
Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
Lec. 2
DISEASES OF THE
APPENDIX
Tues. 17 / 3 / 2015
DONE BY : Ali Kareem
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
2014 – 2015

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
2
INVESTIGATION OF AA.
The diagnosis (DX) of AA is essentially clinical. However clinically based DX
can lead to removal of the normal appendix in 15-30% of cases. Alvarado score is
widely used to assist diagnosis:
Symptoms; -Migratory RIF pain 1
- Anorexia 1
-Nausea& vomiting 1
Signs; -Tenderness (RIF) 2
-Rebound tenderness 1
-Elevated temp. 1
Laboratory; -Leucocytosis 2
-Shift to left (segmented neutrophil) 1
A score of 7 or more is strongly predictive of AA. If equivocal score (5-6), U/S or
CT scan examination of the abdomen are helpful in diagnosis of AA.
Preoperative investigations in AA include:
-The routine investigation: complete blood count, urinanalysis.
-Selective investigation: Pregnancy test, BU& electrolytes, abdominal XR, U/S of
abdomen & pelvis, CT scan of abdomen.
Finding in ultra sound of the abdomen in AA showing distended oedematous
appendix, a faecolith is seen.
Contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen showing a faecolith at the base of the
distended appendix with intramural gas with stranding of periappendiceal fat
indicative of AA.
TREATMENT;
Treatment of AA is Appendicectomy. Urgent operation is essential to prevent the
morbidity & mortality of peritonitis. Preoperative preparations include IVF,
antibiotics, however single peroperative dose of antibiotics reduce the incidence of
postoperative wound infection. When peritonitis is suspected, antibiotic against
gram -ve & anaerobic organism should be given IV.
DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
3
APPENDICECTOMY
-Should be done under general anesthesia with the Pt. supine, either
laparoscopically or by conventional appendicectomy.
-Palpate RIF for a mass & if found, a conservative approach should be adopted
-Appropriate antiseptic solution for the entire abdomen
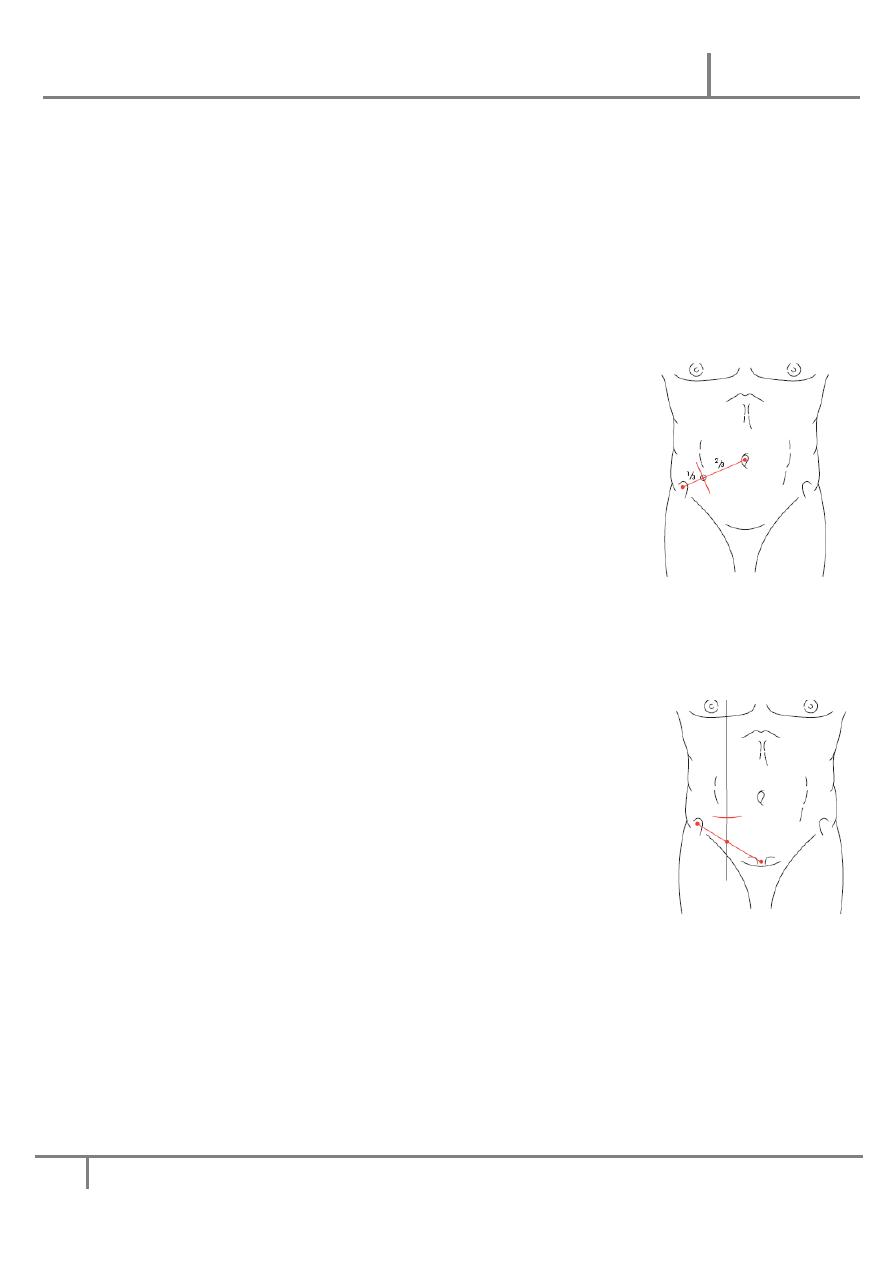
-Gridiron incision is made at right angle to a line joining the anterior superior iliac
spine to the umbilicus, its center at McBurney point, ext. oblique is incised in the
line of its fibres. The fibres of int. oblique & transverses are split & peritoneum is
opened
If better access is required, it's possible to convert the
Gridiron to the Rutherford Morison incision by cutting the
int. oblique& transverses muscle in the line of the incision
-In recent years, a transverse skin crease incision (Lanz) has
become more popular, better exposure & extension when
needed is easier, it's made 2cm below the umbilicus centered
on the midclavicular-midinguinal line. The ext., int. &
transverses are split in the direction of the fibres, Peritonium
is opened
-When DX is in doubt especially when IO is suspected, a lower midline abdominal
incision or Rt lower paramedian incision, the later difficult to extend, difficult to
close & provide poorer access to the pelvis& peritoneal cavity.
-When the abdomen has been opened, if pus or exudates
present, it must be removed with a sucker, Identify the caecum,
the appendix will be found at the base of the caecum, remove
the inflammatory adhesions.
The base of mesoappendix is clamped, divided & ligated. The
appendix is now clear, crushed near its junction with the
caecum, ligate the crushed portion, the appendix is amputated,
purse string suture is inserted into the caecum, the stump of the appendix is
invaginated, thus burying the appendix stump. Many surgeons believe that
invagination of the stump is unnecessary.
-Patients undergo laparoscopic appendicectomy are likely to have less
postoperative pain, discharged from hospital sooner than open appendicectomy,
post operative infection lower after the laparoscopic appendicectomy but the
incidence of postoperative sepsis may be higher in Pts with gangrenous or
perforated appendicitis.

