Lecture 1
Immunoglobulin

Objectives
Define Immunoglobulin
Draw the Molecular Structure of Ig
Enumerate the 5 Classes of Ig
Differentiate between Fc Region & FAB
Discuss Biological Activity of Ab
Judge Why IgG consider as the most
protective Ab

Immuno globulins=Ig
They are a group of (glycoproteins) which present
In serum, tissue and all body fluids of all
vertebrates ,
that have Antibody (Ab) activities
(react Specifically with the Antigen (Ag) that
causes their Productions
These Abs play a major role in defense mech. and
Protection against infections
Ig are synthesized and secreted by
plasma cell
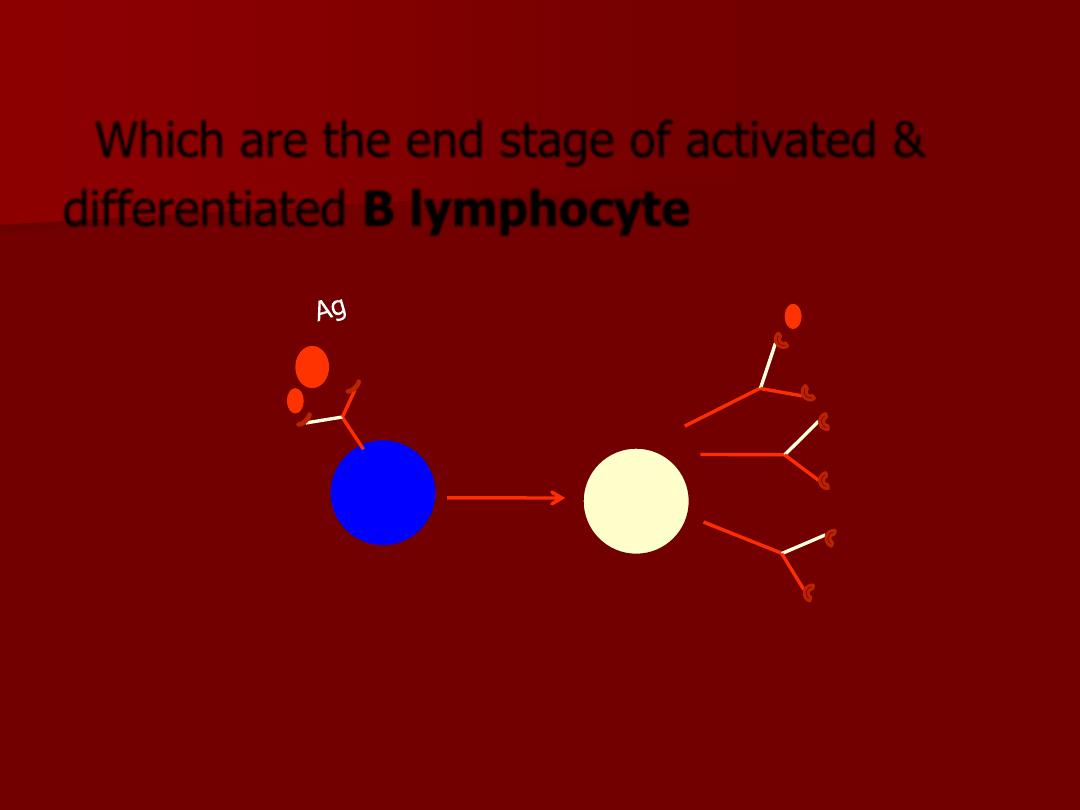
Which are the end stage of activated &
differentiated
B lymphocyte
B
P
Ab
Ab

constitute about
20% of serum proteins
&
consist of 82-96% polypeptide (back bone)
4-18% CHO which support them against proteolytic
enzymes
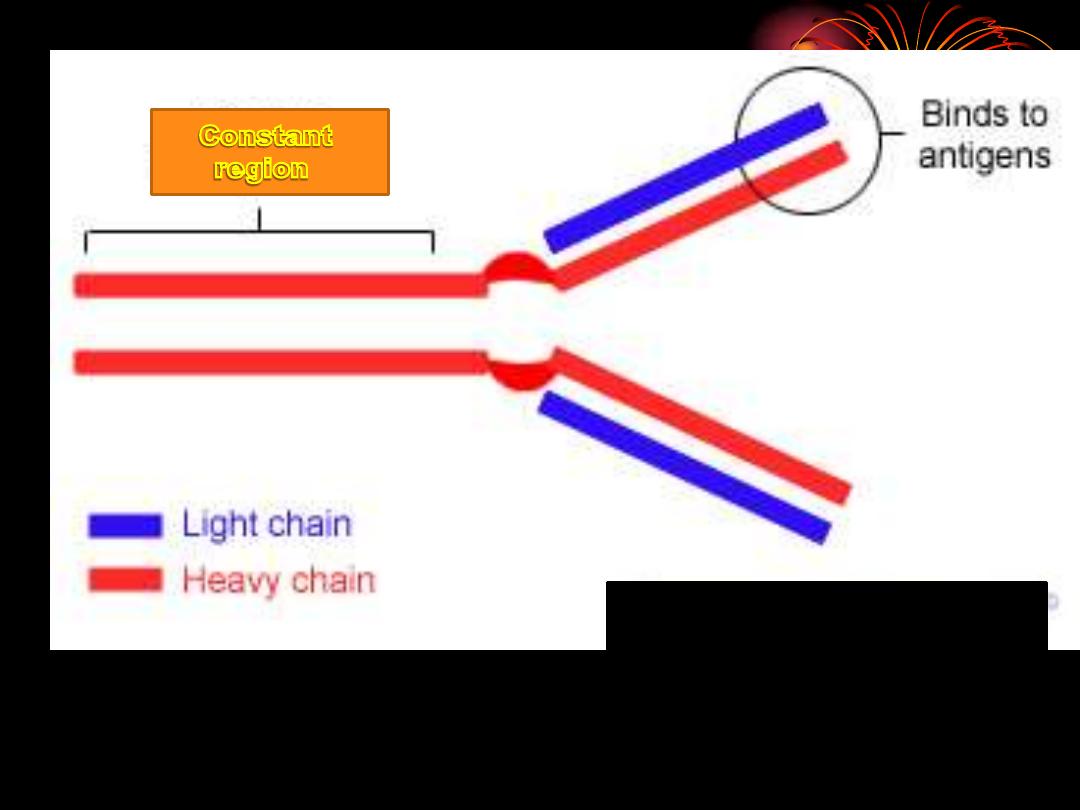
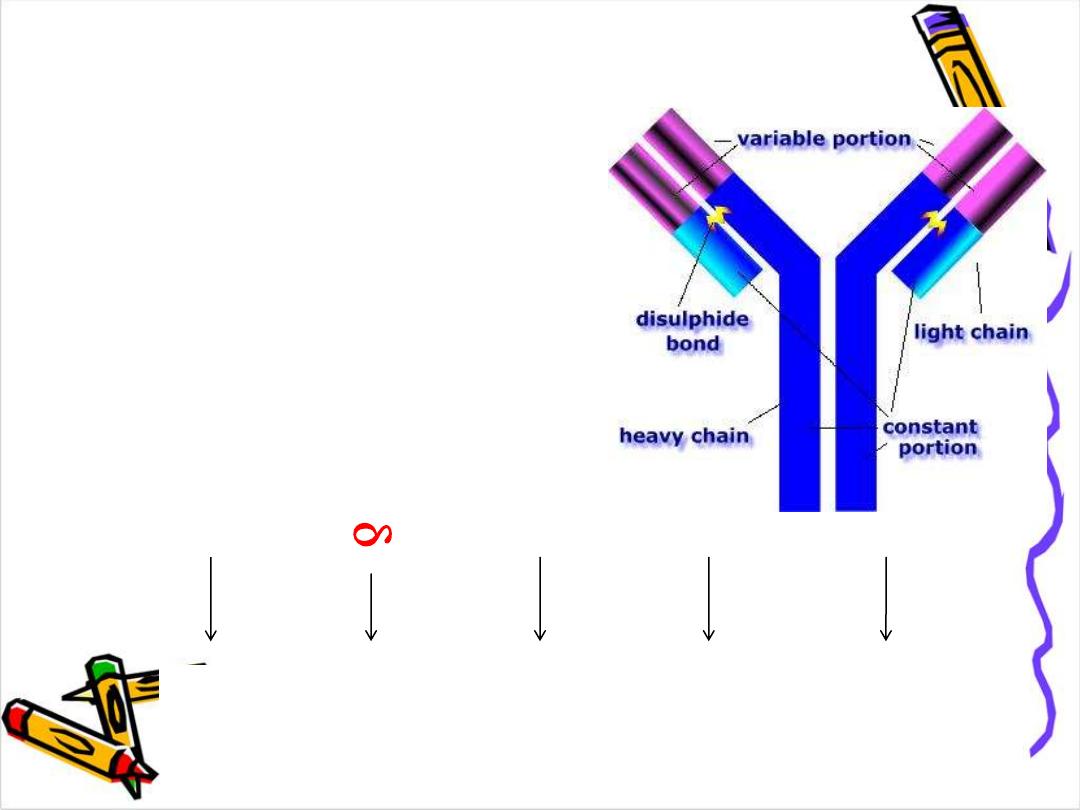
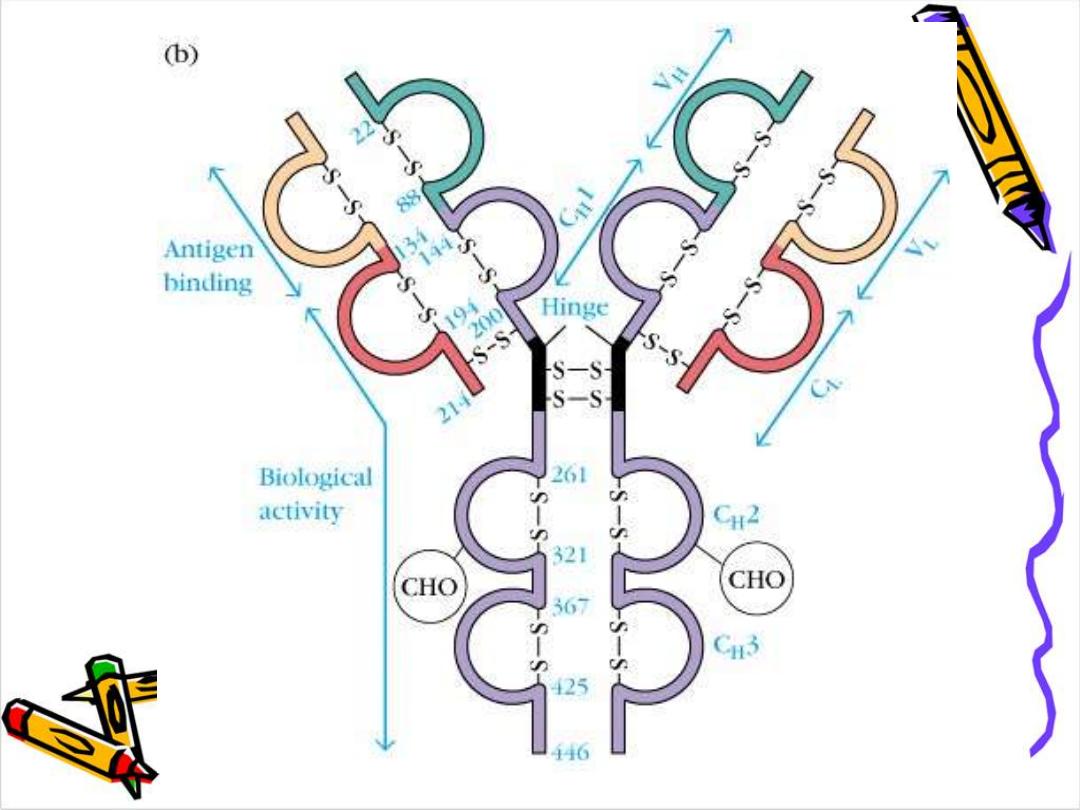
Basic structure of Ig
: The
backbone of Ig consist of
2 pairs of polypeptid
chains each pair are identical.
