
Immune System
introduction to immune system
By prof. Israa f.jaffar

Learning objectives
•
To know the Organization of the Lymphatic System
•
To describe the functions of the lymphatic system
•
To delineate the difference between specific and non
specific immune system.
•
To identify the Nonspecific Defenses which includes
:
–
Physical barriers
–
natural killer cells
–
Phagocytes and phagocytosis
–
Immunological surveillance
–
Interferons
–
Complement system

Introduction
•
Pathogens: microorganisms responsible for
human diseases
–
Bacteria
–
Viruses
–
Fungi
–
Parasites
•
Lymphatic system
–
Keeps us alive and healthy

Functions of Lymphatic System
•
Production, maintenance, distribution of
lymphocytes
–
Respond to presence of:
•
Invading pathogens
•
Abnormal body cells (virus-infected cells, cancer cells)
•
Foreign proteins (toxins released by bacteria)
•
Return of fluid and solutes from peripheral tissues to
blood
•
Distribution of hormones, nutrients, and waste
products from tissues of origin to general circulation

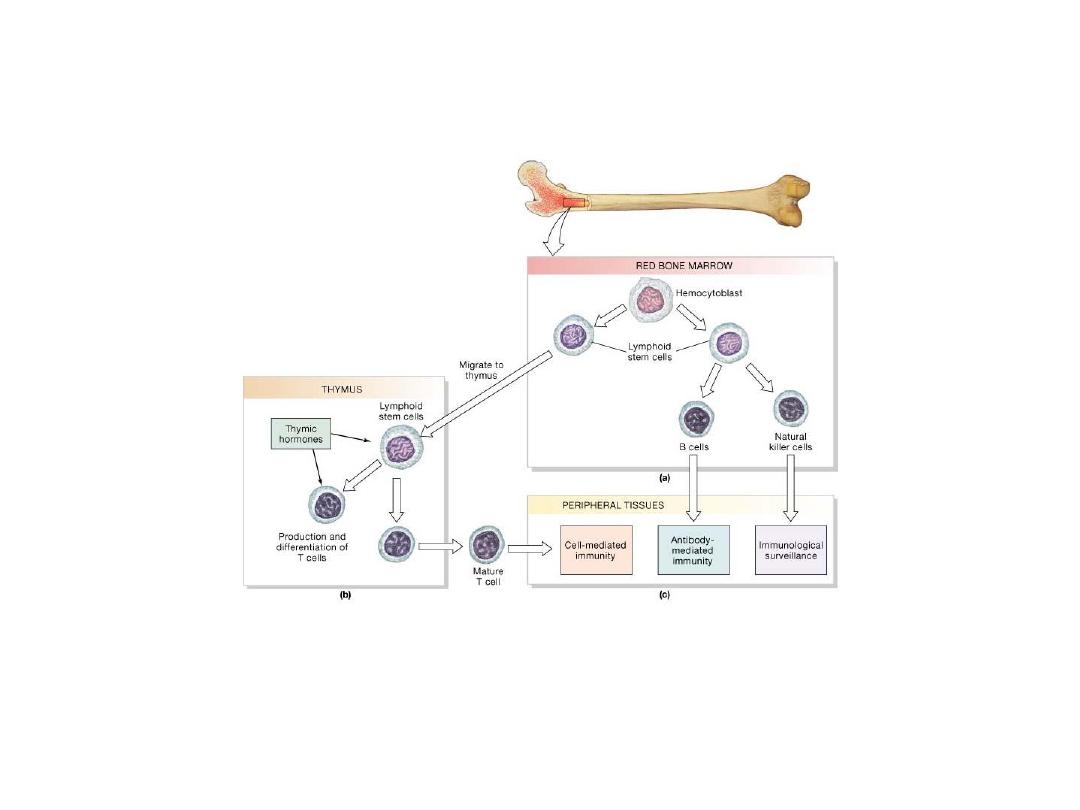
Types of Lymphocytes
•
T cells (Thymus dependent)
–
80% of circulating lymphocytes
–
Cytotoxic T cells
•
Directly attack foreign cells or body cells infected by
viruses (cell-mediated immunity)
–
Helper T cells
•
Stimulate activities of both B and T cells
–
Suppressor T cells
•
Inhibit both T and B cells

