1
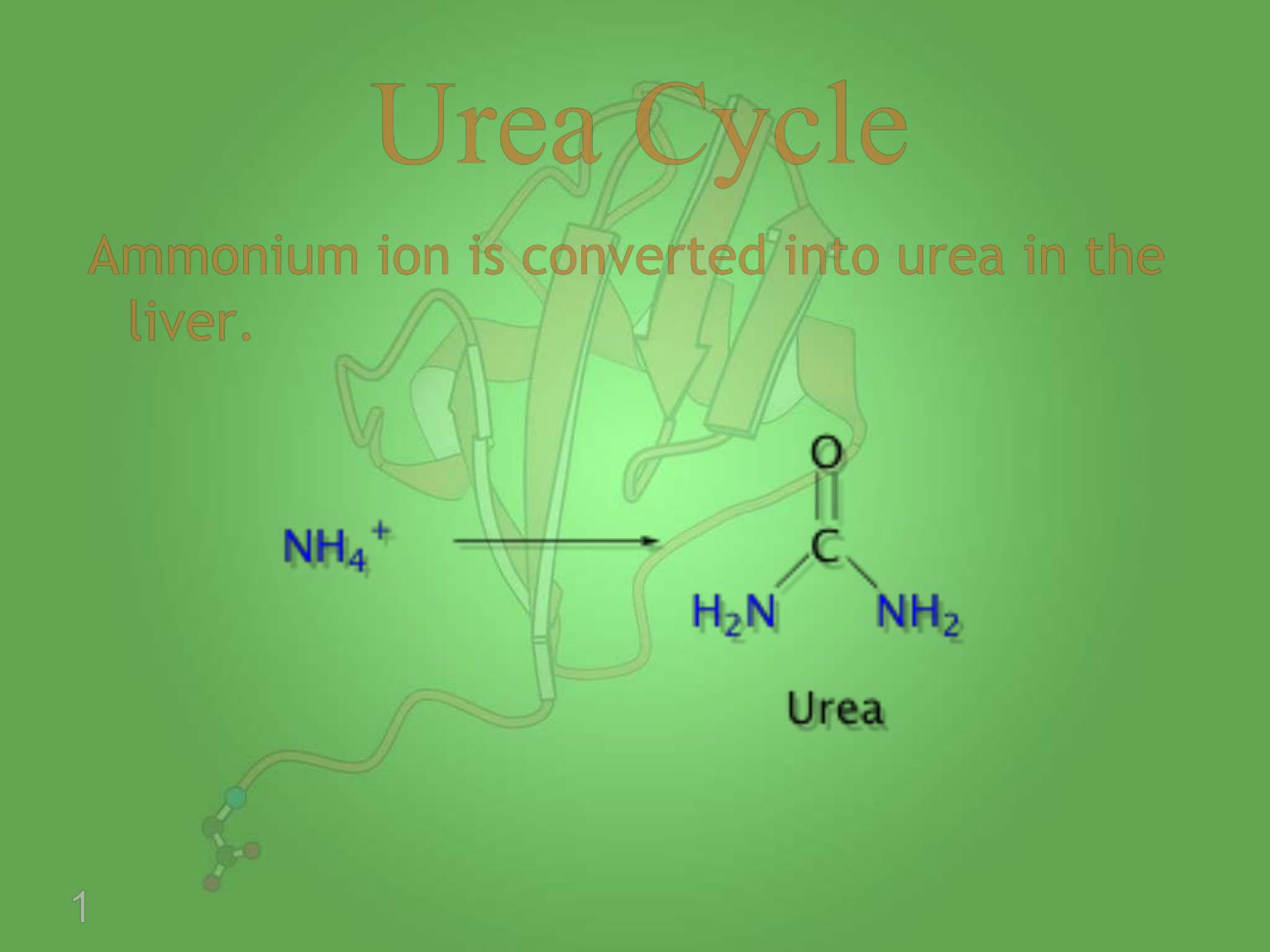
Ammonium ion is converted into urea in the
liver.