One pair nearly double the molecular weight of the
other pair so called
heavy & light chain
respectively
Basic str. Of
Ig
.
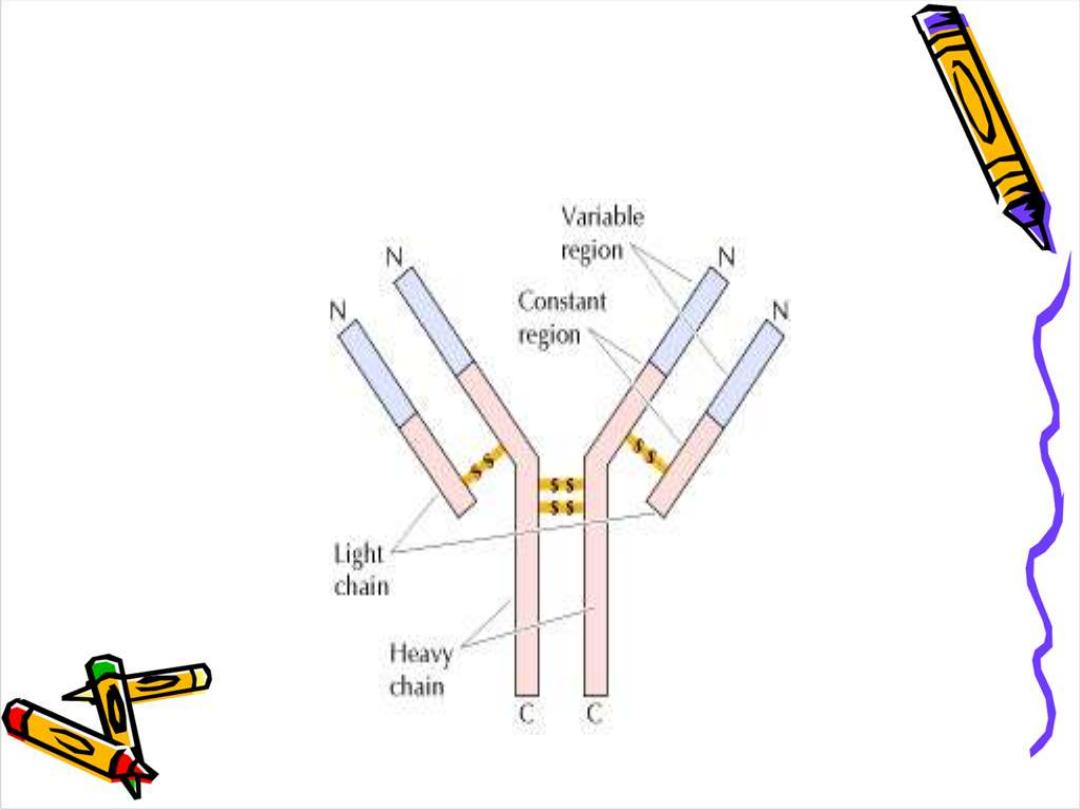
The 4 chains are hold together by inter chain
disulphide bonds to give us this
monomeric
Structure .
