
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
(MM)
objective:
definition of MM
B
iochemical investigation in
D
iagnosis and prognosis
Basil O M Saleh

MULTIPLE
MYELOMA
(MM)
•
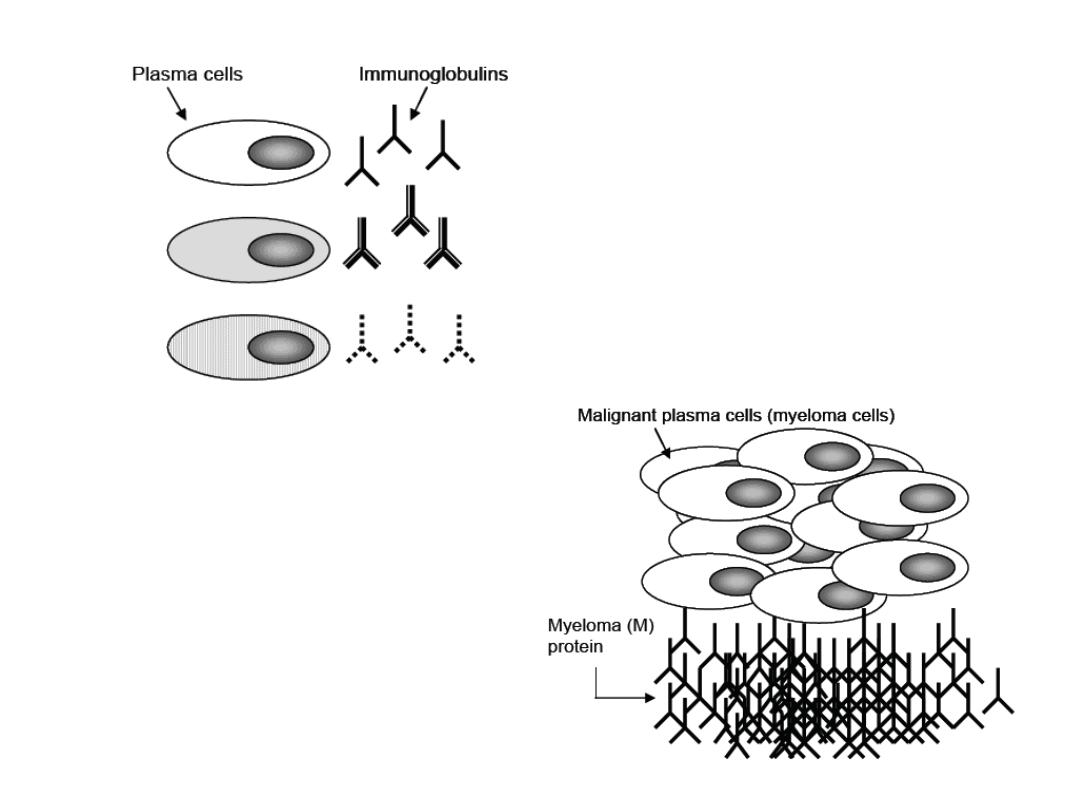
A neoplastic (malignant) proliferation of a
single clone (group) of plasma cells in the bone
marrow
•
Major
laboratory
diagnostic
criteria
• >10% plasma cells in bone marrow
•
Complete
or
incomplete
monoclonal
immunoglobulin(s) in serum and/or urine at
elevated
concentrations