Urea Cycle
2
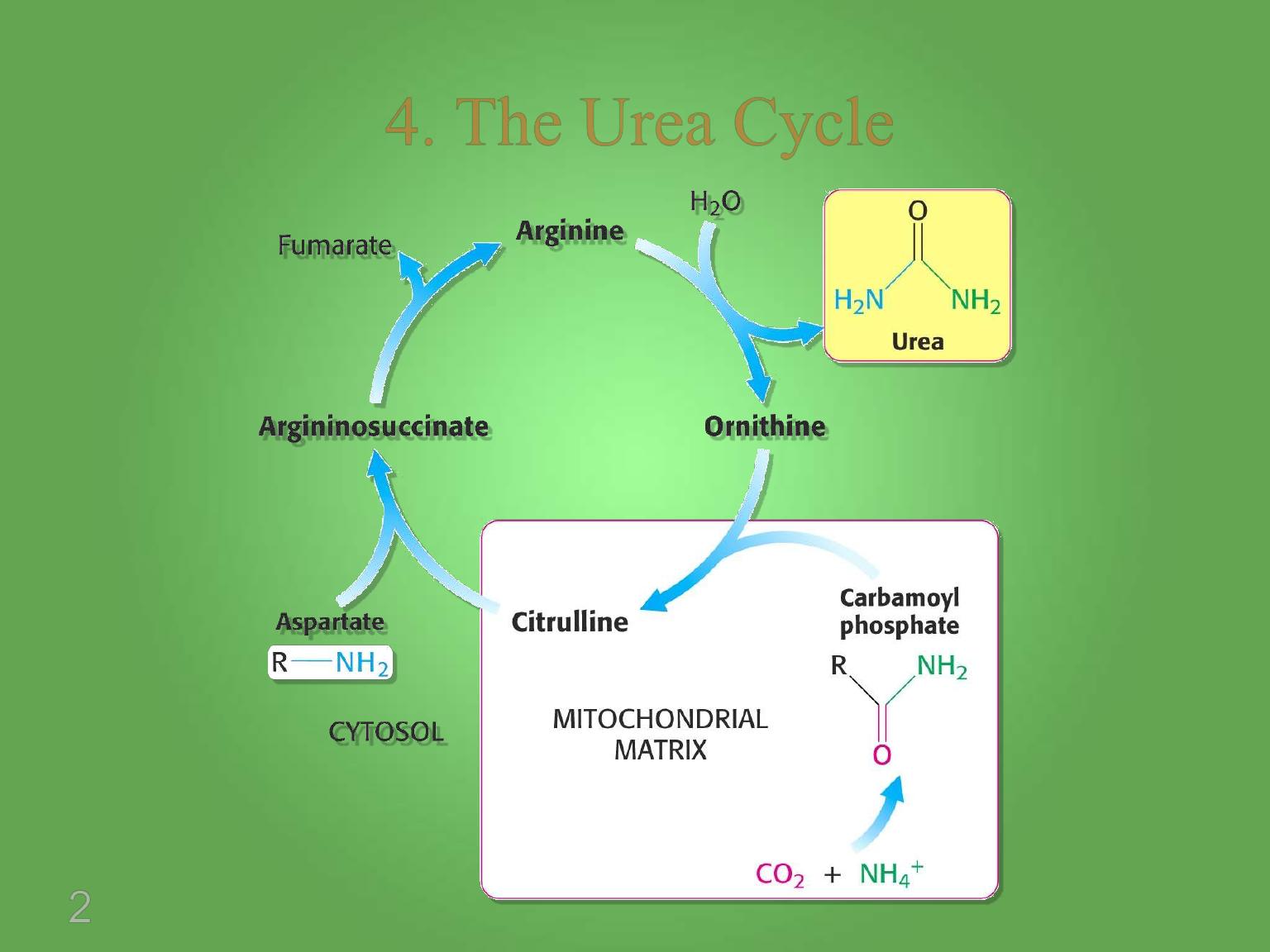
4. The Urea Cycle

high ammonia levels are toxic to humans. A complete (or
less severe partial) lack or mutant of one or more of urea
cycle
enzymes
due
to
genetic
defects
leads
to
hyperammonemia which is fatal( since there is no known
quantitative alternative pathway for the synthesis of
urea). The toxicity of ammonia is due to its depletion of
alpha-ketoglutarate intermediate of CAC pathway and
impairment
of
ATP
production(ammonia+
alpha-
kjetoglutarate= glutamate).
