Lecture 4
T lymphocytes

•Objectives
•
Types of T cells
•
Types of T helper cell (CD4+)
•
Activation of T cells
•
Interleukins
•
Super Ag
•
T Cytotoxic cells (CD 8+)

T lymphocytes
-They constitute 60-80% of total lymphocytes
-They differentiated into ;
-
T helper Th (CD4+ cells)
kills the target Ag in
association with class II MHC by secreting of IL s
that regulate the immune reactions
-
Th 17
(CD4+ cells)
-
T reg. CD4+ &CD25+ (T h 3)
-
T cytotoxic Tc CD8+
kills the target Ag in
association with class I MHC
-
Memory cell
(CD4+ OR CD8+)

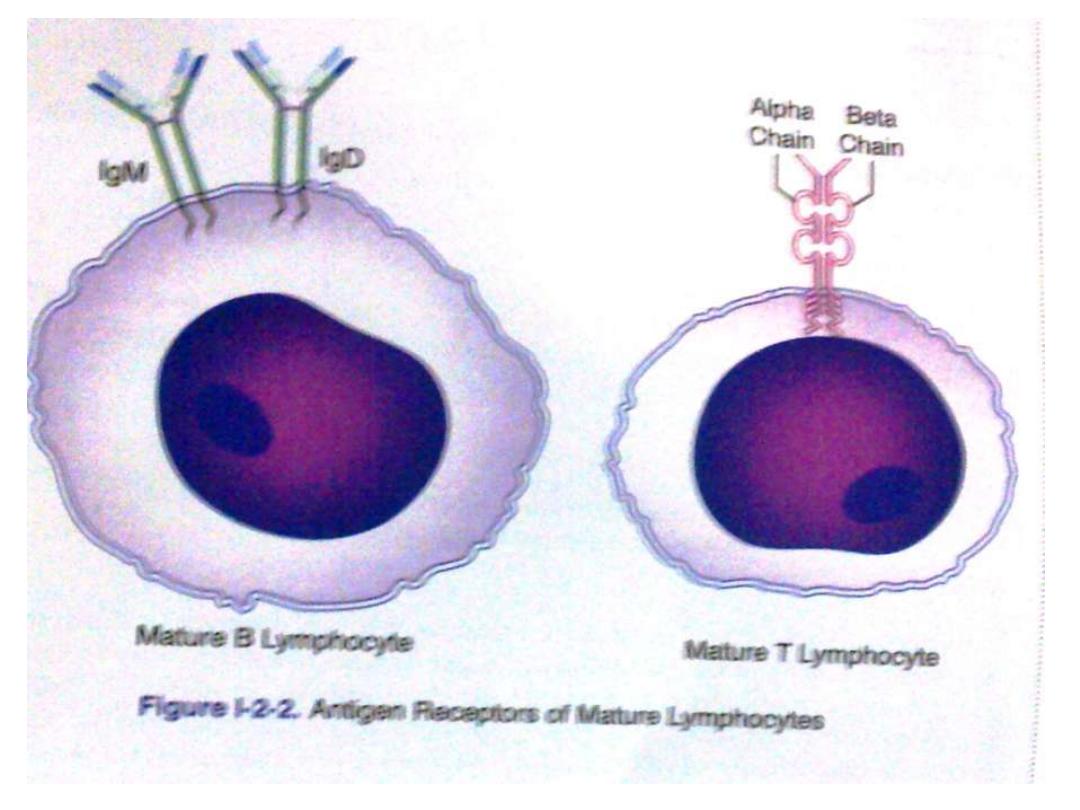
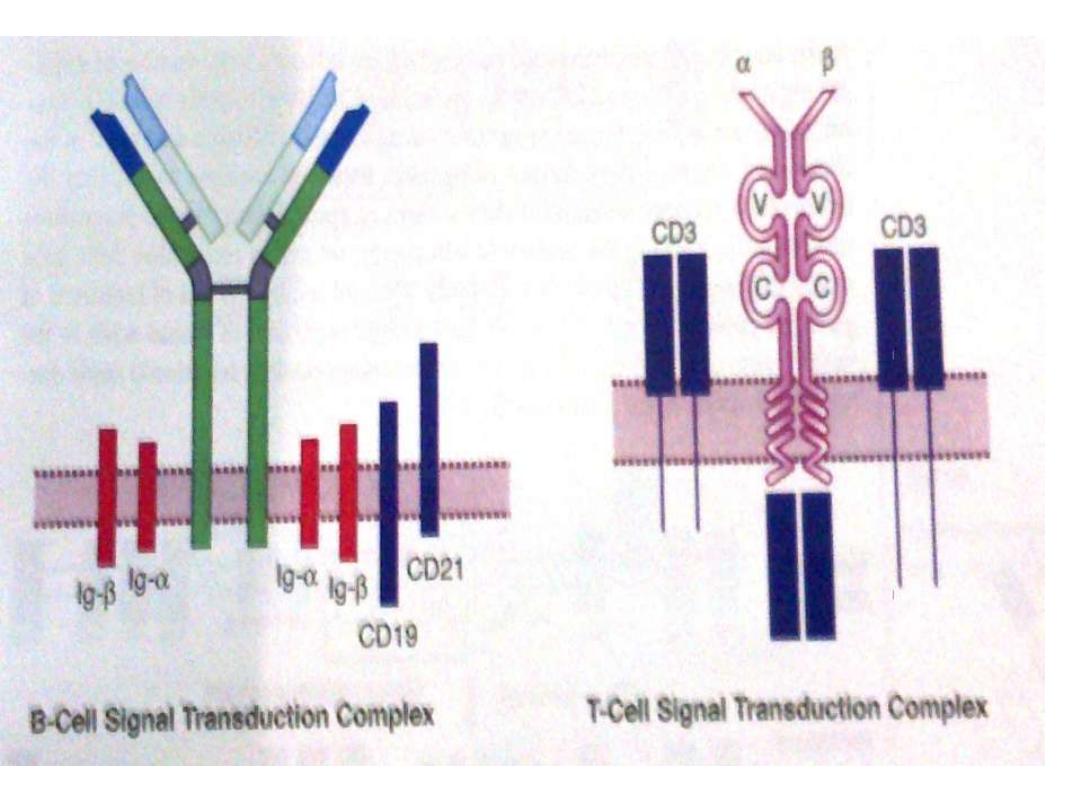
T cell markers ( Receptors & Molecules)
Antigen receptor ; (TCR
) heterodimer non
identical polypeptide chain linked by disulphide
bond divided intoTCR1 α,β while
TCR2 γ,δ chains
TCR varies in their a.a. as the variable region of
Ig
Receptor for sheep RBCs (E-Roseate)
T
cell
Sheep
RBC

MOL. Of T Lymphocytes
CD2 (LFA)
adhesion Mol
. Present in all T
cells
