
Boxes
are a popular way of presenting
information and are particularly useful for revision.
Emergency
These boxes describe management of many of the
most common emergencies in medicine
Hussien Mohammed Jumaah
CABM
Lecturer in internal medicine
Mosul College of Medicine
Thursday , 28 April , 2016

Emergency management of anaphylaxis

Clinical decisions in the critically ill

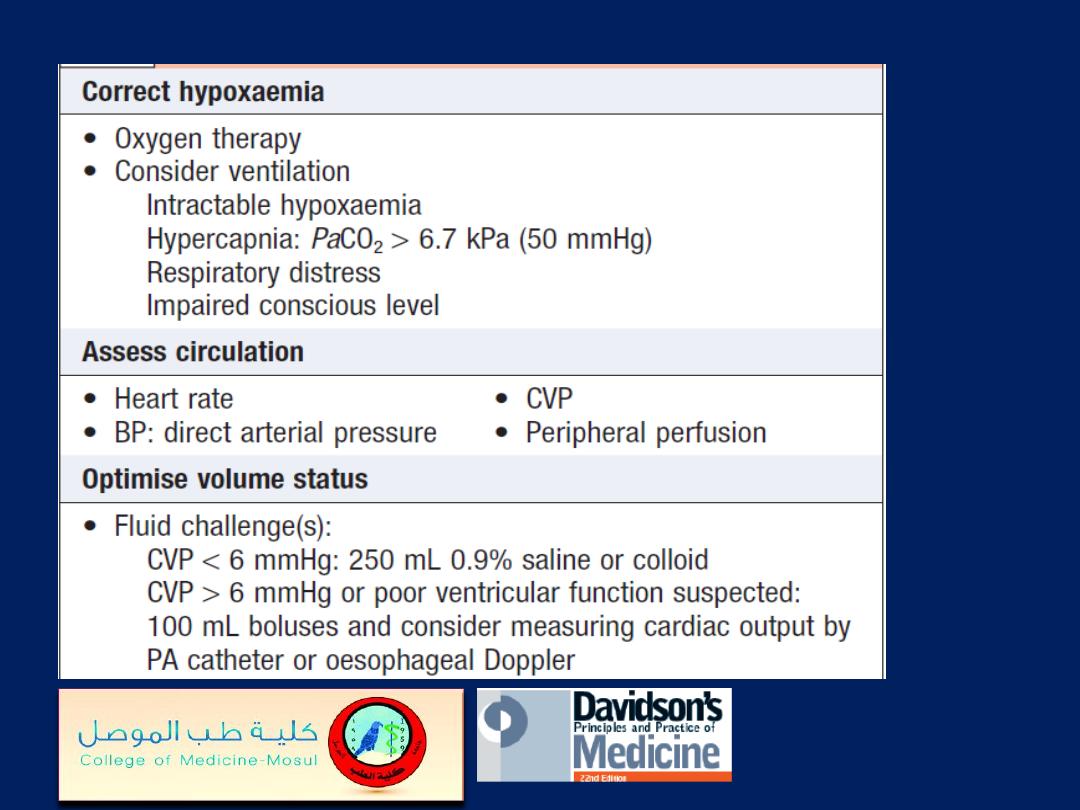
Immediate management of circulatory collapse
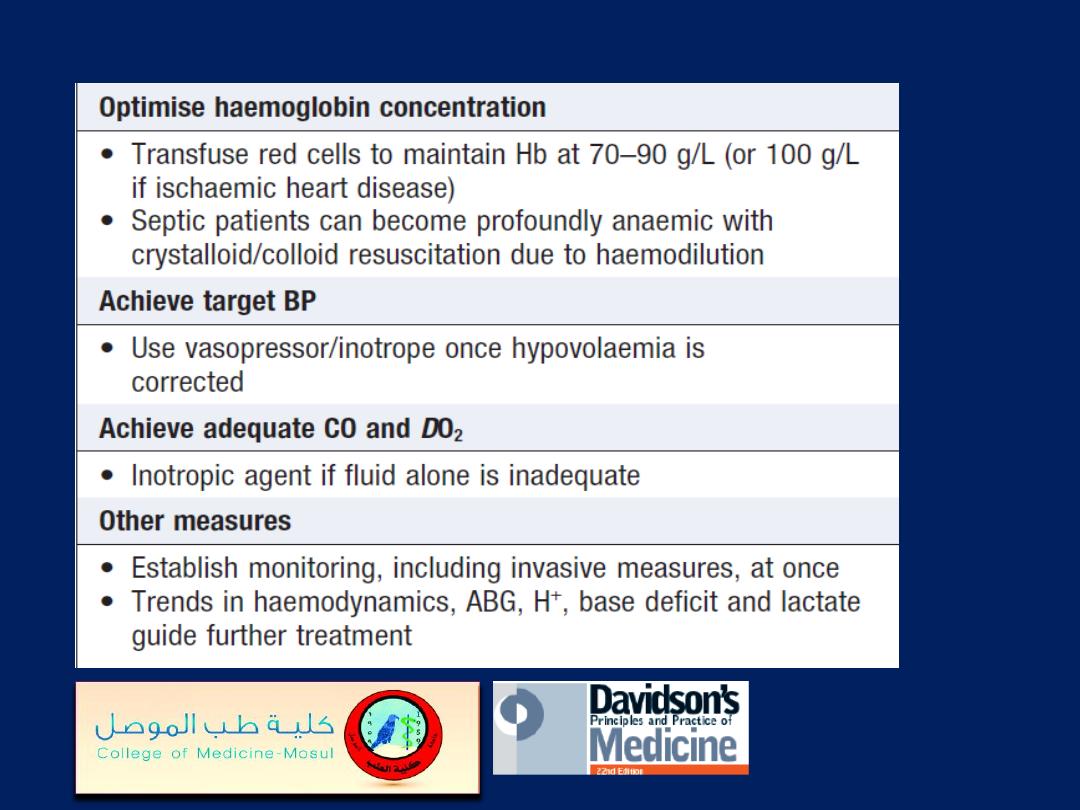
Immediate management of circulatory collapse'cont'd

