
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Dr.Mohammad A.Alfaham
M.Sc :Ph.D Microbiology Dept.

Polymerase Chain Reaction
Polymerase:
DNA polymerase enzyme
– DNA polymerase duplicates DNA
– Before a cell divides, its DNA must be
duplicated
–
Chain Reaction:
The product of a reaction
is used to amplify the same reaction
– Results in rapid increase in the product
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
PCR performs the chemistry of DNA
duplication
in vitro
Numerous PCR applications make this
process a staple in most biology
laboratories
Understanding properties of DNA
polymerases helps understanding PCR

Discovery
PCR was discovered by Kary Mullis
– On a long motorcycle drive
– Mentally visualized the process
Nobel Prize in Chemistry
– 1993

DNA polymerase
Duplicates DNA
Necessary for reproduction of new
cells
More than one DNA polymerases exist
in different organisms

Properties of DNA polymearse
3’
5
’
5
’
3
’
Needs a pre-existing DNA to duplicate
– Cannot assemble a new strand from
components
– Called template DNA(Unknown DNA)
Can only extend an existing piece of
DNA
– Called primers

Properties of DNA polymearse
DNA polymerase needs Mg
++
as
cofactor
Each DNA polymerase works best
under optimal temperature, pH and
salt concentration
PCR buffer provides optimal pH and
salt condition
Properties of DNA polymearse
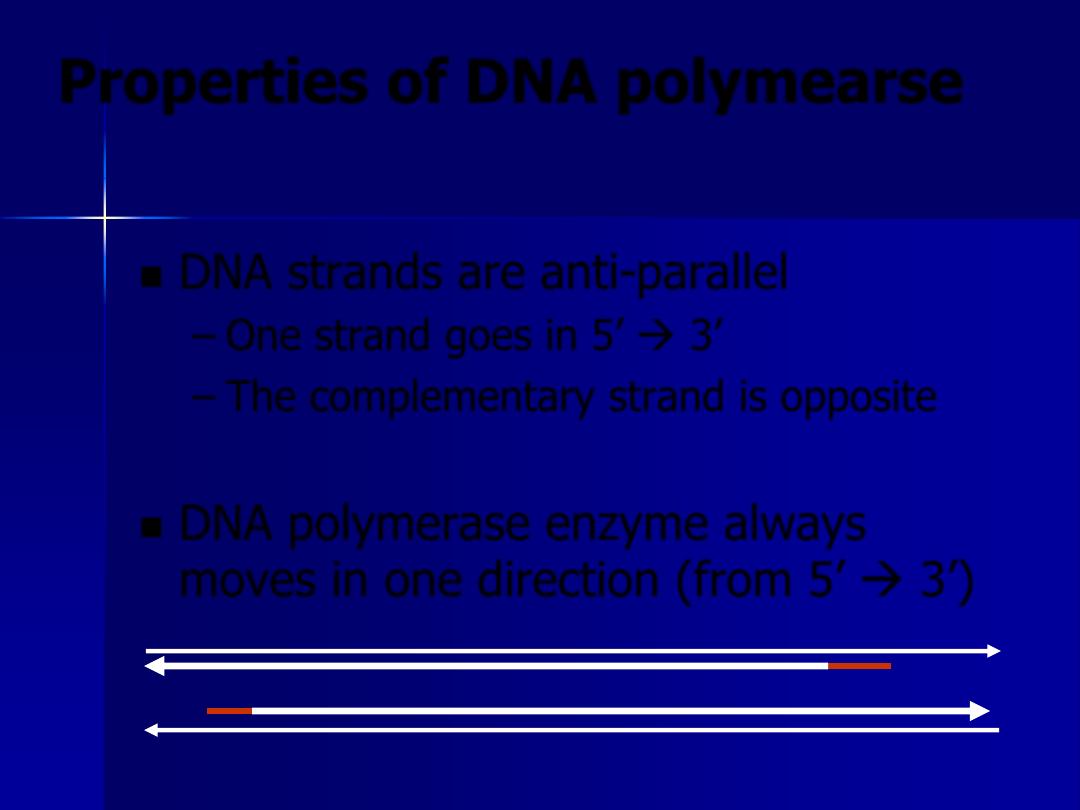
DNA strands are anti-parallel
– One strand goes in 5’ 3’
– The complementary strand is opposite
DNA polymerase enzyme always
moves in one direction (from 5’ 3’)
3
’
5
’
5
’
3
’