Types of Lymphocytes
•
B cells (Bone-marrow derived)
–
10-15% circulating lymphocytes
–
Plasma cells
•
Responsible for production and secretion of antibodies
(immunoglobulins)
–
Responsible for antibody-mediated immunity
•
NK cells (Natural Killer)
–
5-10%
–
Attack foreign cells, normal cells infected with viruses, and
cancer cells
–
Immunological surveillance

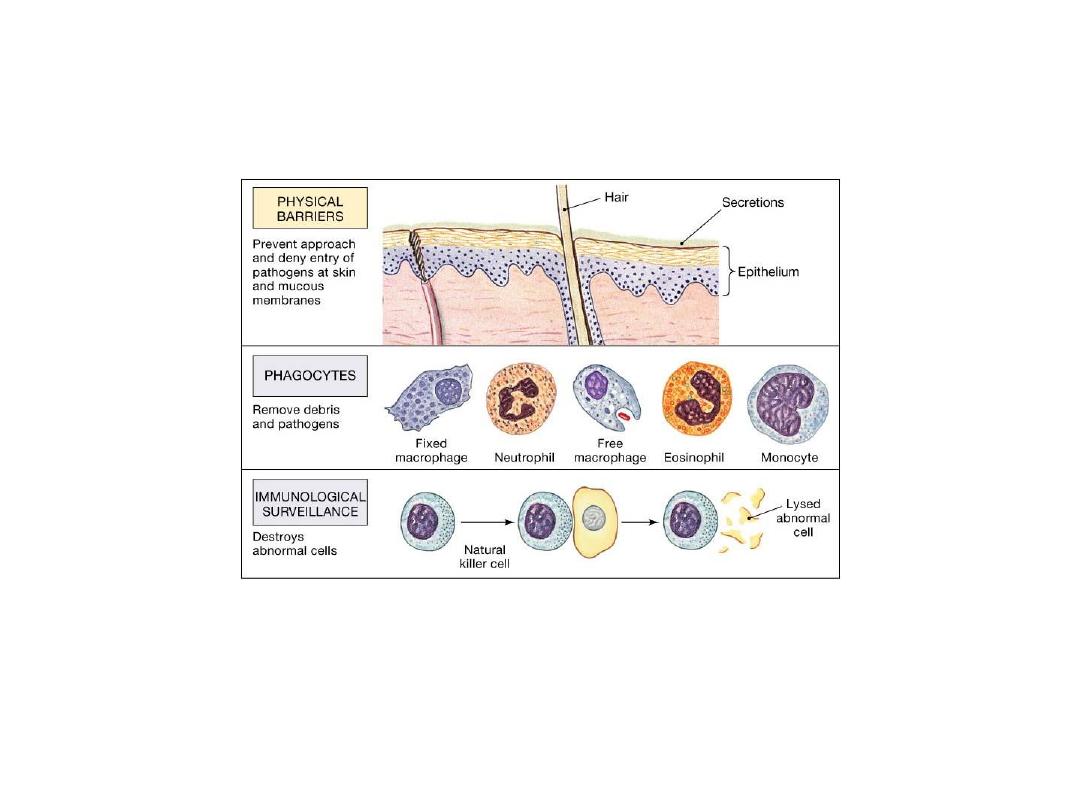
The types of Body Defenses
•
Nonspecific Defenses
–
Do not distinguish one threat
from another
–
Physical barriers
–
Phagocytic cells
–
Immunological surveillance
–
Interferons
–
Complement
–
Inflammation
–
Fever
•
Specific Defenses
–
Protect against particular
threats
–
Develop after birth
–
Dependent on activity of
lymphocytes
–
B cells
–
T cells
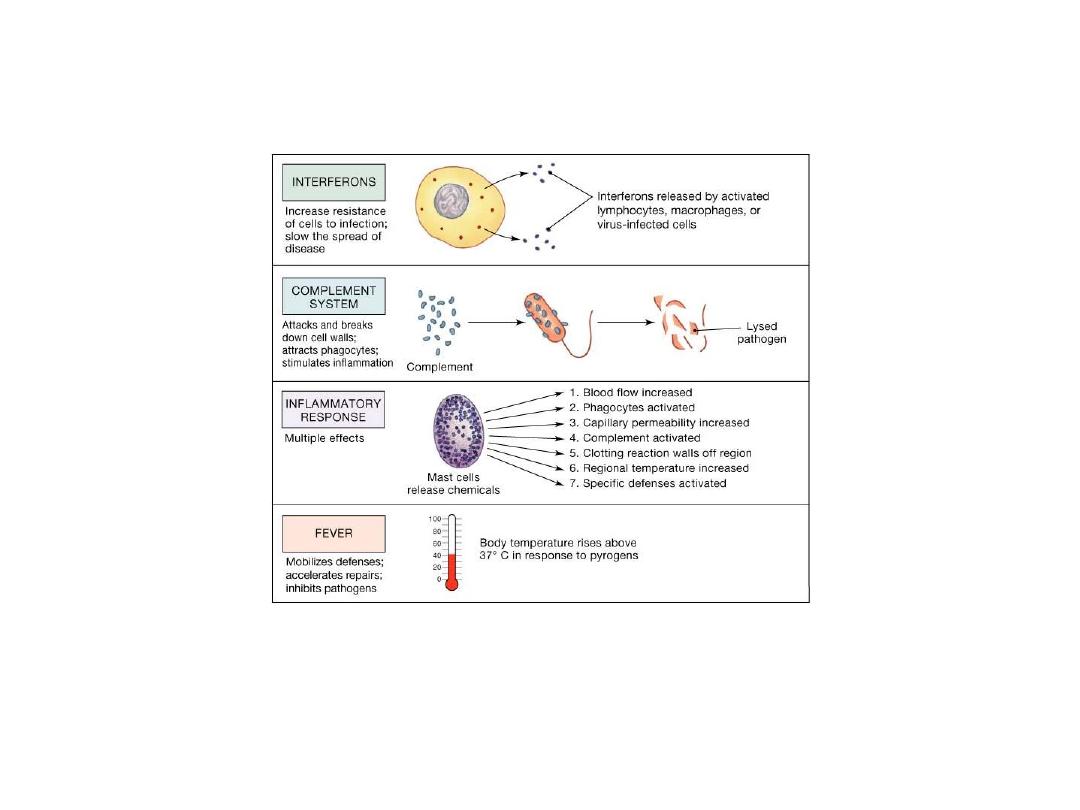

