Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
1
Cardio-vascular system
In the middle of the 4
th
week, the sinus venosus receives venous
blood from the right and left sinus horns.
Each horn receives blood from :
1- vitelline vein (omphalomesenteric vein).
2- umbilical vein.
3- common cardinal vein.
Later on, a communication between the sinus and atrium will occur,
and the blood will be shifted from left to right shunt. Then, obliteration of
the right umbilical vein and the left vitelline vein will occur during 5
th
weeks. Then at the 10
th
week the left common cardinal vein is obliterated.
This leave the sinus with only the oblique vein of the left atrium and the
coronary sinus.
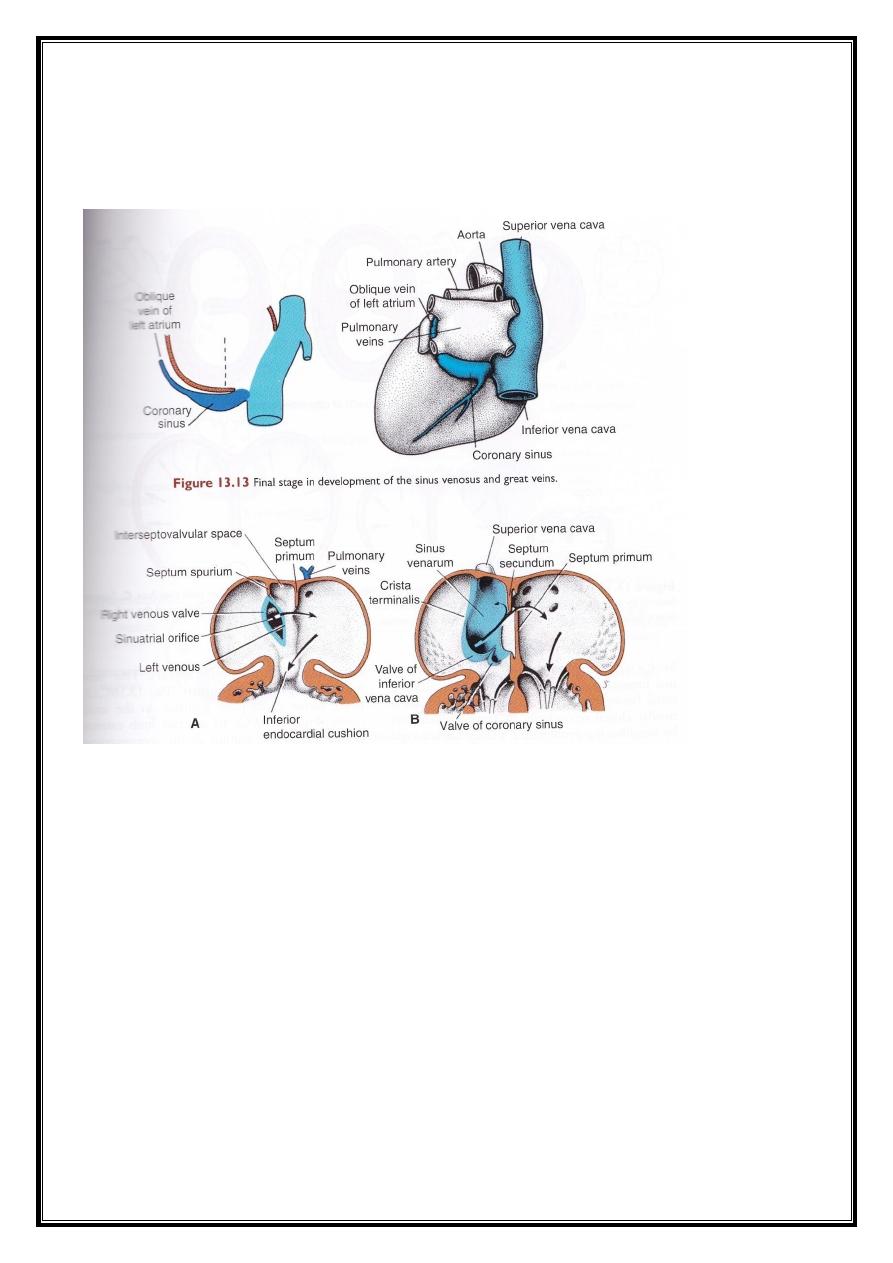
As a result of left to right shunt of the blood, the right sinus horn,
and vein enlarge greatly. The right horn is incorporated into the right
atrium forming the smooth part of it.
