
Prof. Dr. Malak A. Al-yawer
First Week of
Development
Edited by : Ahmed A. Alkhafaji

outline the changes that occur during the
2
nd
week of development
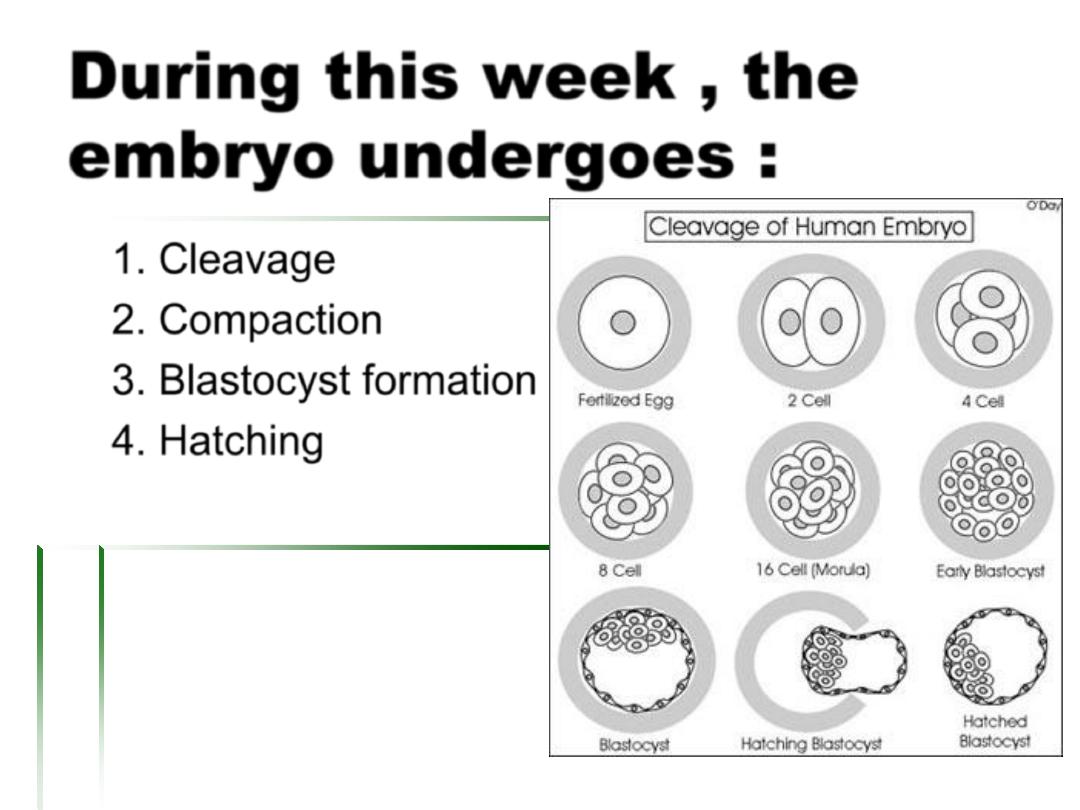
During this week , the
embryo undergoes :
1. Cleavage
2. Compaction
3. Blastocyst formation
4. Hatching

Is a series of mitotic divisions takes place
in a 2-cell stage zygote resulting in the
production of a progressively larger
number of increasingly smaller cells
called blastomeres.
Cleavage

Compaction
Inner cells of the morula constitute the
Inner cell mass
which gives rise to tissues of the embryo proper, and
surrounding cells compose the Outer cell mass which
forms the Trophoblast, which later contributes to the
placenta
Is the process where by the blastomeres become
flattened , thereby maximizing intercellular contacts