CD3 5 polypeptide chains near TCR for
signal transduction
. Present in all T cells
CD4 only on Th cells react with class II MHC
to control Th cell activation
(immune
restriction
)
CD8 on Tc cells react with class I MHC to
control Tc cell activation (immune
restriction)
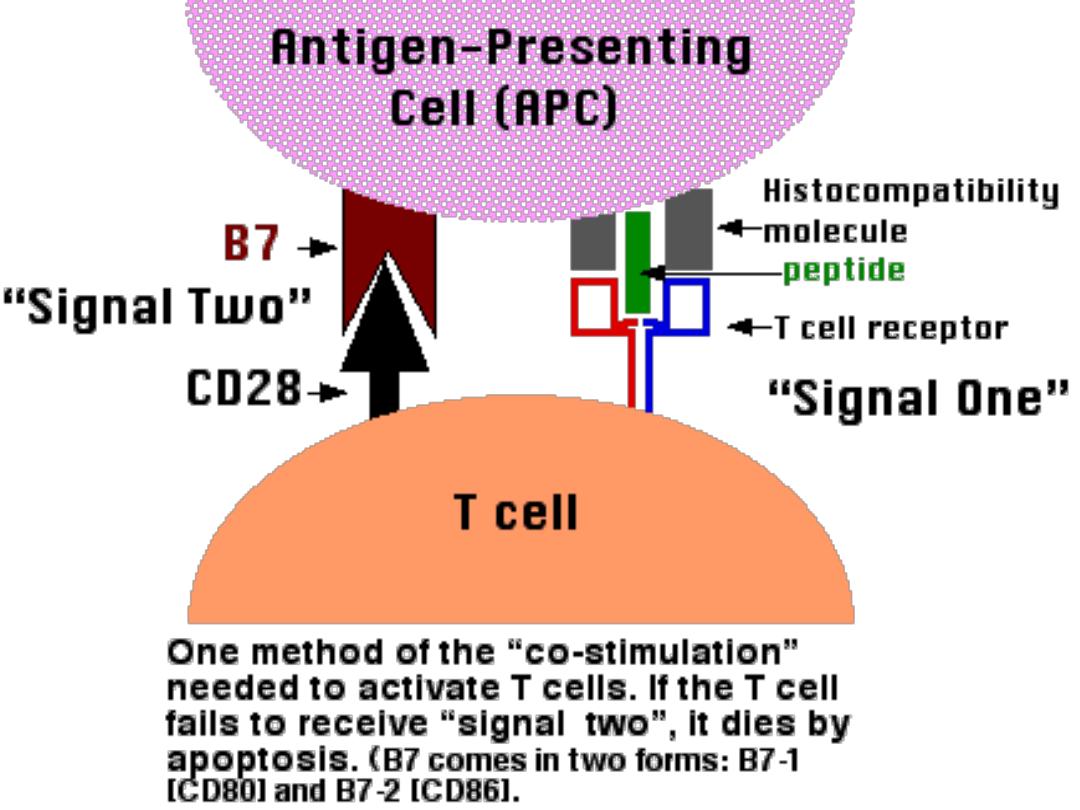
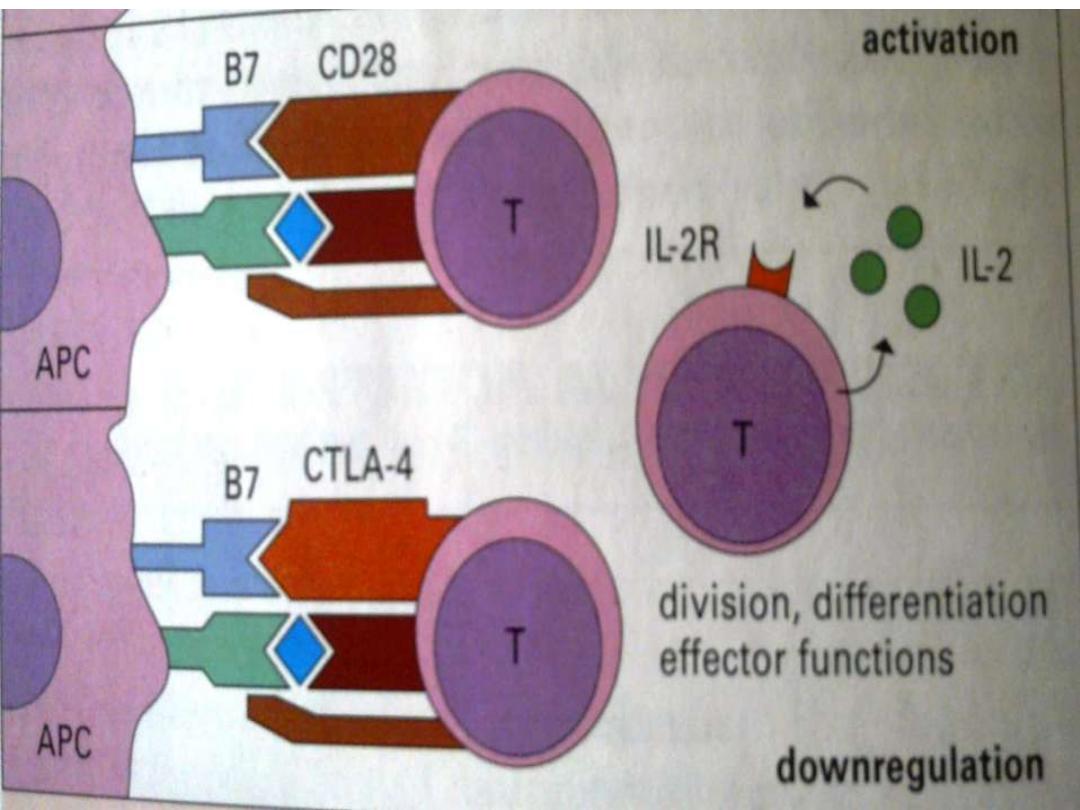
CD 28 on Th cells react with B7
mol.(
Co-stimulatory signal)

T Cells Immunity
Types of T cells
1. T Helper (T
H
) Cells
:
Central role in immune
response.
