
Physiology of
The blood
WBC
By prof. Israa f. jaafar

Learning objectives
•
Describe WBC structure and function
•
Know the types of WBCs:
–
neutrophils
–
eosinophils
–
basophils
–
monocytes
–
lymphocytes
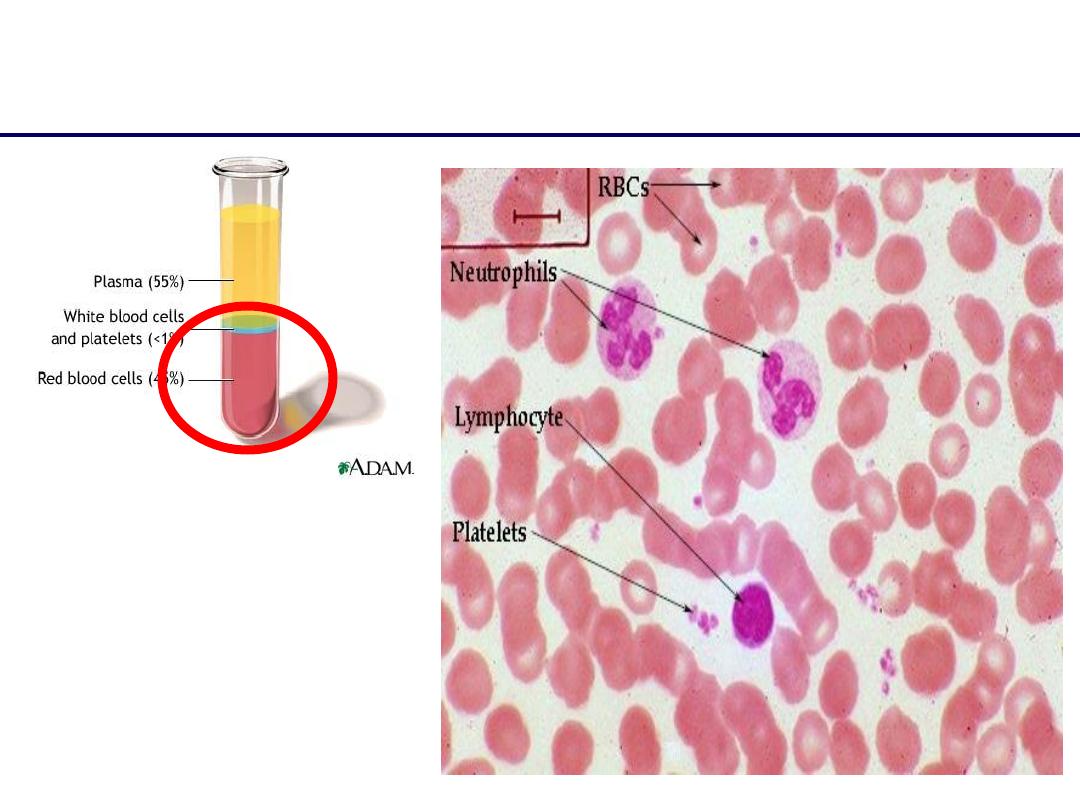
3 Cellular Elements of Blood
1. Red Blood Cells
2. White Blood Cells
3. Platelets

Based on structures and functions,
what are the types of white blood
cells, and
what factors regulate the
production of each type?

