
Physiology of
The Blood
The bone marrow

Learning objectives
•
Red marrow versus yellow marrow
•
To understand the Process of blood
cell formation (hemopoiesis) in the
bone marrow
•
To describe the process of RBC
maturation.
•
To understand WBC production .

Bone Marrow
In adults, red blood cells, many white blood cells, and
platelets are formed in the bone marrow.
In the fetus, blood cells are also formed in the liver
and spleen,
while in adults such extramedullary
hematopoiesis may occur in diseases in which the
bone marrow becomes destroyed or fibrosed.
In children, blood cells are actively produced in the
marrow cavities of all the bones.
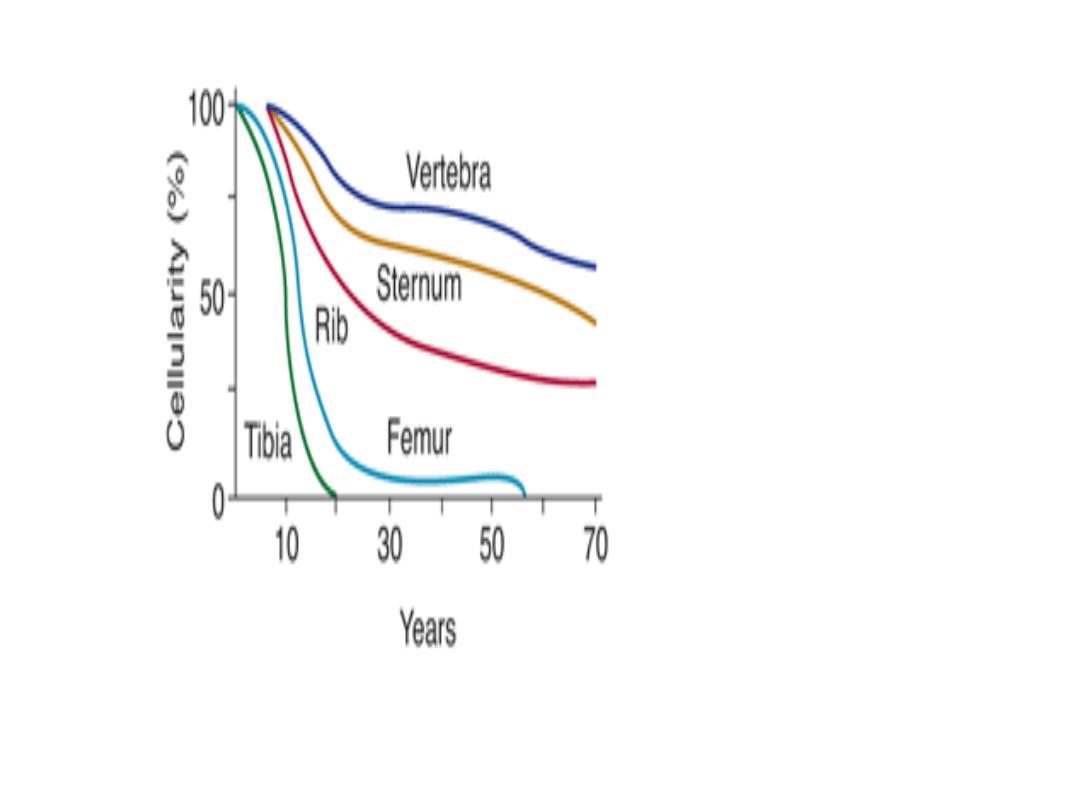
By age 20, the marrow in the cavities of the long
bonesbecome inactive, except for the upper humerus
and femur.
Active cellular marrow is called red marrow; inactive marrow
that is infiltrated with fat is called yellow marrow.

