Physiology of the
Mature Sperm:
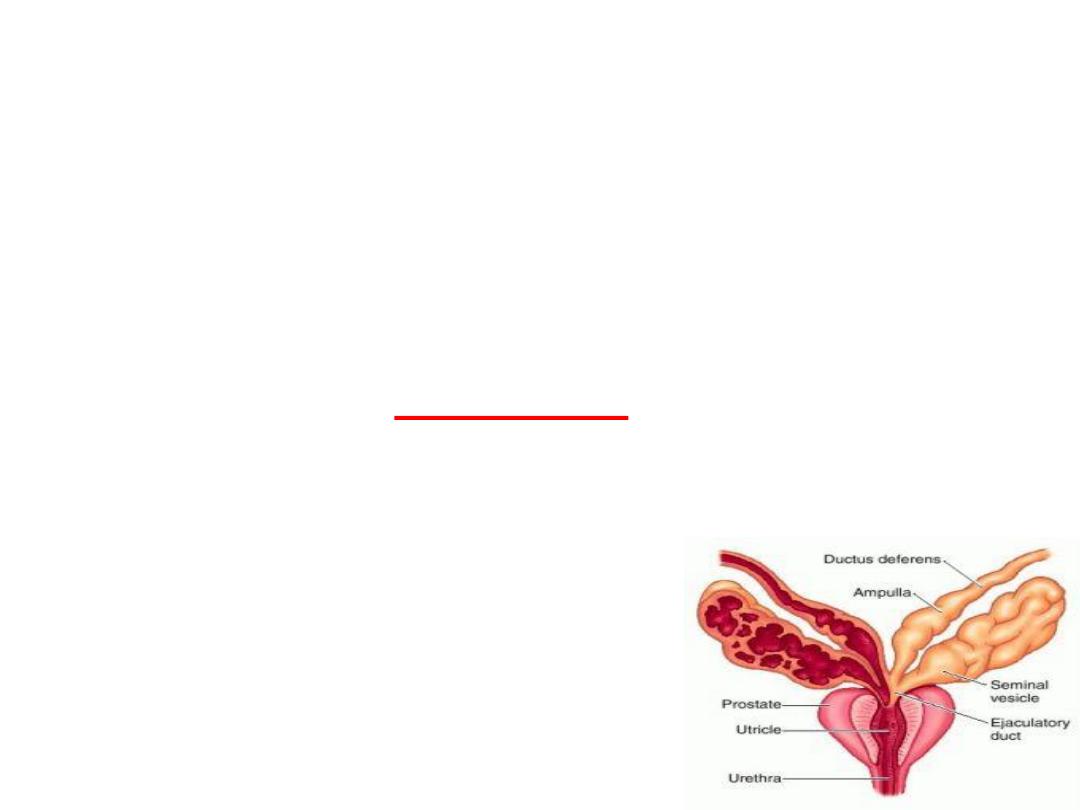
Function of the Seminal
Vesicles:
Secretes a mucous material
containing an abundance of
fructose
,
citric acid
, and other
nutrient substances, as well as large
quantities of
prostaglandins and
fibrinogen
.