The inferior portion of the sinus develops into :
1- the valve of inferior vena cava.
2- the valve of coronary sinus.
The formation of the cardiac septa
The major septa of the heart are formed between the 27
th
-37
th
days
of development, when the embryo grows in length from 5 mm to
approximately 16-17 mm.
The septum is formed actively by one of these methods :
1- two actively growing masses of tissue approach each other till they are
fused together.
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
2
2- Septum formed by active growth of one side of the tissue till reaching
the opposite tissue wall.
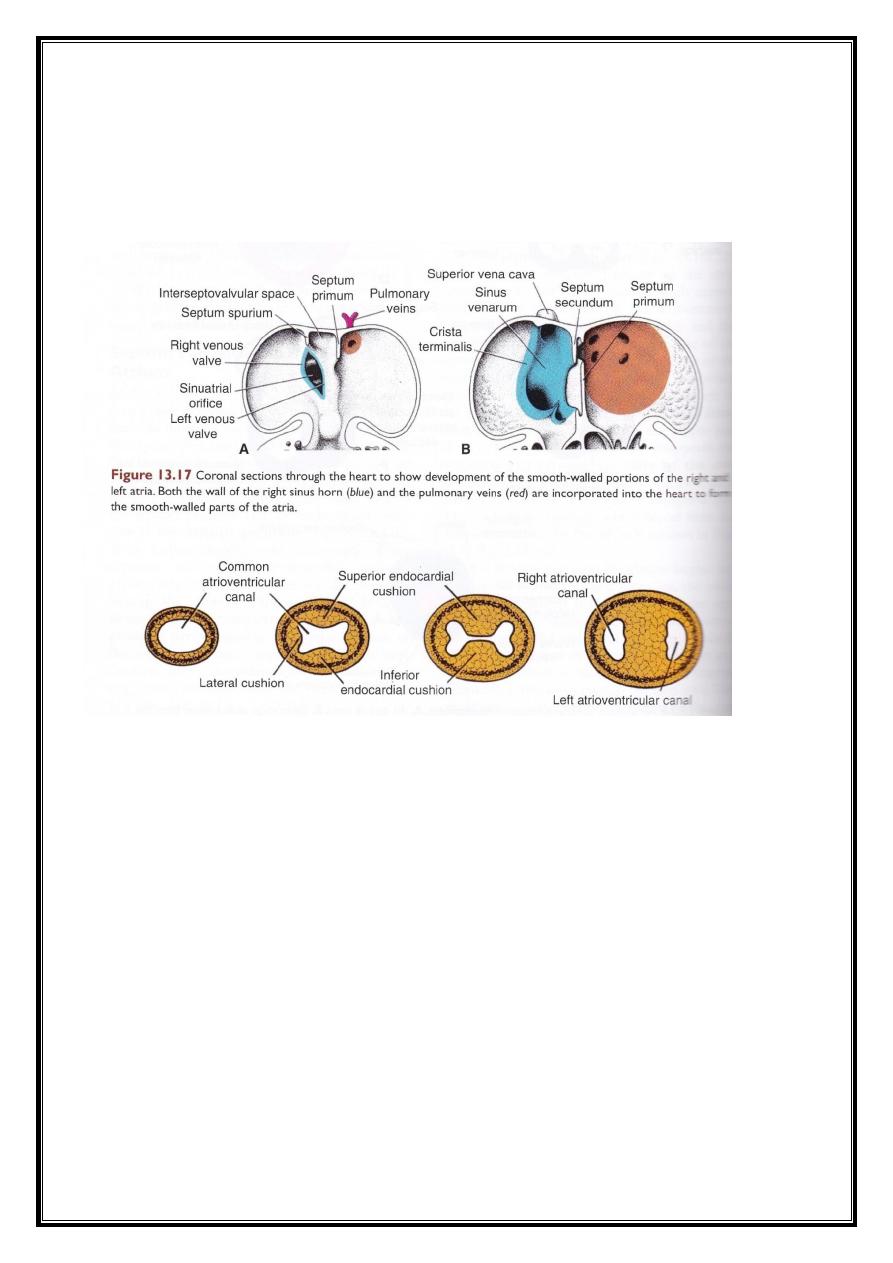
This tissue growth is called the endocardial cushion. By these
methods, the atrio-ventricular septa will be formed, and the pulmonary
and aortic channels will be formed. A defect in the growth of this
endocardial cushion will lead to V.S.D., A.S.D., T.O.F., or transposition of
the great vessels.
