
1
Systemic Bacteriology
Gram Positive Cocci
Genus: Staphylococcus spp.
This genus include about 30 spp., 3 main spp. Are of medical
importance:
1. Staphylococcus aureus (Staphylococcus pyogenes). So called
coagulase +ve cocci, are the most pathogenic causing
suppurative infection either as localized lesion abscess, boil, &
wound infection; or systemic infection such as U.T.I.,
osteomylitis, meningitis, & septicemia; may cause toxic
mediated illnesses as food poisoning by enterotoxin. Also
present as nasal carriage in 40 – 50%.
2. Staphylococcus epidermidis (Staphylococcus albus). Usually
present as normal flora of human skin & mucous membranes
(non - pathogenic) but may cause infection in immune –
compromised patient if accidentally introduced during
catheterization & use of prosthetics.
3. Staphylococcus saprophyticus. Free living non – pathogenic but
may produce U.T.I.
Microscopical Appearance:-
A Gram's stained film will shows spherical G+ve cocci arranged in
grape like irregular clusters about 1 mm in diameter, non – motile, &
non – capsulated.
Cultural Characteristics:-
Are aerobic or facultatively anaerobic, grow readily on ordinary
media as (nutrient agar & blood agar) & can tolerate 9% NaCl. The
colonies are round, smooth, raised, & glistening, producing pigments
(Staphylococcus albus appear gray to white, while Staphylococcus
aureus appear gray to golden – yellow), & as Staphylococcus aureus
produce haemolysis, a zone of β – haemolysis will appear around the
colony. Only Staphylococcus aureus can ferment mannitol, so the
selective media used to isolate Staphylococcus aureus especially from
nasal carriage is (Mannitol Salt Agar), this medium contain:
Mannitol + 7.5% NaCl + Phenol red (indicator), pink colour will turn
to yellow because of mannitol fermentation & acid production, the
salt inhibit most other normal flora.
Department of Microbiology
College of Medicine
University of Baghdad
Bacteriology lab.
No. 7
2
Toxins & Enzymes produced by Staphylococcus
aureus:-
1. Haemolysin.
2. Coagulase (clotting factor).
3. Catalase. Inactivate H2O2.
4. Gelatinase.
5. Lipase.
6. Hayluronidase.
7. Leuckocidin.
8. Exotoxin. Cause necrosis in skin.
9. Enterotoxins. (A - F) toxins produced by 50% of
Staphylococcus aureus which cause food poisoning cases.
10. Exfoliative
Toxin.
Responsible
for
generalized
desquamation of skin.
11. Toxic Shock Syndrome.
Laboratory Diagnosis:-
The specimen usually sent to the lab. For isolation of
Staphylococcus spp. is pus (from abscess, osteomylitis, or otitis
media), swab, urine, C.S.F., or blood in cases of septicemia).
1. Microscopic.
2. Culture.
3. Biochemical tests:
Coagulase test. Is recognized as the most important
test for testing the virulence of Staphylococci spp.
Staphylococcus aureus is the only coagulase positive
Staphylococci, coagulase convert soluble fibrinogen
into insoluble fibrin.
1. Slide method. Emulsify one or two colonies in a drop of water on a
clean slide, then add one loopful of undiluted plasma & mix
gently, white clumping of fibrinogen around bacteria.
2. Tube method. 0.5 ml of diluted citrated plasma added to same
volume of broth culture of Staphylococcus aureus, then incubated
for 6 hrs. at 37 C, a visible clot will be formed.
Catalase test. This is done to differentiate
Staphylococci From Streptococci, a drop of hydrogen
peroxide solution placed on a slide, & a small amount
of the bacterial growth is placed in the solution. The
formation of bubbles indicates a positive test of
oxygen release.