and minimizing intercellular spaces . This process
results in a uniform cellular mass named
morula
(
Latin; mulberry ) which can be used for embryos when
about a dozen or more cells are present and until the
blastocystic cavity appears .
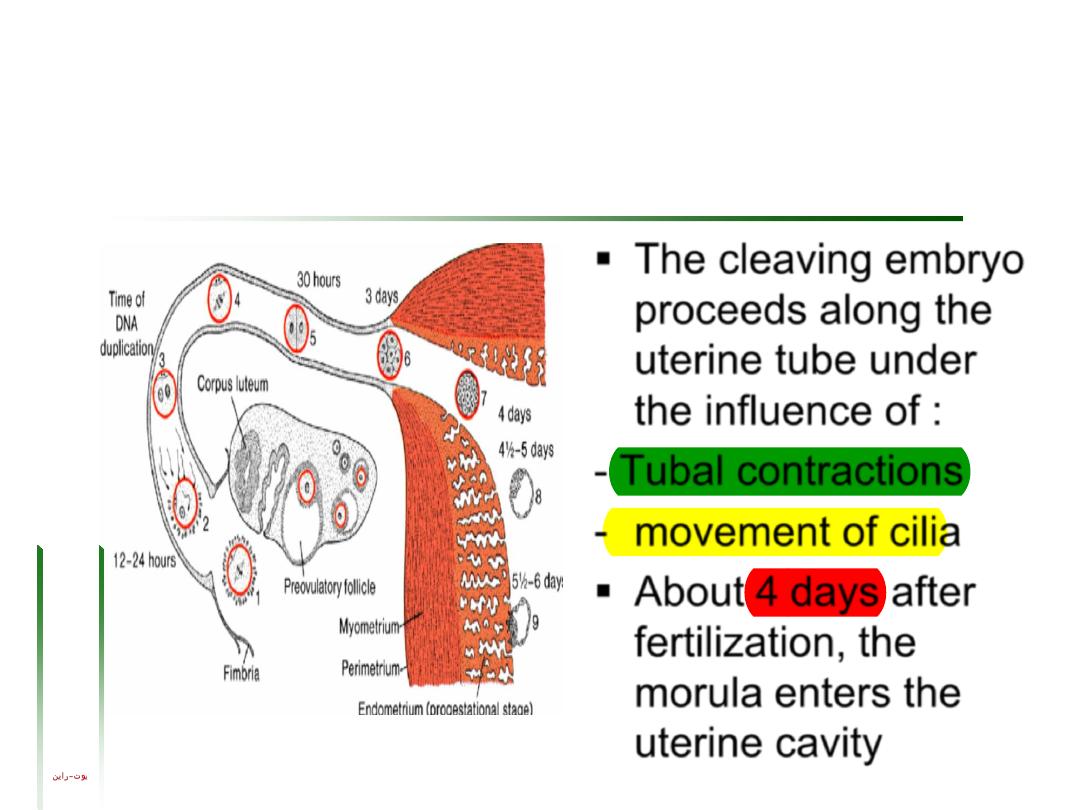
The cleaving embryo
proceeds along the
uterine tube under
the influence of :
- Tubal contractions
- movement of cilia
About 4 days after
fertilization, the
morula enters the
uterine cavity
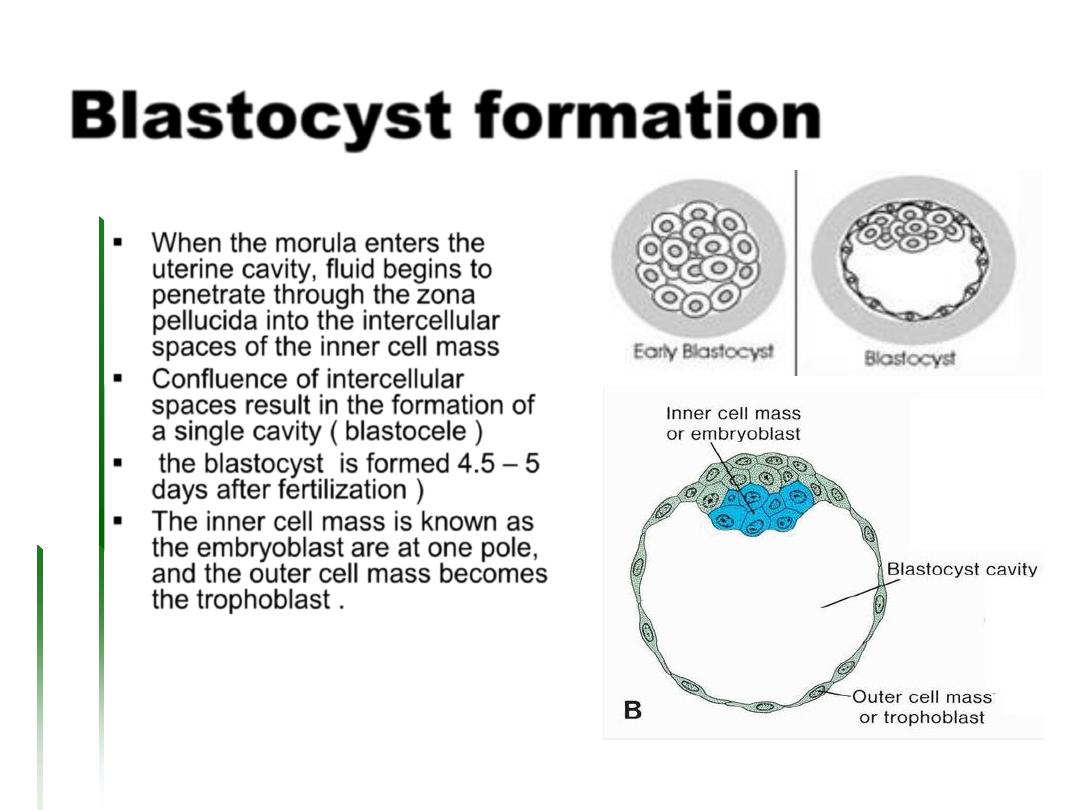
Blastocyst formation
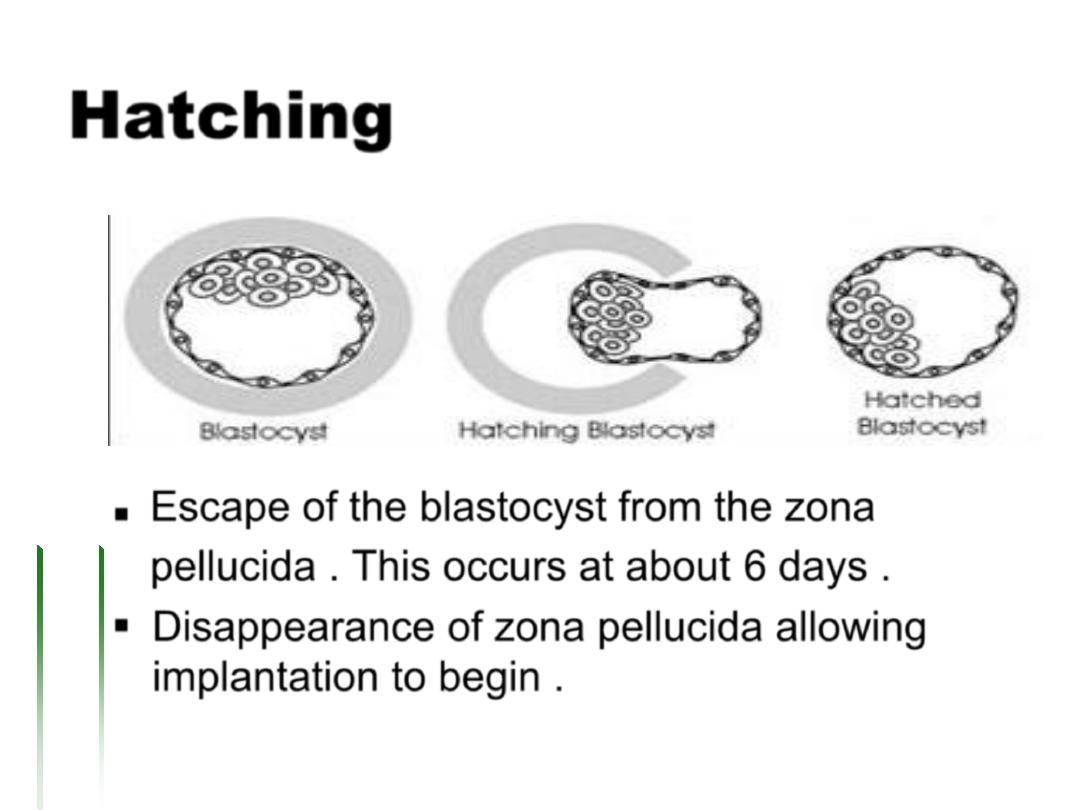
Hatching
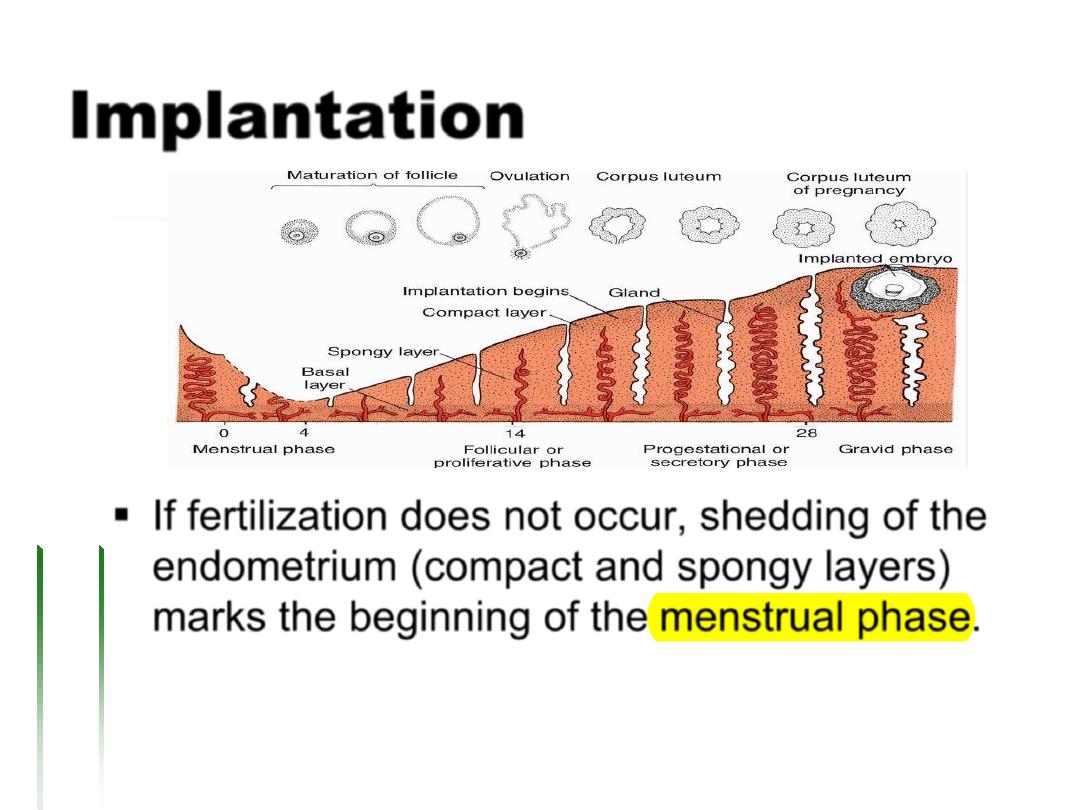
Implantation
If fertilization does not occur, shedding of the
endometrium (compact and spongy layers)
marks the beginning of the menstrual phase.

If fertilization does occur, the endometrium
assists in implantation and contributes to
formation of the placenta.

implants in the
endometrium
along the posterior or
anterior wall of the
body of the uterus
becomes embedded
between the
openings of the
glands.
Normally , the
blastocyst

Implantation
attaches at the
embryonic pole probably
around 6 days
Is the result of mutual
trophoblastic and
endometrial action.
Trophoblast cells invade
the epithelium and
underlying endometrial
stroma with the help of
proteolytic enzymes.

At the time of implantation , the
endometrium

week of twos
2
nd
week of
development

Two cavities, the amniotic and yolk sac
cavities, form.
The extraembryonic mesoderm splits into two
layers, the somatopleure and splanchnopleure.
The embryoblast forms two layers, the epiblast
and hypoblast.
The trophoblast differentiates into two layers,
the cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast.
