & over hydration.

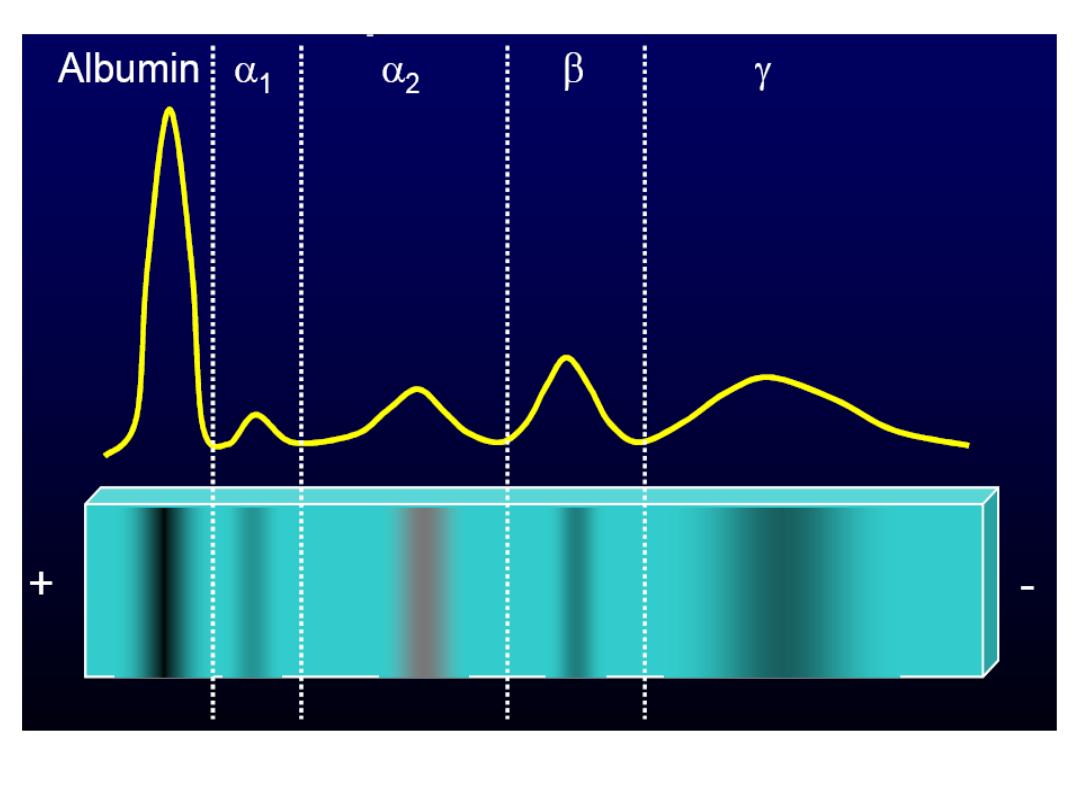
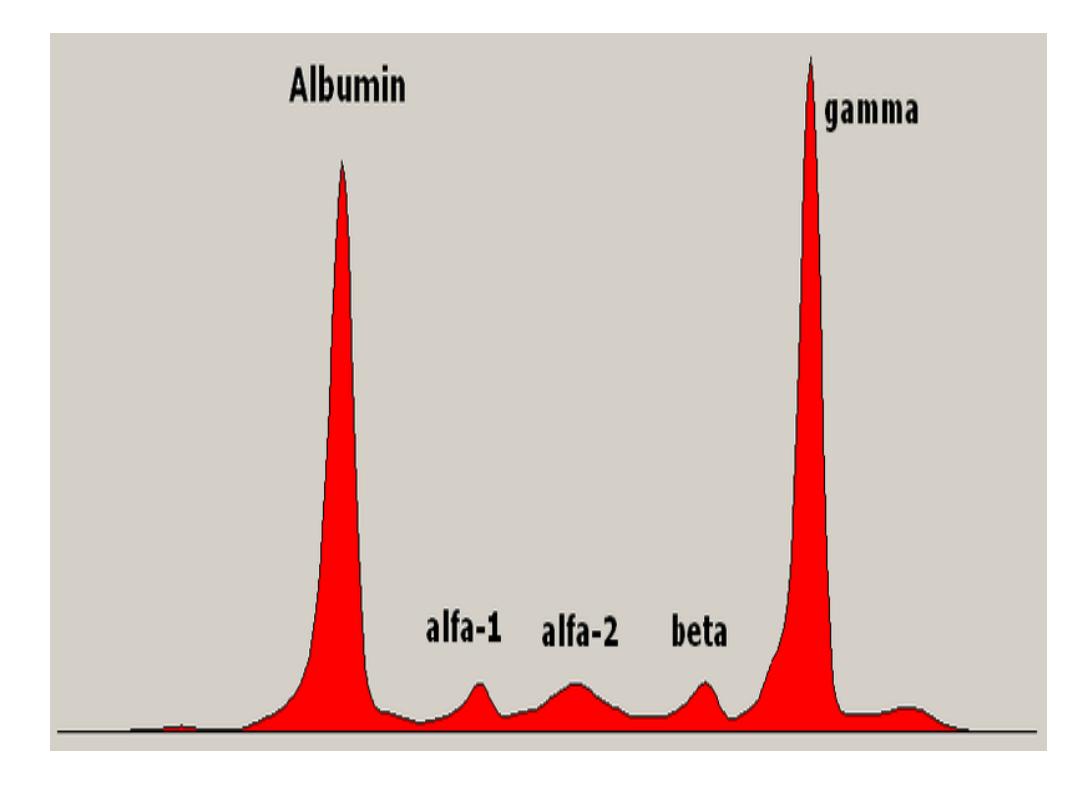
Proteins
in blood involved two types:
Albumin & total Globulin. Albumin is the
major single protein accounts to 60 % of
total serum protein, while globulin is
consisted of 4-5 fractions; α
1,
α
2,
β
1,
β
2,
and
γ globulins. These Proteins
components
are
separated
by
electrophoresis technique in which
serum (but not plasma) is introduced to
filter paper in a media of PH 8.6 to make