4. Antibiotic Sensitivity Test. Because of the frequency of drug
resistant strains, Staphylococcal isolates should be tested for
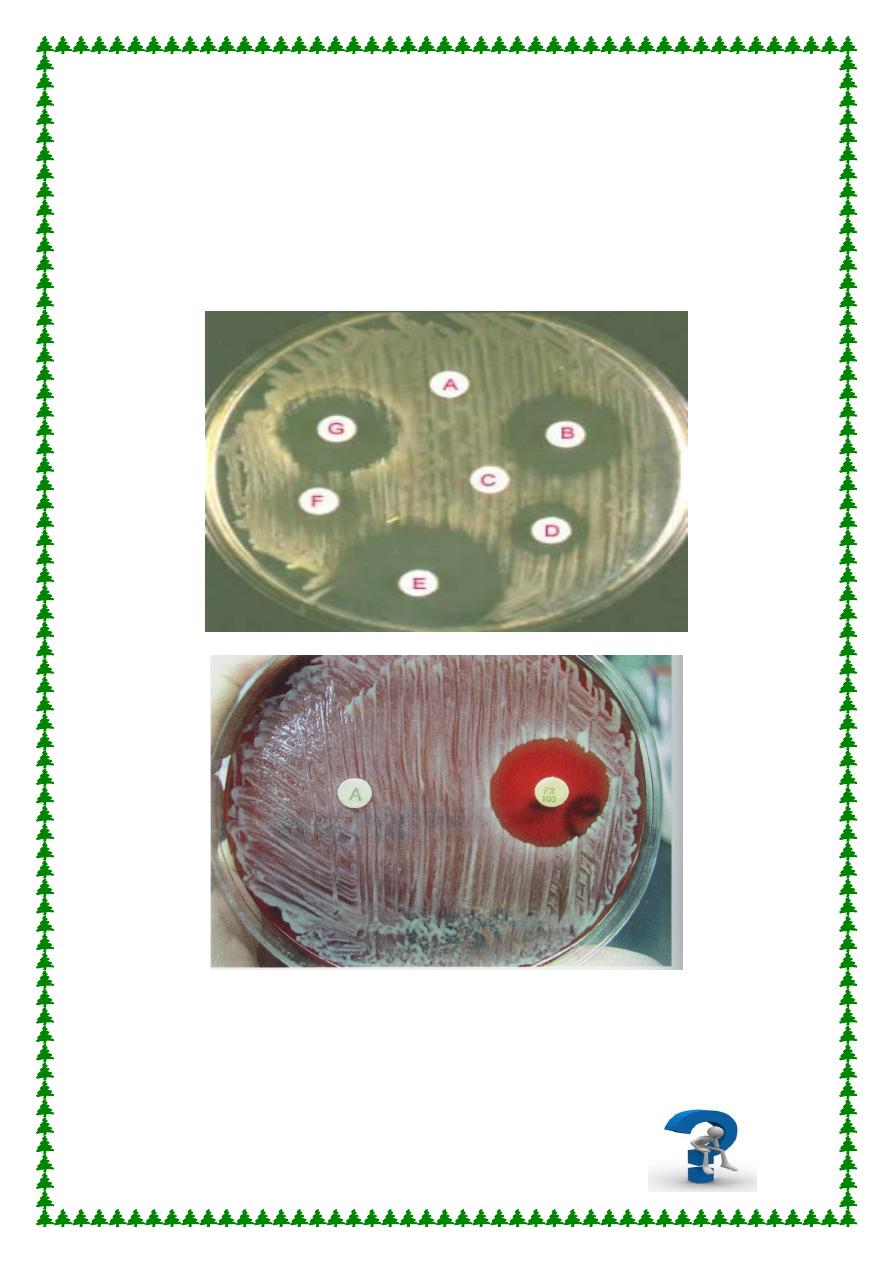
3
antimicrobial susceptibility to help in the choice of systemic
drugs. This is done by growing Staphylococci on Muller –
Hinton agar & use of disks impregnated is specific dilution of
different Ab. which results in zones of growth inhibition vary
with the sensitivity of the growth to the applied Ab. The disk
test measures the ability of drugs to inhibit the growth of
bacteria & the results correlate with therapeutic responses in
diseases progresses.