White Blood Cells (
WBCs
)
•
Also called
leukocytes
•
Do not have hemoglobin
•
Have nuclei and other organelles
WBC Functions:
•
Defend against pathogens
•
Remove toxins and wastes
•
Attack abnormal cells

WBC Movement
•
Most WBCs in:
–
connective tissue proper
–
lymphatic system organs
•
Small numbers in blood:
–
6000 to 9000 per microliter
Circulating WBCs
.1
Migrate out of bloodstream
.2
Have amoeboid movement
.3
Attracted to chemical stimuli (
positive chemotaxis
)
.4
Some are phagocytic:
–
neutrophils, eosinophils, and monocytes

White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
•
Mobile units of body’s defense system:
•
“Seek and Destroy” Functions:
.1
Destroy invading microorganisms
.2
Destroy abnormal cells (ie: cancer )
•
Clean up cellular debris (phagocytosis)
3. Assist in injury repair
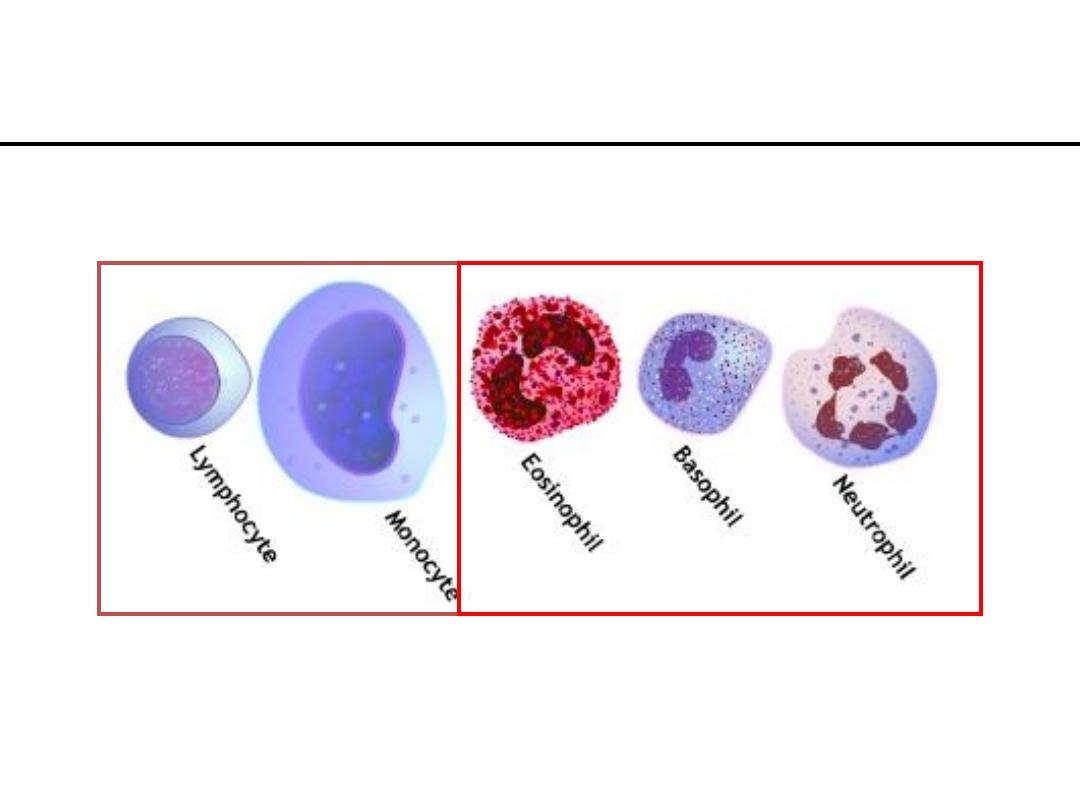
5 - Types of WBC’s
Each WBC has a specific function
Granulocytes
Agranulocytes
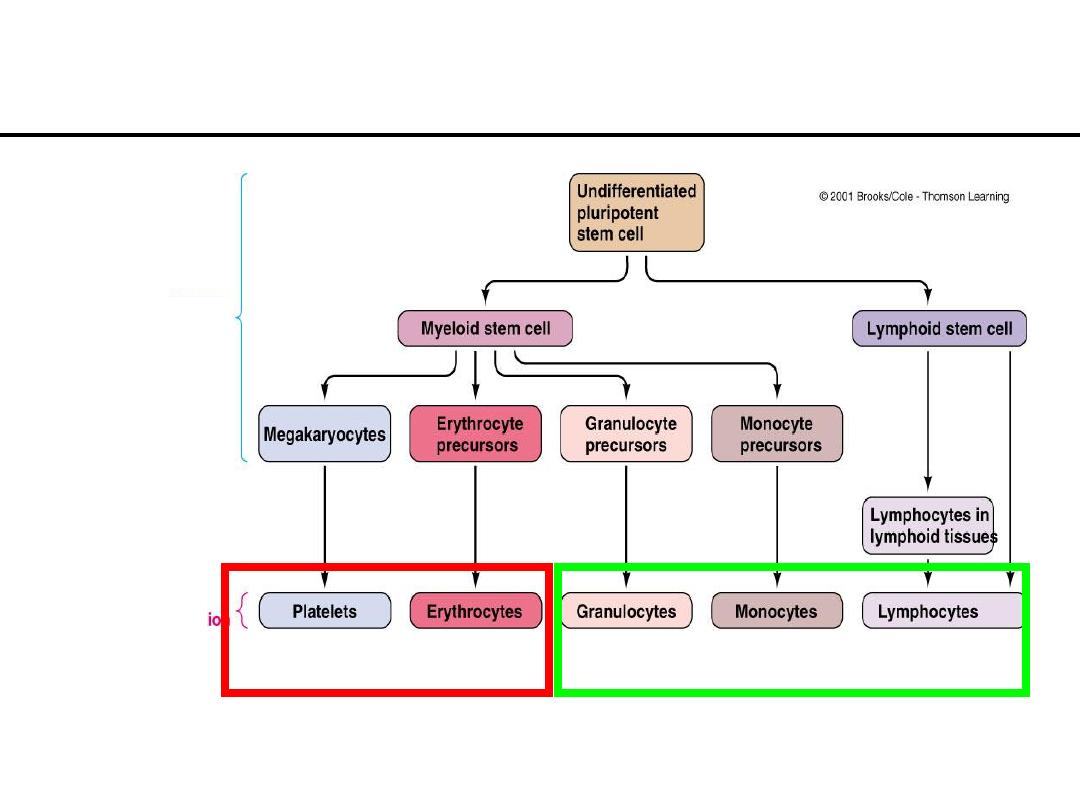
Blood Cell Origin and Production
Bone Marrow
Circulation
Figure 11-8

Types of WBC’s
Polymorphonuclear Granulocytes