The bone marrow is actually one of the largest organs
in the body, approaching the size and weight of the
liver.
It is also one of the most active.
Normally, 75% of the cells in the marrow belong to
the white blood cell-producing myeloid series but only
25% are maturing red cells, even though there are over
500 times as many red cells in the circulation as there
are white cells.
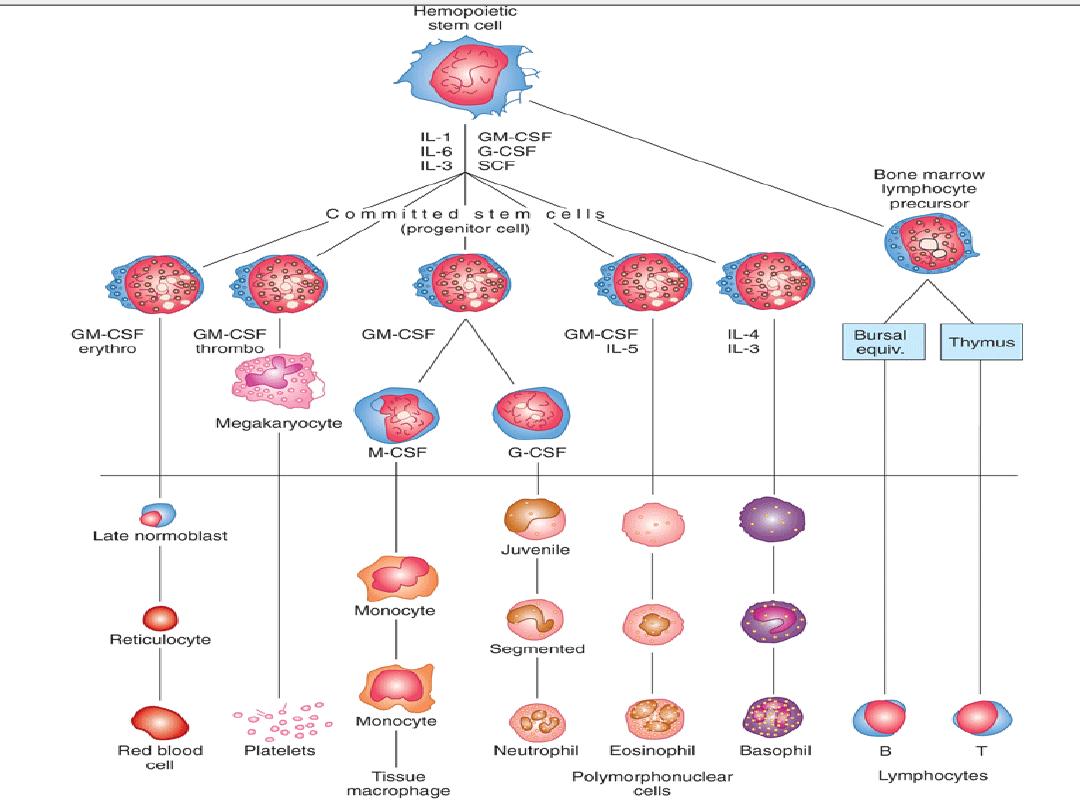
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are bone marrow
cells that are capable of producing all types of blood
cells. They differentiate into one or another type of
committed stem cells (progenitor cells). These in turn
form the various differentiated types of blood cells.

There
are
separate
pools
of
progenitor
cells
for
megakaryocytes, lymphocytes, erythrocytes, eosinophils, and
basophils; neutrophils and monocytes arise from a common
precursor.
The bone marrow stem cells are also the source of
osteoclasts), Kupffer cells, mast cells, dendritic cells, and
Langerhans cells.
The
HSCs are few in number but are capable of completely
replacing the bone marrow when injected into a host whose
own bone marrow has been completely destroyed.
The HSCs are derived from uncommitted, totipotent stem cells
that can be stimulated to form any cell in the body.
Adults have a few of these, but they are more readily obtained
from the blastocysts of embryos
.

Formation of New RBC’s
Ruptured cells must be replaced by new cells by a
process called……… ..
Erythropoiesis
Secretion of the hormone erythropoietin
New RBC’s (and platelets & leukocytes) are produced
in the Bone Marrow

Stages of RBC Maturation
•
Myeloid stem cell
•
Proerythroblast
•
Erythroblasts
•
Reticulocyte
•
Mature RBC
Components for Building red blood cells
–
amino acids
–
iron
–
vitamins B
12
, B
6
, and folic acid