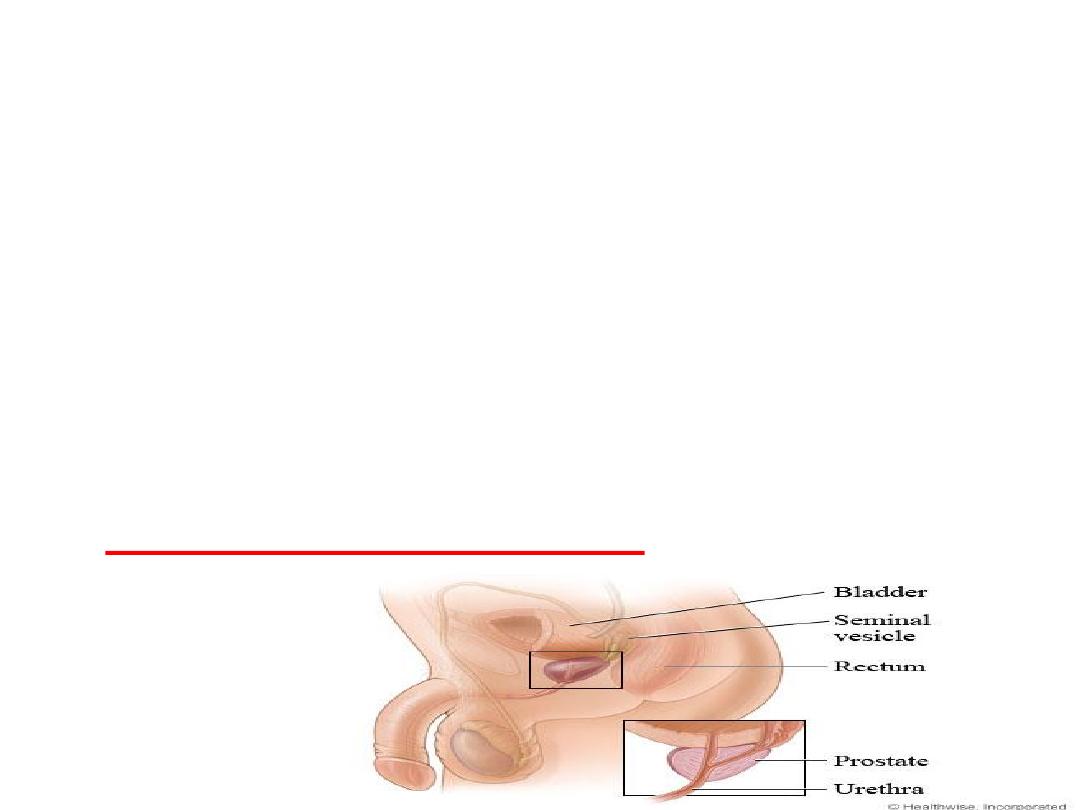
Function of the Prostate Gland:
• Secretes a thin, milky fluid that
contains calcium, citrate ion,
phosphate ion, a
clotting enzyme
,
and a
profibrinolysin
with slight
alkaline characteristic