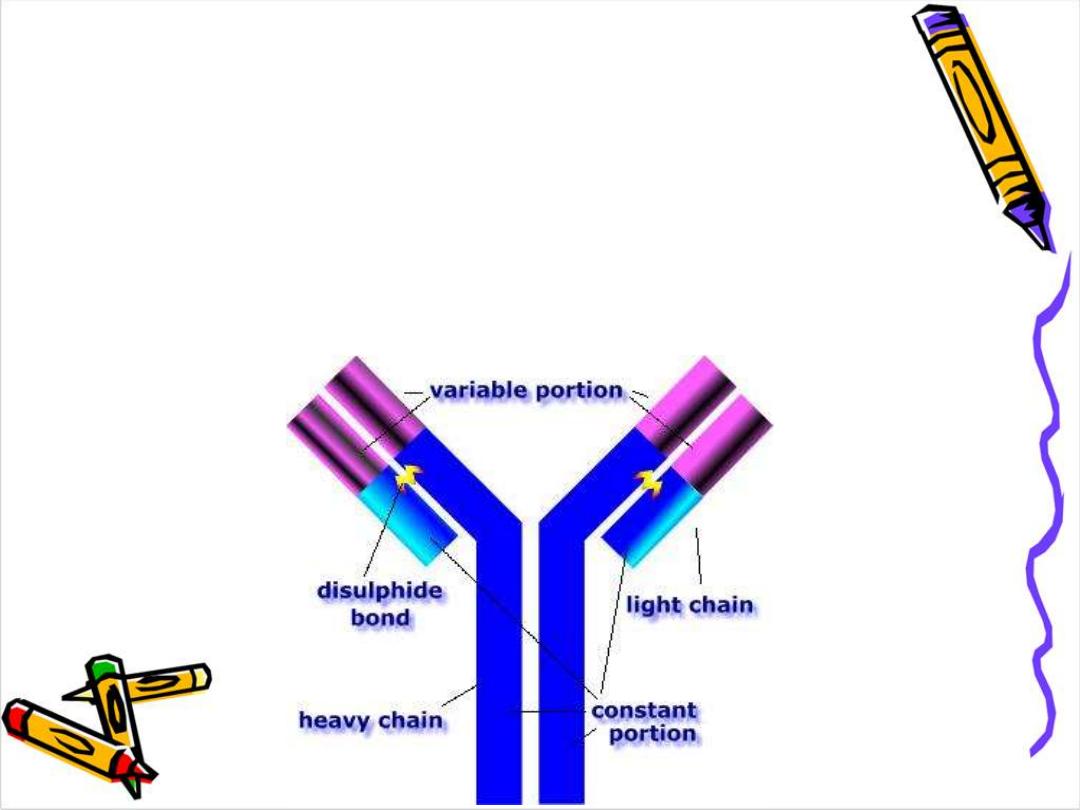
Each chain has 2 terminals:
1-Amino ter. In which the a.a. are variable
called (variable region)
2-Carboxy ter. In which the a.a. sequence rather
consist & heterogeneous (constant region)
Hot spot (hyper variable region):
3 areas in the variable region of each chain
with a high variability in the a.a. sequence to form
the Ag binding site
(paratope)
Paratope=Ag binding site
A cleft formed by 3 hot spots from the light chain &
a farther 3 from the adjacent heavy chain ,it is
complementary to the specific chemistry & shape
of the epitope (Ag determinant)
=paratope +hot spots
Idiotype
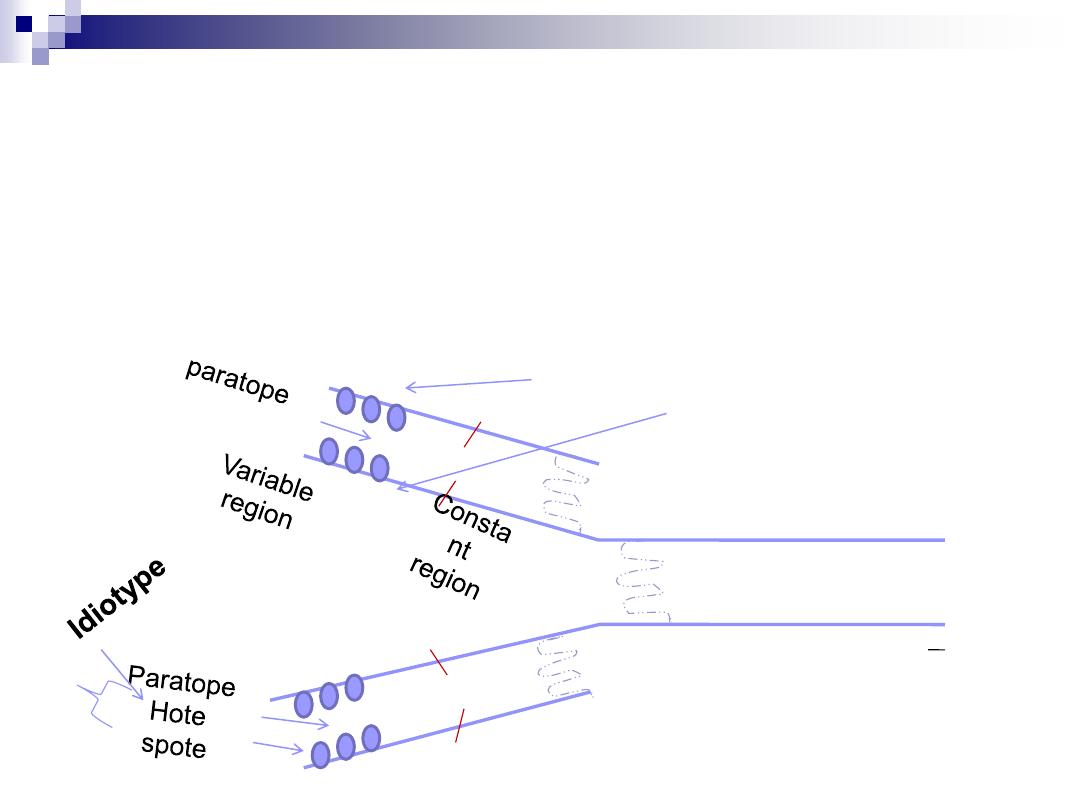
Constant
region
Variable R. light
heavy
COO
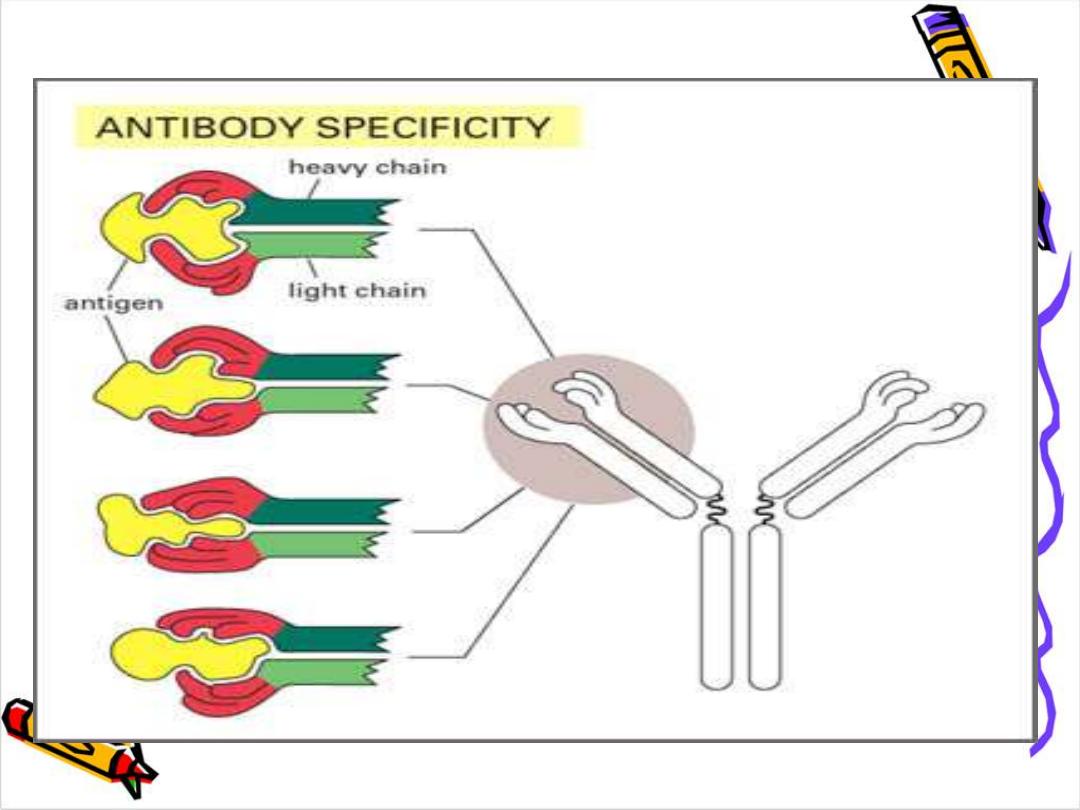