week of twos
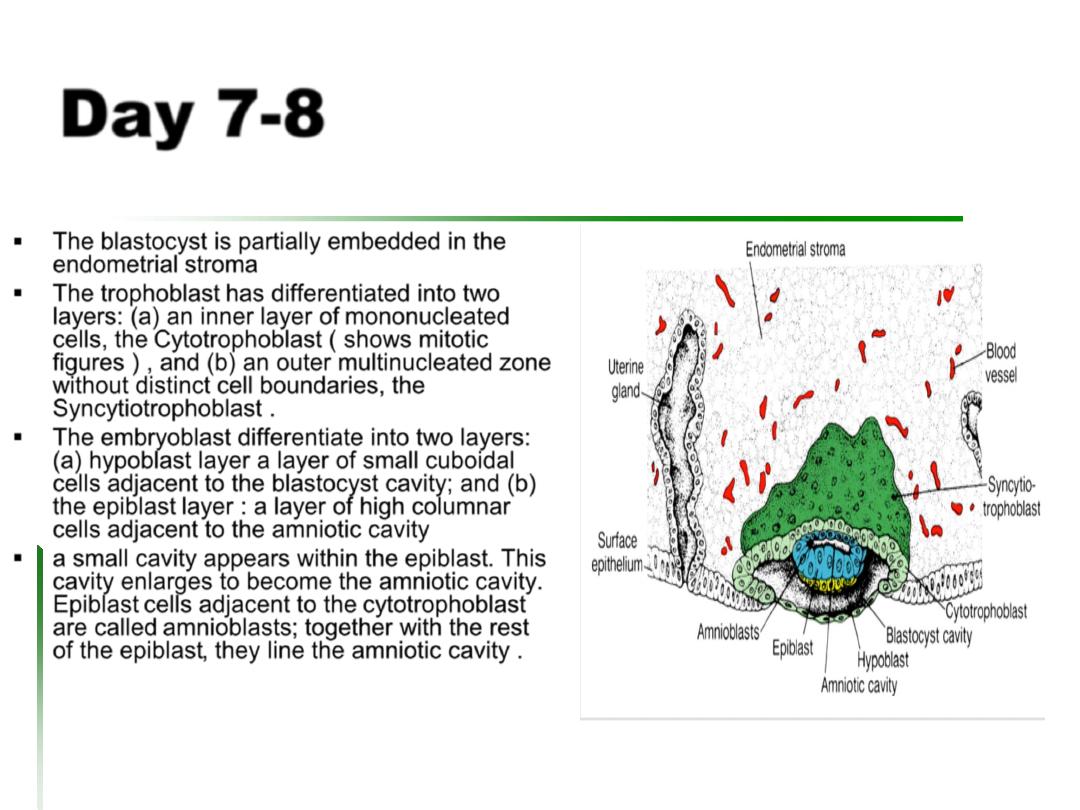
a small cavity appears within the epiblast. This
cavity enlarges to become the amniotic cavity.
Epiblast cells adjacent to the cytotrophoblast
are called amnioblasts; together with the rest
of the epiblast, they line the amniotic cavity .
The embryoblast differentiate into two layers:
(a) hypoblast layer a layer of small cuboidal
cells adjacent to the blastocyst cavity; and (b)
the epiblast layer : a layer of high columnar
cells adjacent to the amniotic cavity
The trophoblast has differentiated into two
layers: (a) an inner layer of mononucleated
cells, the Cytotrophoblast ( shows mitotic
figures ) , and (b) an outer multinucleated zone
without distinct cell boundaries, the
Syncytiotrophoblast .
The blastocyst is partially embedded in the
endometrial stroma
Day 7-8

the amniotic cavity
.
A small cavity appears within
the epiblast. This cavity
enlarges to become the
amniotic cavity. Epiblast cells
adjacent to the
cytotrophoblast are called
amnioblasts; together with the
rest of the epiblast, they line
Day 7-8

Exocoelomic (
Heuser’s ) membrane :
flattened cells probably originating from the
hypoblast form this membrane, that lines
the inner surface of the cytotrophoblast .
This membrane, together with the
hypoblast, forms the lining of the
exocoelomic cavity, or primitive yolk sac.
Embryoblast
– bilaminar germ disc :
epiblast ( columnar ) and hypoblast (
cuboidal )
The trophoblast ( lacunar stage ) :
vacuoles, appearing in the syncytium, fuse
and form large lacunae.
The blastocyst is more deeply embedded
in the endometrium, and the penetration
defect is closed by a fibrin coagulum
Day 9
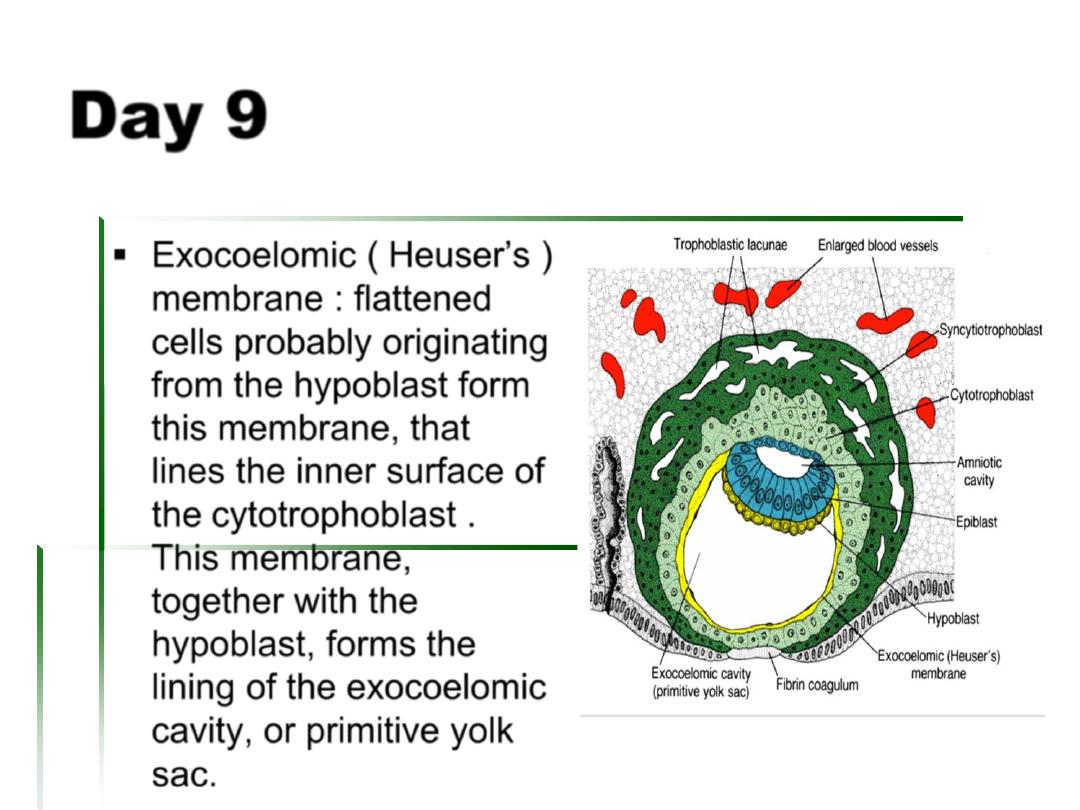
Exocoelomic (
Heuser’s )
membrane : flattened
cells probably originating
from the hypoblast form
this membrane, that
lines the inner surface of
the cytotrophoblast .