.

Semen composed of:
• Fluid and sperm from the vas deferens (about
10 per cent of the total).
• fluid from the seminal vesicles (almost 60 per
cent).
• Fluid from the prostate gland (about 30 per
cent).
• Small amounts from the mucous glands,
especially the bulbourethral glands.
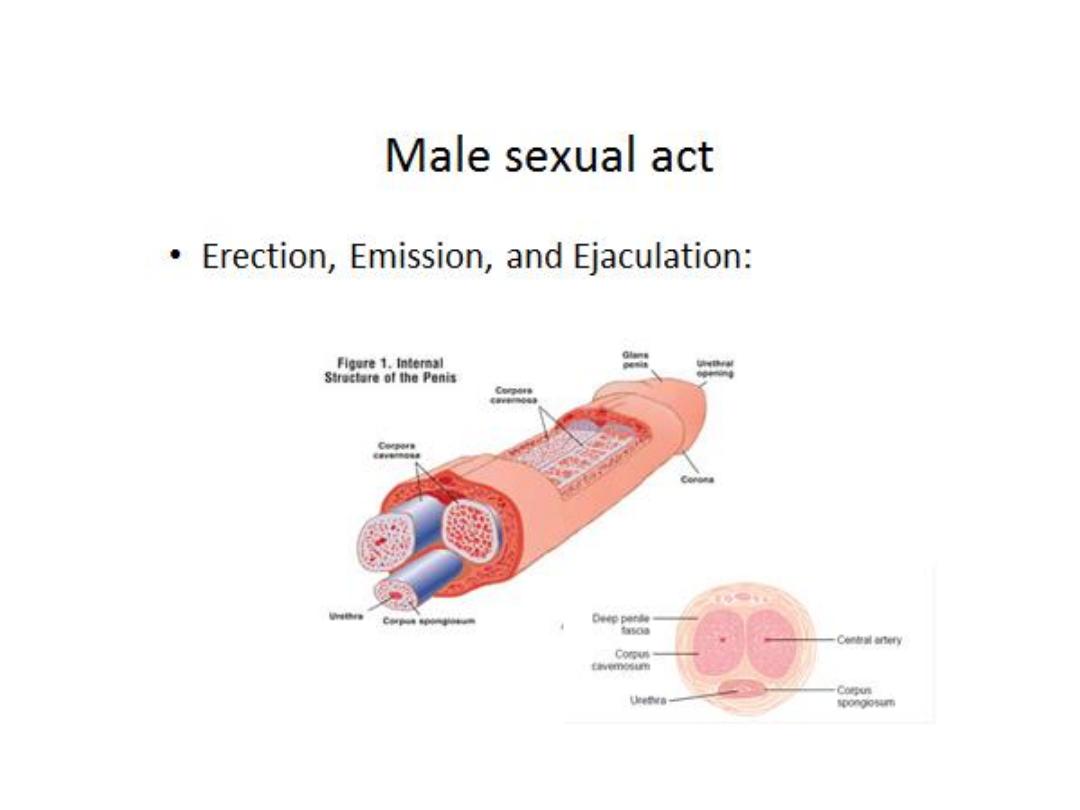
Testosterone:
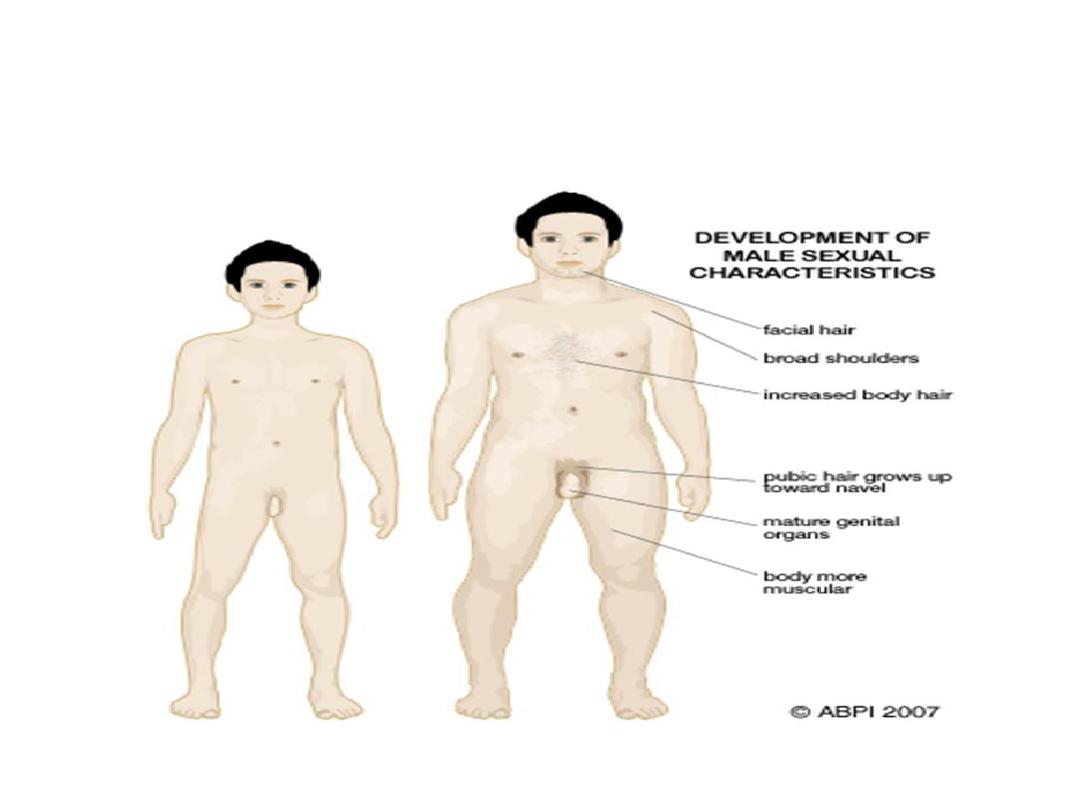
Effect of Testosterone on Development of
Adult Primary and Secondary Sexual
Characteristics