Hyperammonemia leads to
mental damage, coma and death if not diagnosed and
treated. Liver cirrhosis due to any causes can lead to
hyperammonemia even with normal urea cycle enzymes
activites; referred to hepatic coma.(all hepatocells are
dead so lack enzymes)
.
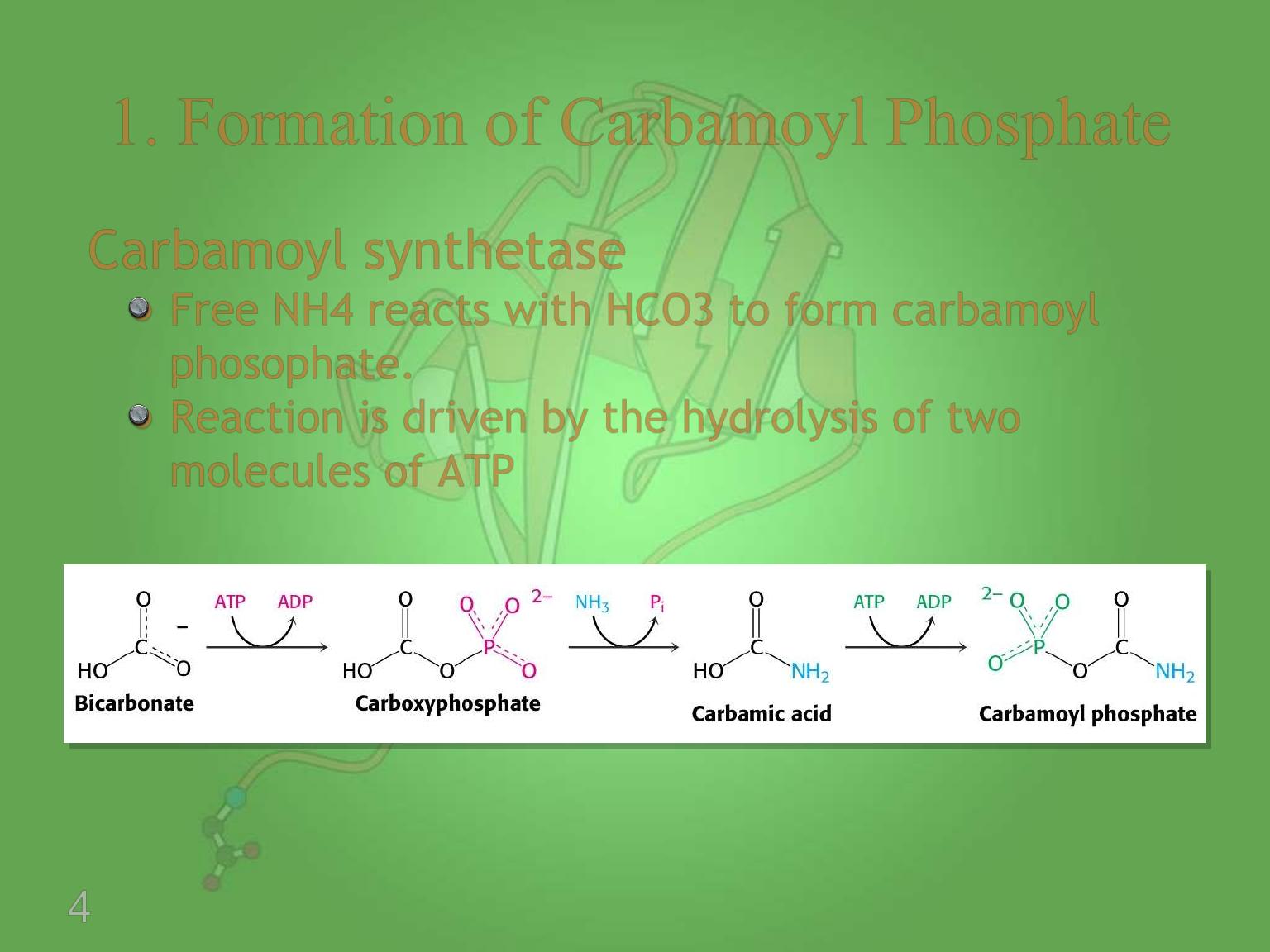
4
Carbamoyl synthetase
Free NH4 reacts with HCO3 to form carbamoyl
phosophate.
