
Reproductive and Hormonal
Functions of the Male:
After studying this lecture you should
understand:
(1) spermatogenesis, which means
simply the formation of sperm;
(2) performance of the male sexual act;
and
(3) regulation of male reproductive
functions by the various hormones.
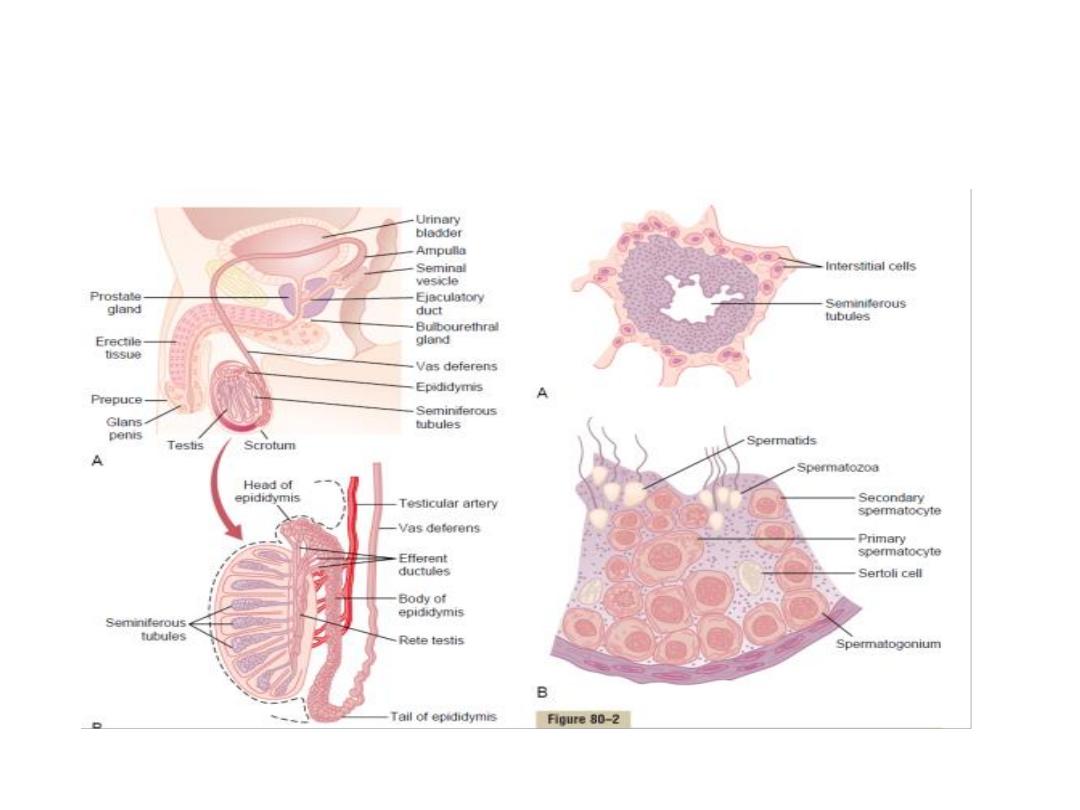
Physiologic Anatomy of the Male
Sexual Organs:
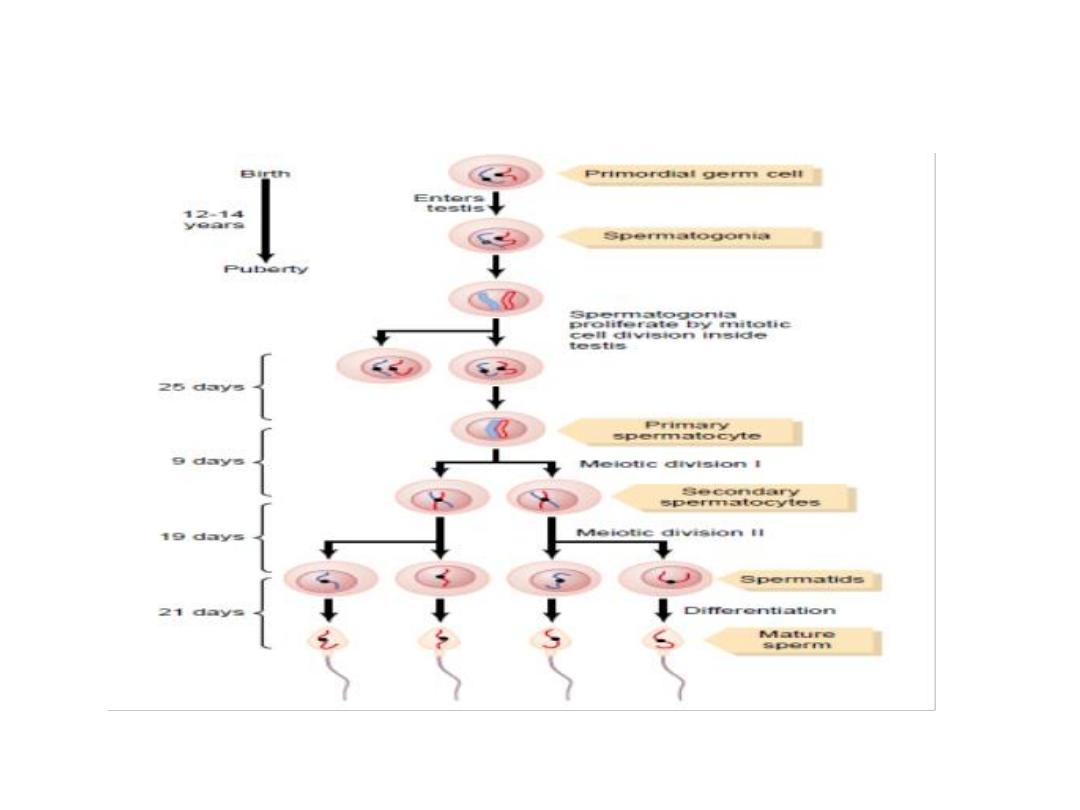
Spermatogenesis
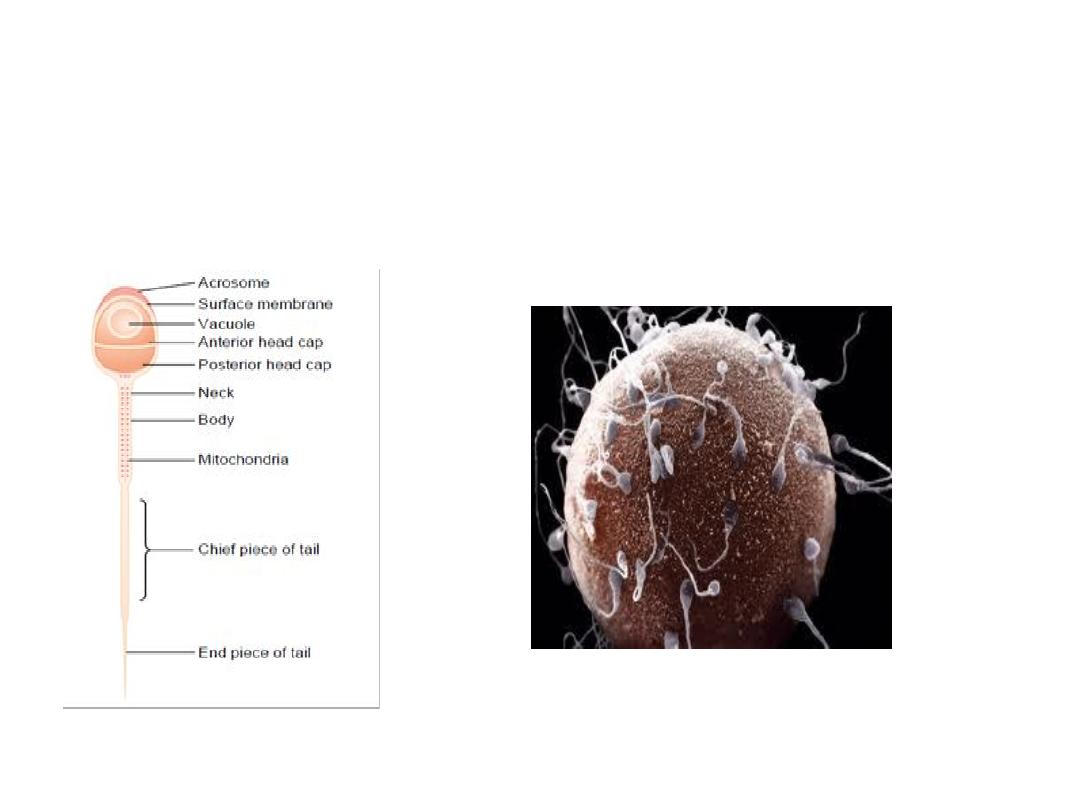
Sperm

Hormonal Factors That Stimulate