Properties of DNA polymearse
DNA polymerase incorporates the four
nucleotides (A, T, G, C) to the growing
chain
dNTP follow standard base pairing rule
3
’
5
’
5
’
3’
dCTP
dTTP
dCTP
dGTP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP
dTTP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP
dTTP
dATP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP dTTP
dATP
dGTP
dATP
dGTP
dTTP
dATP
dCTP
dTTP

Properties of DNA polymearse
The newly generated DNA strands
serve as template DNA for the next
cycle
PCR is very sensitive
Widely used

Setting up a PCR Reaction
Add template DNA and primers
3
’
5
’
5
’
3
’
dCTP
dTTP
dCTP
dGTP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP
dTTP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP
dTTP
dATP
dATP
dGTP
dCTP dTTP
dATP
dGTP
dATP
dGTP
dTTP
dATP
dCTP
dTTP
Add dNTPs
Add DNA polymerase

Taq DNA polymerase
It was derived from Bacteria called
Thermus aquaticus
Heat stable DNA polymerase enzyme
Ideal temperature 72C

Thermal Cycling
A PCR machine controls temperature
Typical PCR go through three steps
– Denaturation
– Annealing
– Extension
Denaturation
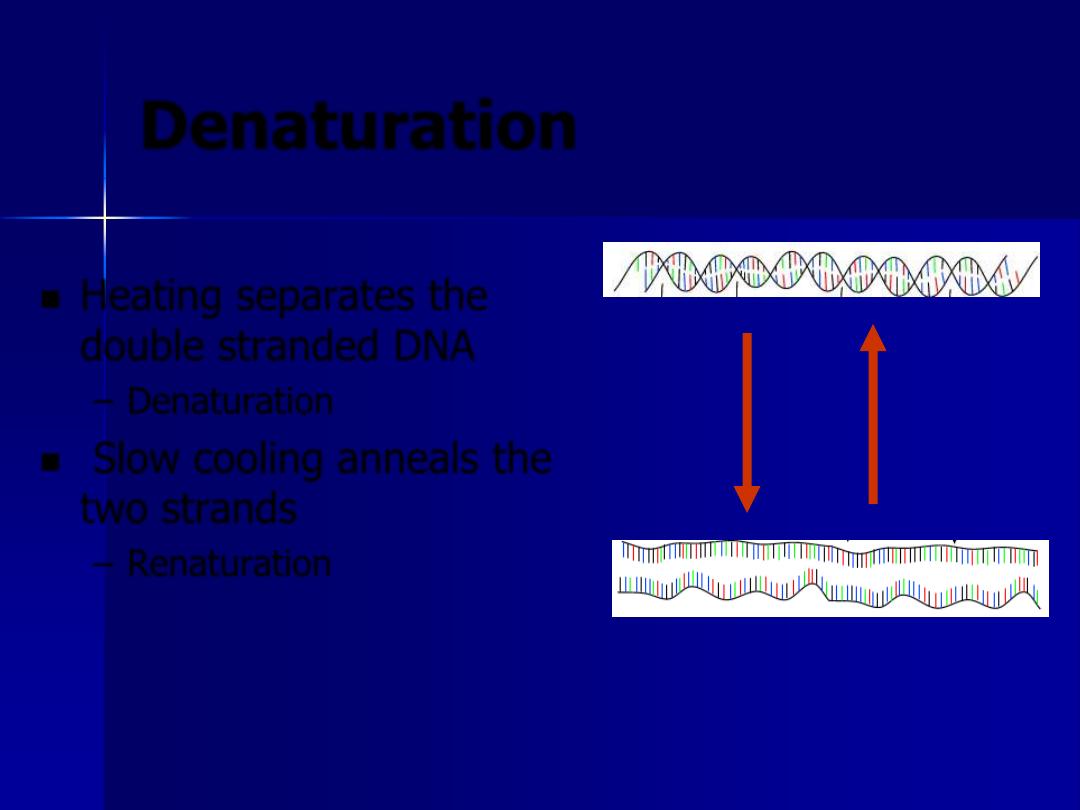
Heating separates the
double stranded DNA
– Denaturation
Slow cooling anneals the
two strands
– Renaturation
Heat
Cool