Reaction is driven by the hydrolysis of two
molecules of ATP
1. Formation of Carbamoyl Phosphate
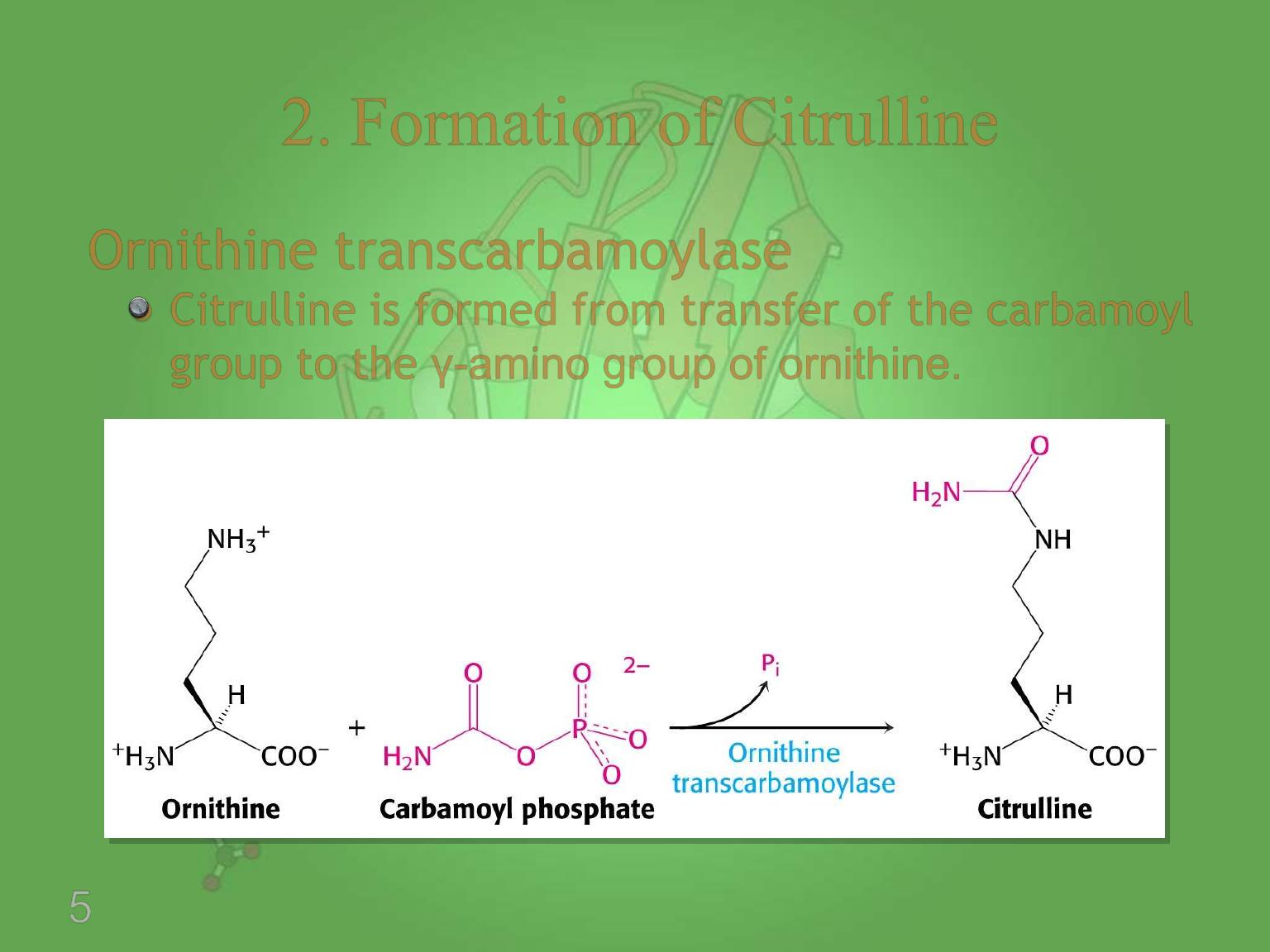
5
Ornithine transcarbamoylase
Citrulline is formed from transfer of the carbamoyl
group to the γ-amino group of ornithine.