1.Neutrophils
2.Eosinophils
3.Basophils
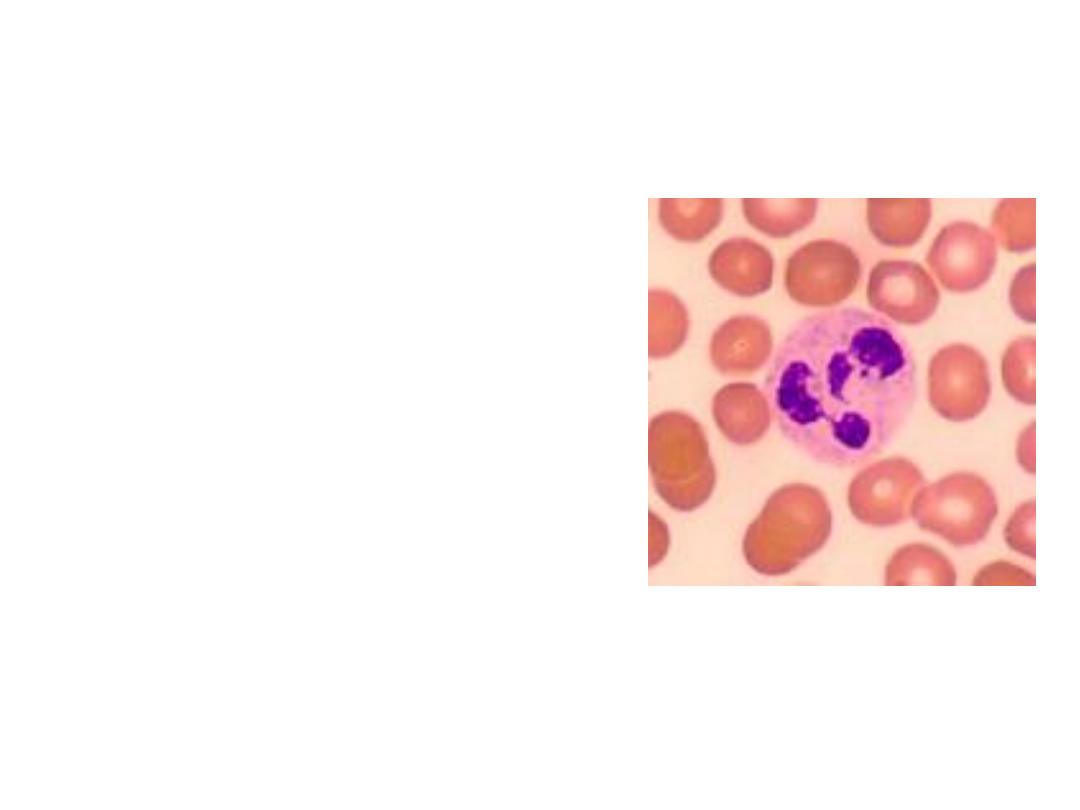
1. NEUTROPHILS
* 50-70% of all leukocytes
(most abundant of WBC’s)
* Phagocytes that engulf
bacteria and Debris
* Important in inflammatory
responses
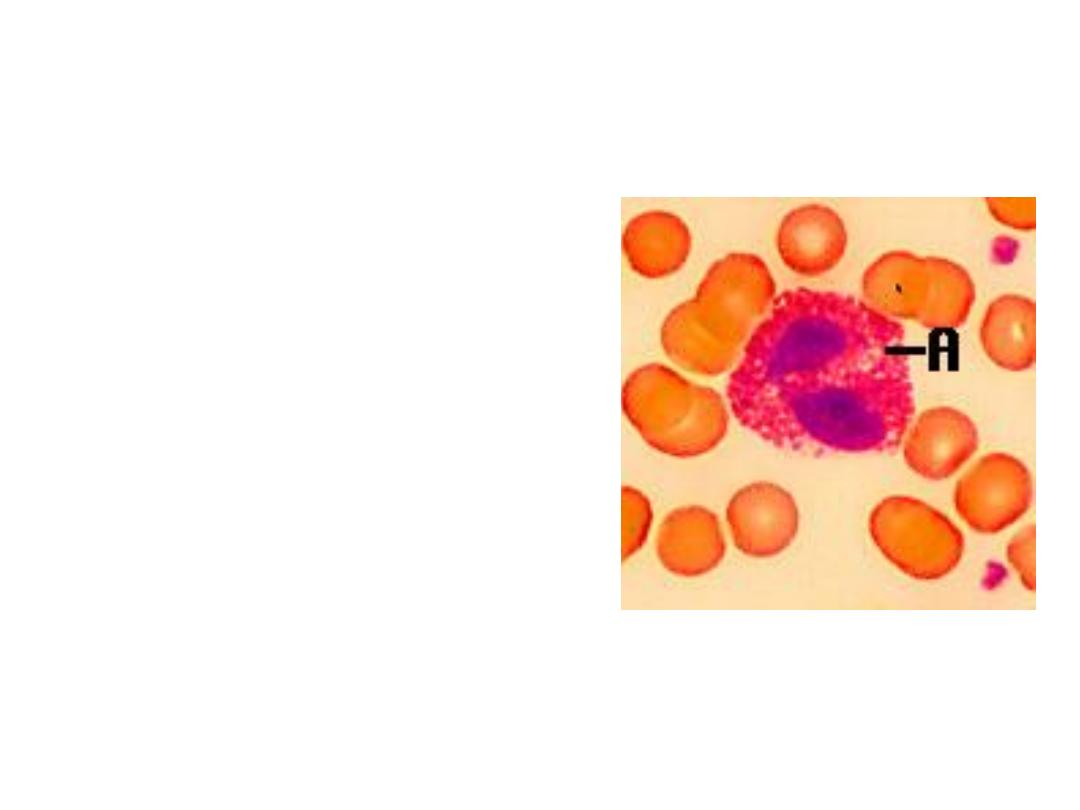
2. EOSINOPHILS
* 1-4% of the WBC's
* Attack parasitic worms