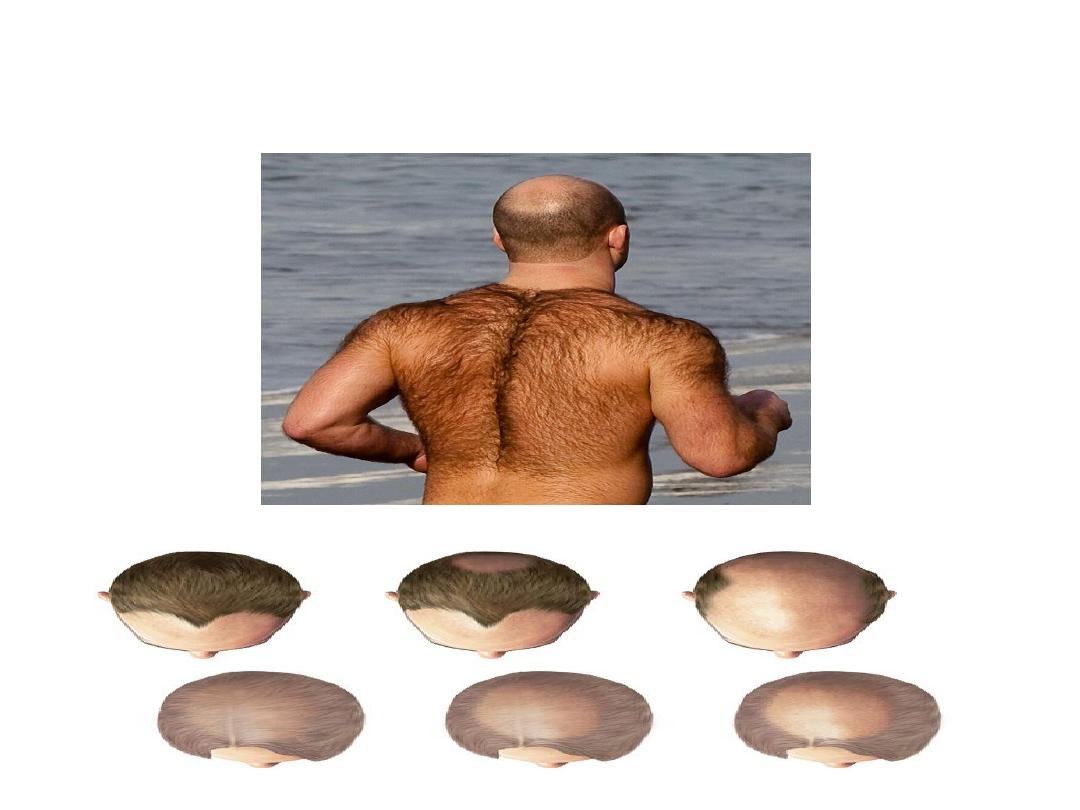
Effect on the Distribution of Body Hair:
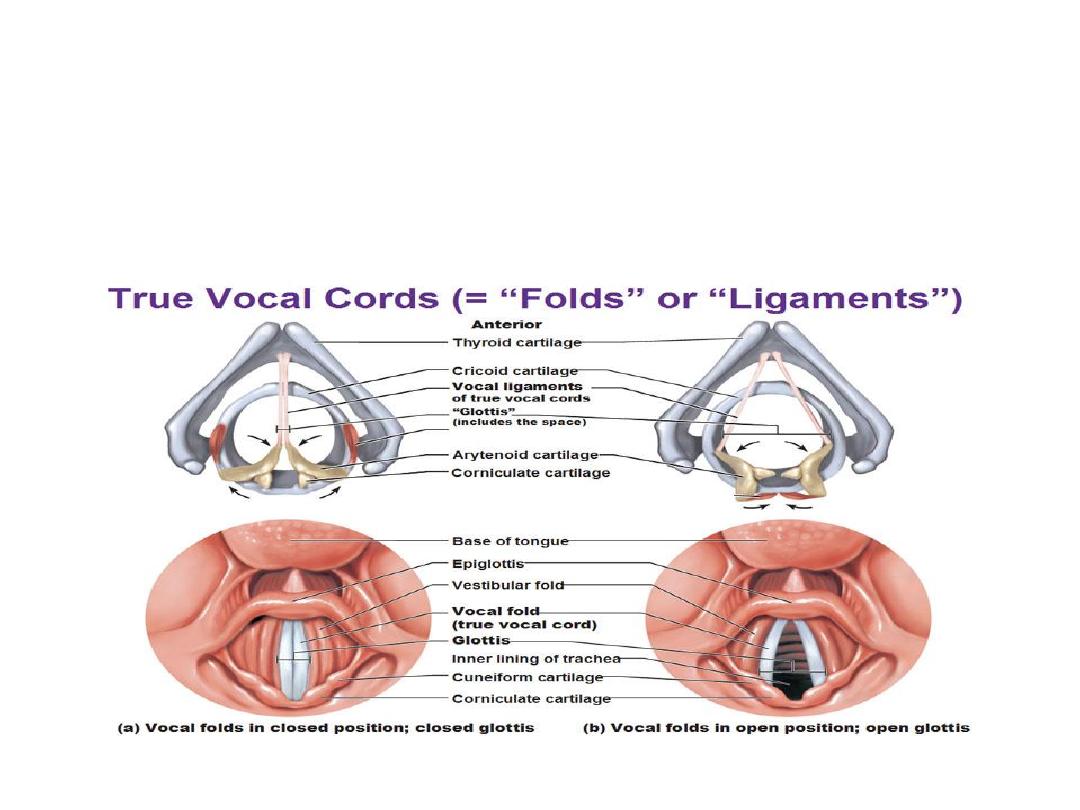
Effect on the Voice:
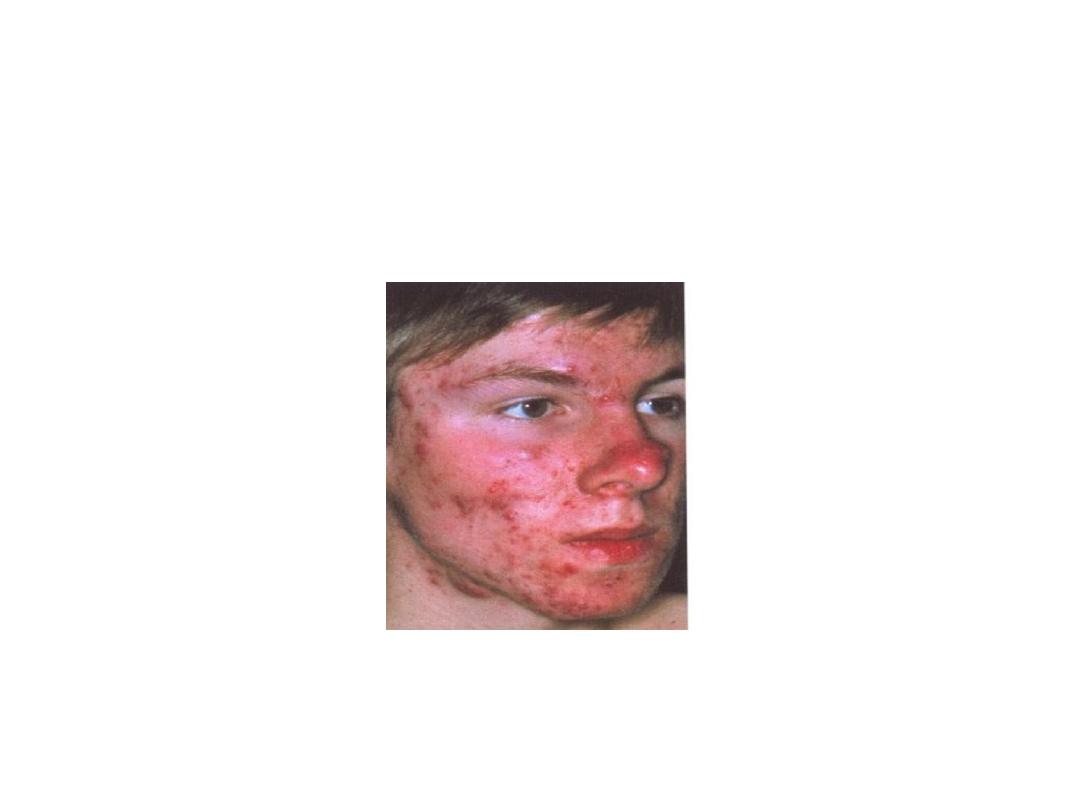
Testosterone Increases Thickness of the