Immediate management of severe sepsis

Management of patients on admission to ICU

Psychiatric emergencies

Management of suspected spinal cord
compression

Medical management of severe hypercalcaemia

Severe manifestations/complications of falciparum
malaria and their immediate management
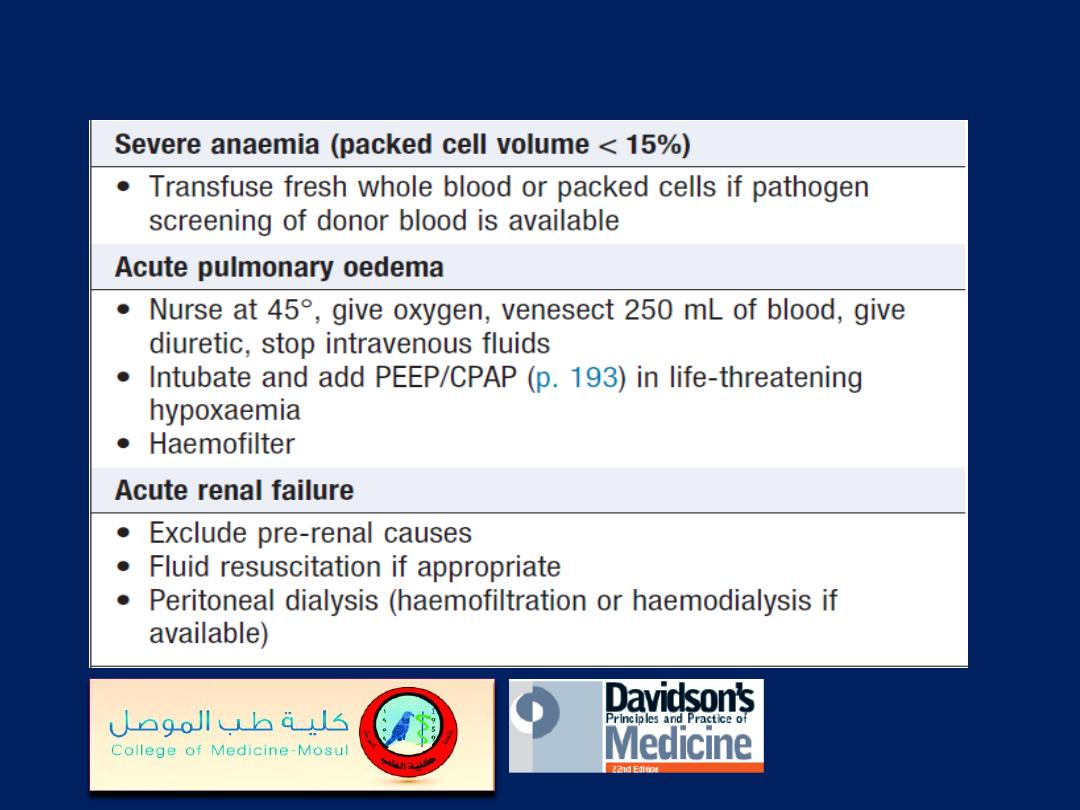
Severe manifestations/complications of falciparum
malaria and their immediate management'cont'd
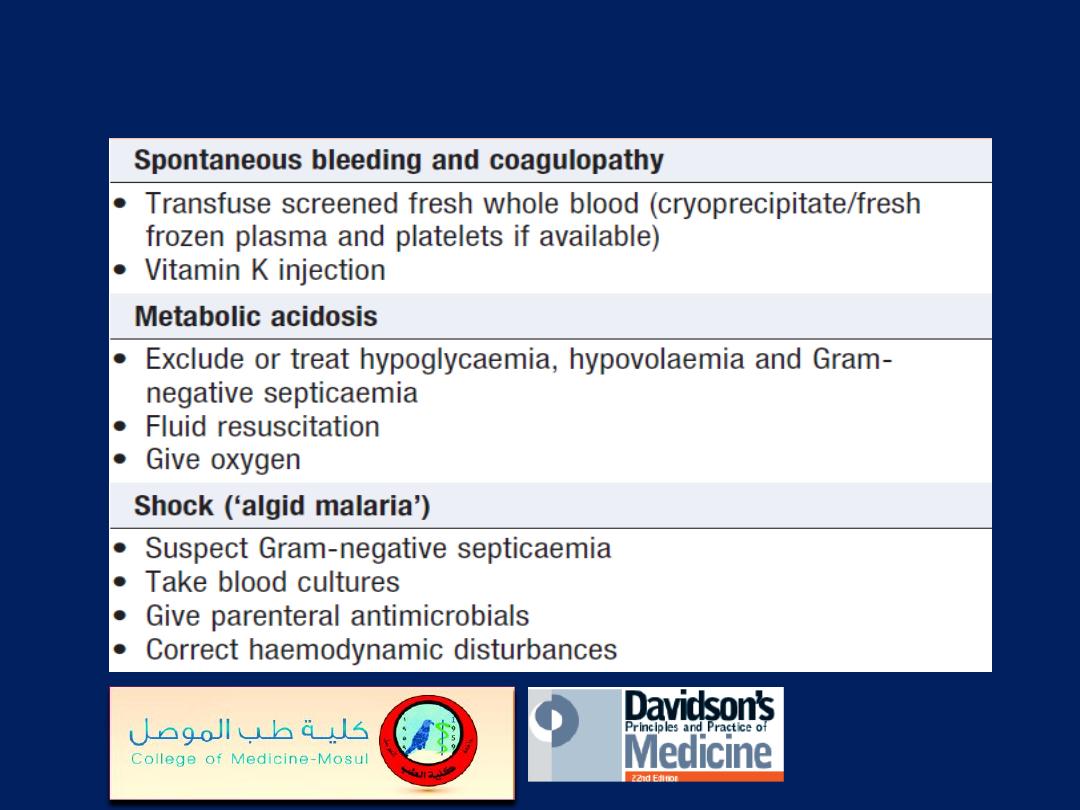
Severe manifestations/complications of falciparum
malaria and their immediate management'cont'd