protein which are polar substances
negatively charged. Then electrical
current is passed into media and the
serum proteins are separated according
to their MW and charge intensity into five
–six fractions or bands: albumin, α1-
globulin, α2-globulin, β-globulin (may be
β
1
&
β
2
), and γ-globulin.
Total Serum Protein=S. albumin + total
serum globulin.



Total Serum Protein in human is ≈56-86
gram/l, albumin alone is ≈38-51 gram/l.
The total globulin is calculated by
subtraction of total protein from
albumin.
Measurement of total serum protein
alone is of little clinical value ?.
Hyperproteinemia
and
hyperalbuminemia are rare and are
of no clinical significance value and
may obtained from prolonged vein
stasis
during
blood
collection,
posture (due to fluid redistribution)
and from excessive dehydration.
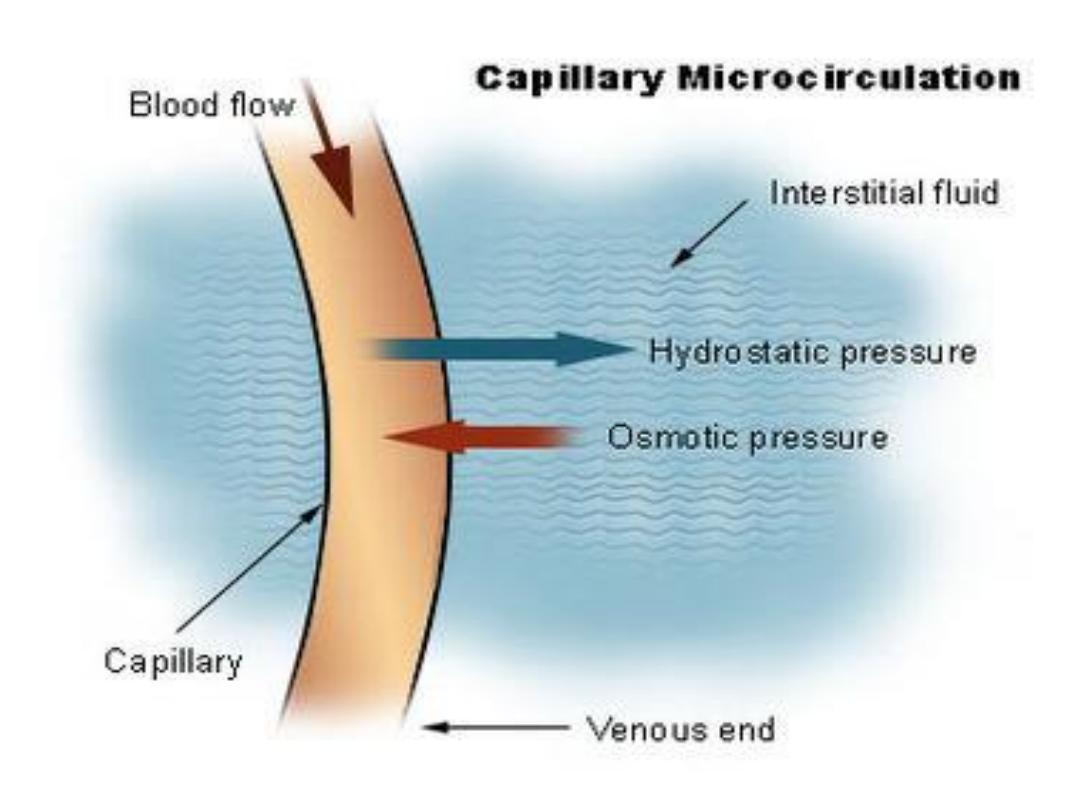
Hypoalbuminemia:
It is clinically an important condition
because albumin is one of the major

components of osmotic colloid pressure
of blood vessels and involved in normal
fluid
distribution
between
the
Intravascular
and
Extra
vascular
compartments and in maintenance of
normal blood pressure. Albumin is also
the major transporter substance in the
blood; transporting bilirubin, fatty acids,
steroid
drugs,
steroid
&
thyroid
hormones,
…..
.

Causes of Hypoalbuminemia
1. Chronic liver disease ; liver cirrhosis
2. Advanced kidney disease; Nephroteic
syndrome
&Chronic
renal
failure
3.
Malnutrition
(Kwashiorkor
&
Marasmus diseases) and Malabsorption
like in Tropical intestinal diseases;
Celiac
disease
4. Loss through GIT; Enteropathy
5. skin lesions; extensive burns.