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
4
METHODS TO BE ADAPTED IN SPECIAL CERCUMSTANCES
-When the caecal wall is oedematous, the purse string suture is in danger of
cutting out. If odema is of limited extend, the purse string suture can be inserted
into healthy caecal wall, if odema is extensive, it's better not to attempt
invagination.
-when the base of the appendix is inflamed, it should not be crushed but ligated
close to the caecal wall just tightly enough to occlude the lumen, after which the
appendix is amputated and the stump invaginated. Should the base of the appendix
be gangrenous, neither crushing nor ligation must be attempted. Two stitches are
placed through the caecal wall closed to the base which is amputated flush with
the caecal wall, after which these stitches are tied. Further clossur is effected by
means of a second layer of interrupted sero-muscular sutures.
-Retrograte appendecectomy when the appendix is retrocaecal and adherent.
-Drainage of the peritoneal cavity. This is usually unnecessary providing adequate
peritoneal toilet has been done. If there is considerable purulent fluid in the
retrocaecal space or the pelvis, a soft silastic drain may be inserted through a
separate stab incision.
PROBLEMS ENCONTERED DURING APPENDICECTOMY
-If normal appendix is found, this needs careful exclusion of other causes, ex
terminal ileitis, Mickels diverticulitis, tubo-ovarian diseases in women. It's usual
to remove appendix to avoid future diagnostic difficulties even although the
appendix is macroscopically normal, particularly if a skin crease or gridiron
incision has been made.
-If appendix can't be found, caecum should be mobilized & taenia coli should be
traced to their confluence before the DX of "absent appendix" is made.
-If appendix tumour is found, small tumour less than 2 cm can be removed by
appendicectomy. Larger tumour should be treated by Rt hemicolectomy.
-If appendix abcess is found& appendix can't be removed easily, local peritoneal
toilet, drainage of abscess & IV antibiotic. Rarely caecectomy or Rt
hemicolectomy is required.