* Important in allergic reactions
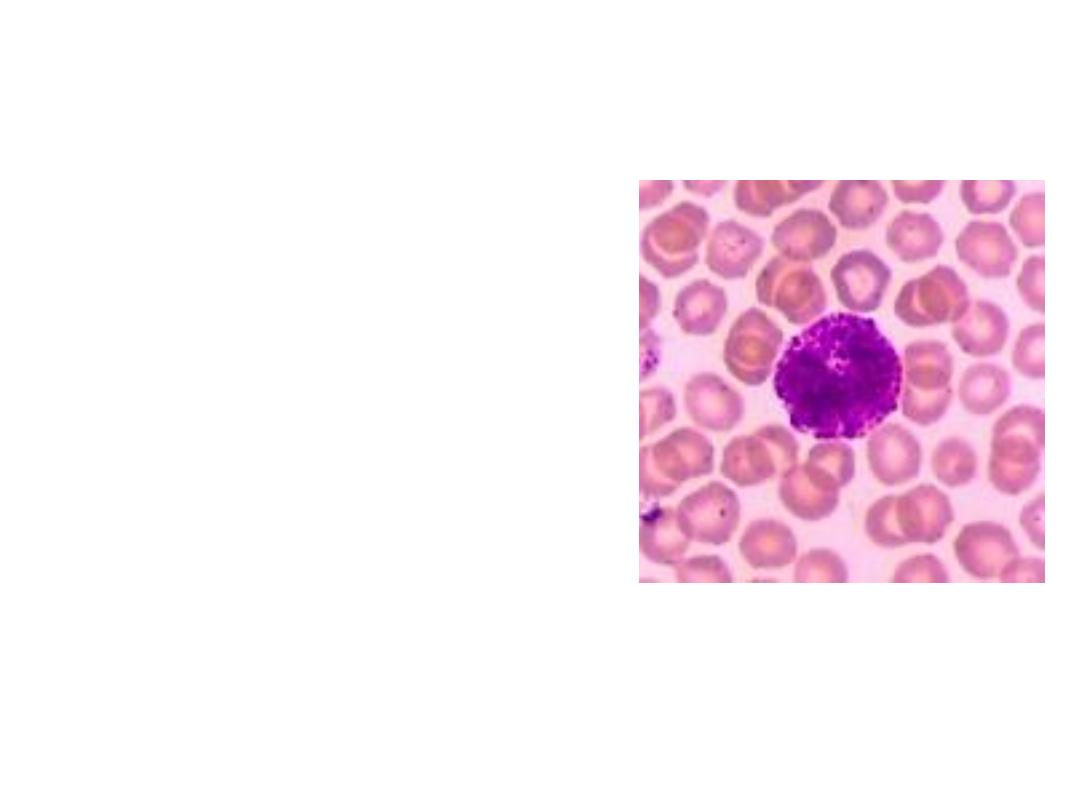
3. BASOPHILS
* Release
histamine
and
heparin
* 0.5% of the WBC's
*
Important in Allergic
Reactions
* Heparin helps clear fat from blood

Types of WBC’s
Mononuclear Agranulocytes
4. Monocytes
5. Lymphocytes
(B and T cells)
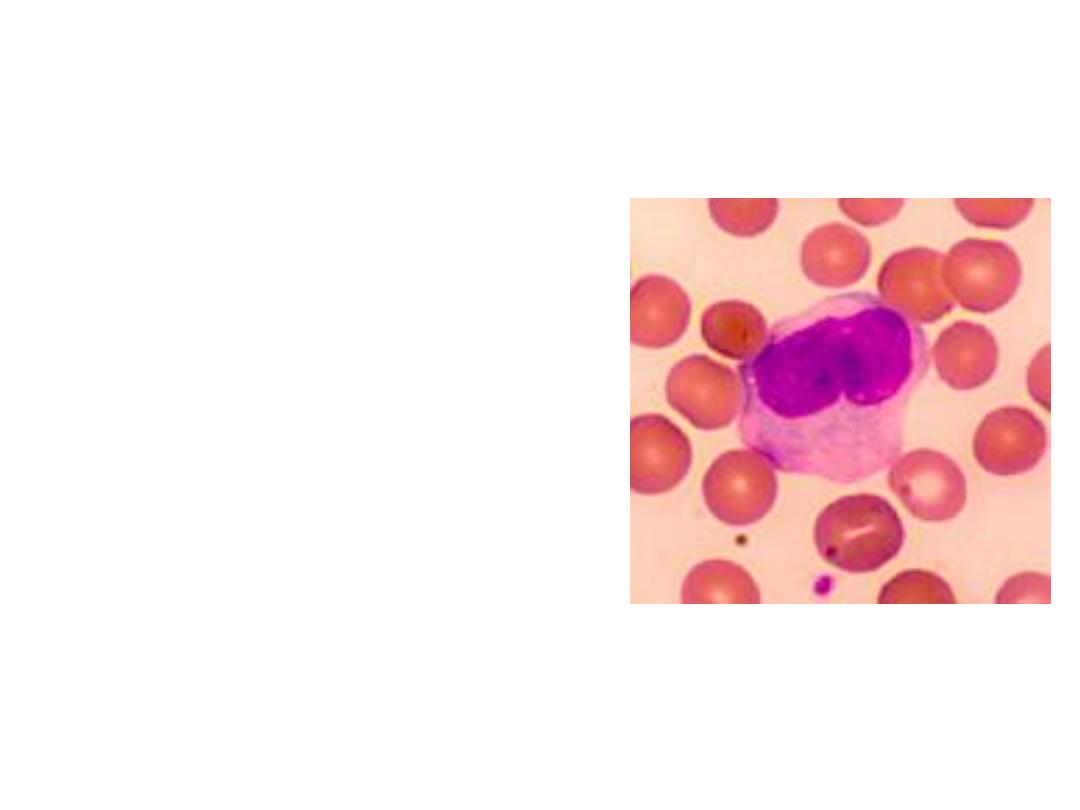
4. MONOCYTES
* Exit blood (diapedesis)