Stimulating Hormones
•
Erythropoietin
(EPO)
•
Also called
erythropoiesis-stimulating
hormone
:
–
secreted when oxygen in peripheral tissues is low
(
hypoxia
)
–
due to disease or high altitude
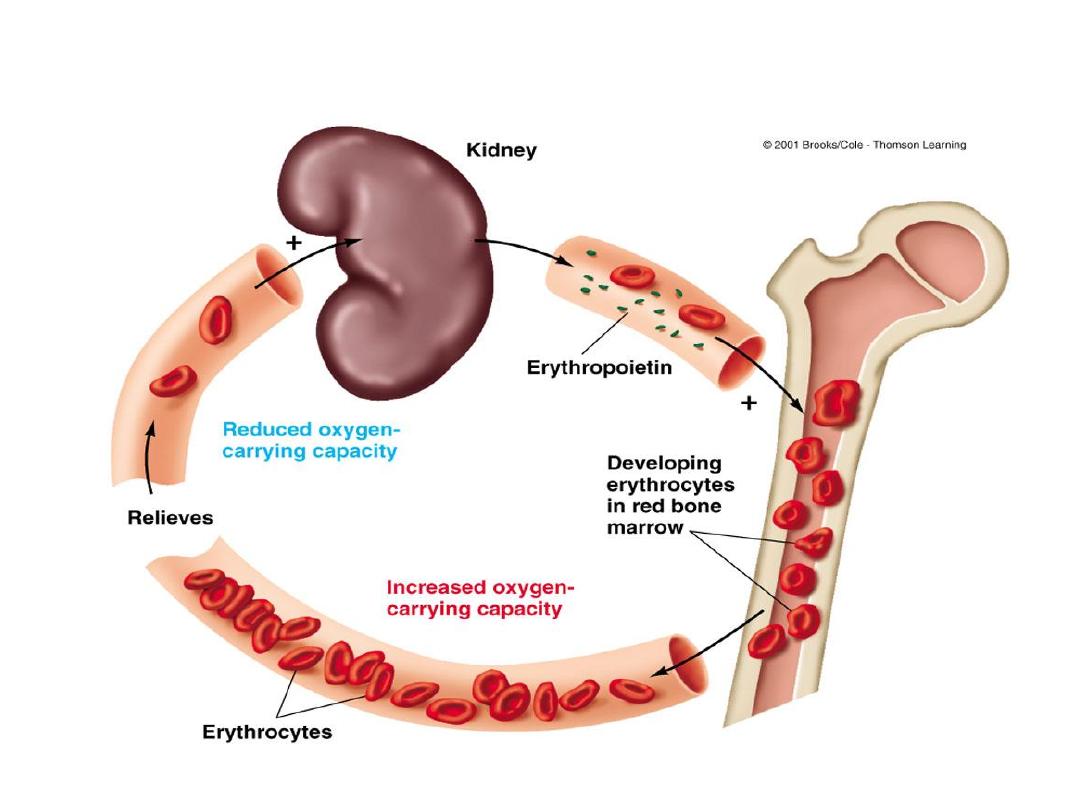
Figure 11-4
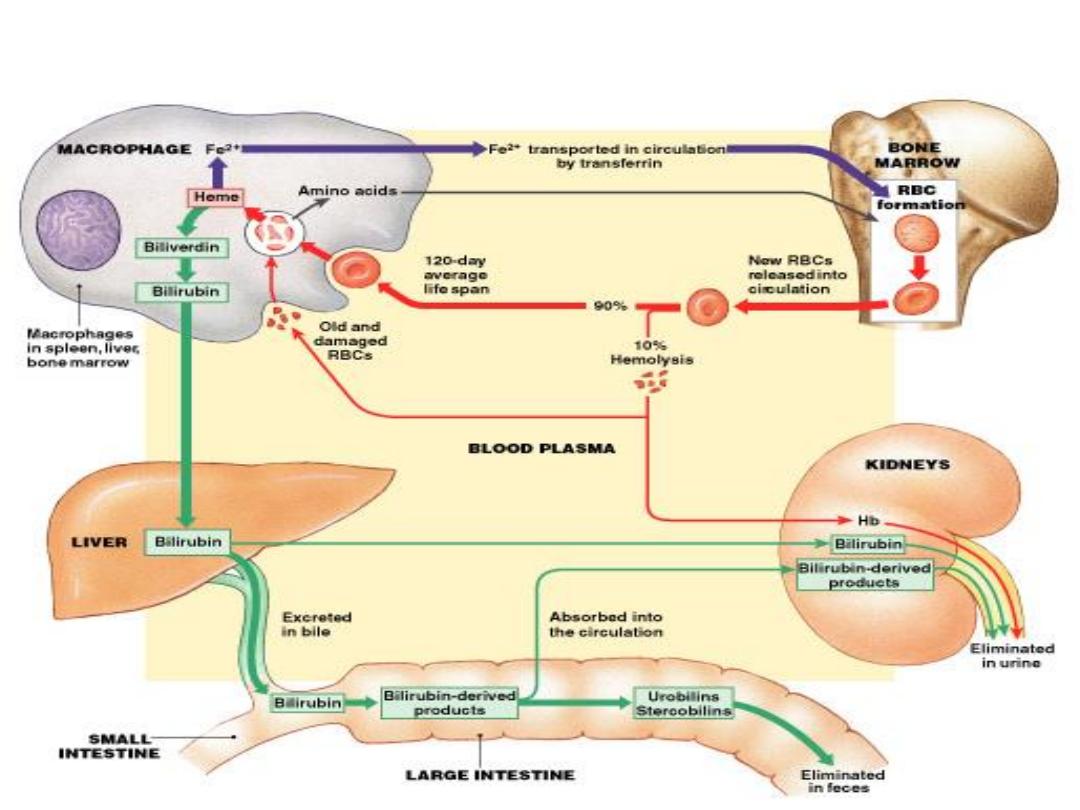
Figure 19–4
Recycling RBCs