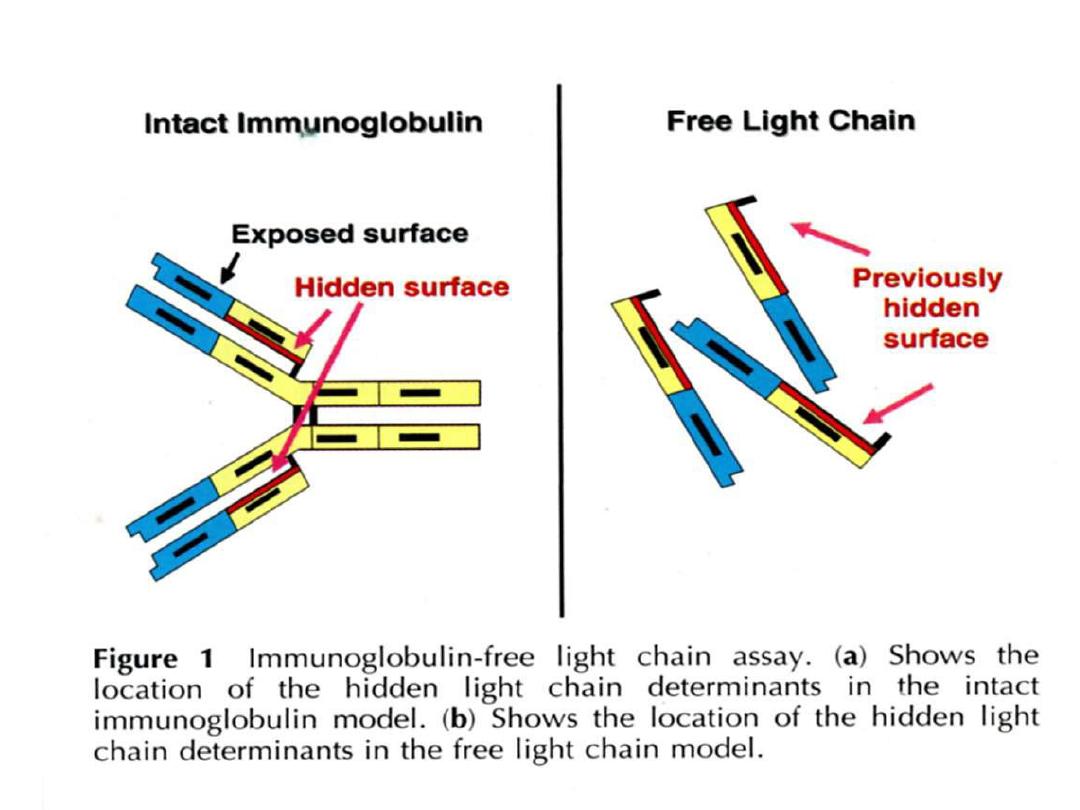
PARAPROTEINS ("M-proteins“)
Paraprotein
is a complete or fragment (only
light or heavy chain or part of them) of an
immunoglobulin molecule, usually IgG or IgA.
Greatly increased
amounts is called
paraproteinemia;
Increased of a single or
clone of Immunoglobulin (Monoclonal
Immunoglobulin).
Paraprotein is also referred to
M-protein
("M" means both monoclonal and myeloma,
the usual cause of an M-protein)
In Sha ALLHA, you will refer to Lab.
SPE for M band or SPE for Paraprotein