Skin and Can Contribute to Development
of Acne:
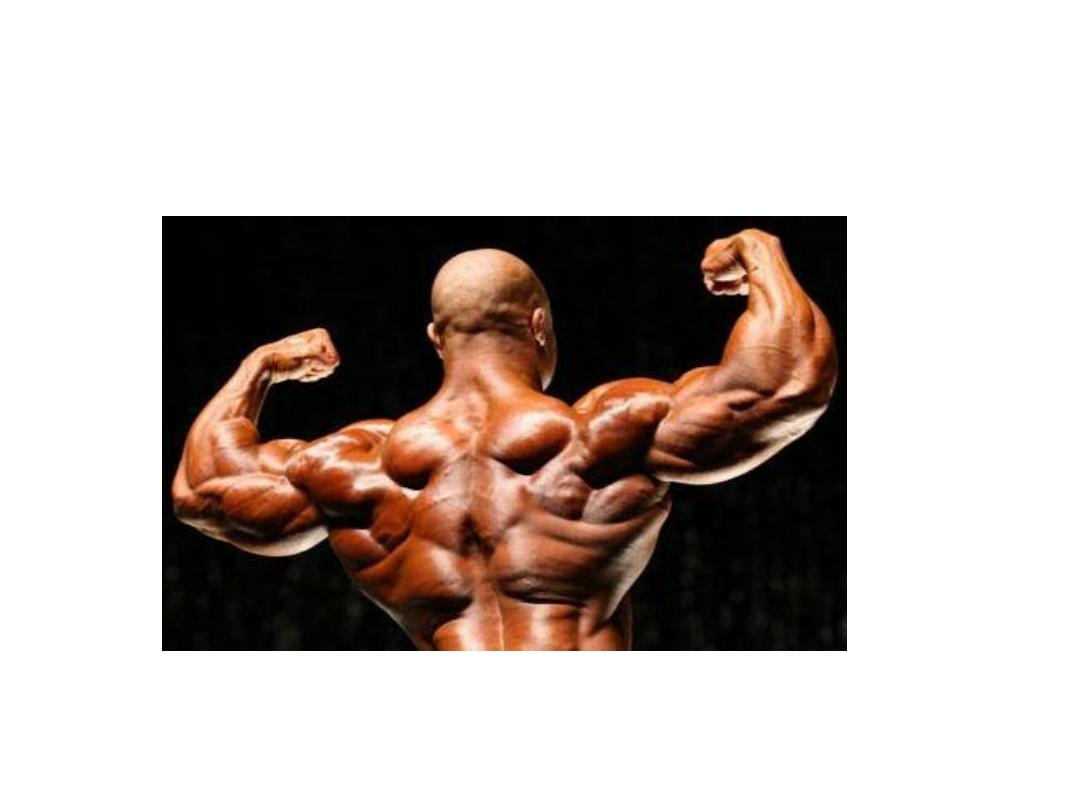

Testosterone Increases Protein
Formation and Muscle Development
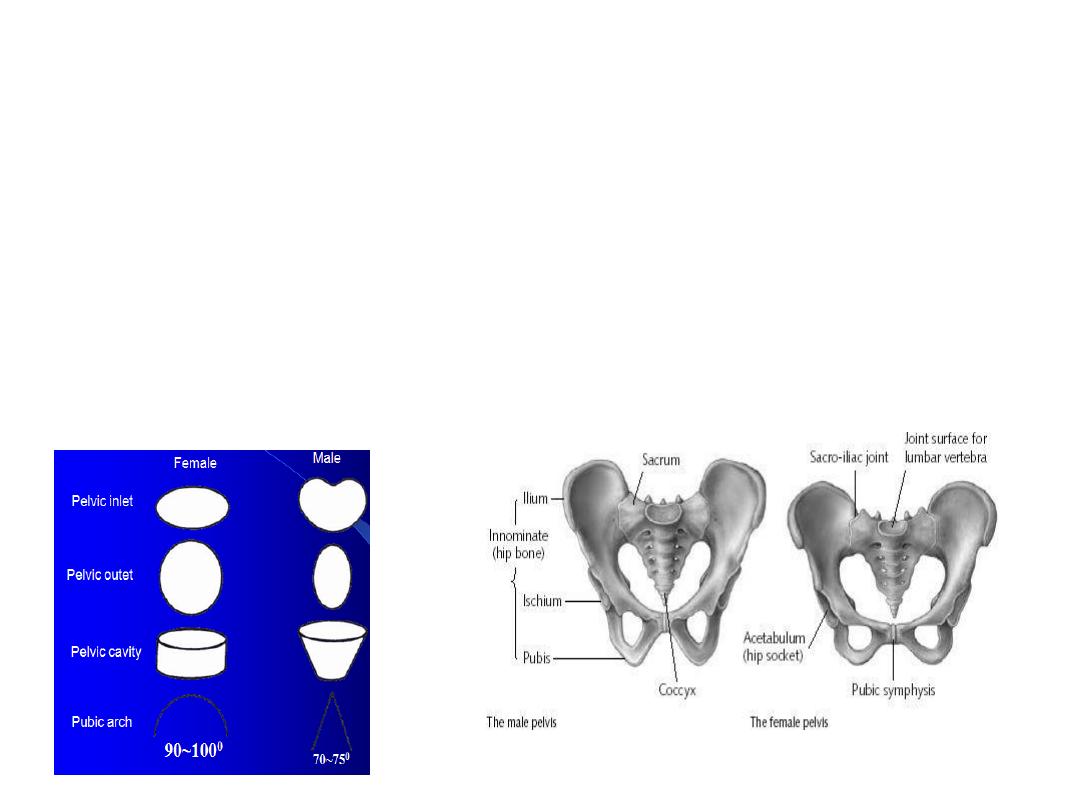
Testosterone and Bone
1. Causes Calcium Retention.