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
5
APPENDICITIS COMPLICATING CROHNS DISEASE
If concomitant crohns is found during appendicectomy, providing caecal wall is
healthy, appendicectomy can be done without increasing risk of enterocutaneous
fistula.
Rarely appendix is involved with the crohn's disease; in this case a conservative
approach& a trial of IV steroid & systemic antibiotic to resolve the acute
inflammatory process.
APPENDIX ABSCESS
Failure of resolution of the appendix mass or continued spiking pyrexia usually
indicates that there is pus within the phlegmonous appendix mass. U/S, CT scan
may identify an area suitable for insertion of percutaneous drain, if unsuccessful
laparotomy through a midline incision is indicated.
PELVIC ABSCESS
It's an occasional complication of AA& can occur irrespective of the position of
the appendix. The most common presentation is spiking pyrexia several days
following appendicitis, pelvic discomfort associated with loose stool& tenesmus.
PR reveals boggy mass in the pelvis anterior to the rectum. Pelvic U/S or CT scan
will confirm. Treatment is by trans-rectal drainage under GA.
MANAGEMENT OF AN APPENDIX MASS;
If an appendix mass is present& the condition of the Pt is satisfactory, the standard
treatment is the conservative Ochsner-sherren regimen. It's based on that the
inflammatory process is already localized& surgery is difficult& may be
dangerous. It may be impossible to find the appendix & occasionally a faecal
fistula may form.
Conservative management includes:
1. Admission of the patient to the hospital
2. Nothing by mouth
3. I.V. fluid therapy, daily requirement according to the weight of patient
4. Antibiotics therapy against aerobic and anaerobic organisms

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
6
5. Regular measurements of temperature and pulse rate every 4 h.
6. It’s helpful to mark the mass on the abdominal wall using skin pencil
7. A contrast-enhanced CT examination of the abdomen should be performed
Criteria for improvement:
1. Improvement of general condition of the patient
2. Improvement of appetite
3. Decrease in the abdominal pain
4. Decrease in temp. and pulse rate
5. The mass decreased in its size and tenderness.
It’s advisable to remove the appendix after an interval of 6-8 weeks
Criteria for stopping conservative treatment of appendix mass:
1. Increasing or spreading abdominal pain
2. Rising temp. and pulse rate
3. Increase in the size of the mass and become more tender
4. Evidence of peritonitis
It needs early laparotomy.
POST-OPERATIVE COMPLICATIONS OF APPENDECECTOMY
1-WOUND INFECTION
It occurs in 5-10 % of all Pts, presented with pain, erythema of the wound on the
4
th
or 5
th
post operative day. Treatment is by wound drainage & antibiotic.
Organism responsible usually mixture of G-ve& anaerobic bacteria (Bacteroid&
anaerobic strep.).
2-INTRA-ABDOMINAL ABSCESS
Rare with use of peroperative antibiotic. Postoperative spiking fever, malaise,
anorexia 5-7 postoperative days suggest an intraperitoneal collection (interloops,
paracolic, pelvic or subphrenic).
U/S& CT scan assist the DX & allow percutaneous drainage.
3-ILEUS
A period of adynamic ileus is to be expected after appendicectomy.