Septum formation in the common atrium :
At the end of the 4
th
week, a sickle-shaped crest grows from the roof of
the common atrium into the lumen. This crest is the 1
st
part of septum
primum. The two limbs of this crest extend downward toward the
endocardinal cushion in the atrio-ventricular canal. The opening left will be
called ostium primum.
The endo cardinal cushion continues to grow from the two sides of
the atrio-ventricular canal (on the right side) leading to the closure of the
osium primum. Before the closure of ostium primum, cell death occurs in
the upper part of upper part of septum primum forming a foramen called
ostium secundum (which connects the primitive left and right atria).
Due to the incorporation of te sinus horn with the right atrium, a
new crescent-shaped fold appears. This new fold is called setpum
secundum. Yet, this septum never separate the two atria completely. The
septum secundum will extend to cover the ostium secundum. Yet, the
closure of ostium secundum is incomplete, leaving a space called foramen
ovale. When septum primum disappears, the remaining part will form the
valve of foramen ovlae.
During birth, the pulmonary circulation begins, and the pressure
within the left atrium will be higher than that of the right atrium;
therefore, septum secundum will be pressed against septum primum.
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
3
Sometimes a small opening is left between the left and right atria, and is
called probe patency (which never let the blood to shunt from the left to
right side).
Differentiation of the atria :
The primitive right atrium is enlarged by the incorporation of the right
sinus horn.
The primitive left atrium is expanded. Initially, a single embryonic
pulmonary vein develops as an outgrowth of the posterior atrial wall. This
vein gains a connection with the veins of the developing lung buds. Later
on, these pulmonary veins will be incorporated within the left atrium.
In fully developed heart, the true atrial wall is a trabeculated wall
(left atrial appendages), while the smooth wall is the come from the
pulmonary veins.
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
4
Regarding the right atrium, the true atrial wall is the part containing
the pectinate muscles, while the remaining part is the remnant of the right
horn of sinus venosus.
Septum formation of the ventricles :
By the end of the 4
th
week, two primitive ventricles begin to expand.
This is accomplished by the continuous growth of the myocardium on the
outside, and continuous diverticulation and trabeculae formation on the
inside.
From the inside, the muscular interventricular septum will be
formed from the inner surface of the ventricles. The space left between
the free rim of the muscular ventricular septum and the fused
endocardinal cushion, permits a communication between the two
ventricles.

Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
5
From the inferior surface of the endocardinal cushion, a
membranous growth will be formed complete the interventricular septum,
and is called the membranous part of the interventricular suptum.