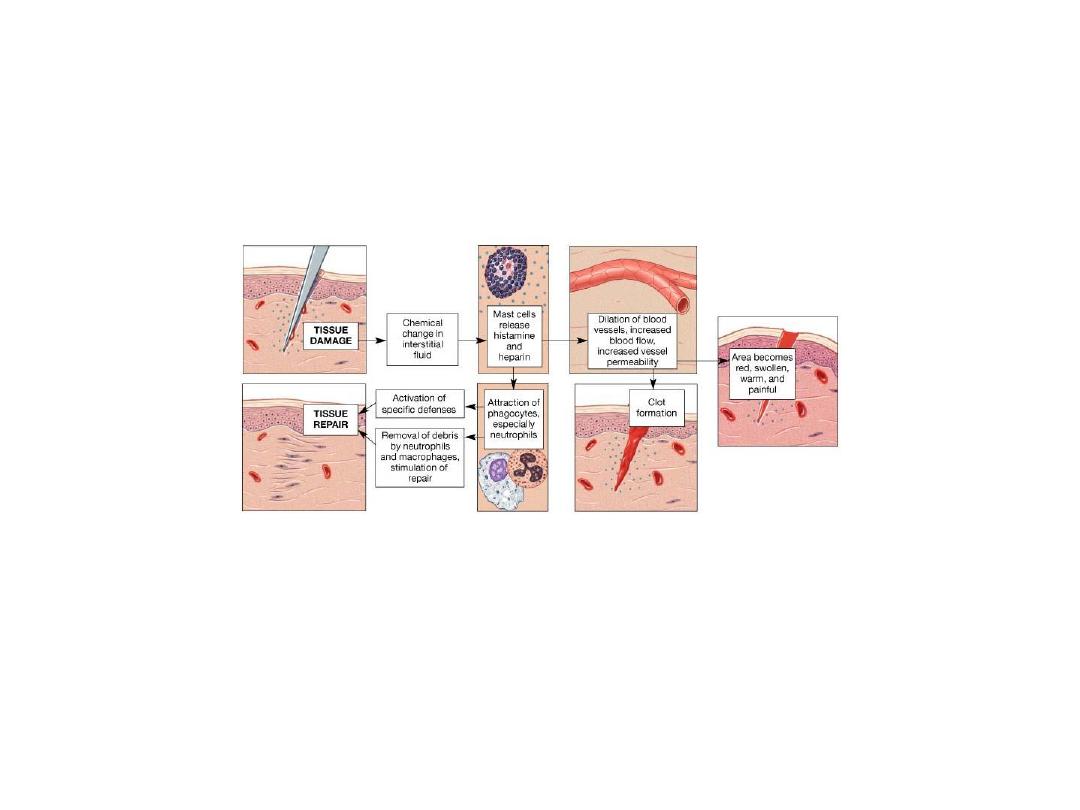
The Complement System

Cytotoxic T Cells
•
Responsible for cell-mediated immunity
•
Activated by exposure to antigens bound to
Class I MHC proteins
–
Activated cells under cell division that produce
active cytotoxic T cells and memory cells
•
Track down and attack bacteria, fungi,
protozoa, or foreign transplanted tissue

Cytotoxic T Cells natural killer cell
•
Destruction occurs by:
–
Releasing perforin (destructive protein)
•
Ruptures antigenic cell membrane
–
Secreting lymphotoxin (poison)
•
Kills target cell
–
Apoptosis
•
Genetically programmed cell death
•
T cells activate the genes within the target cell
•
Also called Killer T cells