Annealing
Two primers are supplied in molar
excess
They bind to the complementary
region
As the DNA cools, they wedge between
two template strands
Optimal temperature varies based on
primer length etc.
Typical temperature from 40 to 60 C

Extension
DNA polymerase duplicats DNA
Optimal temperature 72C
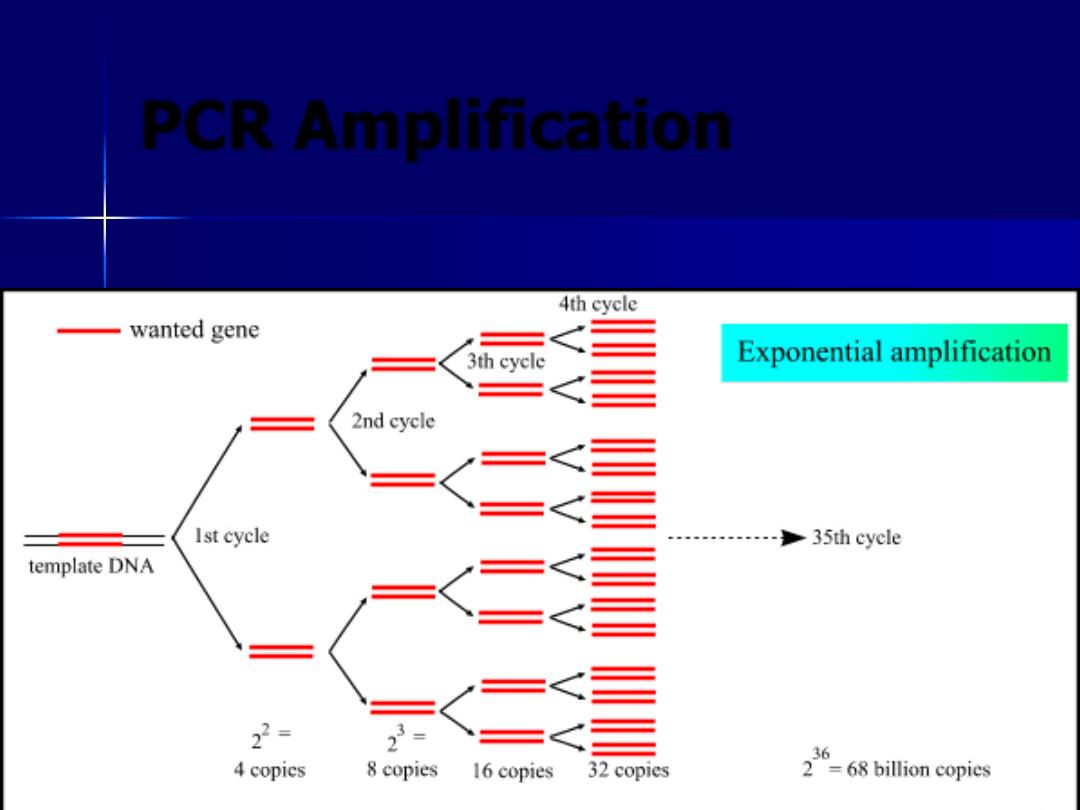
PCR Amplification
Exponential Amplification of template DNA

Typical PCR mix
In a thin wall Eppendorf tube assemble the
following
PCR components
Amount
Template DNA(extructed DNA) (5-200 ng)
1 mM dNTPs (200 uM final)
10 X PCR buffer
25 mM MgCl2 (1.5 mM final)
20 uM forward primer (20 pmoles final)
20 uM reverse primer (20 pmoles final)
5 units/uL Taq DNA polymerase (1.5 units)
Water
Final Volume
variable
10 uL
5 uL
3 uL
1 uL
1 uL
0.3 uL
Variable
50 uL

Applications
Ubiquitous applications
Revolutionized how we study biology
– Research;For molecular analysis to
explain the pathogenisty of many
diseases and genotyping of
organism,human and animal
– Diagnostics
– Forensics medicine