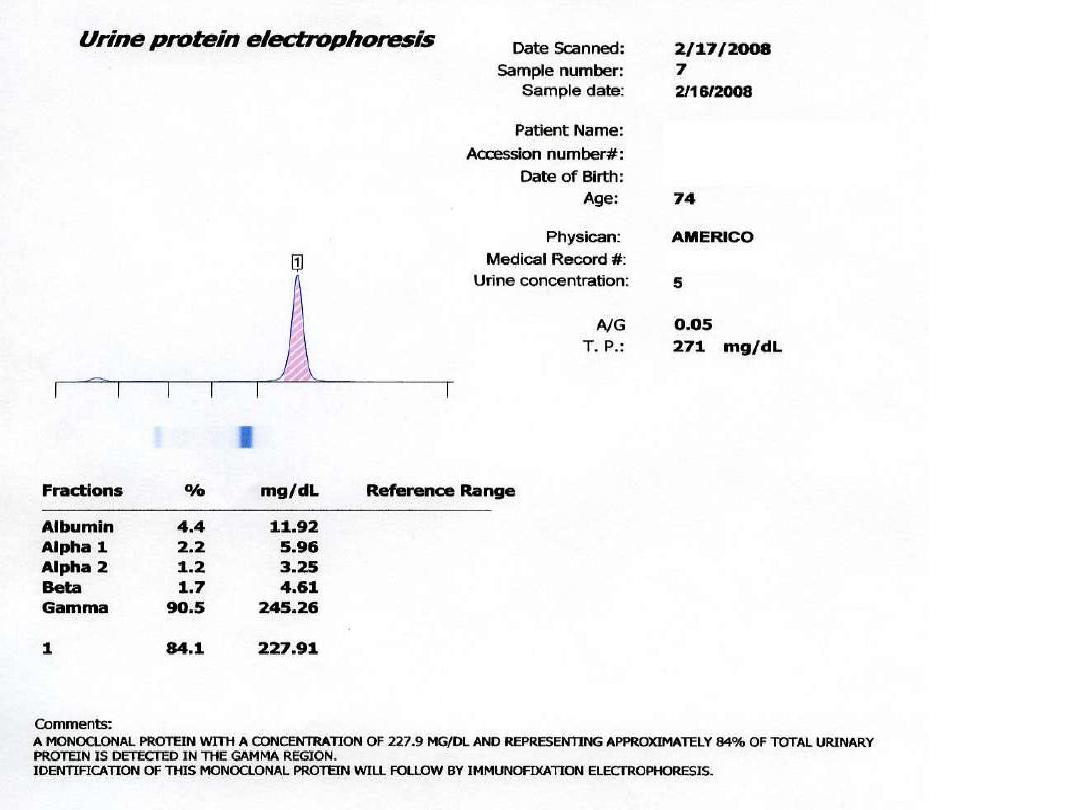
It may
spill into the urine, especially if the
paraprotein is light chain (low MW 22 KD), and
referred to "
Bence-Jones protein BJP
“ is a
light or dimer of light chain (MW 44 KD).
You can test urine for Bence-Jones protein by
yourself, using a test tube and a Bunsen
burner.
Bence-Jones protein precipitates on heating
around 40-60 °C.
You will refer
Urine for BJP

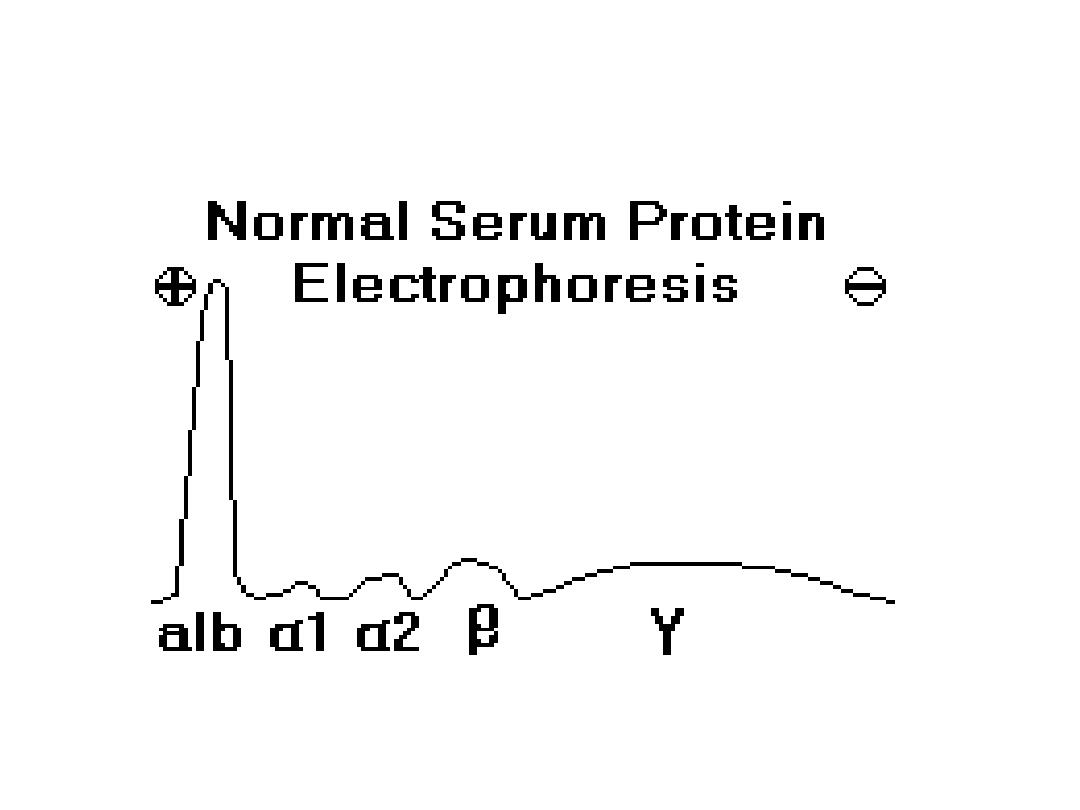
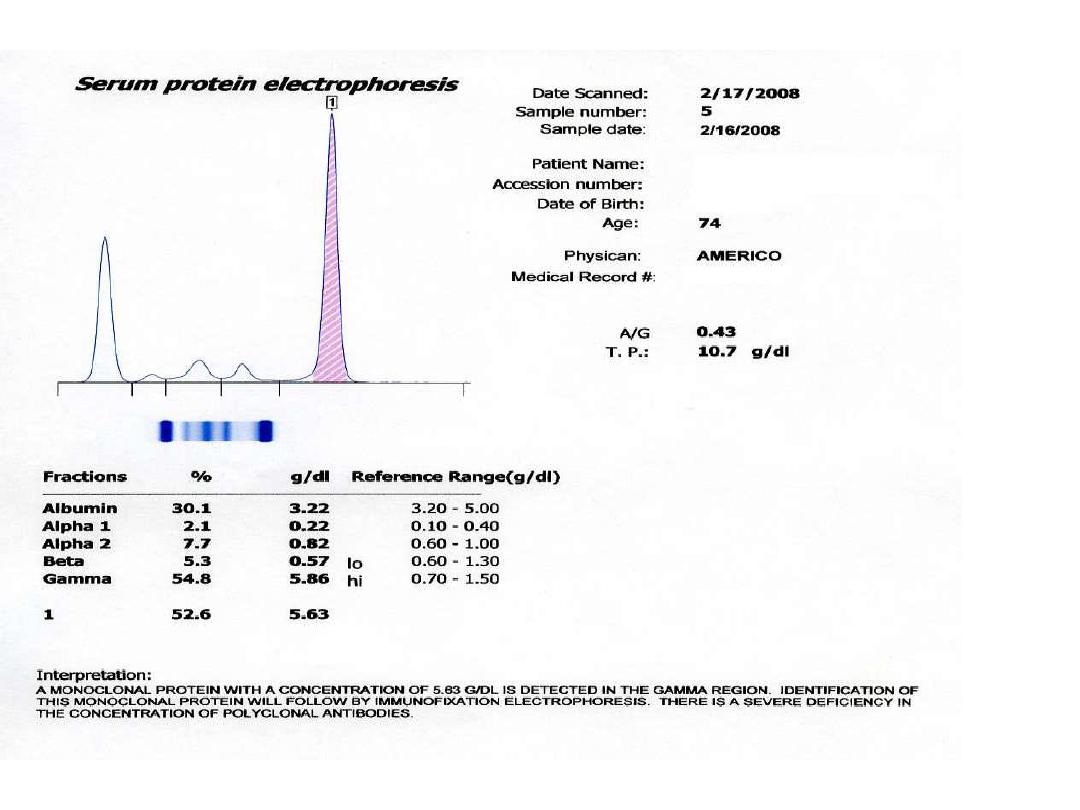
Paraprotein
appears as a sharp peak (a
"spike"), most often in the gamma region,
though it may be anywhere. Such a peak
indicates the presence of a monoclonal
gammopathy
A majority of detected monoclonal
gammopathies are
the result of plasma cell myeloma. These
patients
typically have depression (decreased) of other
gamma globulins (Igs)
and albumin.

Some other causes of monoclonal
gammopathies
include: Waldenstrom's macroglobulinemia
heavy chain disease
CLL, lymphoma, amyloidosis (occasional
cases.