Spermatogenesis
1.
Testosterone
, secreted by the Leydig cells located in the
testis, is essential for growth and division of the testicular
germinal cells, which is the first stage in forming sperm.
2.
Luteinizing hormone
, secreted by the anteriorpituitary gland,
stimulates the Leydig cells to secrete testosterone.
3.
Follicle-stimulating hormone FSH
, also secreted by the
anterior pituitary gland, stimulates the Sertoli cells; without this
stimulation, the conversion of the spermatids to sperm (the
process of spermiogenesis) will not occur.
4.
Estrogens
, formed from testosterone by the Sertoli cells
when they are stimulated by FSH hormone, are probably also
essential for spermiogenesis.
5.
Growth hormone (as well as most of the other body
hormones).
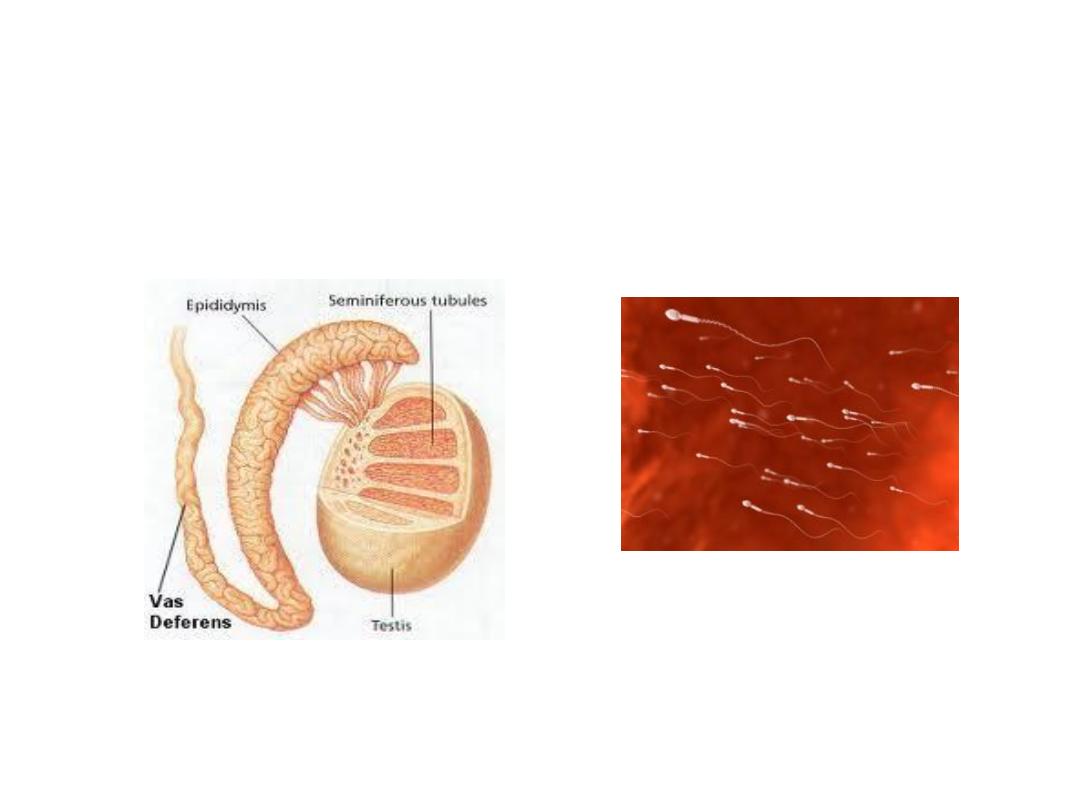
Maturation and Storage of Sperm in
the Epididymis
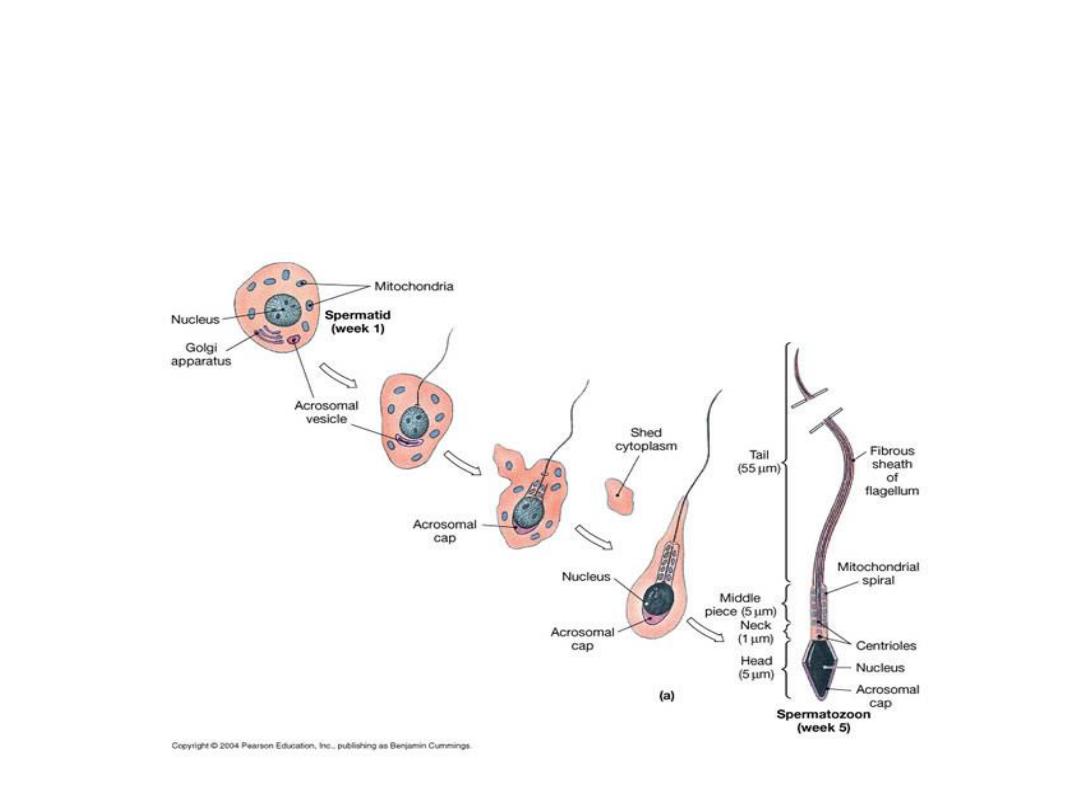
Physiology of the Mature Sperm:
Semen
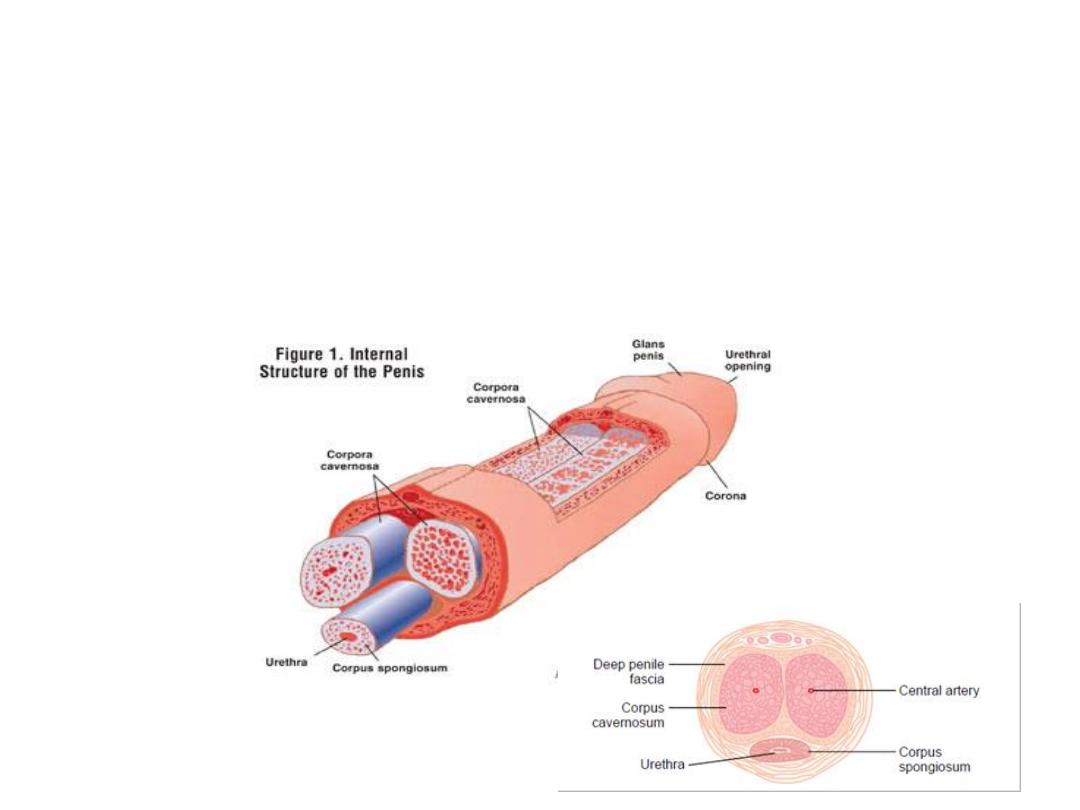