Severe manifestations/complications of falciparum
malaria and their immediate management'cont'd
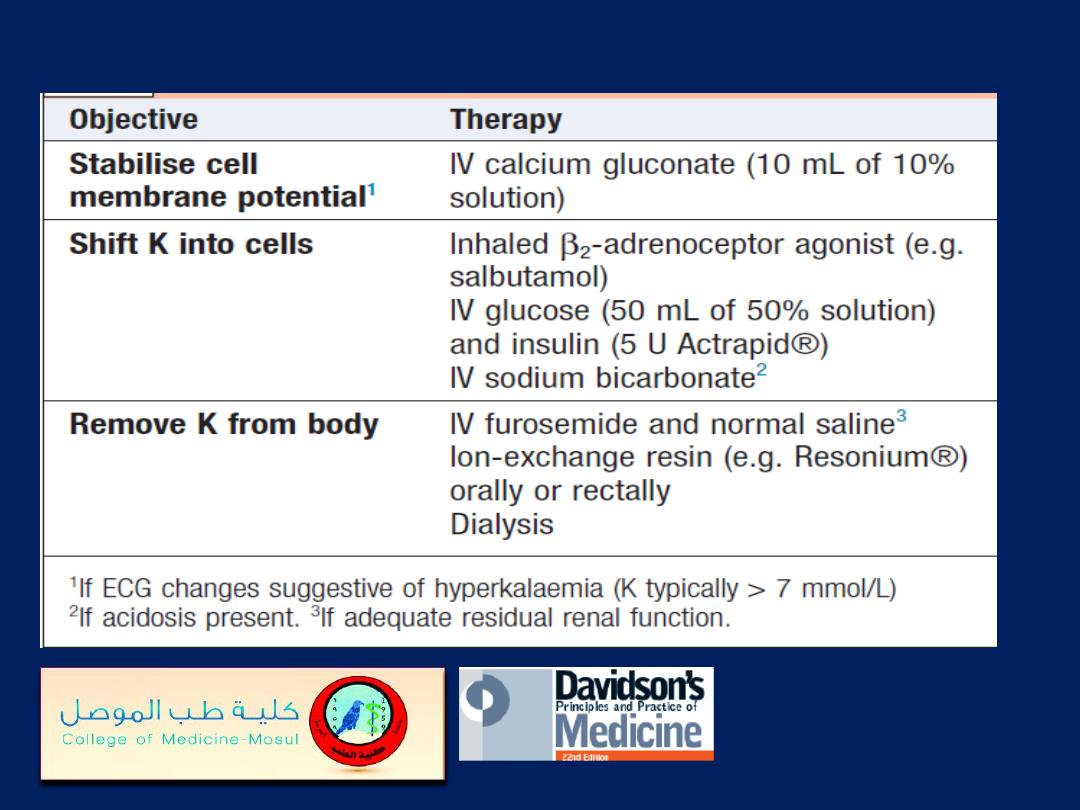
Treatment of severe hyperkalaemia
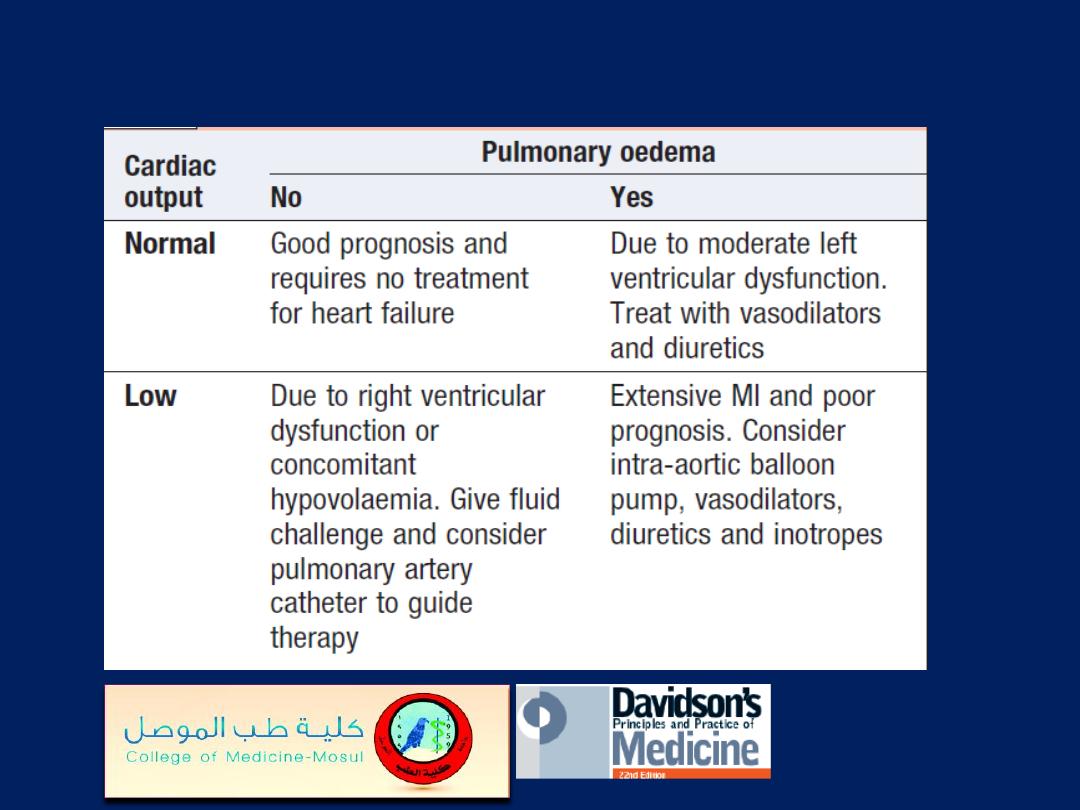
Acute myocardial infarction:
haemodynamic subsets
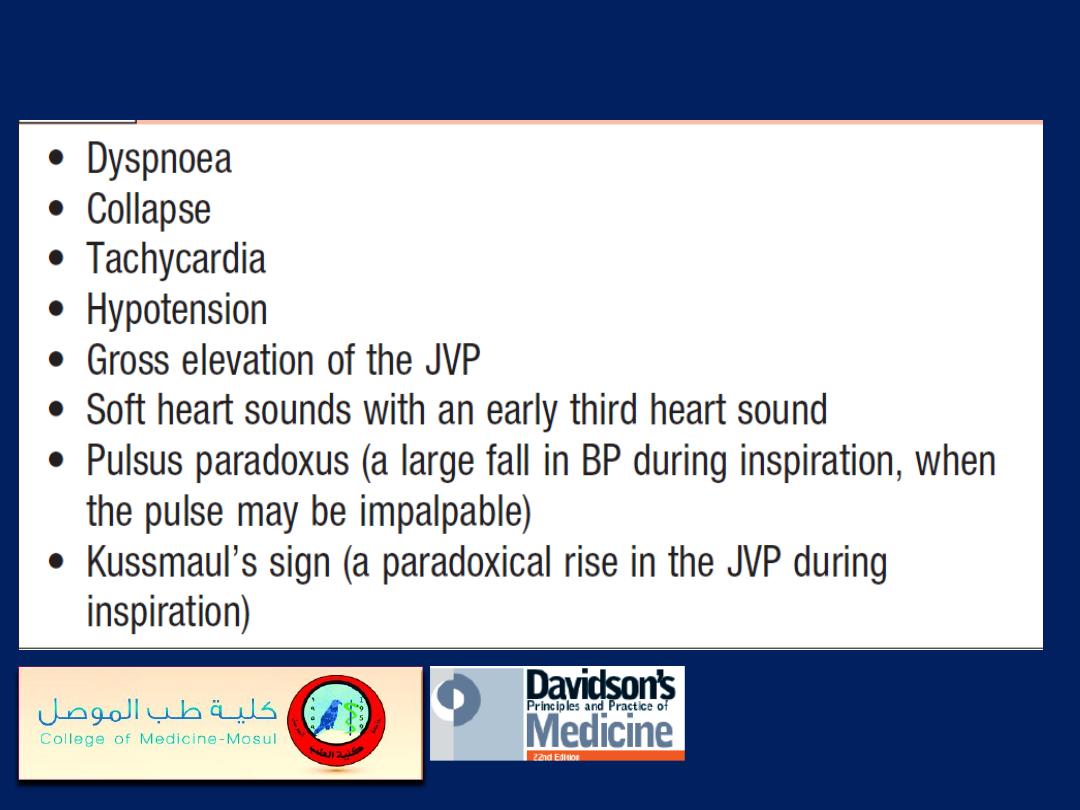
Clinical features of pericardial tamponade
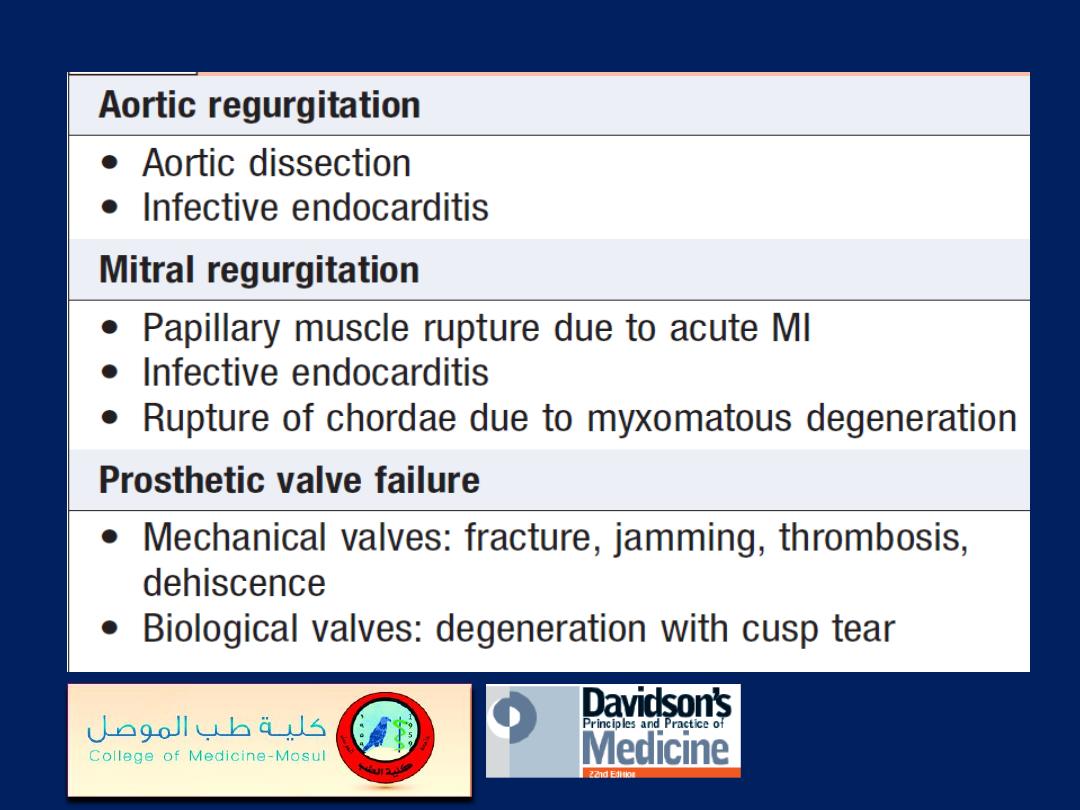
Causes of acute valve failure