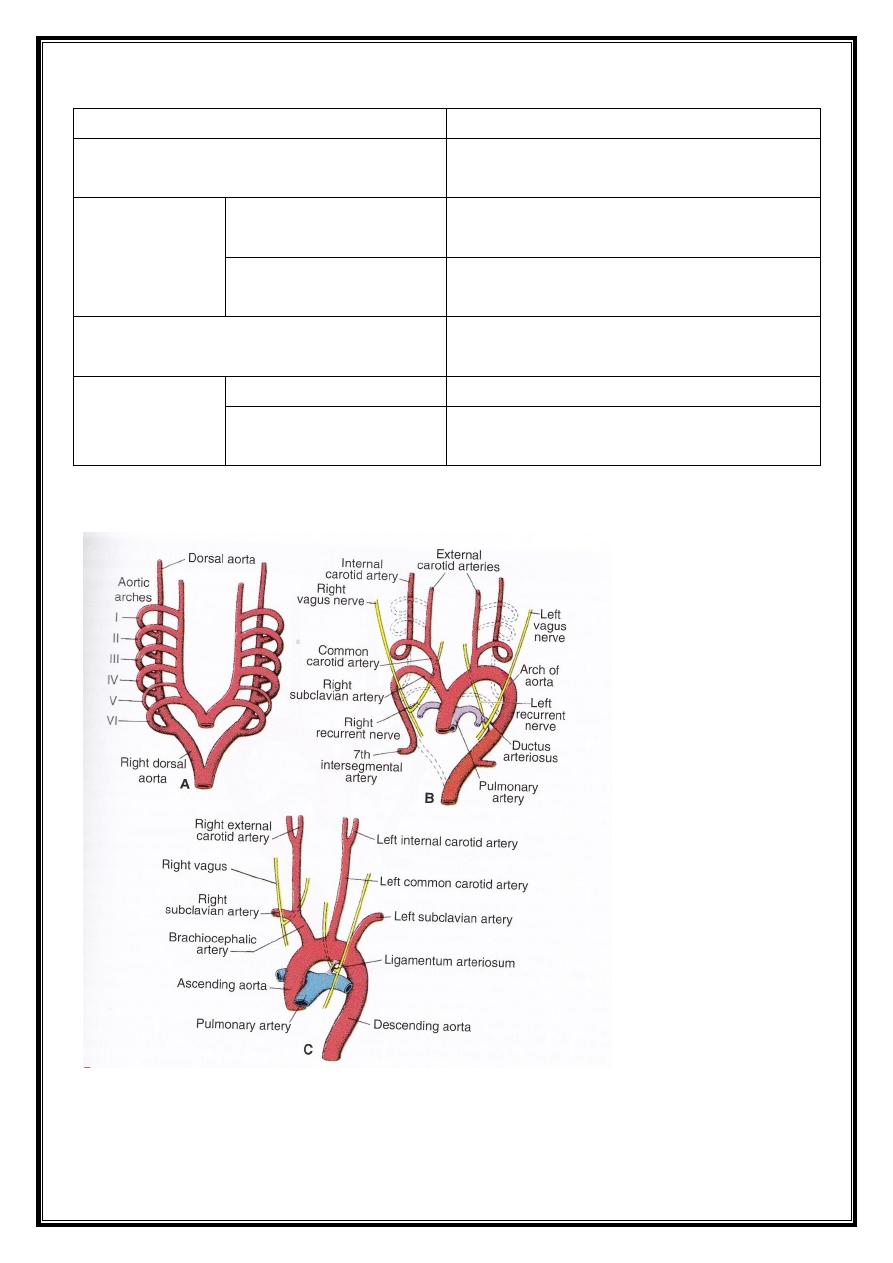
Arterial system :
During the 4
th
and 5
th
weeks of development, the pharyngeal arches
will be formed, and each arch receives its own artery. These arteries are
the aortic arches. These are 6 in number, yet the 5
th
one is either not
formed or is formed incompletely and then regresses.
The aortic arches and their fate are shown in this table :
Arterial derivatives
Arch
Maxillary artery
1
st
arch
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
6
Hyoid and stapedial arteries
2
nd
arch
Common carotid and 1
st
part of the
internal carotid arteries
3
rd
arch
Right subclavian artery (proximal
portion)
Right side
4
th
arch
Arch of aorta, from left common
carotid to left subclavian arteries
Left side
If present, it will disintegrate and
disappear
5
th
arch
Right pulmonary artery
Right side
6
th
arch
Left pulmonary artery and ductus
arteriosus
Left side
Dr.Maan Alkhalisy Embryology lec.8
7
Notes :
- The remainder of the internal carotid arteries are derived from the dorsal
aorta, while the external carotid arteries sprout from the 3
rd
aortic arch.