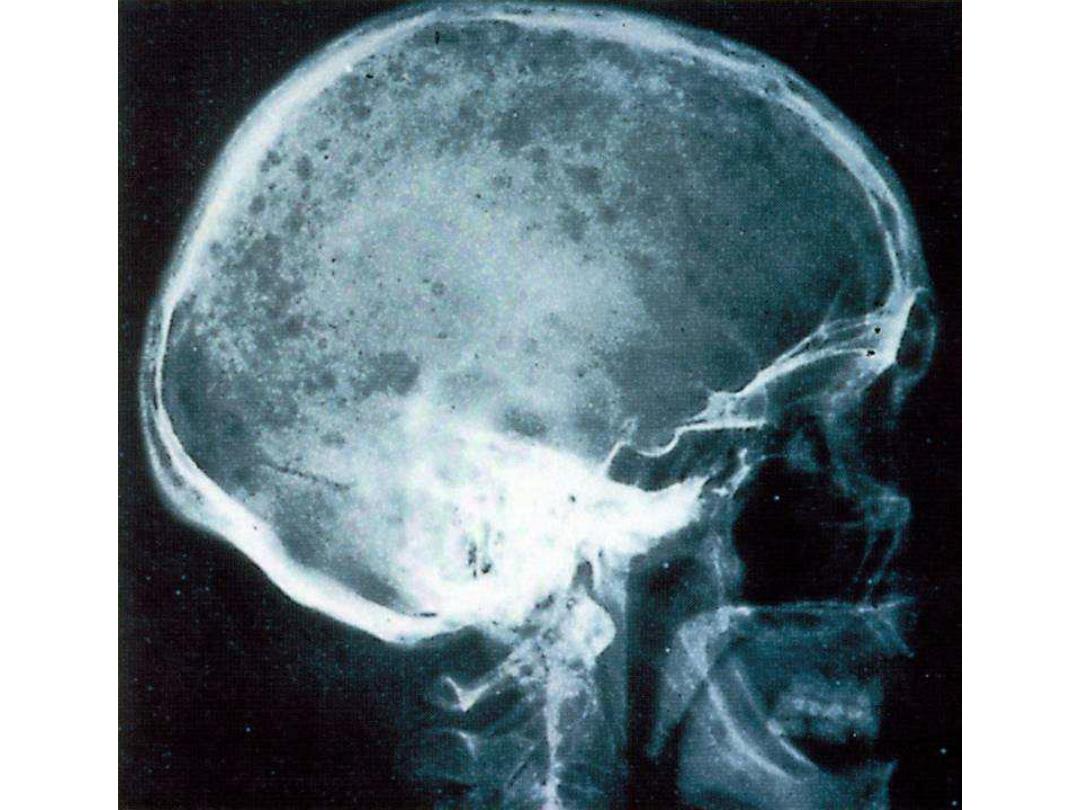
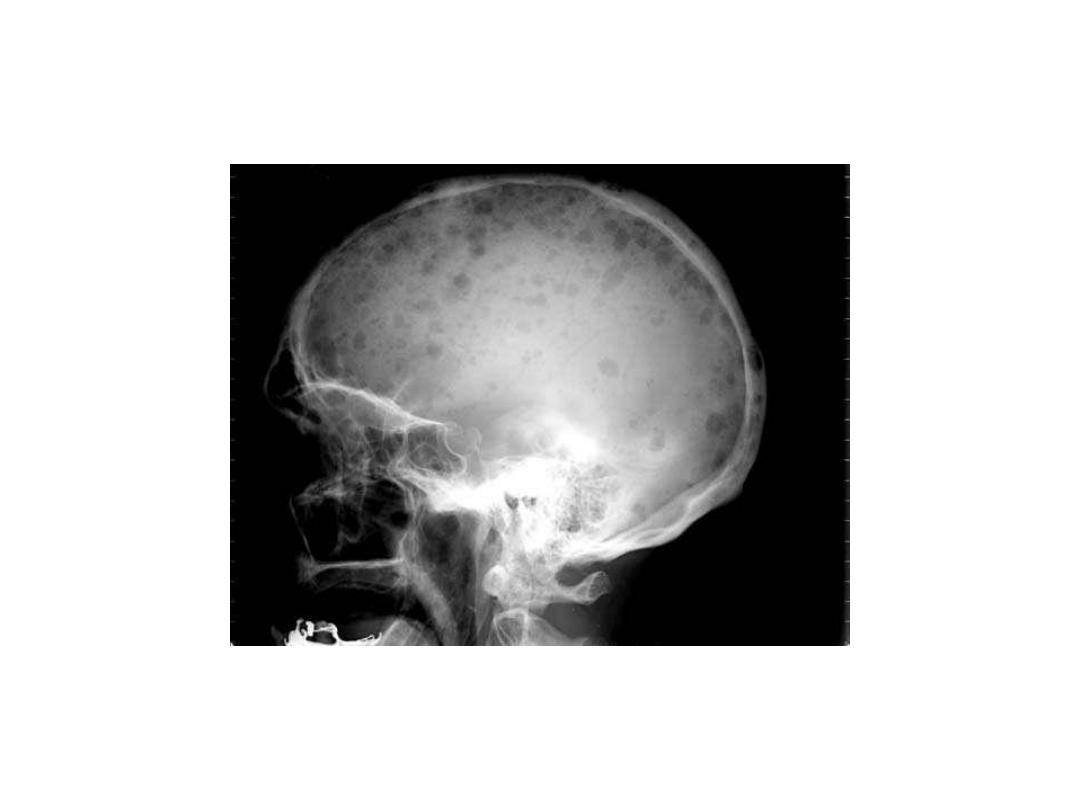
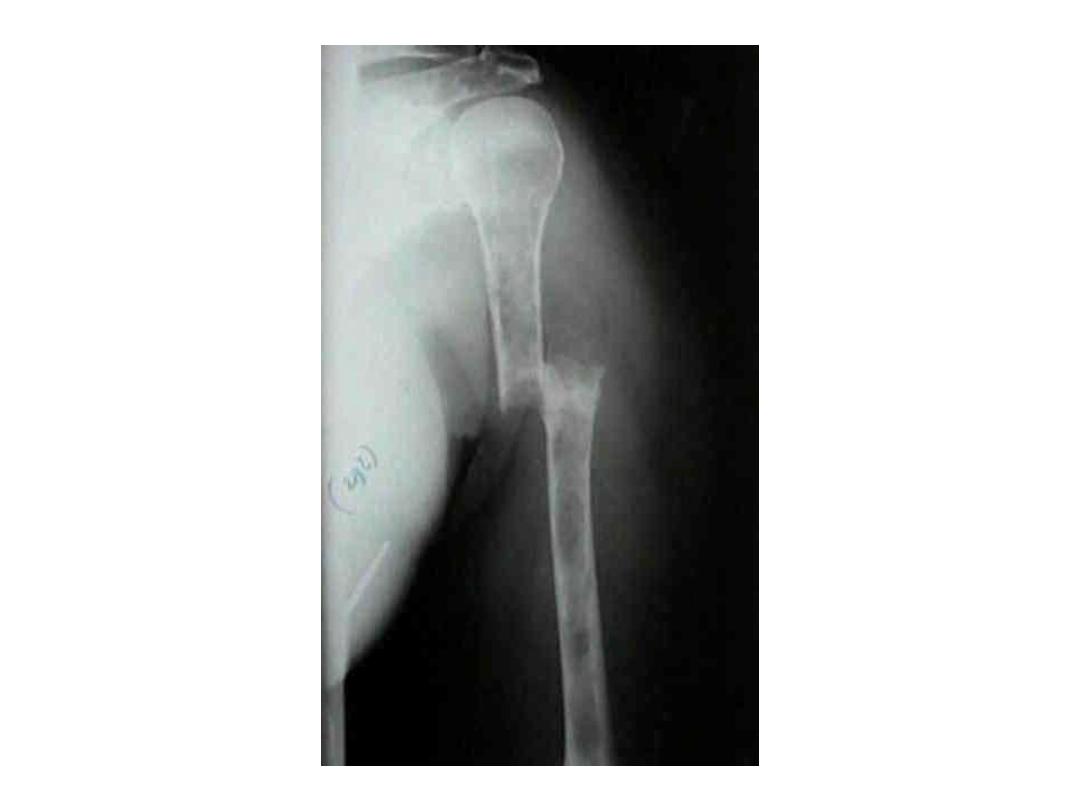
RADIOLOGY DIAGNOSIS OF
MULTIPLE MYELOMA
• Skeletal bone X-ray series
• Skull, spine, ribs, arms, legs and pelvis
• Alternative procedures
• Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
• Computed tomography (CT)
• Computerized axial tomography (CAT)