This membrane,
together with the
hypoblast, forms the
lining of the exocoelomic
cavity, or primitive yolk
sac.
Day 9
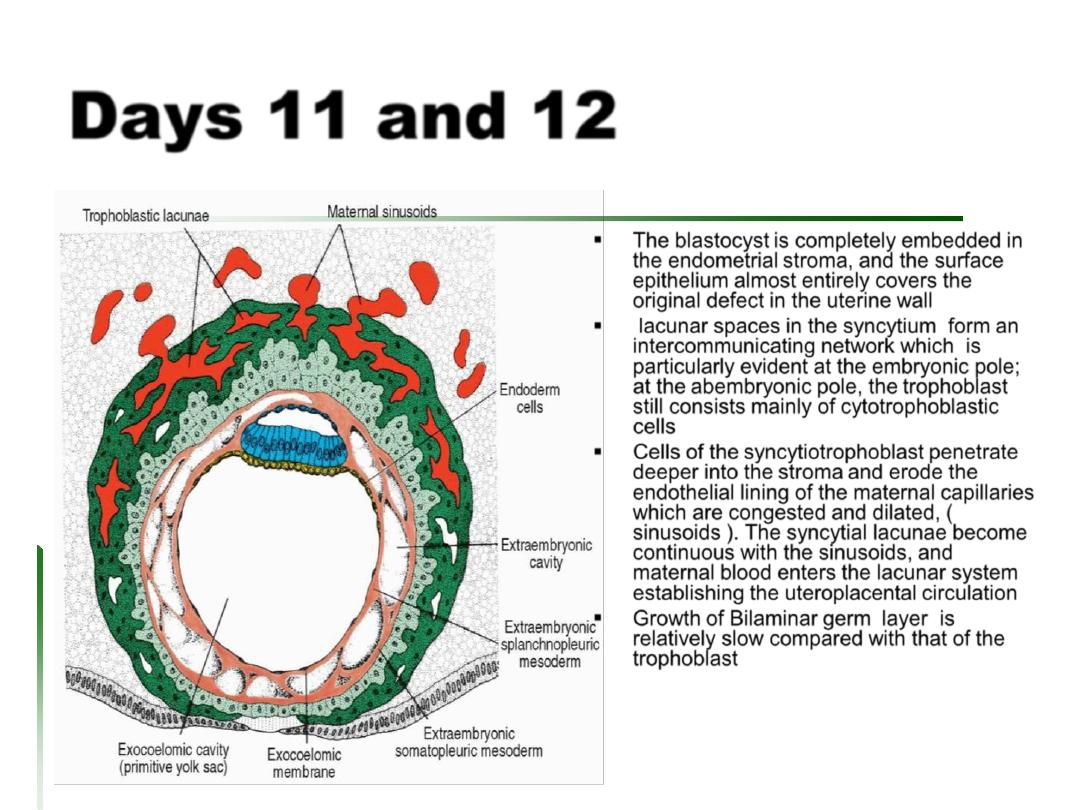
Growth of Bilaminar germ layer is
relatively slow compared with that of the
trophoblast
Cells of the syncytiotrophoblast penetrate
deeper into the stroma and erode the
endothelial lining of the maternal capillaries
which are congested and dilated, (
sinusoids ). The syncytial lacunae become
continuous with the sinusoids, and
maternal blood enters the lacunar system
establishing the uteroplacental circulation
lacunar spaces in the syncytium form an
intercommunicating network which is