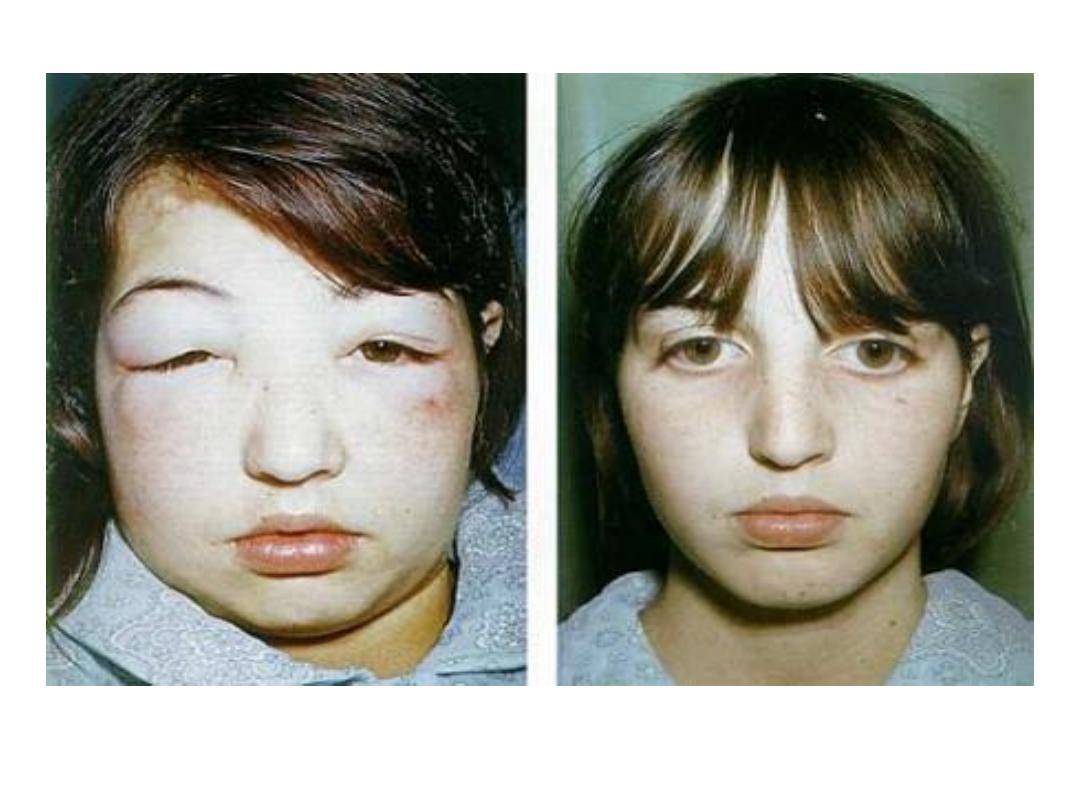
Clinical
consequences:
1. edema due to migration of fluid from
IV
to
interstitum
compartment
2. transporting and binding capacity
defects; such as for fatty acids, bilirubin,
steroid Hs and drugs which may leads to
toxicity
with
appropriate
dose.
Analbuminemia is a rare disorder
characterized by low blood albumin (s.
albumin 10 gram/l; but of no edema or