2. Formation of Citrulline
6
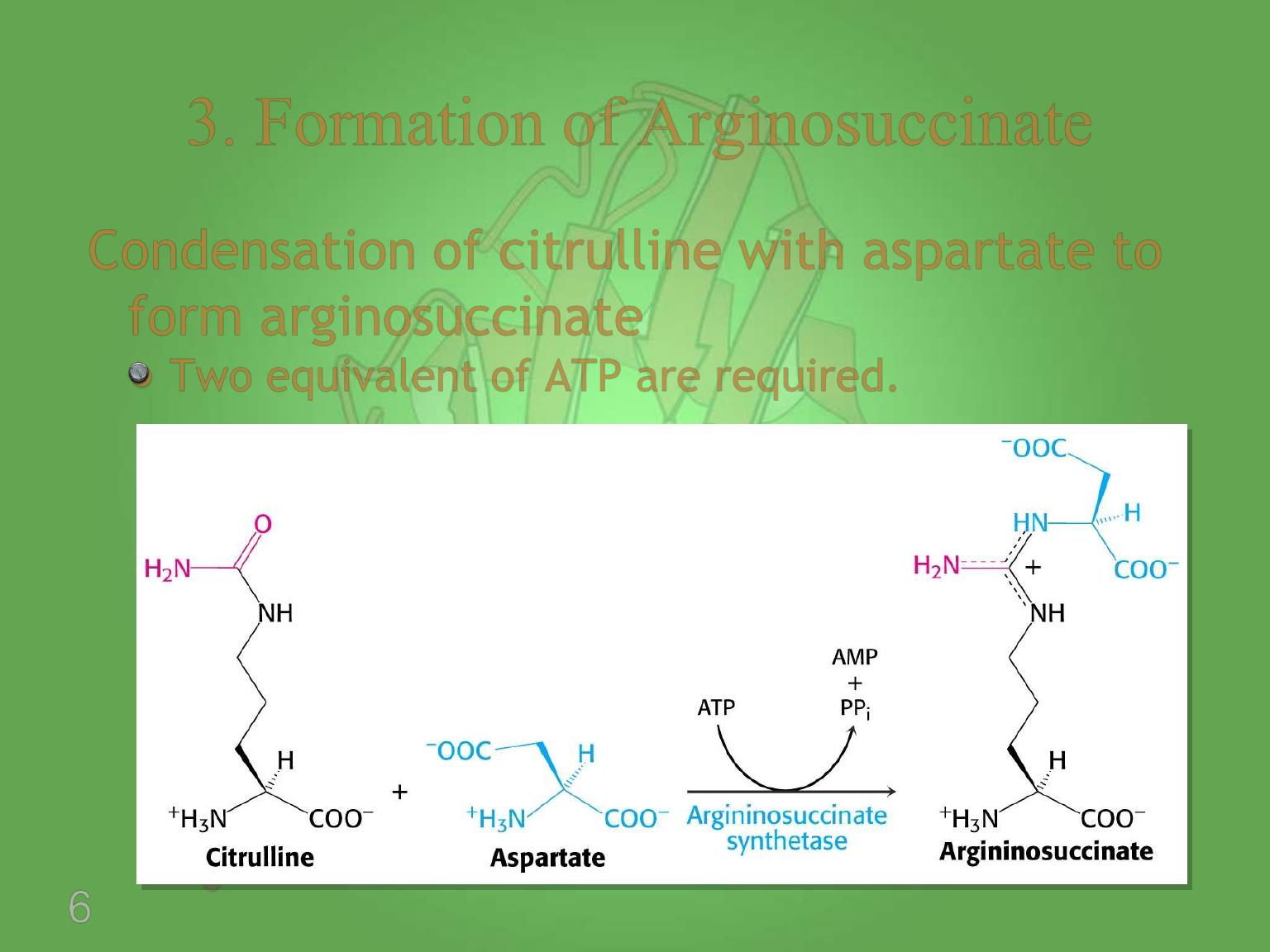
Condensation of citrulline with aspartate to
form arginosuccinate
Two equivalent of ATP are required.