particularly evident at the embryonic pole;
at the abembryonic pole, the trophoblast
still consists mainly of cytotrophoblastic
cells
The blastocyst is completely embedded in
the endometrial stroma, and the surface
epithelium almost entirely covers the
original defect in the uterine wall
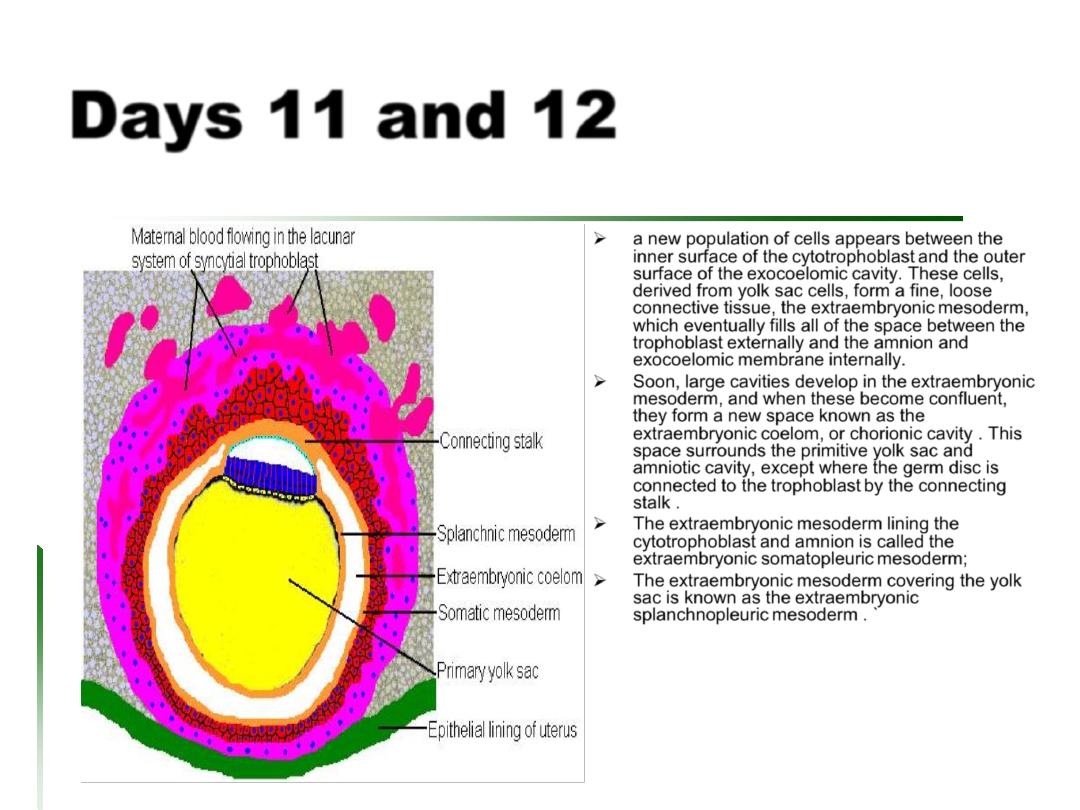
Days 11 and 12
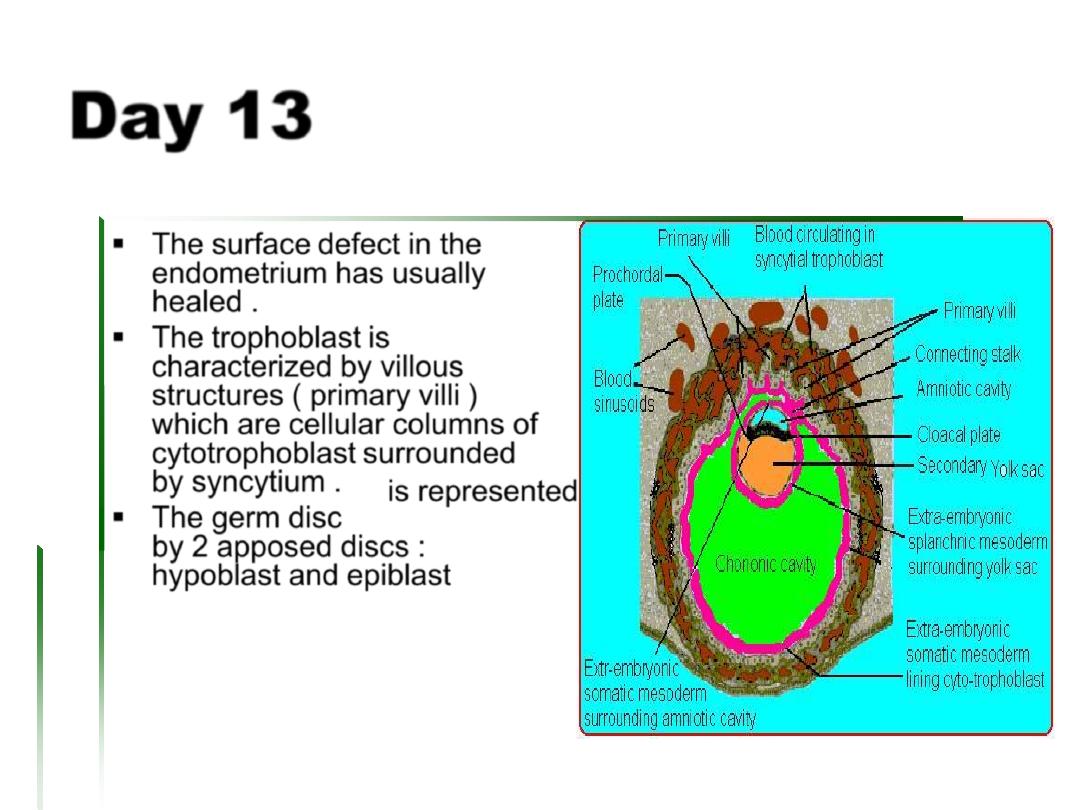
Day 13
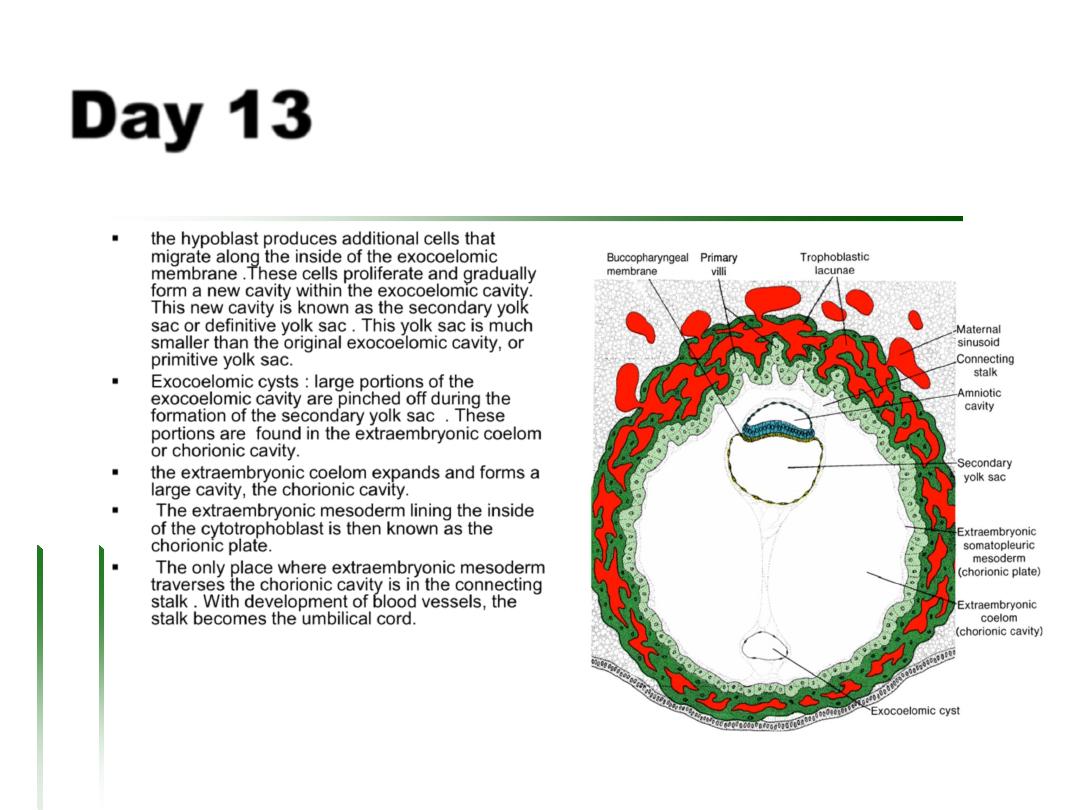
the hypoblast produces additional cells that
migrate along the inside of the exocoelomic
membrane .These cells proliferate and gradually
form a new cavity within the exocoelomic cavity.