other symptoms and signs).

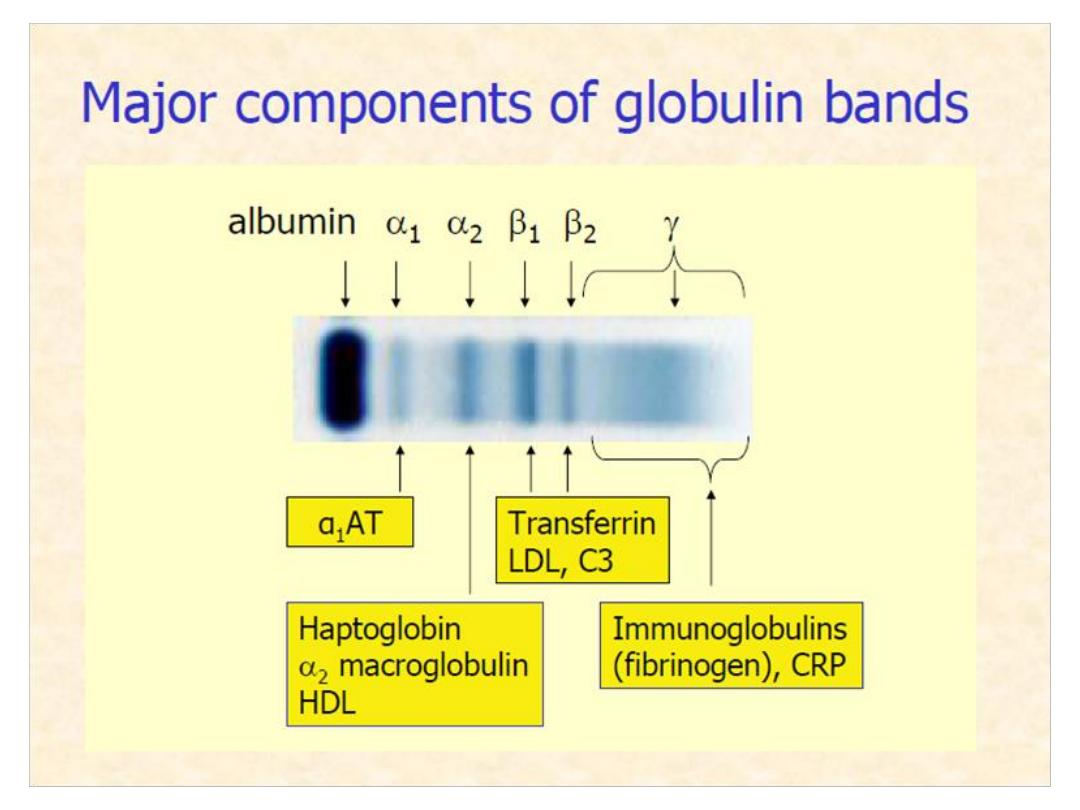
Globulin
This include 4-5
fractions (alpha 1, alpha 2, beta, and
gamma fractions).
Increased in globulin may be due to
increased in one or more of its
fractions;α,β, and γ. The α-1 and -2
include : α
1
-Antitrypsin, haptoglobin,
ceruloplasmin, C- reactive
protein(CRP), α2- macroglobulin….
etc.