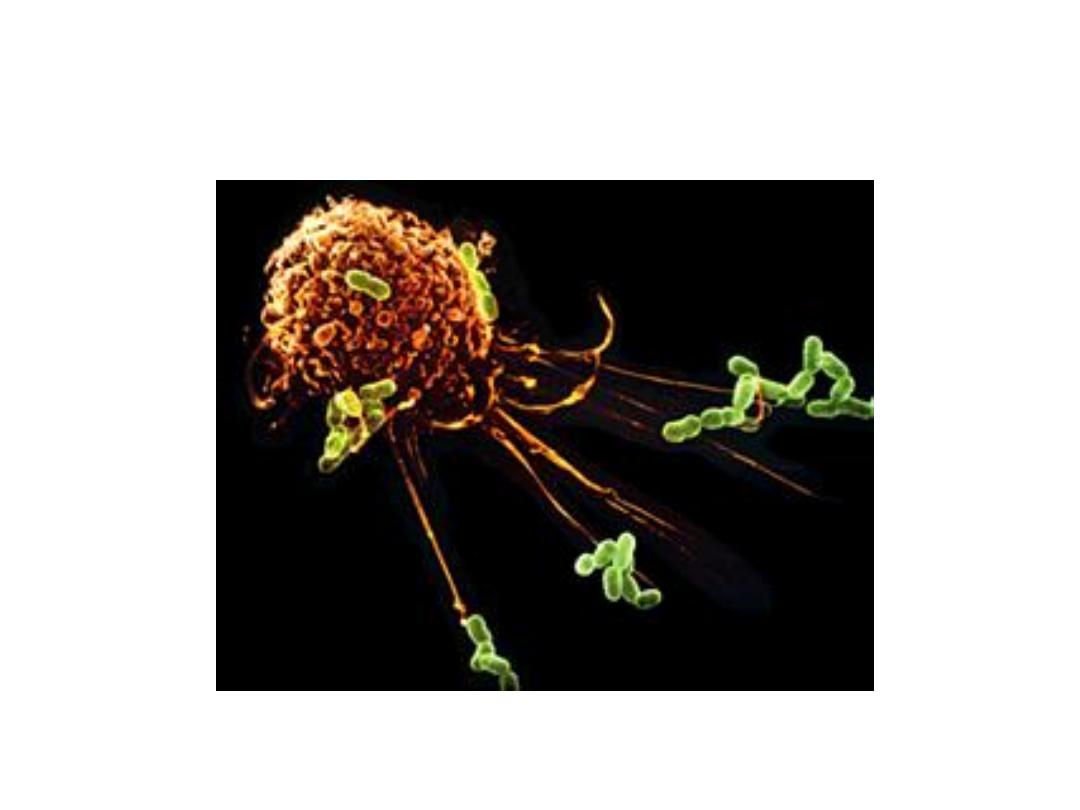
Macrophage
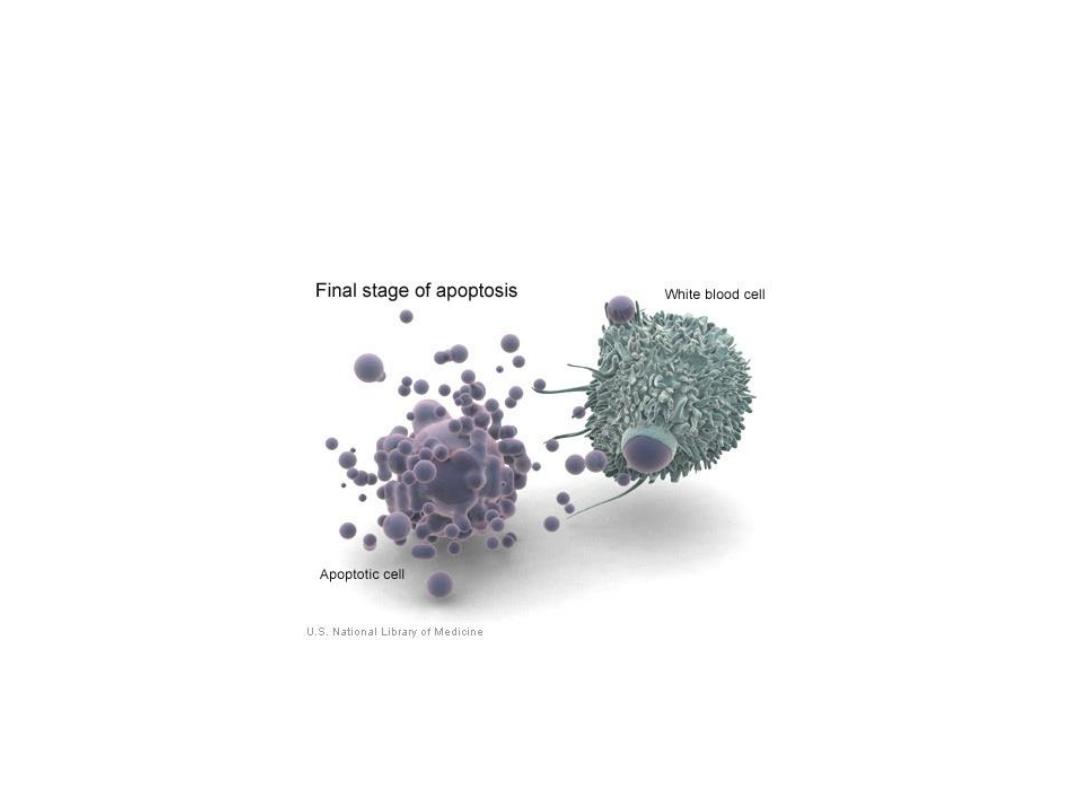
Apoptosis and Macrophages

How the granulocytes get rid of invader?
1-chemotaxis Bacterial products interact with plasma factors and cells to
produce agents(chemokines) that attract neutrophils. The chemotactic
include a component of the complement system (C5a); leukotrienes; and
polypeptides from lymphocytes, mast cells, and basophils.
2-opsonization) opsonins are plasma factors make bacteria "tasty" to the
phagocytes . The principal opsonins are immunoglobulins of a particular
class (IgG) and complement proteins.
3-phagocytosis ingestion of the bacteria by endocytosis
4-degranulation the phagocyte release its contents of granules contain
various proteases plus antimicrobial proteins called defensins. NADPH
oxidase and free radical ;O
2
– ,
O
2
. ,O
2
–
,H
2
O
2
,superoxide dismutase
(SOD-1)