They are CD4
+
,Recognize antigen on the
surface of antigen presenting cells (e.g.:
macrophage) in the groove of class II
Th
Cells
:
Activate macrophages
,NK cells, Th & cytotoxic T
cells
(
Th1
)
Stimulate & regulate B cells
to produce antibodies
(Th2)
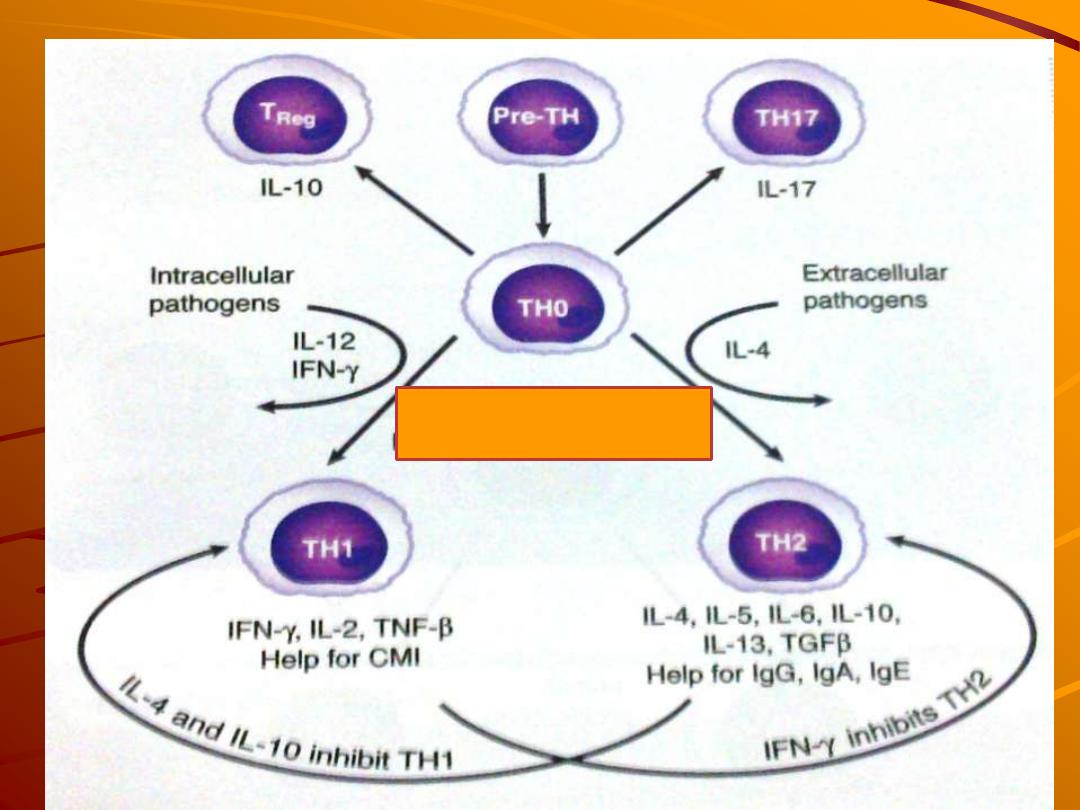
T helper
Th1
Intracellular Ag
presented by
macrophage &
Dendritic cells
Secrete TNF, IL2,
IL3
gamma IFN
Regulate cellular
Immunity
Th2
Extracellular Ag
Presented by
B lymphocyte
Secrete
IL4,IL5, IL6
IL 10
Regulate
humoral
immunity
Th3
Suppress Th1
cell
Secrete
TGF
β
which inhibit
IL12
So anti-
inflammatory cell

Activation of T helper Lymphocyte
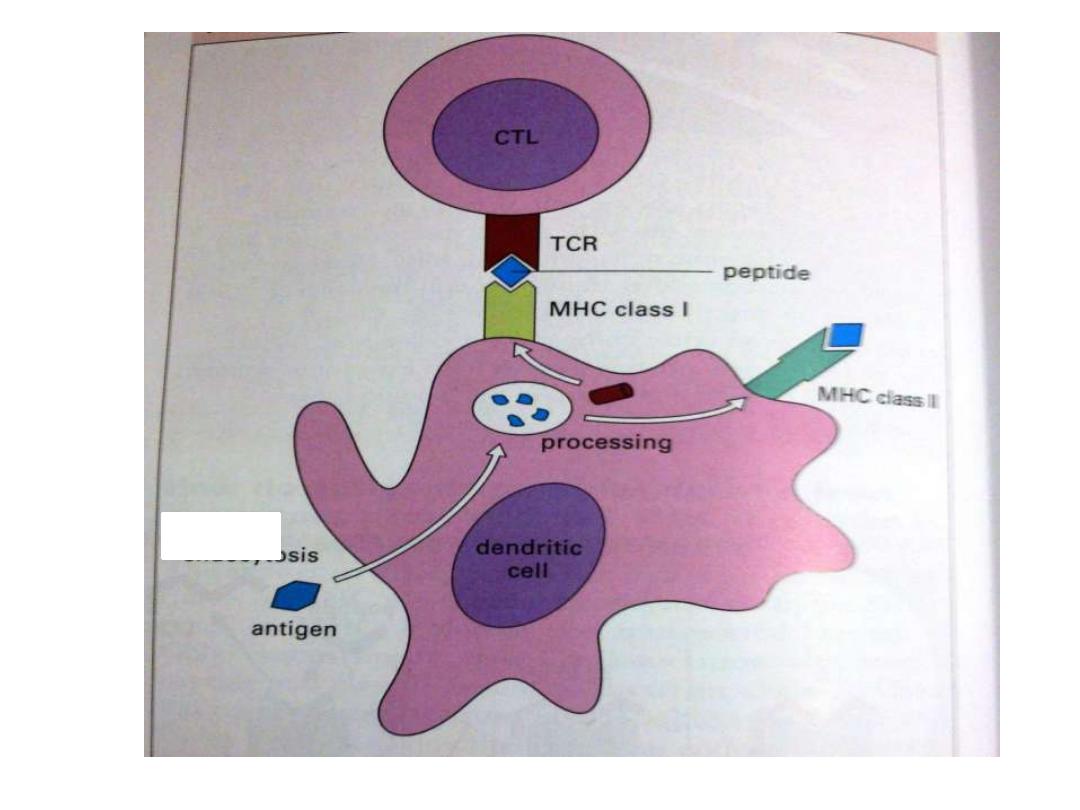
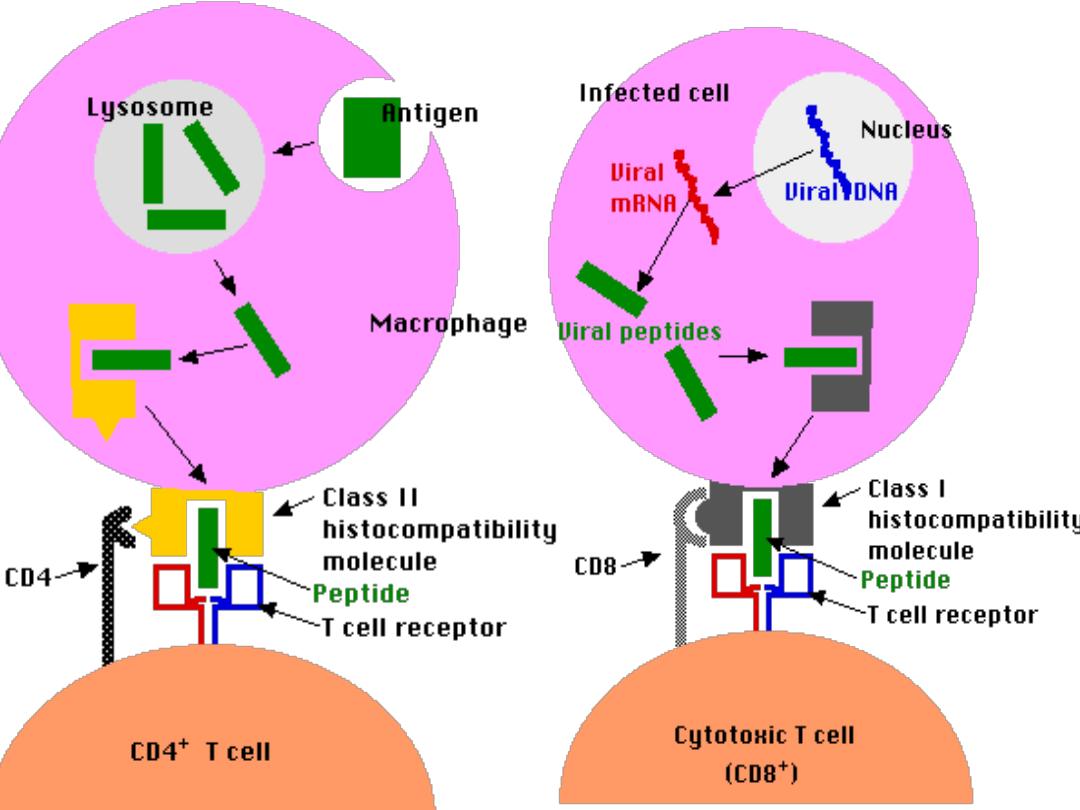
T h cells can not recognize & react with an Ag
unless presented by APC in association with class