Clinical features of acute coronary syndromes

Symptoms and signs of acute limb ischaemia

Assessment and management of ‘acute on
chronic’ type II respiratory failure

Assessment and management of ‘acute on
chronic’ type II respiratory failure'cont'd
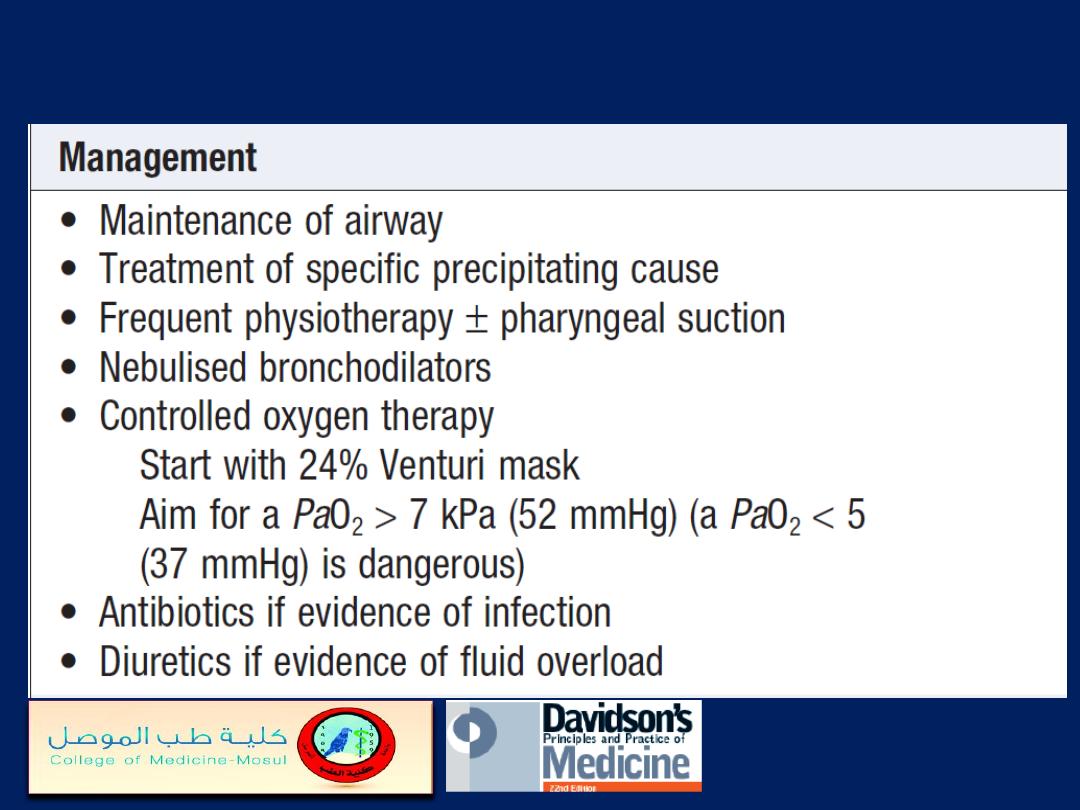
Assessment and management of ‘acute on
chronic’ type II respiratory failure'cont'd

Assessment and management of ‘acute on
chronic’ type II respiratory failure'cont'd
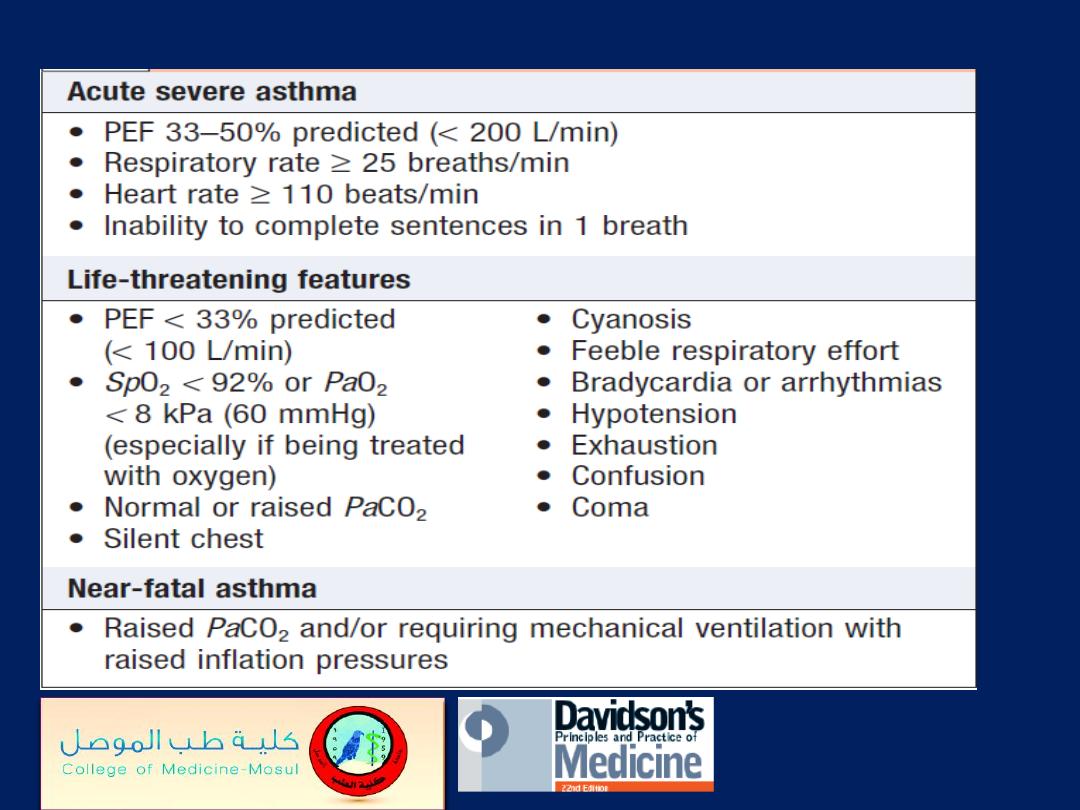
Immediate assessment of acute severe asthma