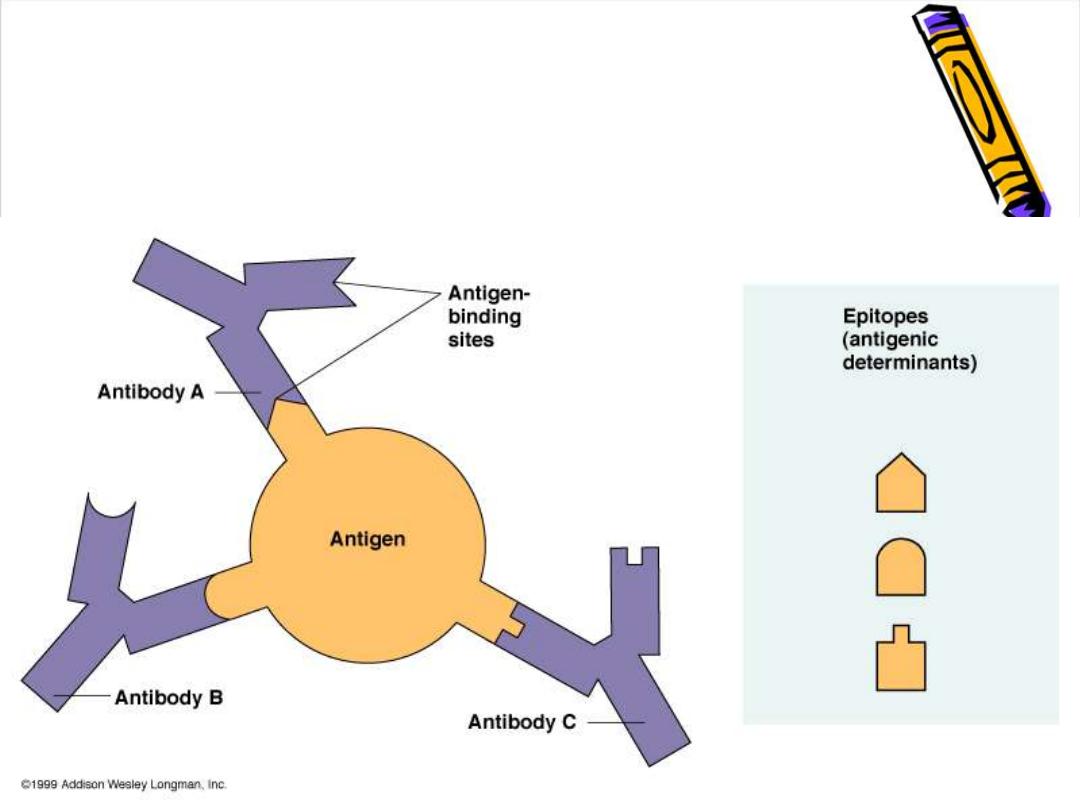
Epitopes: Antigen Regions that Interact
with Antibodies
constant region:
Light chain
either:
Kappa
Lambda
Heavy chain
either:
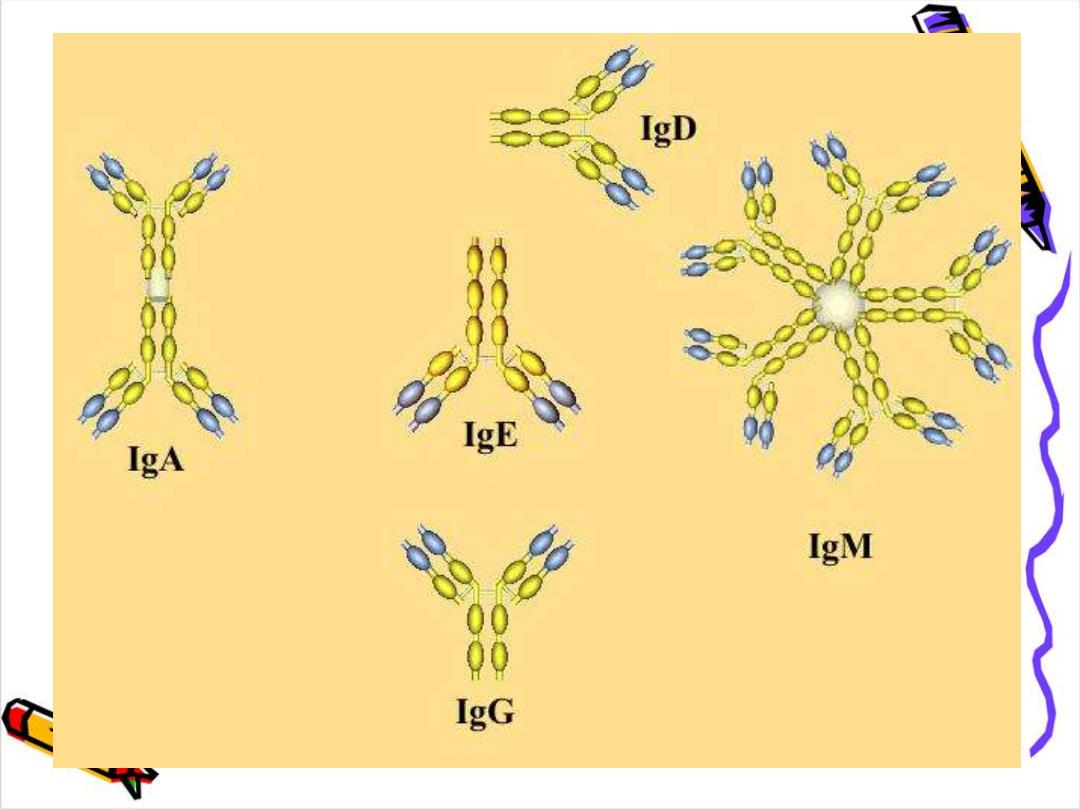
IgG
IgA
IgM
IgD
IgE
(5 classes)
2:1
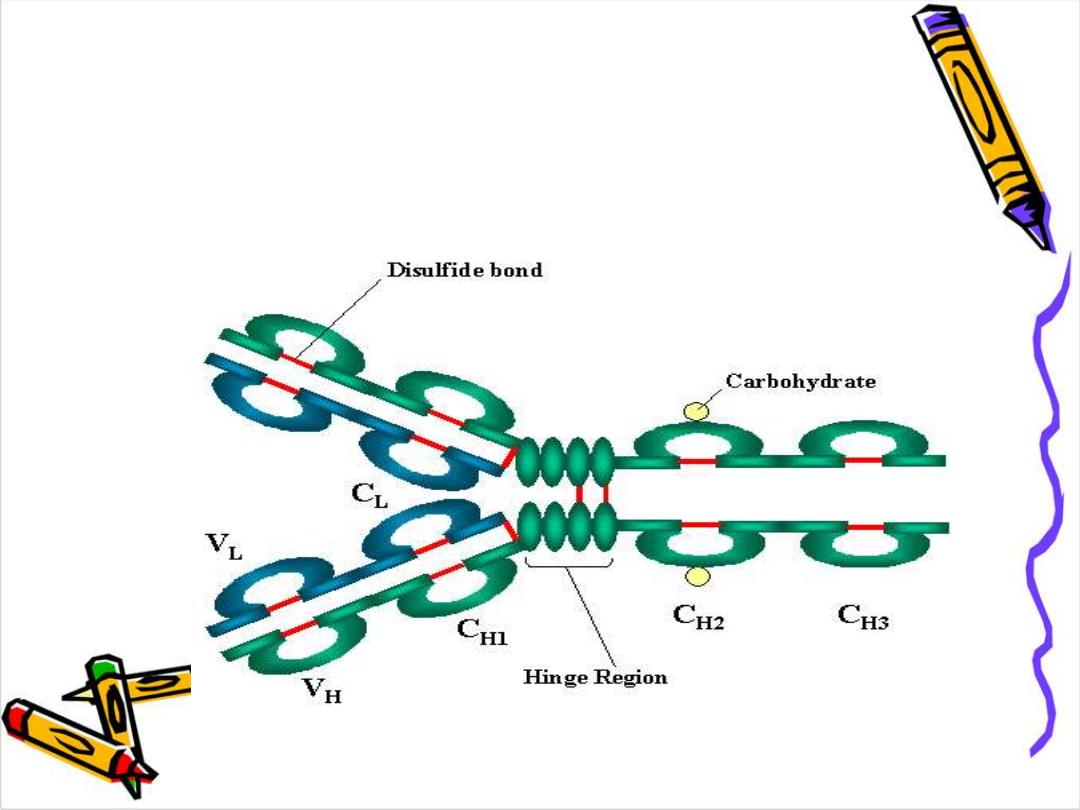
The a.a. sequence in both light & heavy chains is
not a linear sequence but there are domes or
loops due to presence of
intra chain
disulphide
bonds these globular areas
called domains

In the variable region of each chain there is only
one domain VL or Vh
In the constant region of light chain there is one
constant domain CL
In the constant region of heavy chain
There are 3 constant domains
CH1,CH2,CH3
with
exception IgM, IgE there is an extra domain CH4