- The distal portions of the right and left subclavian arteries are formed
from the 7
th
intersegmental arteries.
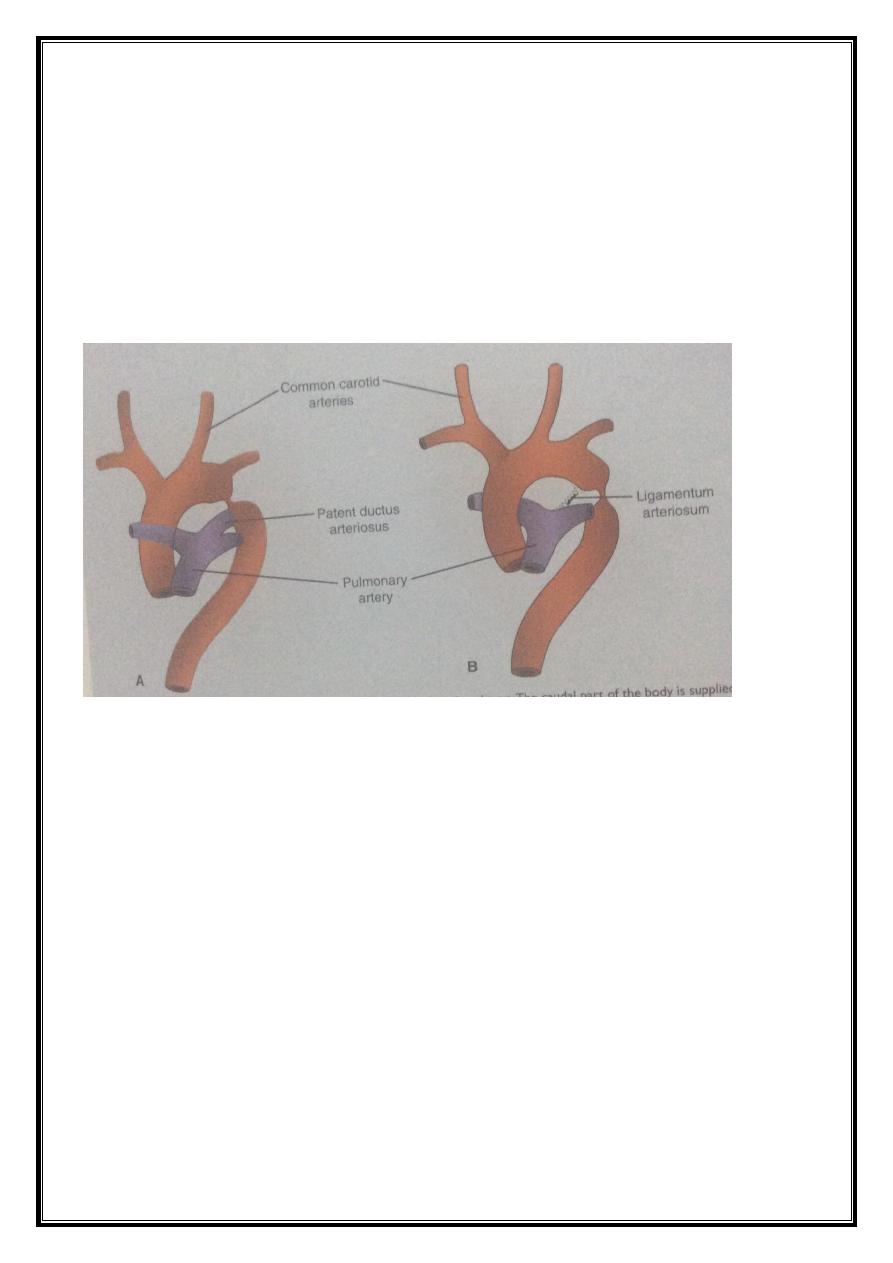
Changes that occur at birth :
1- Ductus arteriosus is closed.
2- Foramen ovale is closed.
3- Umbilical vein is closed.
4- Ductus venosus is closed and remains as ligamentum teres, ligamentum
venosus.
5- Umbilical arteries form the medial umbilical ligaments.