Indications for assisted ventilation in acute
severe asthma

Indications for referral to ITU
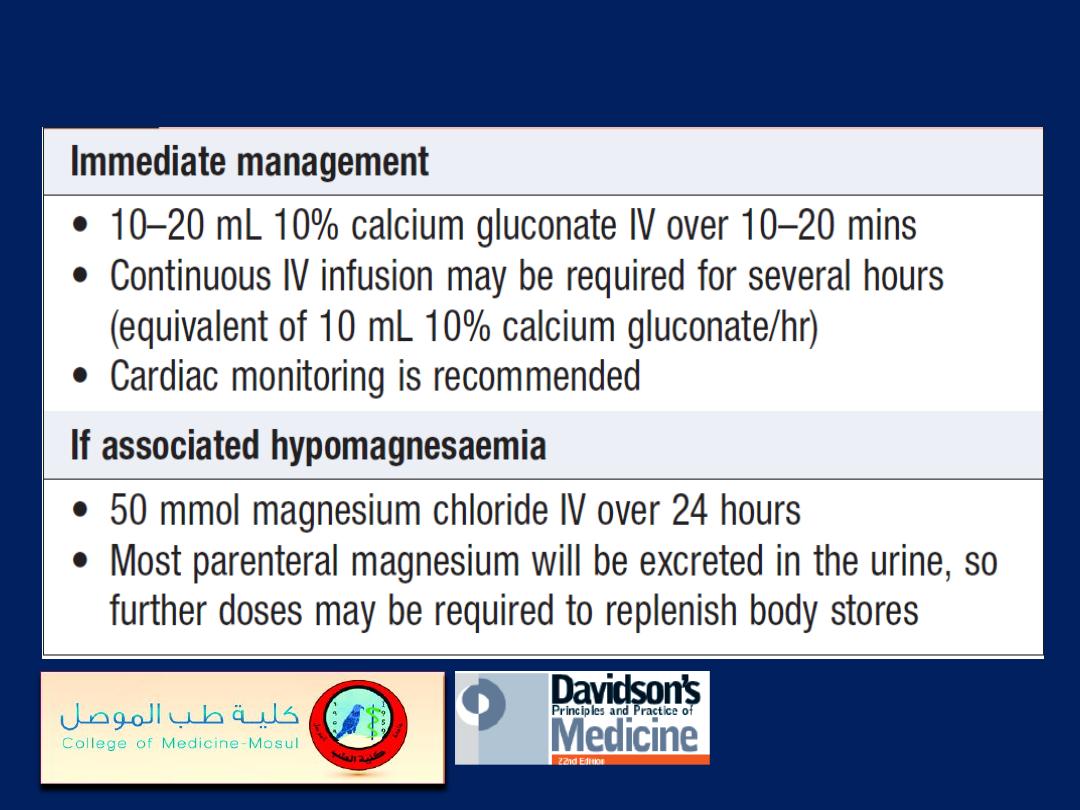
Management of severe hypocalcaemia
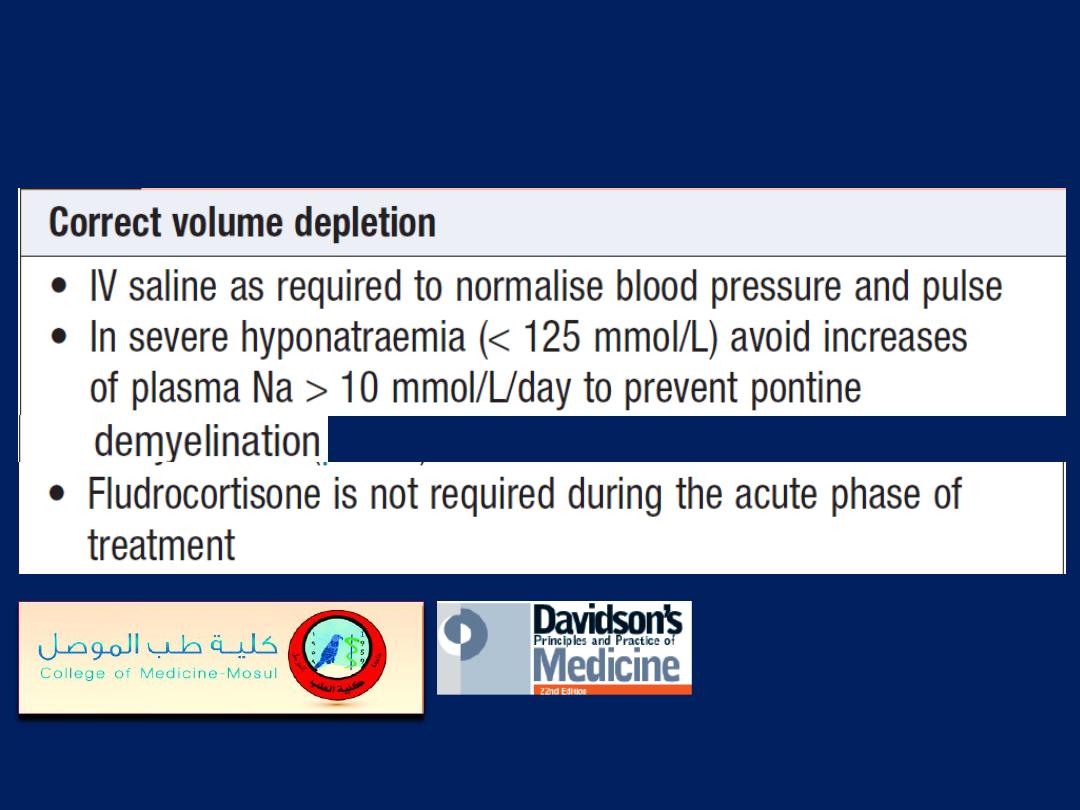
Management of adrenal crisis

Management of adrenal crisis'cont'd
Management of adrenal crisis'cont'd

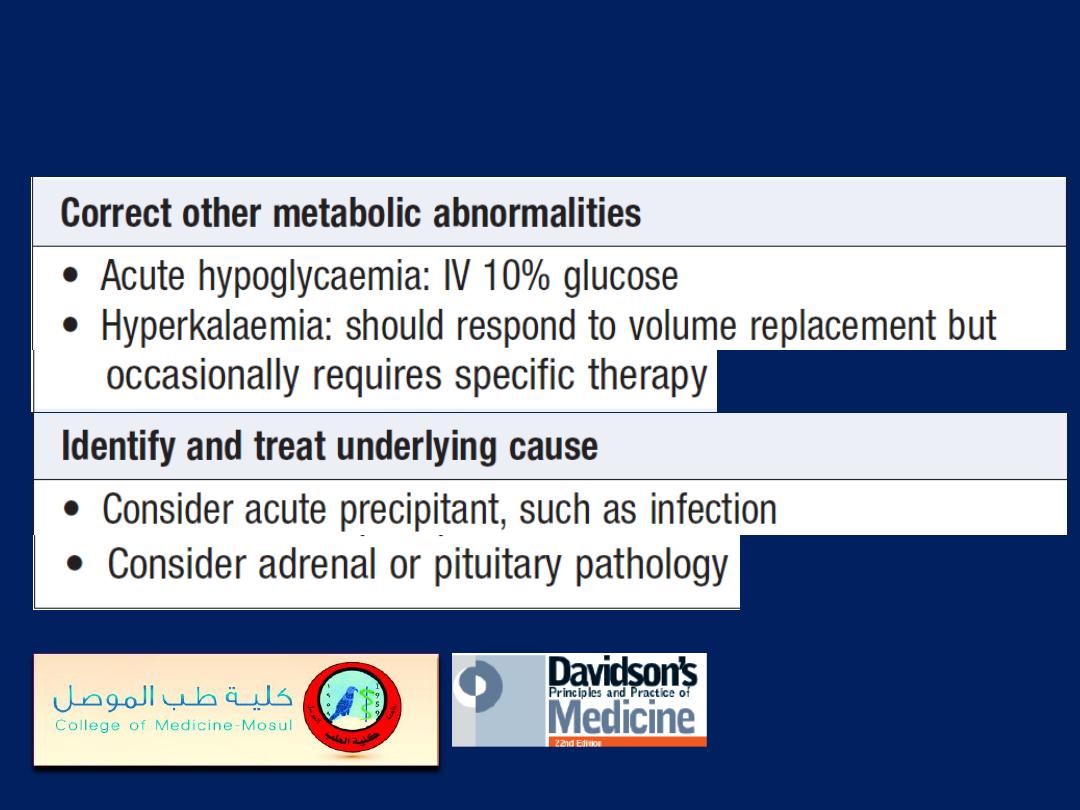
Management of diabetic ketoacidosis

Management of diabetic ketoacidosis'cont'd
Management of diabetic ketoacidosis'cont'd