α
1
-Antitrypsin(AAT)
•Protease inhibitor that binds to, and
inactivates macrophage enzymes like
trypsin, limit their actions during
infection, and protects the body.
•Deficiency
is
associated
with
–
Pulmonary
emphysema.
– Liver Cirrhosis
(measurement of
serum ATT is one of tests used in
investigation of prolonged neonatal
direct hyperbilirubinemia;
Jaundice
).

•α
1
-Fetoprotein(AFP)
–
Principal fetal protein, used in
screening for fetal abnormalities (neural
tube defects) and in adult for liver
carcinoma
investigation.
α
2
-Macroglobulin
• Largest non-immunoglobulin in blood
~750
KD
•Protease
inhibitor
• Increased in Nephrotic syndrome
(largest
in
size)

(α -globulin
)
Ceruloplasmin (Cp)
•Copper
transporting
protein
•Participates in plasma redox reactions
like
Fe
+2
Fe+3.
•serum CP measurement is used in
investigation of Wilson’s disease (Liver
cirrhosis-Copper storage disease) in
which serum Cp level is decreased due
to genetic defect in incorporation of Cu
with apoceruloplasmin in the liver,
leading to precipitation of toxic Cu ion
and damage of liver .

(α
2
)
Haptoglobin
•Binds to, and preserves hemoglobin
and its content of iron during
hemolysis.
•Hemolytic diseases can deplete
haptoglobin
levels.
(β)
Transferrin
•Iron
transporting
protein
•Transferrin is increased in iron
deficiency
anemia.
Apotransferrin+Fe+3=Transferrin

β
2
-Micro
globulin
BMG
•Smallest blood protein (MW=11.8K)
•BMG is filtered through the glomerulus,
but
is
reabsorbed
by
renal
tubules.
- Urinary BMG levels are a sensitive
measure
of
renal
tubular
function

γ
Region
•Includes Immunoglobulins (IgG, IgM,
IgA,
IgD
&
IgE).
They are involved in specific immune
system.
•
CRP
is the most sensitive indicator
of Acute Phase Reaction (non specific
early
immune
defense
system)
– Serum CRP (high sensitive hs-CRP)
increased in Inflammation, trauma,
infection,
etc.

Protein
in
urine
normally less than 100 mg/day of
proteins appears in urine, in kidney
disease this value increased according
to degree of kidney damage which
reflect mainly the glomerular damage.
Normally glomerulus is permeable to
proteins of MW ˂ 60 KD (D Dalton unit of
MW.

In kidney damage(mainly of glomerulus)
excess amounts of proteins of large
MW˃60 KD will pass in the urine and may
reach 5-50 gr/day. Presence of low MW
of proteins, like BMG in the urine
indicates the renal tubules damage as
these tubules normally catabolize and
reabsorbed the low MW proteins. In
tubules damage these proteins will
escape from the damaged tubules and
appear in the urine(Low MW).