Complement
fixation
Complement
fixation
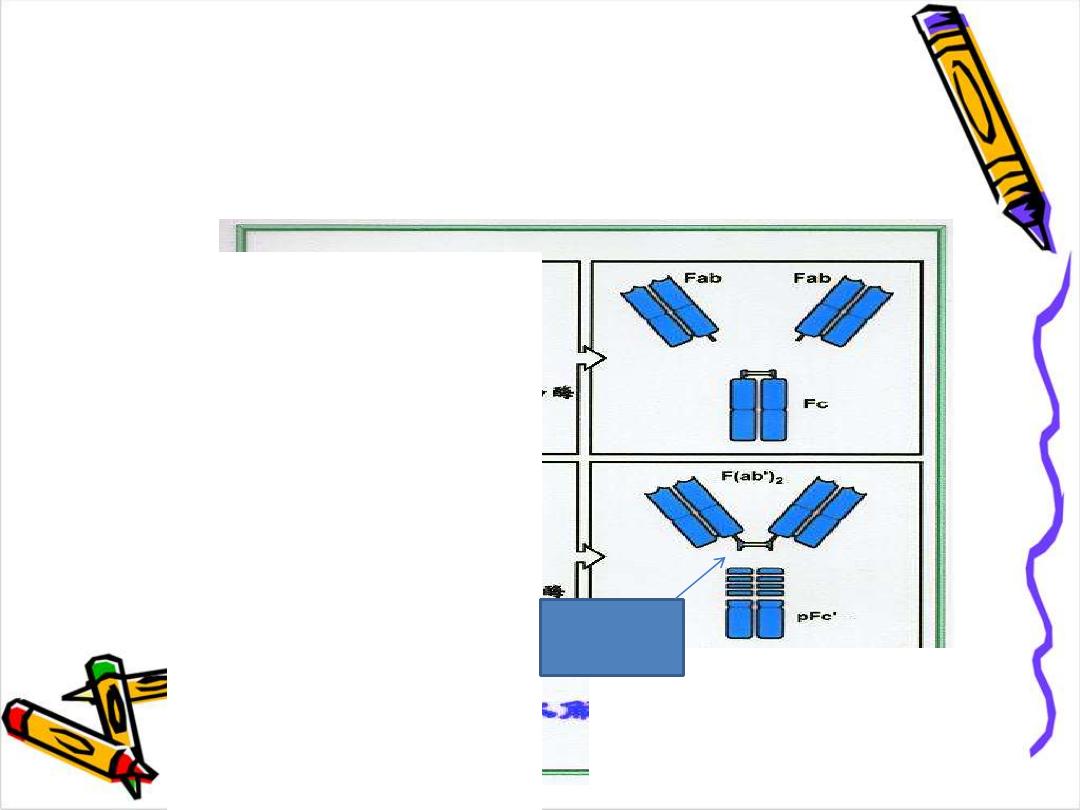
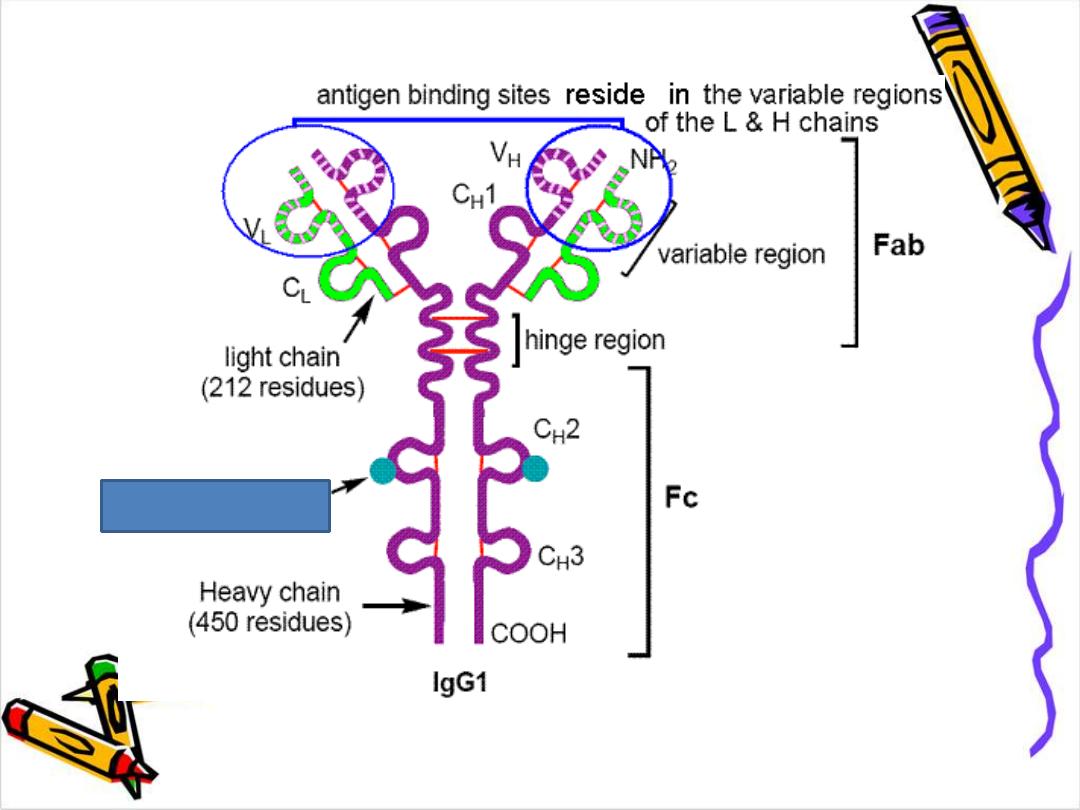
Pepsin
act to the right of hinge region leads to formation
of FAB Dimmer (FAB)2 & FC fragment
Pepsin
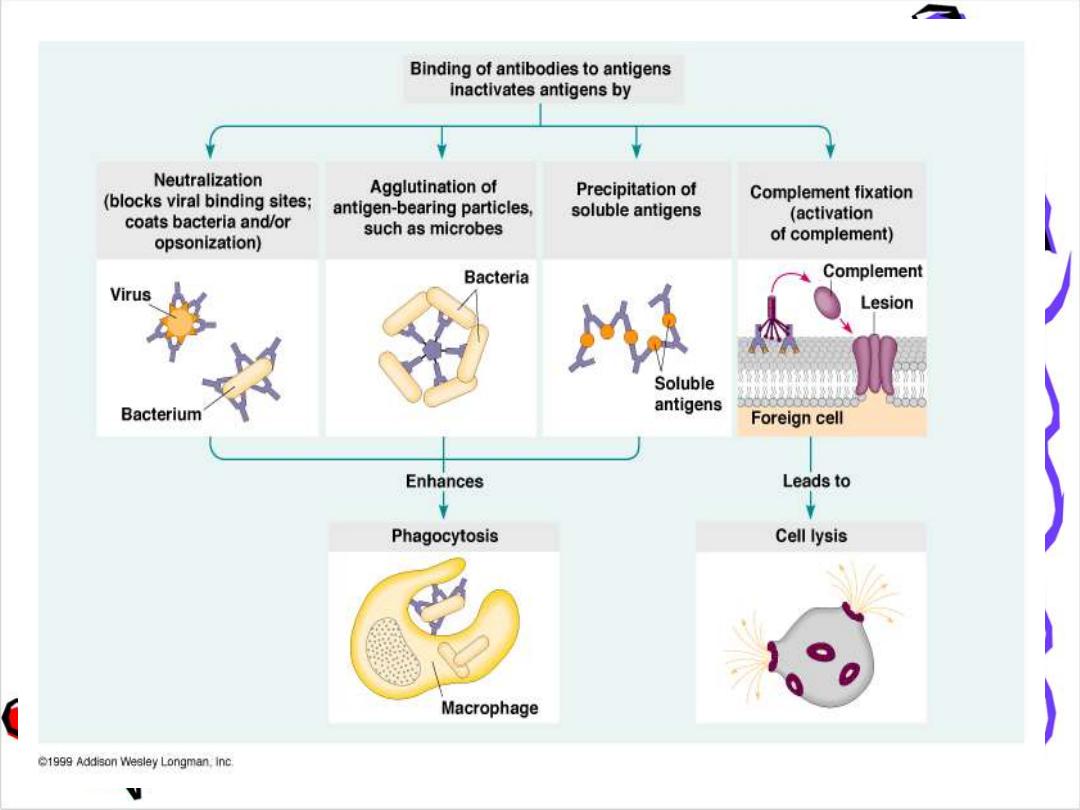
Function of Ig
Ig is a bi-functional mol.
primary binding with Ag
Ag (recognition)
secondary biological activities
to get red of invasion Ag
Cytolysis:
Ag-Ab binding activation of the
complement sys. Lysis of the cell

Opsonization
Ab coat the Ag recognized by phagocytic
cells phagocytosis (phagocytic cell like
macrophage ,monocyte ,natural killer have
receptor For FC fragment of Ig
Neutrilization
Neutralize toxins & viruses
Blocking
block the reaction
Agglutination