to become macrophages
* 2-6 % of the WBC's
* Phagocytic = defend against
viruses and bacteria
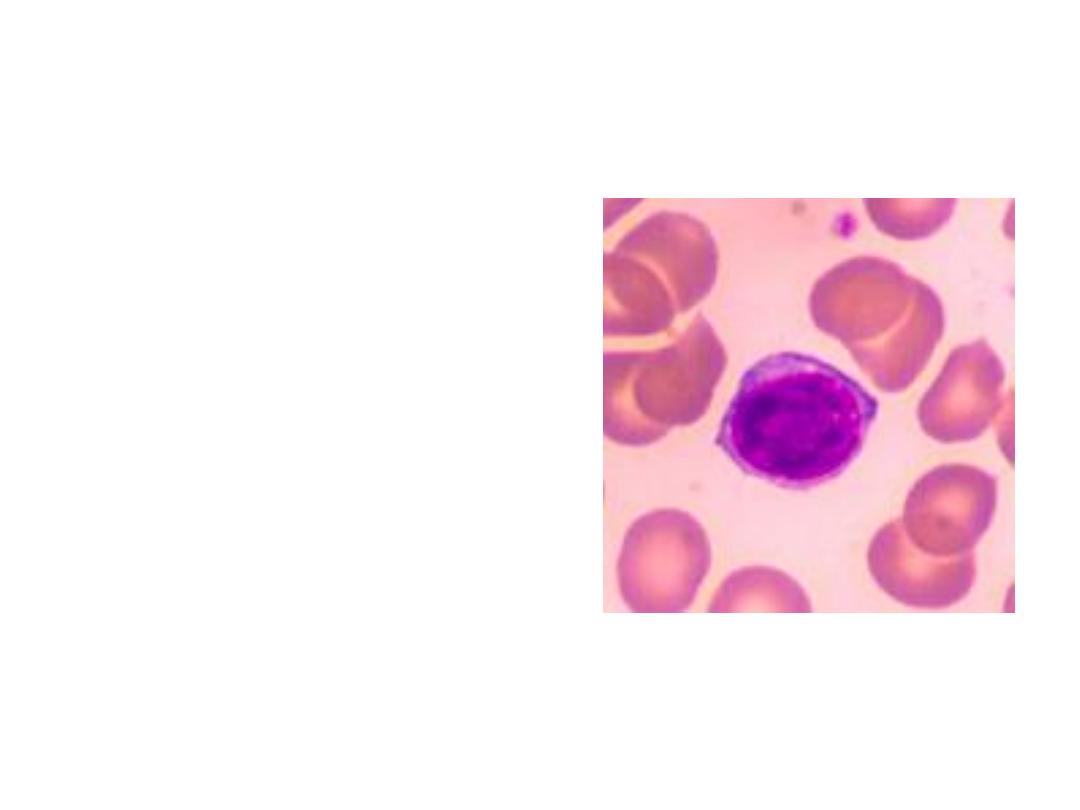
5. LYMPHOCYTES
* B-lymphocytes:
Produce Antibodies
* T-lymphocytes:
Directly destroy virus-
invaded cells and cancer
cells
* 25-33 % of the WBC's
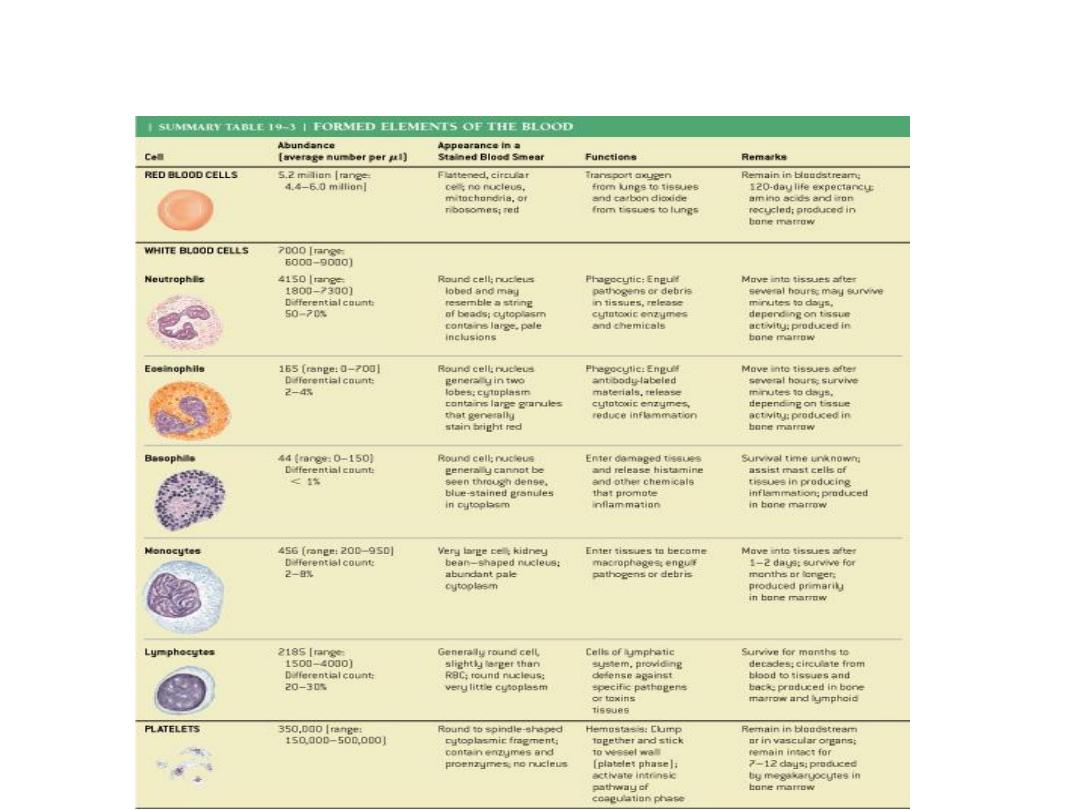
Summary: Formed Elements of Blood