This new cavity is known as the secondary yolk
sac or definitive yolk sac . This yolk sac is much
smaller than the original exocoelomic cavity, or
primitive yolk sac.
Exocoelomic cysts : large portions of the
exocoelomic cavity are pinched off during the
formation of the secondary yolk sac . These
portions are found in the extraembryonic coelom
or chorionic cavity.
the extraembryonic coelom expands and forms a
large cavity, the chorionic cavity.
The extraembryonic mesoderm lining the inside
of the cytotrophoblast is then known as the
chorionic plate.
The only place where extraembryonic mesoderm
traverses the chorionic cavity is in the connecting
stalk . With development of blood vessels, the
stalk becomes the umbilical cord.
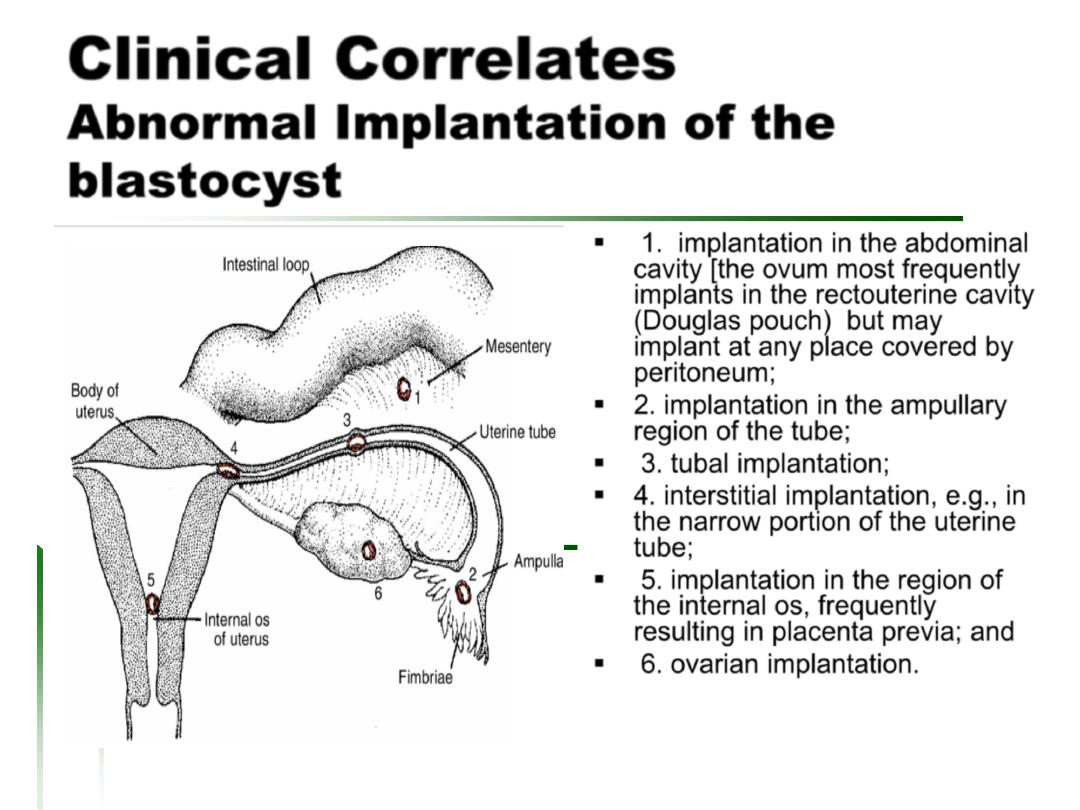
Clinical Correlates
Abnormal Implantation of the
blastocyst
1. implantation in the abdominal
cavity [the ovum most frequently
implants in the rectouterine cavity
(Douglas pouch) but may
implant at any place covered by
region of the tube;
3. tubal implantation;
4. interstitial implantation, e.g., in
the narrow portion of the uterine
tube;
5. implantation in the region of
the internal os, frequently
resulting in placenta previa; and
6. ovarian implantation.