II MHC for activation of Th (CD4+) cells
Class II presented only on the surface of APC
So APC focus & engulf the Ag,(
usually Exogenous
)
slice it through lysozomal enz. With preservation of
its epitops which will be coupled with class II
through the endocystic pathway then distributed
on the surface of APC

Th cells
regulate the
proliferation and
activity of other cells of the immune
system:
TC, NK cells, macrophages,
neutrophils, etc. through Th1
(Cellular immunity)
And regulate B lymphocyte through
Th2 (Humoral immunity)
Th cells regulate the immune system by
Interleukins

Cytokines
Cytokines
:
They are soluble mediators with
hormonal like action secreted by various
cells & act on many target cells & play an
important role in the regulation of the
immune response so they are
Chemical
messengers of immune cells.
Over 100 have been identified.
Stimulate and/or regulate immune
responses.
Interleukins:
Communication between
WBCs.
Interferons
: Protect against viral

Different from hormones
Act locally
Autocrine or paracrine
while the
hormones are
endocrines
IL they have a lower conc. Than
hormones & secreted only on need
not continuous as the
Hormones
IL
either pro inflammatory as IL2,6,
17
, TNF,gamma IFN
Or anti inflammatory as IL 10 TGFβ
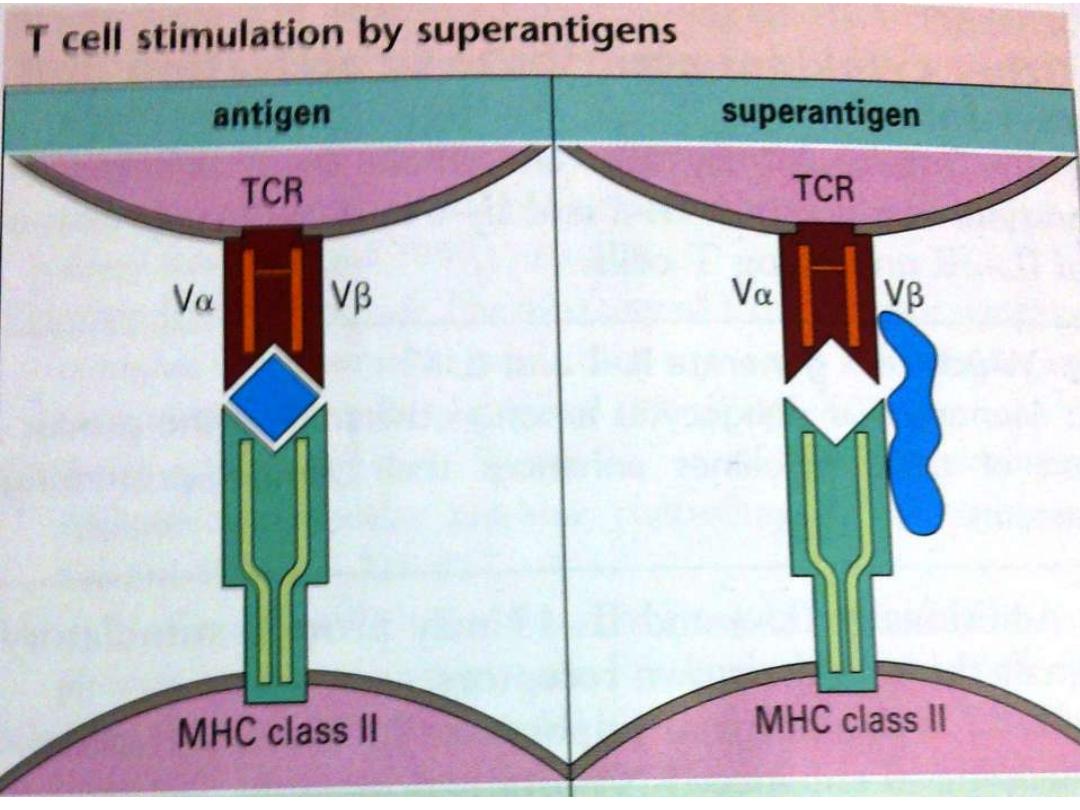
Super Ag
Potent T cell Mitogen trigger mitosis of
CD4+ cells in the absence of Ag
processing . It is able to activate a large
population of T h cells up to
20% of all
peripheral blood Th
cells, so realizing a
large quantity of cytokines as
TNF
toxic shock syndrome(Staph.