3. Formation of Arginosuccinate
7
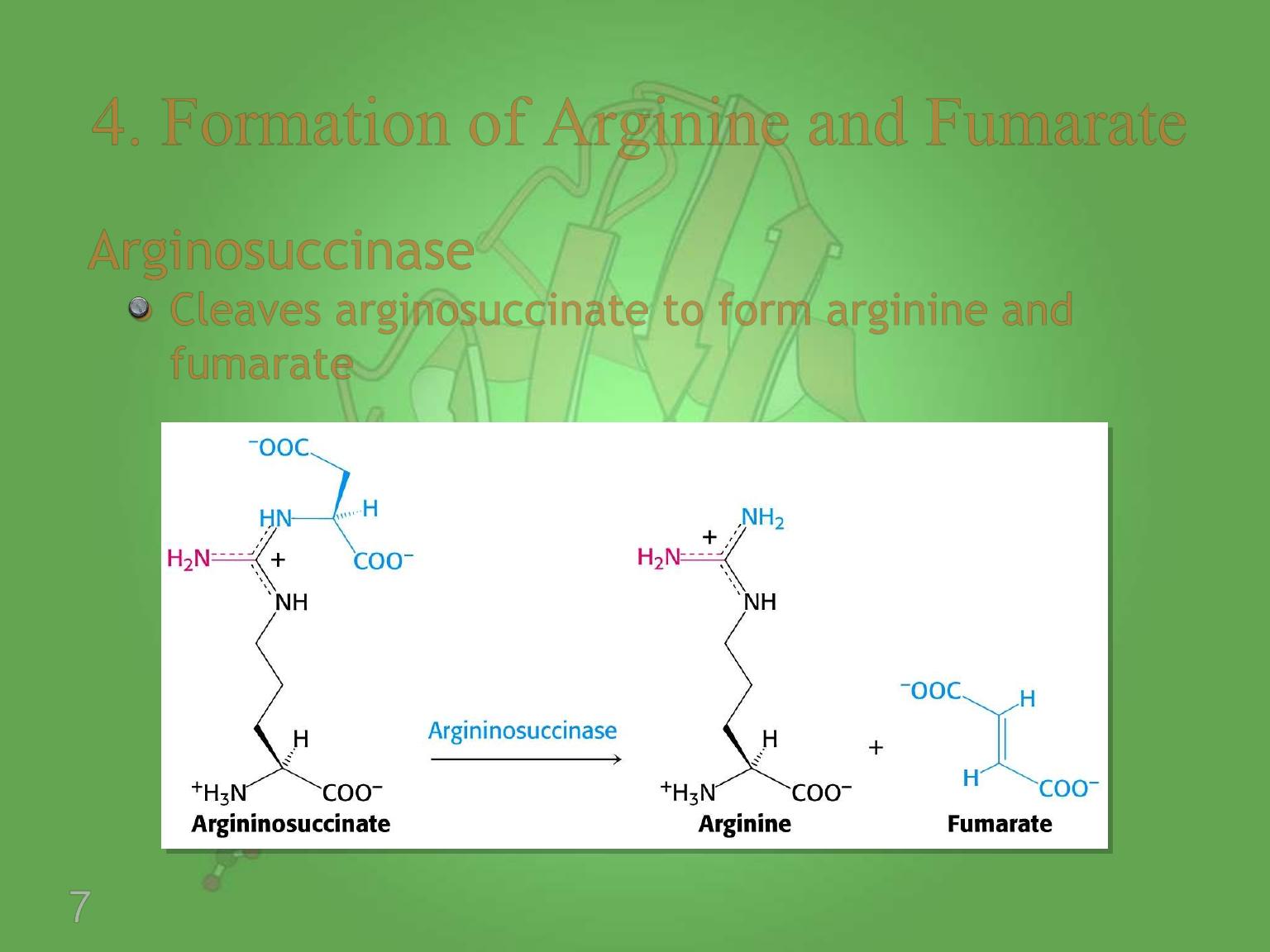
Arginosuccinase
Cleaves arginosuccinate to form arginine and
fumarate
4. Formation of Arginine and Fumarate
8