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
7
Ileus persisting more than 4 0r5 days especially in the presence of fever is
indicative of intraabdominal sepsis.
4-RESPIRATORY COMPLICATIONS
Are rare, adequate postoperative analgesia& physiotherapy reduce the incidence.
5-VENOUS THROMBOSIS& EMBOLISM
Rare except in the elderly& in women on contraceptive pills. Appropriate
prophylactic measures should be taken in such cases.
6-PORTAL PYEMIA
Rare but very serious complication of gangrenous appendicitis. High fever, rigor
jaundice are present. It's caused by septicemia in the portal venous system led to
intrahepatic abscess (multiple). Treatment by systemic antibiotic& percutaneous
drainage of hepatic abscesses.
7-FAECAL FISTULA
Leakage from the appendicular stump occurs rarely, but may follow if the
encircling stitch has been put in too deeply or if the caecal wall was involved by
oedema or inflammation. Occasionally, a fistula may result following
appendicectomy in Crohn's disease.
8-ADHESIVE INTESTINAL OBSTRUCTION
Most common late complication of appendicectomy, usually single band adhesion
is found. Occasionally it causes postoperative RIF pain. Laparoscopy is useful to
confirm the DX & to divide the band.
9-RIGHT INGUINAL HAERNIA
Especially in gridiron incision due to injury to ileohypogastric nerve.
RECURRENT ACUTE APPENDICITIS
Appendicitis is notoriously recurrent, the attack vary in intensity, may occur every
few mths& majority of cases ultimately pass in sever AA. If careful history is
taken from Pts with AA, many remember milder but similar attacks of pain, in
these cases, the appendix shows fibrosis, indicative of previous inflammation.

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
8
LESS COMMON PATHOLOGICAL CONDITIONS
MUCOCELE OF THE APPENDIX
May occur when the proximal end of the lumen slowly occluded, usually by
fibrous stricture& the retained secretions remains sterile, the appendix greatly
enlarged. The symptoms are those of mild subacute appendicitis unless infection
supervenes (empyema).
DIVERTICULA OF THE APPENDIX
Rare, may be true congenital (all coats) or acquired (no muscularis layer). It may
occur in conjunction with mucocele when the intramural pressure rises sufficiently
to cause herniation of the mucous membrane through the muscle coat. Diverticula
is liable to perforate when inflamed, so if it's found during the course of an
operation for another condition should be removed.
INTUSSUSCEPTION OF THE APPENDIX
It's rare the DX only at operation. Untreated, it may pass on to an appendiulocolic
intussusception. Treatment is appendicectomy.
NEOPLASM OF THE APPENDIX
CARCINOID TUMOUR (ARGENTAFFINOMA)
Arise in argentaffin tissue& are most commonly in the appendix. It's found once in
300-400 appendices subjected to histopathological examination. It can occur in
any part of the appendix commonly in distal 1/3. The appendix feels moderately
hard& on sectioning it looks as a yellow tumour between the intact mucosa& the
peritonum.
Unlike carcinoid tumour of other part of GIT, carcinoid tumour of the appendix
rarely gives rise to metastases
Appendicectomy is sufficient treatment unless:
-The caecal wall is involved.
-Tumor is 2 cm or more in size.
-LN involvement, when Rt hemicolectomy is indicated.
PRIMARY ADENOCARCINOMA

DISEASES OF THE APPENDIX Dr. Tarek Al-Obaidi
17-3-2015
9
Is extremely rare, it's of columnar type& should be treated by Rt hemicolectomy.
It may rupture into peritoneal cavity seeding it with mucus-secreting malignant
cells. Presentation is often delayed until the Pt has gross abdominal distension as a
result of pseudomyxoma peritoneii
Treatment by radical resection of all involved parietal peritoneal surfaces &
aggressive chemotherapy.
Done by
Ali Kareem