Male sexual act
• Erection, Emission, and Ejaculation:
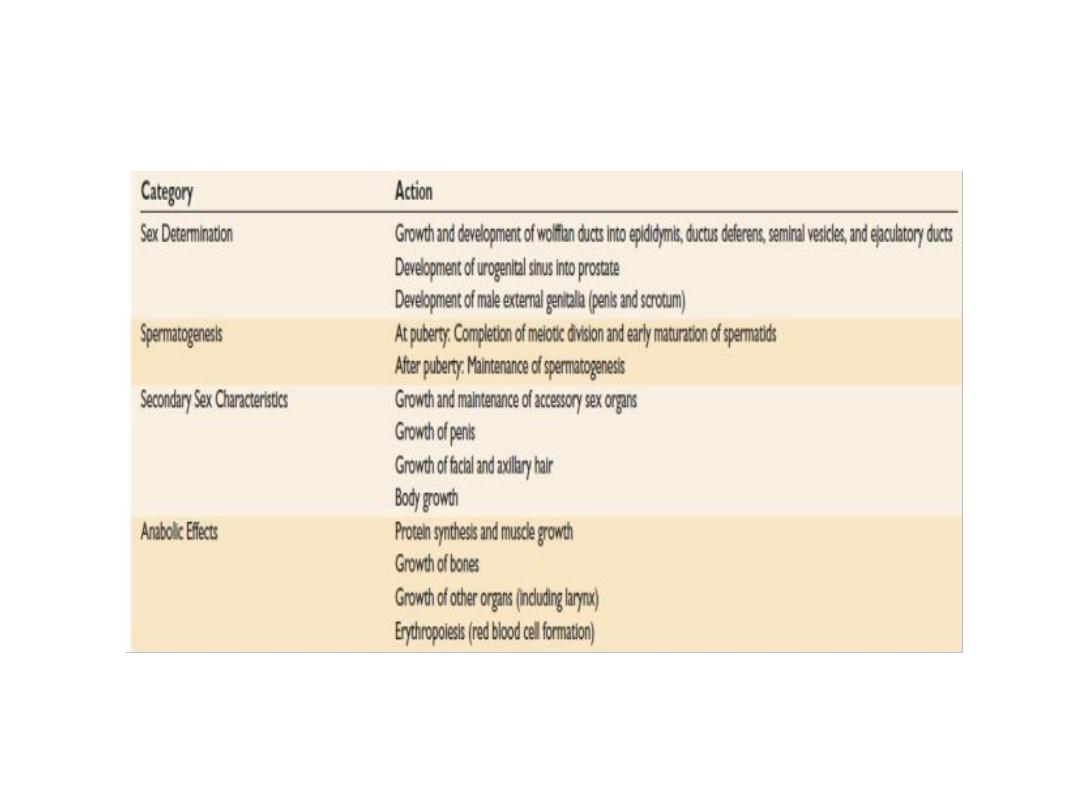
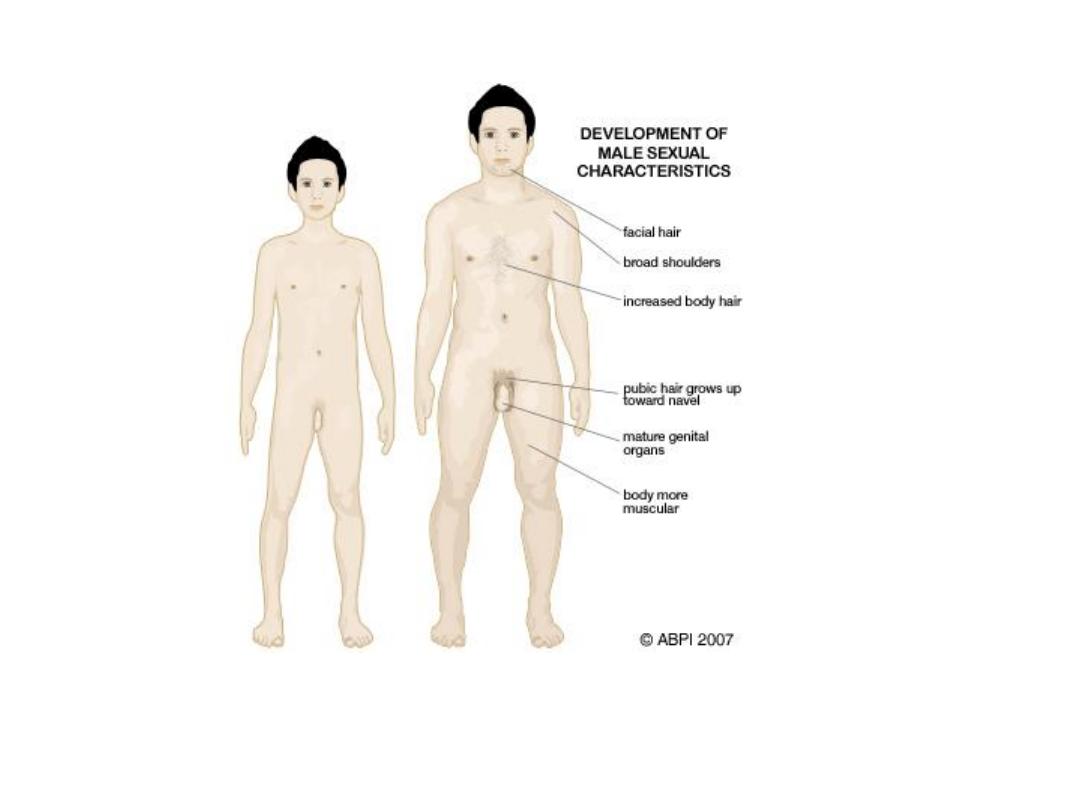
Testosterone:
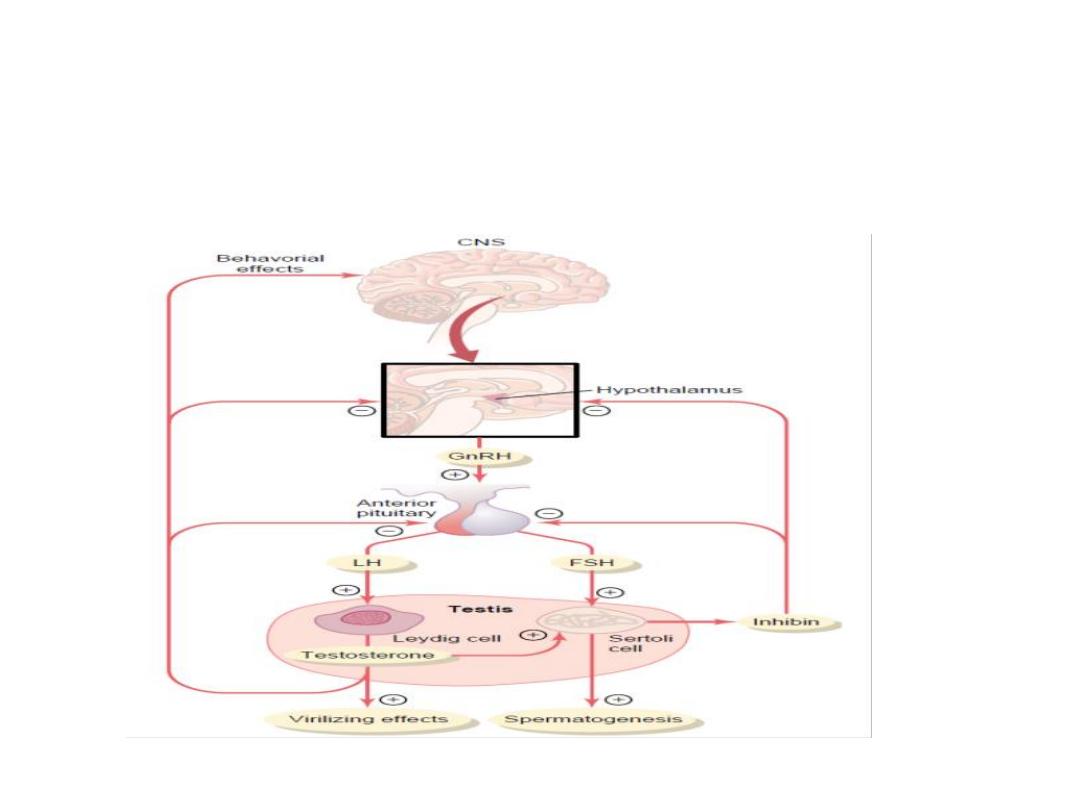
Gonadotropic Hormones: LH and
FSH

Thank you