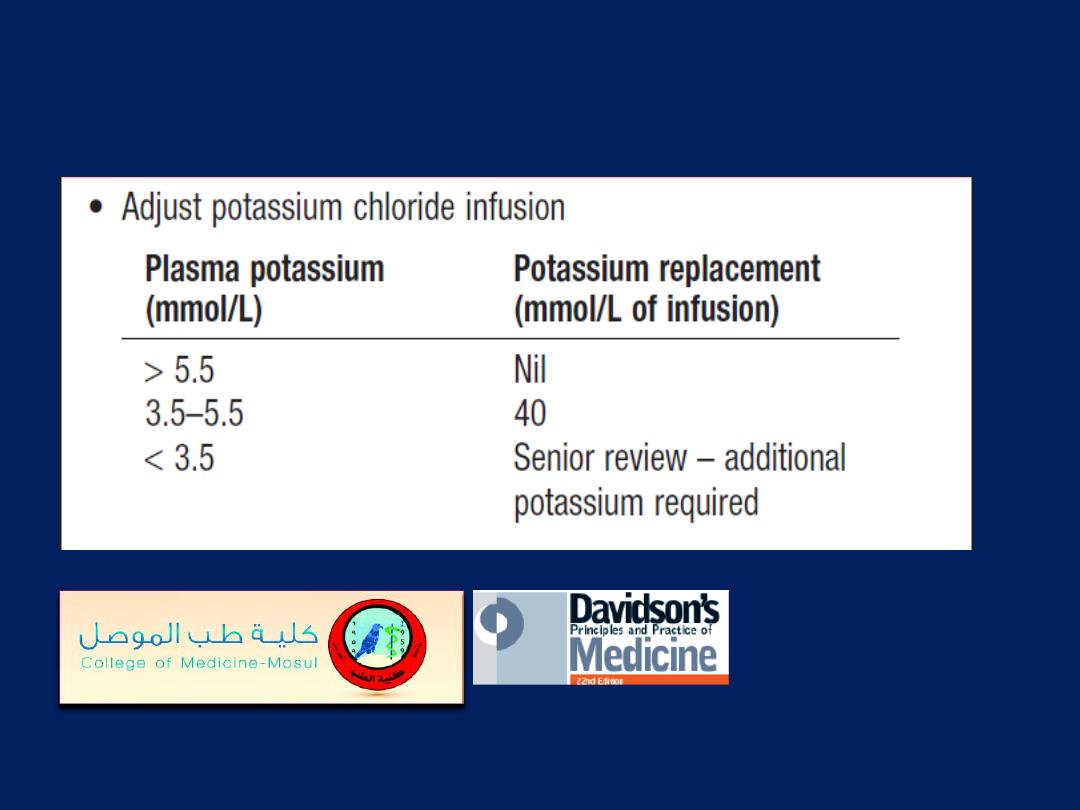
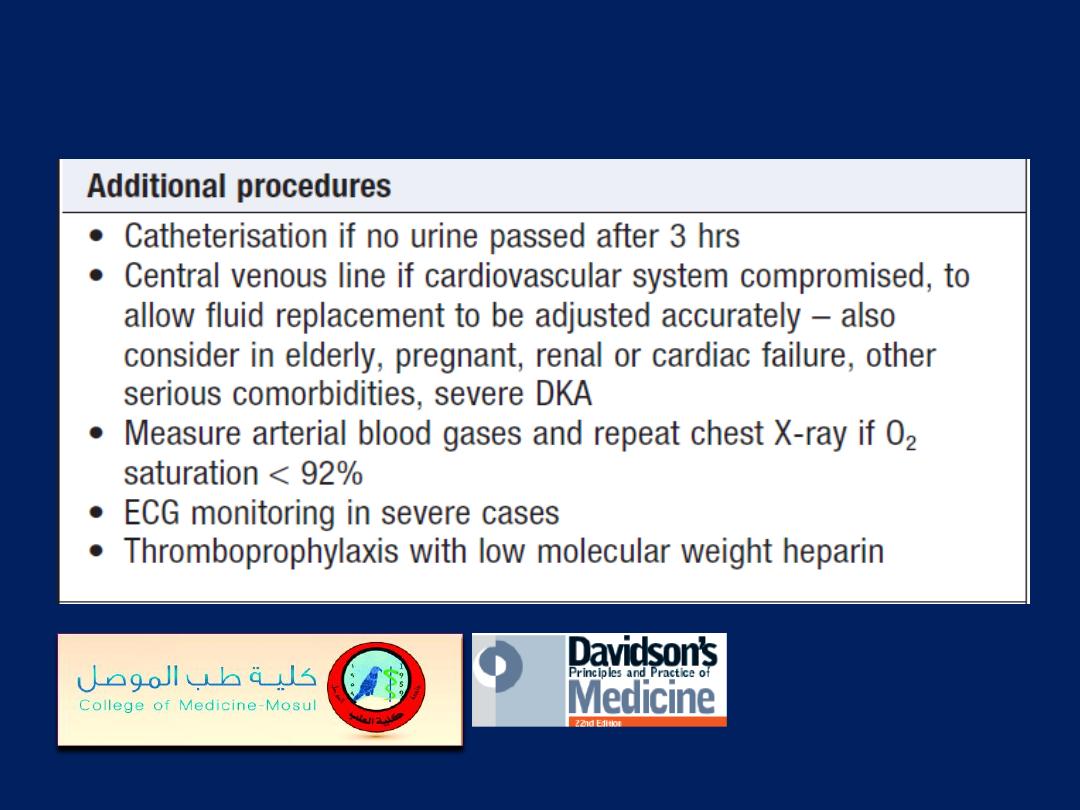
Management of diabetic ketoacidosis'cont'd
Management of diabetic ketoacidosis'cont'd

Emergency treatment of hypoglycaemia
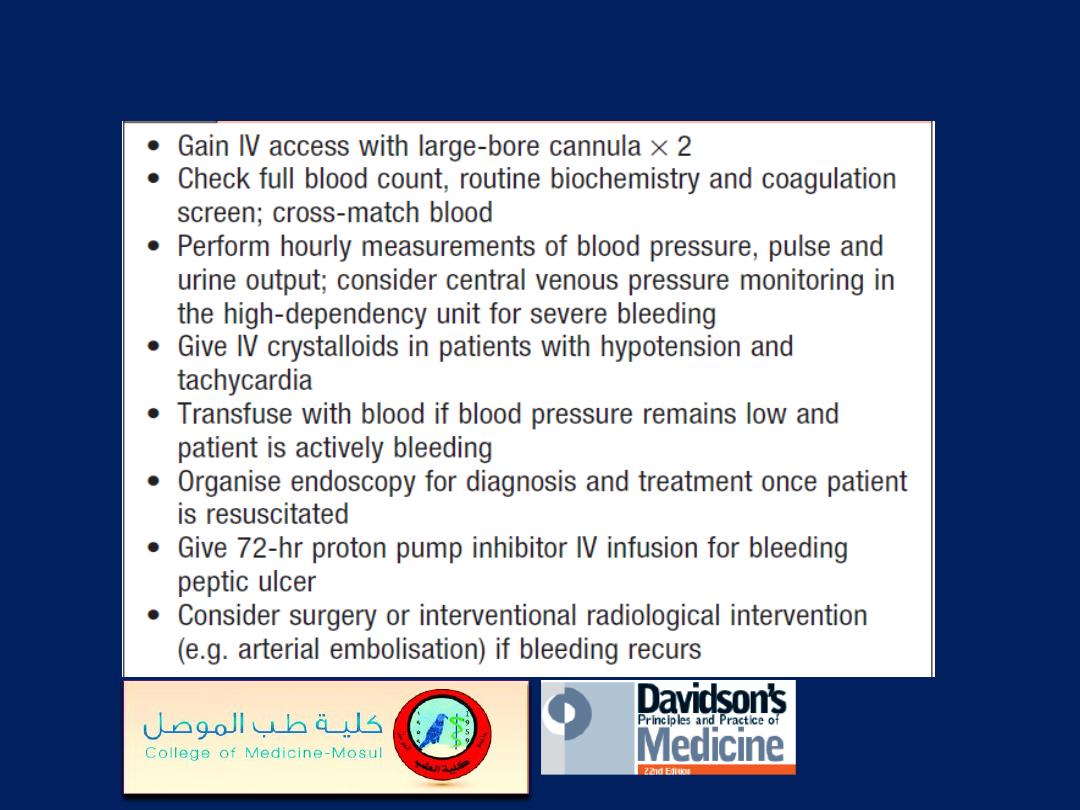
Emergency management of acute non-variceal upper
gastrointestinal haemorrhage

Medical management of fulminant ulcerative colitis

Adverse prognostic criteria in acute liver failure*
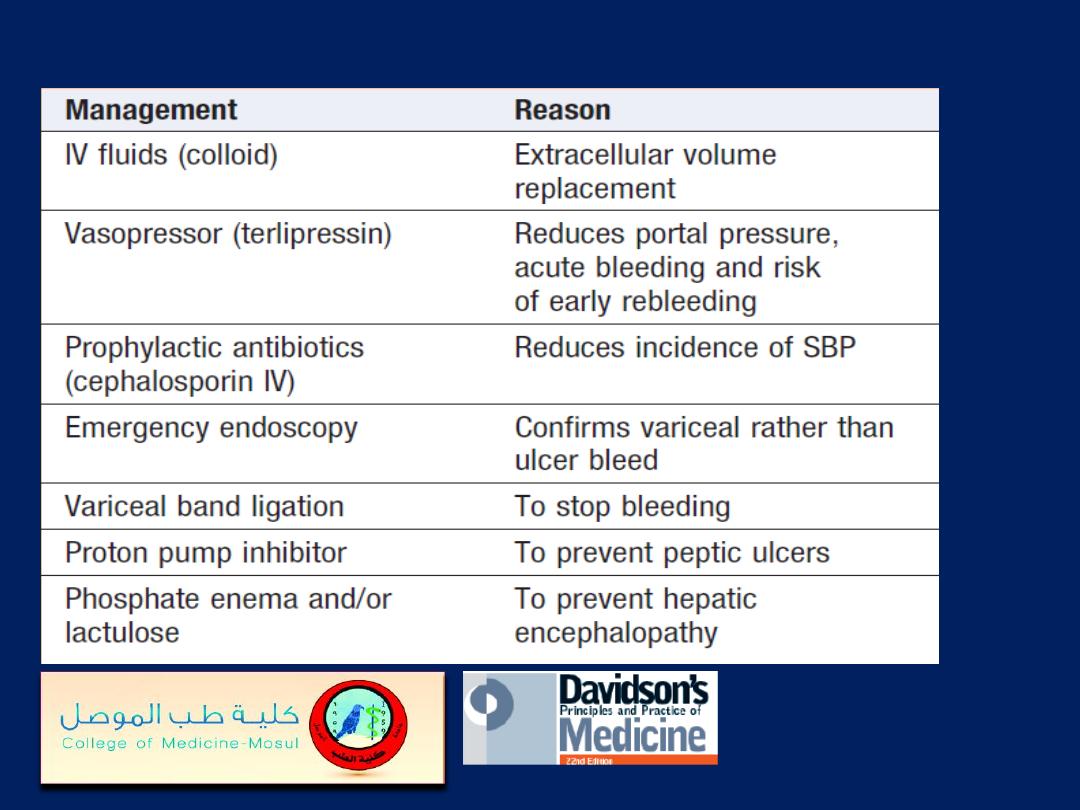
Emergency management of variceal bleeding