Ig classes they are classified:
On the bases of their heavy chain peptide str.
IgG:
-predominant Ig in serum75%
-M.W. low 150000
-can extra-vassate easily to the extract vascular
space so 1
st
line of defense
-
Only Ig can pass the placenta protect the fetus in
the 1
st
few month of life
-Long half time
-Best opsonizing Ab ,it binds the Ag with
high affinity

-Main Ig in the secondary immune response
The chain of IgG is subdivided into: 4
subclasses
IgG
65%
IgG
32%
IgG
8%
IgG
4%
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4

These subclasses differ in their secondary
biological activity
-complement fixation (CH2) through classical
pathway
IgG IgG IgG
While IgG only fix complement through
alternative path
-crossing the plasenta (CH3 ,CH2)
IgG IgG IgG
-binding to monocyte (CH3 ,CH2)
IgG IgG IgG
-
blocking IgE binding only IgG4
3
1
2
4
3
1
2
1
2
3
4

IgG is considered the most protective
Ab: because
1-present in high amount in blood (75%)
2-Extra vassate easily to extra vascular
space
3-can cross the placenta
4-Binds avidly with Ag (of high affinity)
5-Very efficient opsonizing Ab
6-Can activate the complement system
through the classical path way

Opsonization:
Substances that bind to particles & make
them more susceptible to phagocytosis:
1-complement compound C3b
2-Antibodies IgG, IgA
3-Fibronectin glycoprotein glue.
4-Leukotrienes B4
5-C. reactive protein
summary

Ref.
Jawedez microbiology
Hide

Quiz of this Lecture
Enumerate the Classes of
immunoglobulin