2. Causes the pelvis to narrow its outlet and
lengthen it .
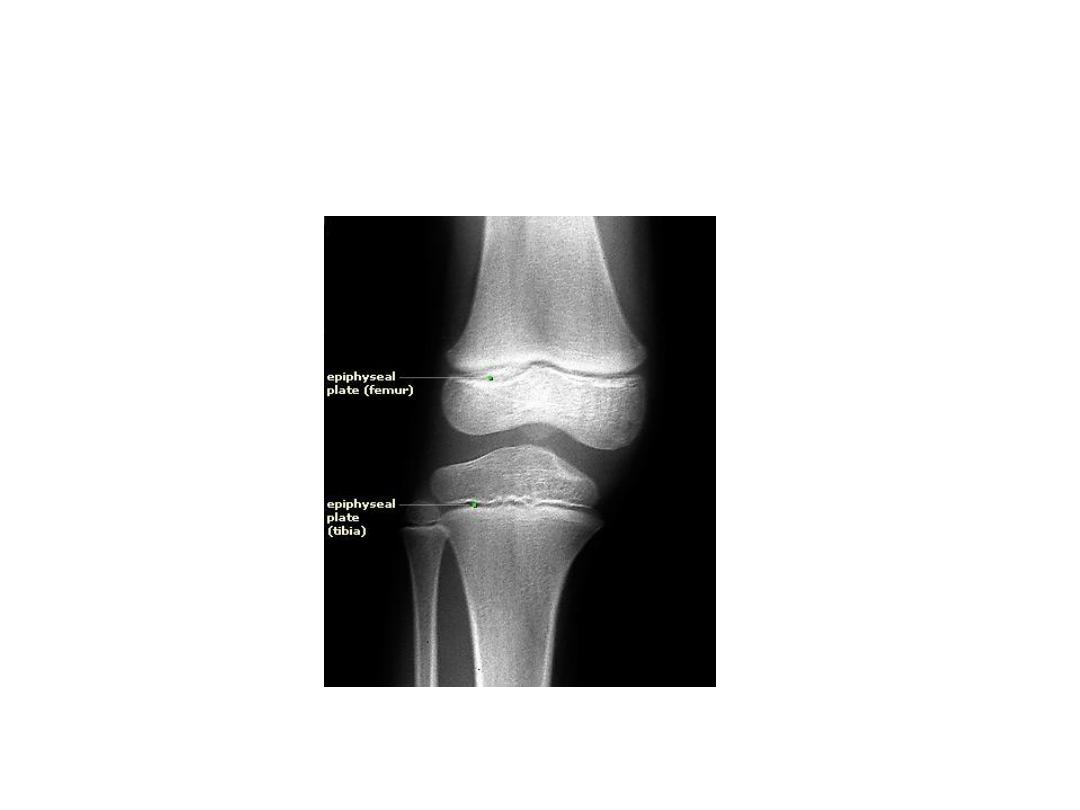
3. The testosterone also causes the epiphyses of
the long bones to unite with the shafts of the
bones at an early age.