• Lytic bone lesions and/or pathologic
fractures
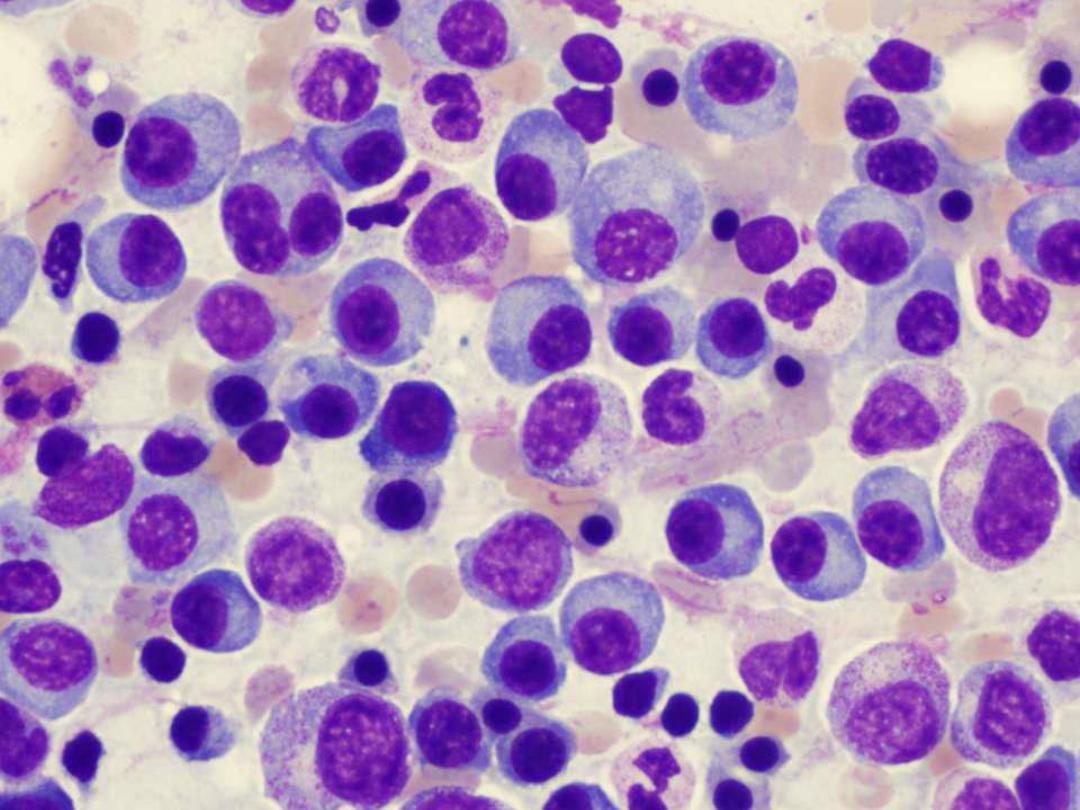

Laboratory analysis
1
. significant increased ESR(erythrocte
sedimentation rate) > 75 mm3/hr.
2.Serum protein electrophoresis SPE(M
band) is positive
3.Bence Jones protein BJP in
urine(positive
band)
Consequences of MM
1. hypercalcemia & hyperphosphatemia
2. hyperuricemia
2. hyperuremia & hypercreatininemia (severe stage)
4. decreased Hb (severe stage)
5. Hypoalbuminemia (severe stage)
6. Normal ALP

These laboratory investigation results
depend on
stage of MM, for example; increased
urea, creatinine, uric acid and
decreased s. albumin occur when
kidney integrity and function decline
because of precipitation of BJP in it.