Disseminated intravascular coagulation
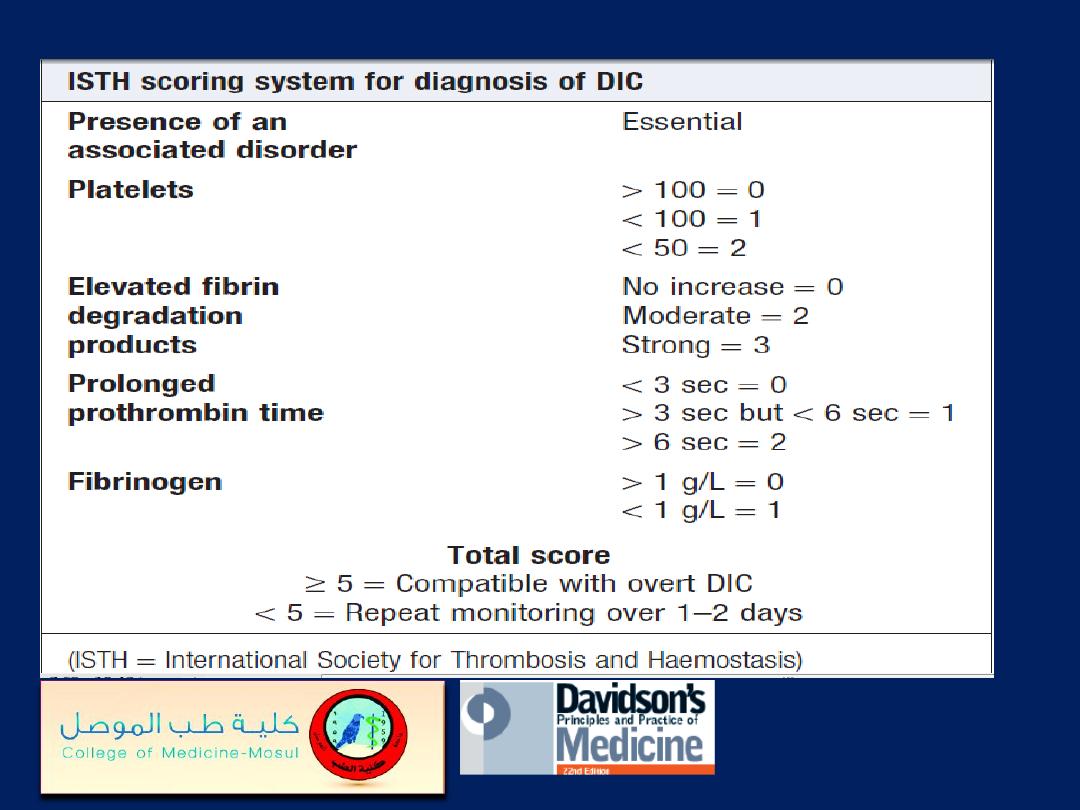
Disseminated intravascular coagulation
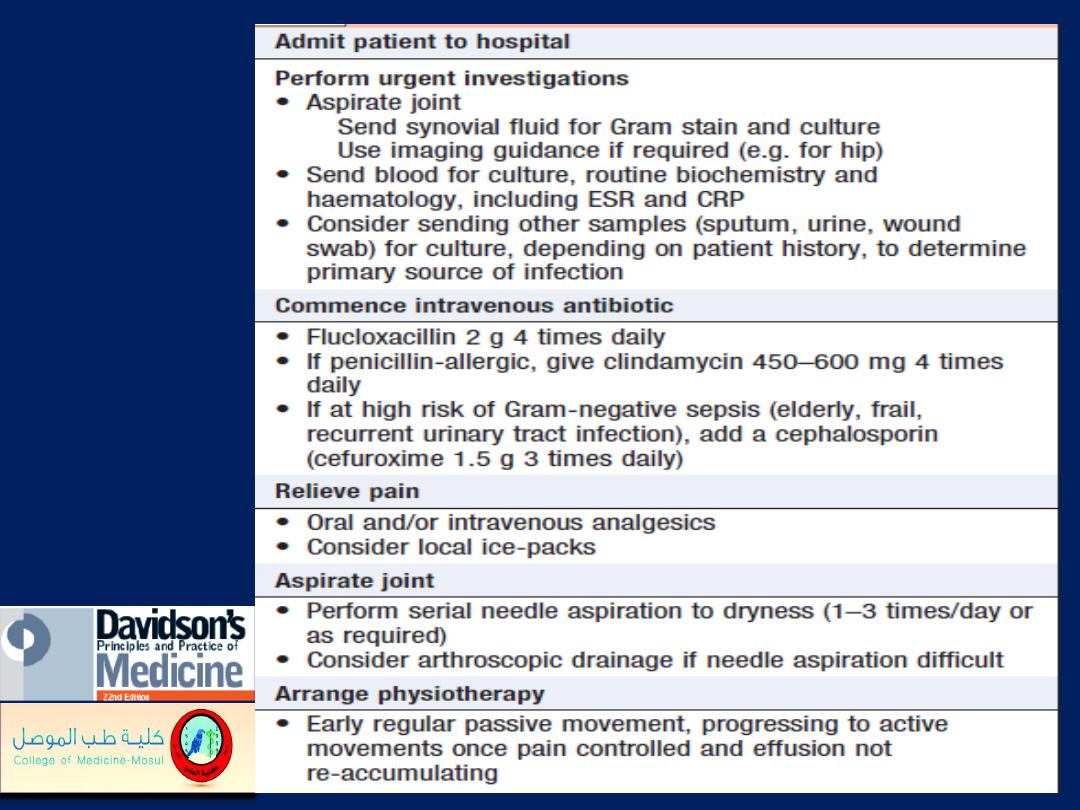
Emergency
management
of suspected
septic arthritis