Testosterone Increases Basal
Metabolism:
Effect on Red Blood Cells:
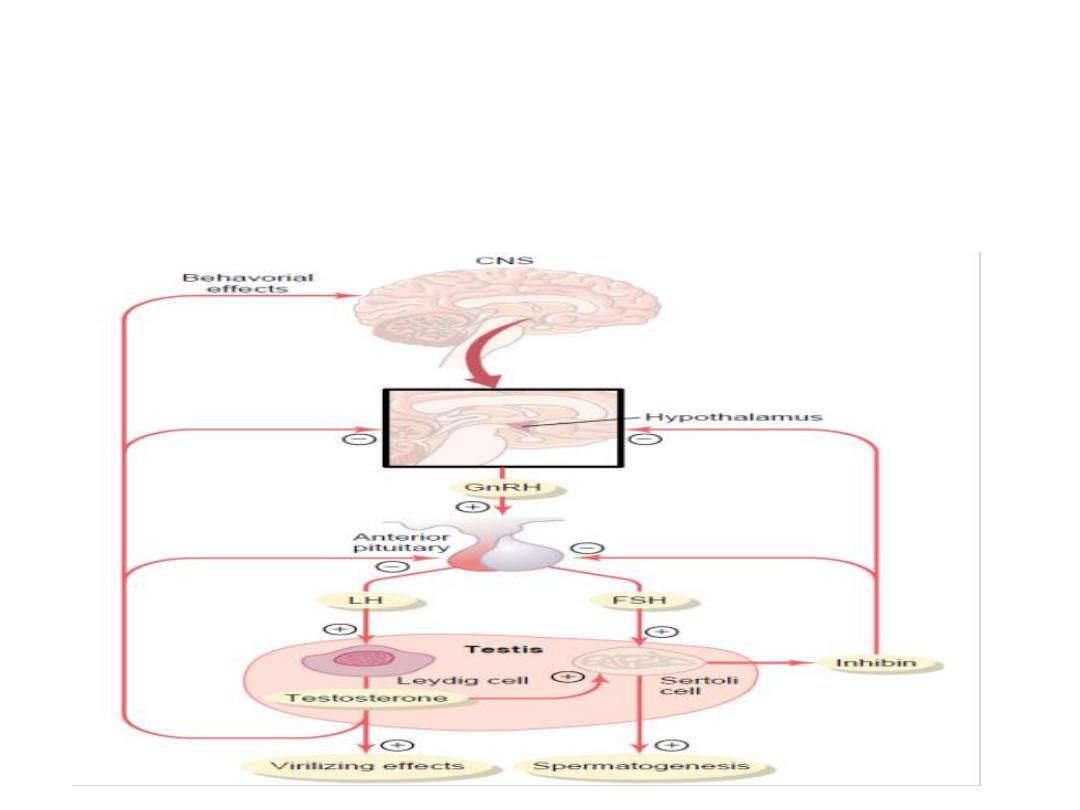
Control of Male Sexual Functions by Hormones
from the Hypothalamus and Anterior Pituitary
Gland:

Thank you
