
Diseases of the Liver
Objectives of this lecture is to:
List the major functions of the liver.
Define Jaundice & Identify its types.
Enumerate diseases affecting the structure and
functions of the liver.

Functions of the liver
1) General Metabolism of : a. Carbohydrates.
b. Fat.
2) Synthetic functions: a. Plasma proteins.
b. Coagulation factors.
3) Excretion& detoxification of: a. Steroid hormones.
b. Drugs.
4) Storage of: a. Vitamins
b. Iron.
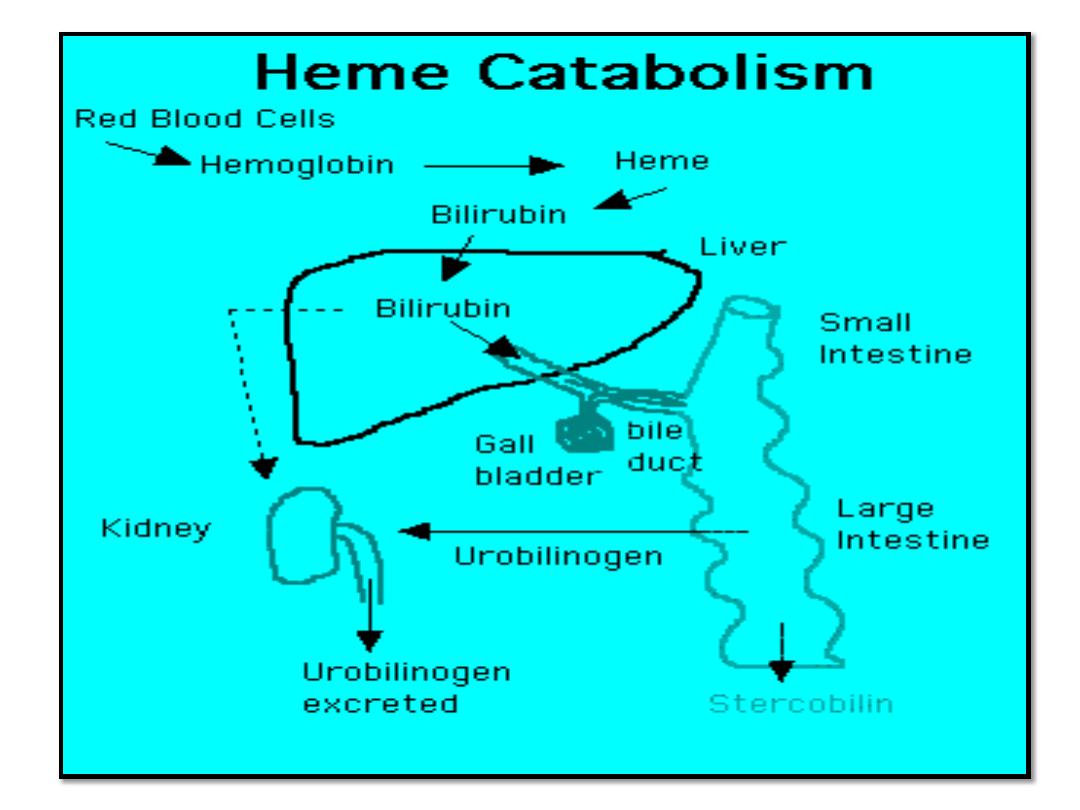
5) Metabolism & excretion of bilirubin.
Formation of bile
Cholesterol 7-α-Hydroxycholesterol
Primary bile acids Cholate Chenodeoxycholate
Taurine/glycine conjugate
Deconjugation by intestinal bacteria
Secondary bile acids deoxycholate Lithocholate

Efficient excretion of the end products of
metabolism and of bilirubin depends on:
1. Normally functioning liver cells.
2. Normal blood flow to/through the liver.
3. Patent biliary ducts.

Jaundice
Yellowish discoloration of skin, nail bed and sclera
due to increase bilirubin level in the blood.
1. Unconjugated:
i. Hemolytic.
ii. Neonatal:
physiological
2. Conjugated: obstruction.
i. Intra-hepatic.
ii. Extra-hepatic.
Types of Hyperbilirubinemia:

Diseases of the Liver
1) Hepatitis:
i. Acute Hepatitis:
1. Viral hepatitis (A,B,C,D,& E)
2. Toxins (alcohol & drugs)
ii. Chronic hepatitis: hepatic inflammation persisting
for more than six months.
1.
Infection (hepatitis B & C)
2.
Autoimmune hepatitis
3.
Toxins (alcohol).

Diseases of the Liver
2) Hepatic failure:
i. Acute Fulminant hepatic failure.
ii. Chronic : (Cirrhosis) fibrosis causing permanent
damage to hepatic tissue.
3) Cholestasis:
i. Intra-hepatic: caused by infection.
ii. Extra-hepatic: obstruction of bile duct by
(gallstone or tumor).

Diseases of the Liver
4) Fatty liver diseases:
i. Alcoholic liver disease.
ii.Non-alcoholic steatotic hepatitis (NASH) caused
by DM and/or obesity.
5) Tumors:
i. Primary (hepatocellular Carcinoma).
α-fetoprotein would be positive in 70% of cases.
ii. Secondary (metastatic deposits).

Diseases of the Liver
6) Inherited diseases:
i. Gilbert's disease: present in 5-7% of normal
population.
ii. Criggler-Najjar syndrome.
7) Uncommon liver diseases:
i. Wilson's disease.
ii. Hemochromatosis.

Diseases of the Liver
8) Liver diseases in children: Neonatal jaundice:
i. Physiological.
ii. Pathological.
9) Liver diseases in Pregnancy:
i. Hyperemesis gravidarum.
ii. Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia:
(HELLP syndrome).

References
1. Clinical chemistry & Metabolic medicine by Martin
A. Crook; 7th edition 2008. Chapter 17.
2. Clinical Chemistry by Michael L. Bishop and
colleagues; 4th edition 2005. Part III, chapter 22.
3. Clinical Chemistry by William J Marshall & Stephen
K Bangert; 6th edition 2008. Chapter 5.