peritoneum;
2. implantation in the ampullary
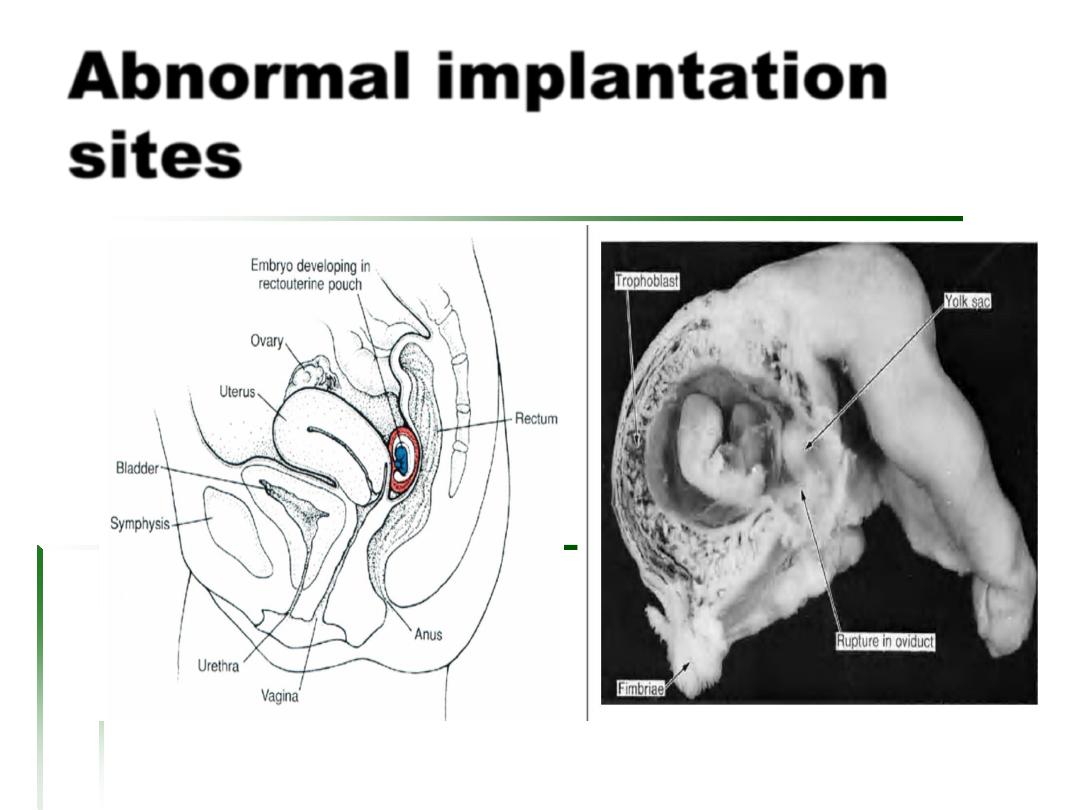
Abnormal implantation
sites
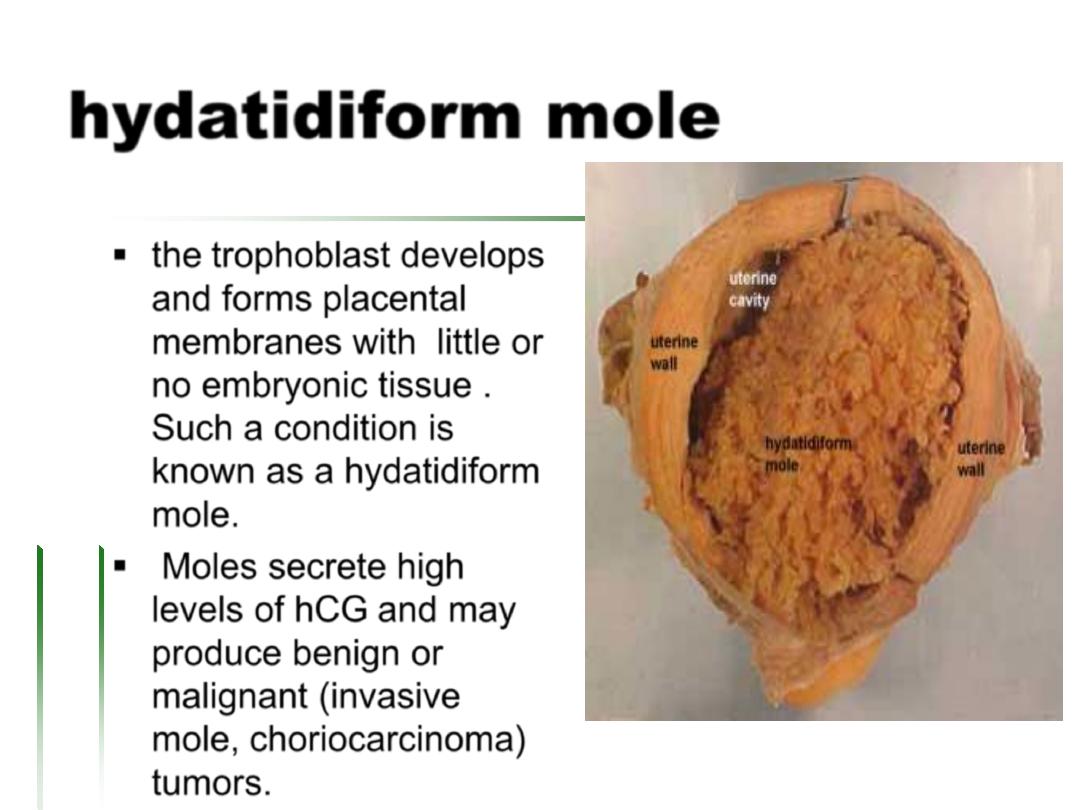
hydatidiform
mole
the trophoblast develops
and forms placental
membranes with little or
no embryonic tissue .
Such a condition is
known as a hydatidiform
mole.
Moles secrete high
levels of hCG and may
produce benign or
malignant (invasive
mole, choriocarcinoma)
tumors.
hydatidiform
mole
most moles arise from fertilization of an oocyte
lacking a nucleus followed by duplication of the
male chromosomes to restore the diploid
number .
These results suggest that paternal genes
regulate most of the development of the
trophoblast .
male and female pronuclei may be genetically
equivalent but they may be different
functionally.

Thank you
Next lecture : Third week o Development
SNipER