Toxin)
(toxins, Mycoplasma some viruses)

. Cytotoxic T (Tc) Cells:
Destroy target cells.
They are CD4 negative (CD4
-
)
but
CD8 positive
(CD8+)
Recognize antigens on the surface of all nucleated
cells:
Kill host cells that are infected with viruses or
bacteria.
Recognize and kill cancer cells.
Recognize and destroy transplanted tissue.
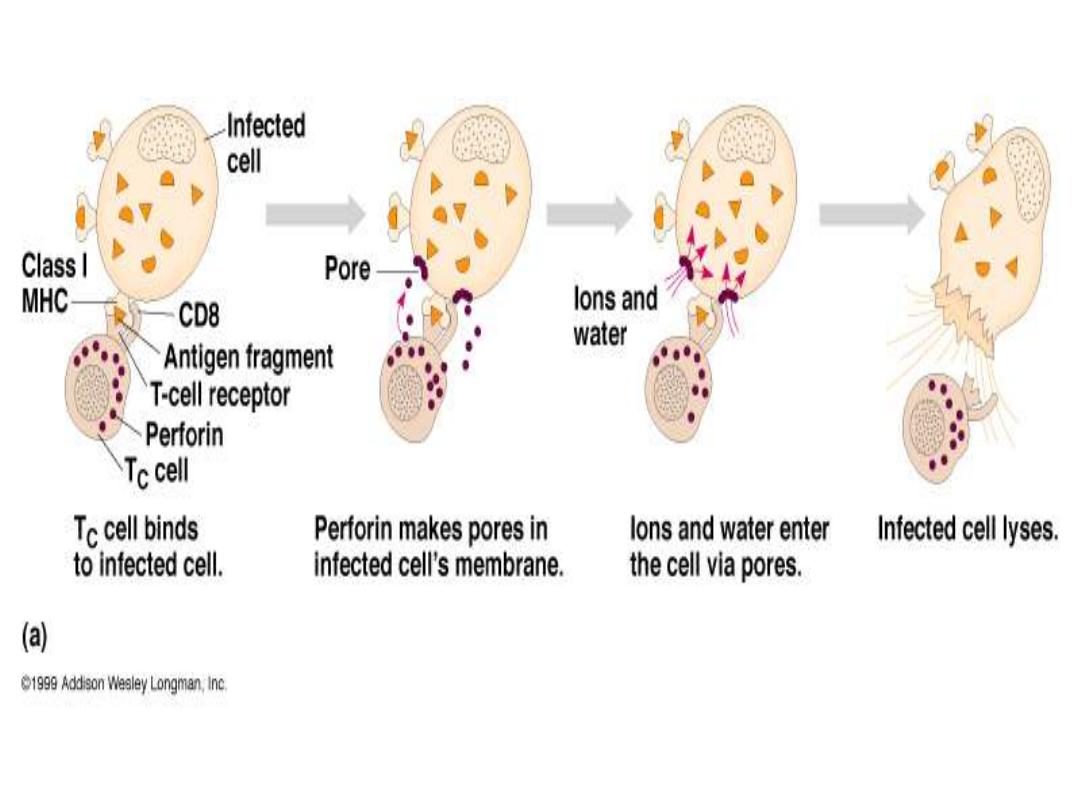
Release protein
called perforin
which forms a pore
in target cell, causing lysis of infected cells.
Release TNF & Granzymes

Cytotoxic T cell Tc=CD8
It lyses the target cell on viral infected cell & get
rid of foreign cell (tumor cell) that exposure
non self Ag associated With class 1 Ag
Mode Of killing = hit & run
1-Releasing preforin protein =pore memb.
2-TNF=depress prot. Synthesis & produce
toxin free radicals
3-granzyme
Esterase
degrade
protein cell
memb.
Nuclease
degrade
Nucleic acid