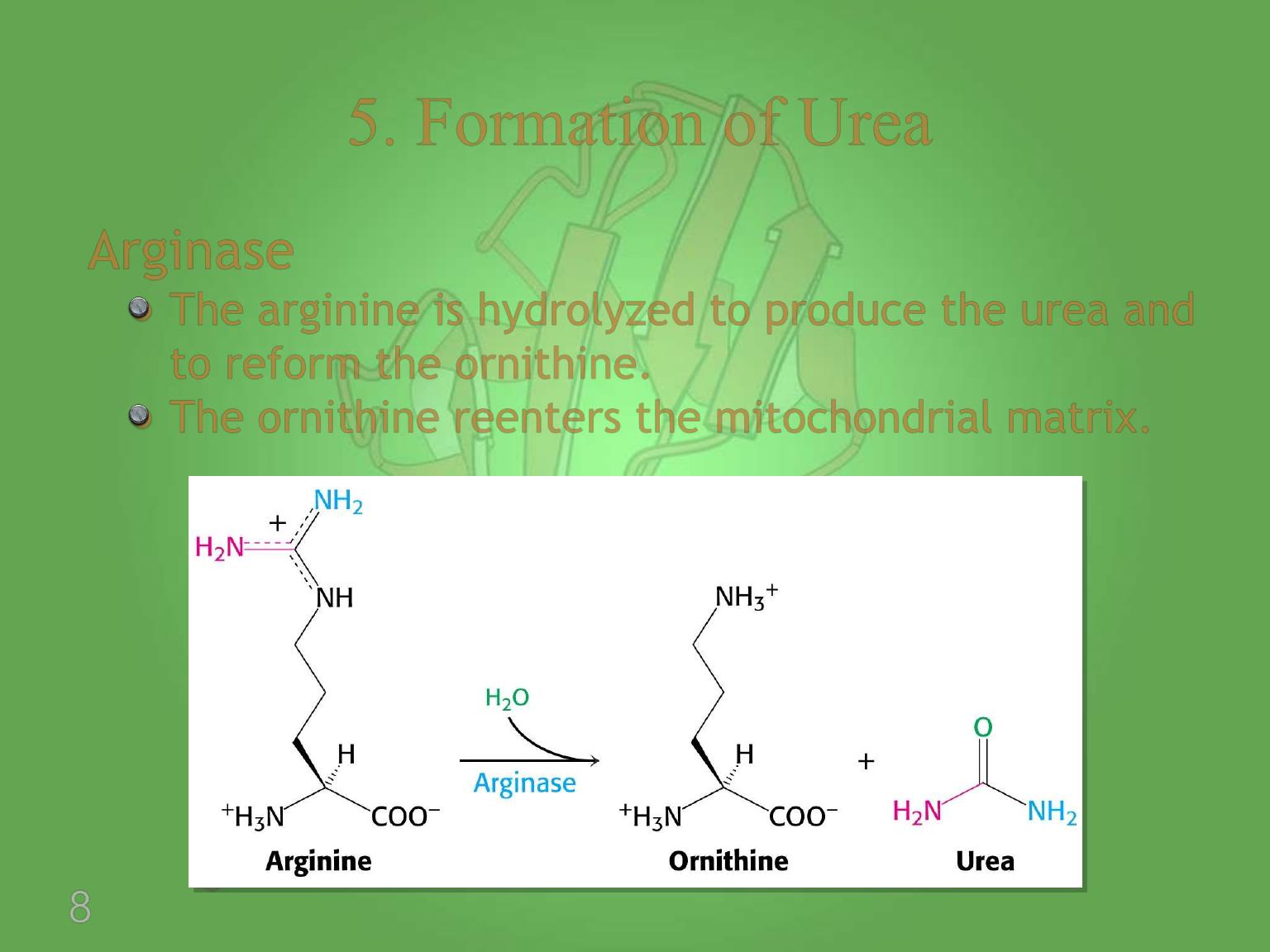
Arginase
The arginine is hydrolyzed to produce the urea and
to reform the ornithine.
The ornithine reenters the mitochondrial matrix.
5. Formation of Urea