Recycling RBCs
•
1% of circulating RBCs wear out per day:
–
about 3 million RBCs per second
•
Macrophages of liver, spleen, and bone
marrow:
–
monitor RBCs
–
engulf RBCs before membranes rupture
(
hemolyze
)
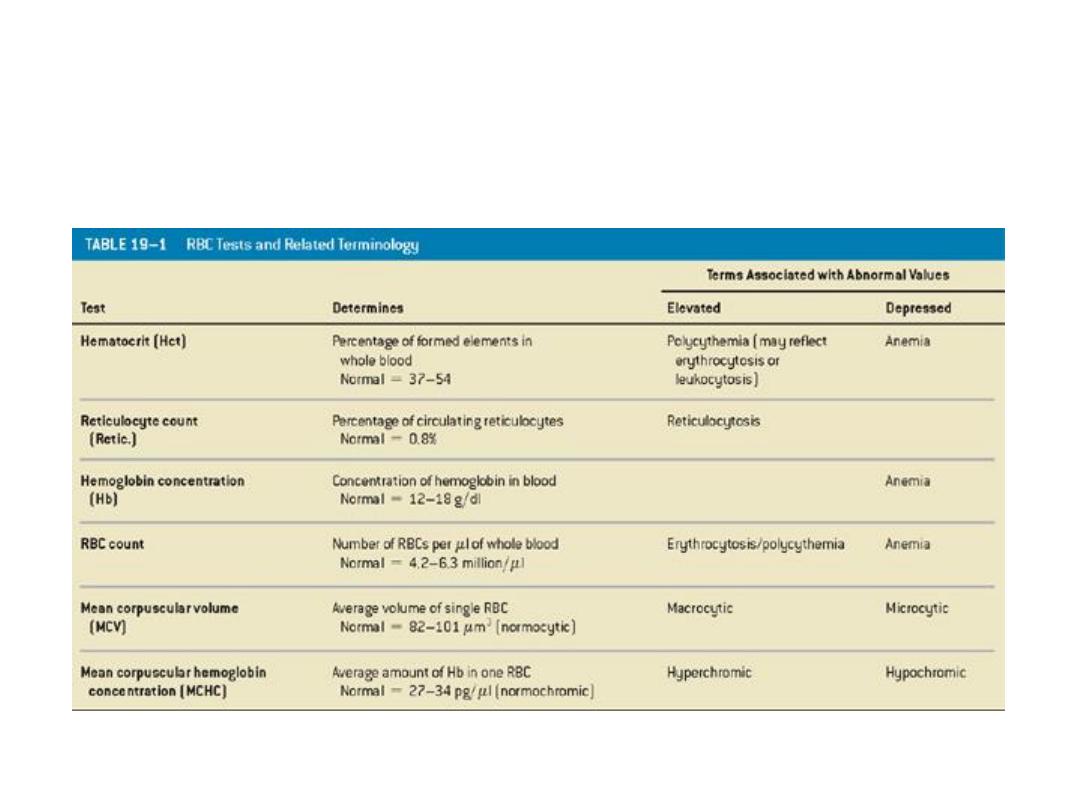
RBC Tests
Table 19–1

KEY CONCEPT- RBC
•
Red blood cells (RBCs) are the most
numerous cells in the body
•
RBCs circulate for approximately 4 months
before recycling
•
Several million are produced each second
•
Hemoglobin in RBCs transports:
–
oxygen from lungs to peripheral tissues
–
carbon dioxide from tissues to lungs