Emergency management of giant cell arteritis

• Status epilepticus
• Stroke (if thrombolysis available)
• Guillain–Barré syndrome
• Myasthenia gravis (if bulbar and/or respiratory)
• Spinal cord compression
• Subarachnoid haemorrhage
• Neuroleptic malignant syndrome
Neurological emergencies
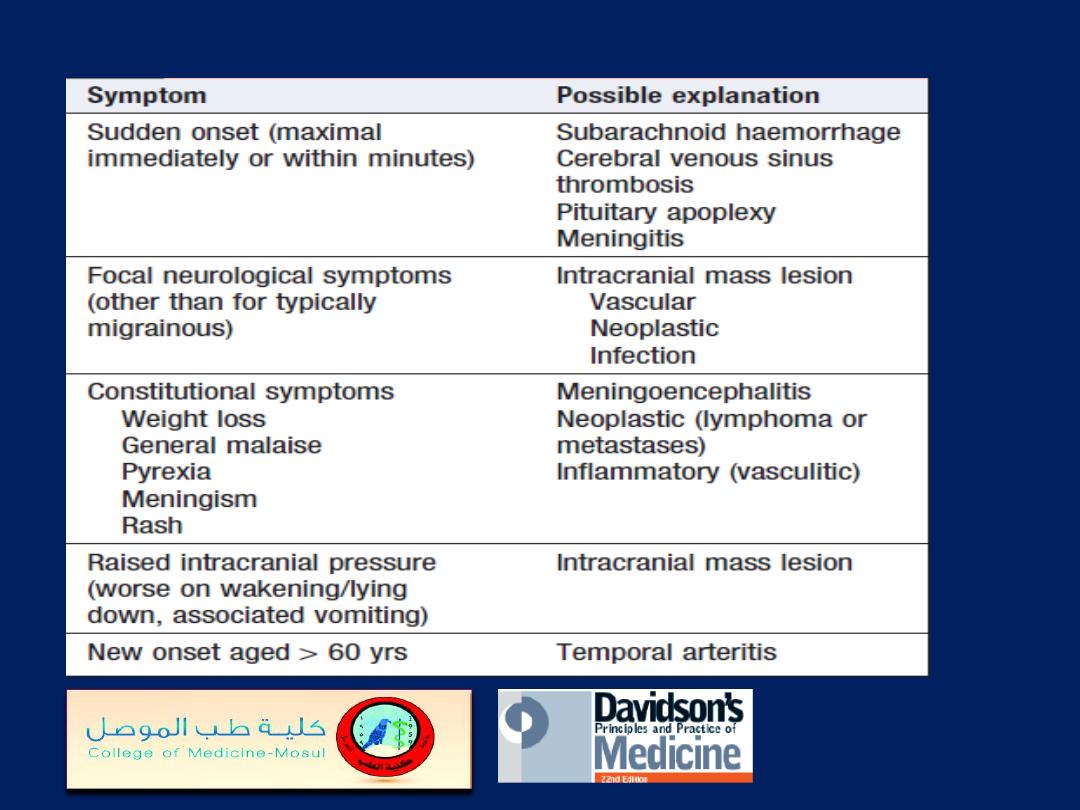
‘Red flag’ symptoms in headache

Management of status epilepticus

Management of status epilepticus'cont'd

Management of status epilepticus'cont'd
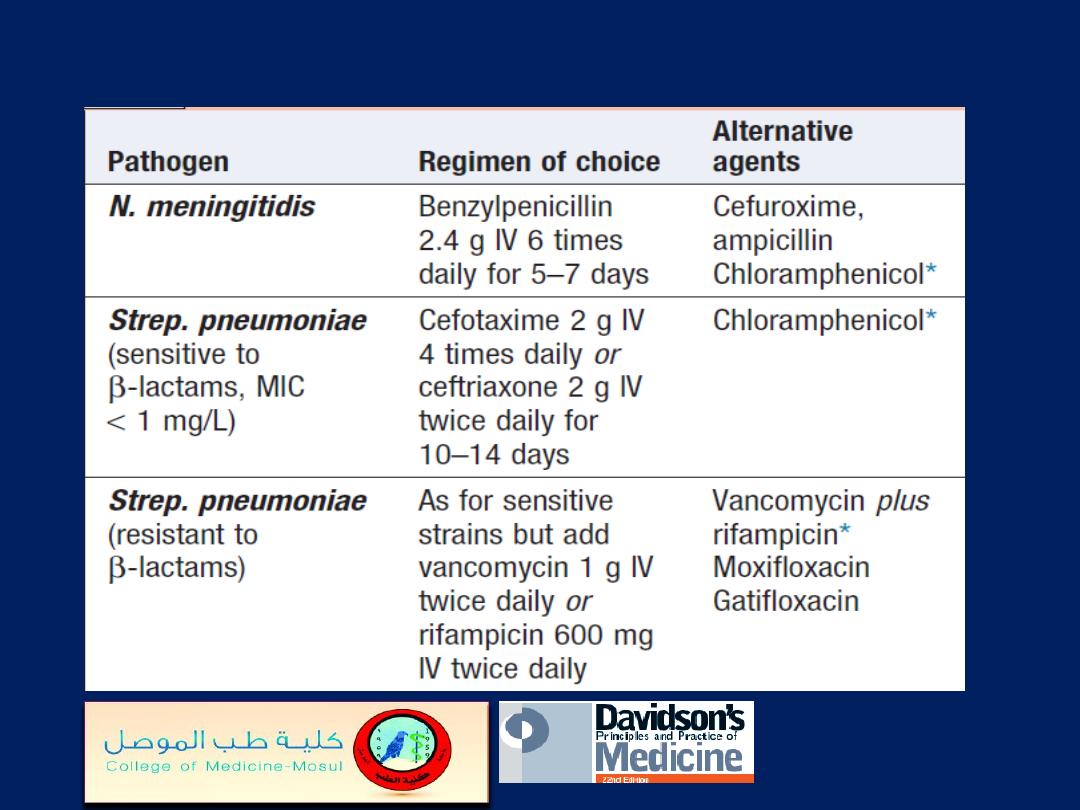
Chemotherapy of bacterial meningitis when the
cause is known
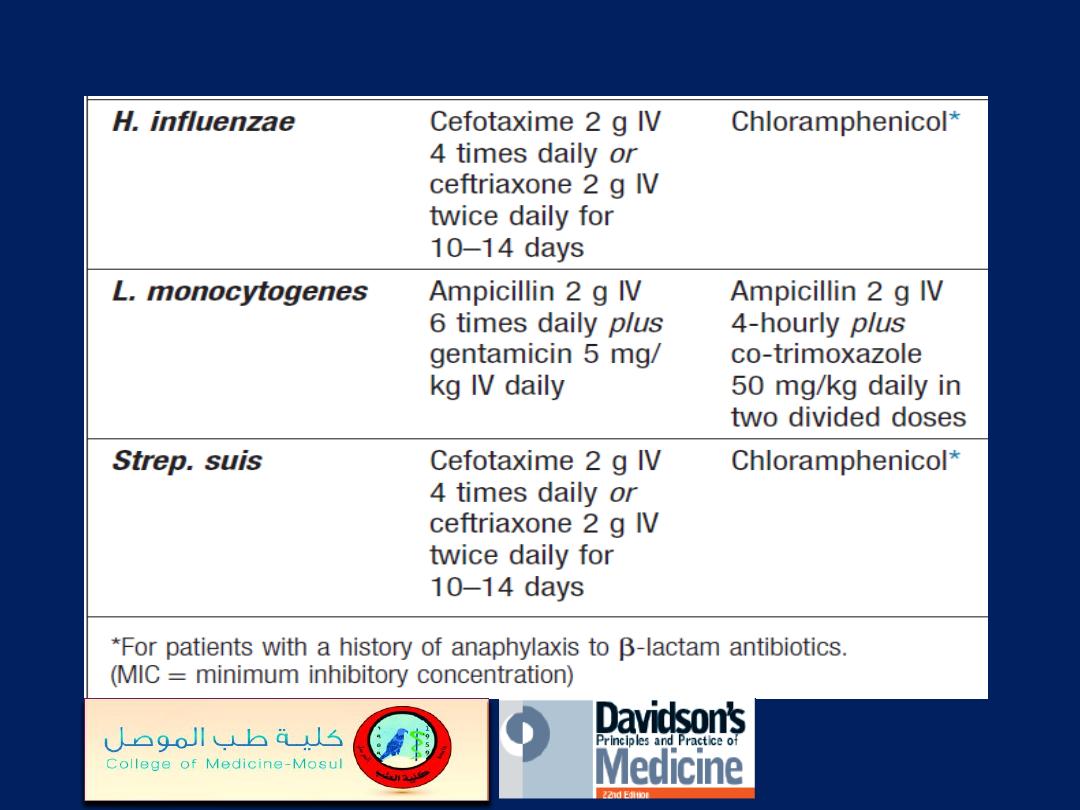
Chemotherapy of bacterial meningitis when the
cause is known'cont'd

Treatment of pyogenic meningitis of unknown cause
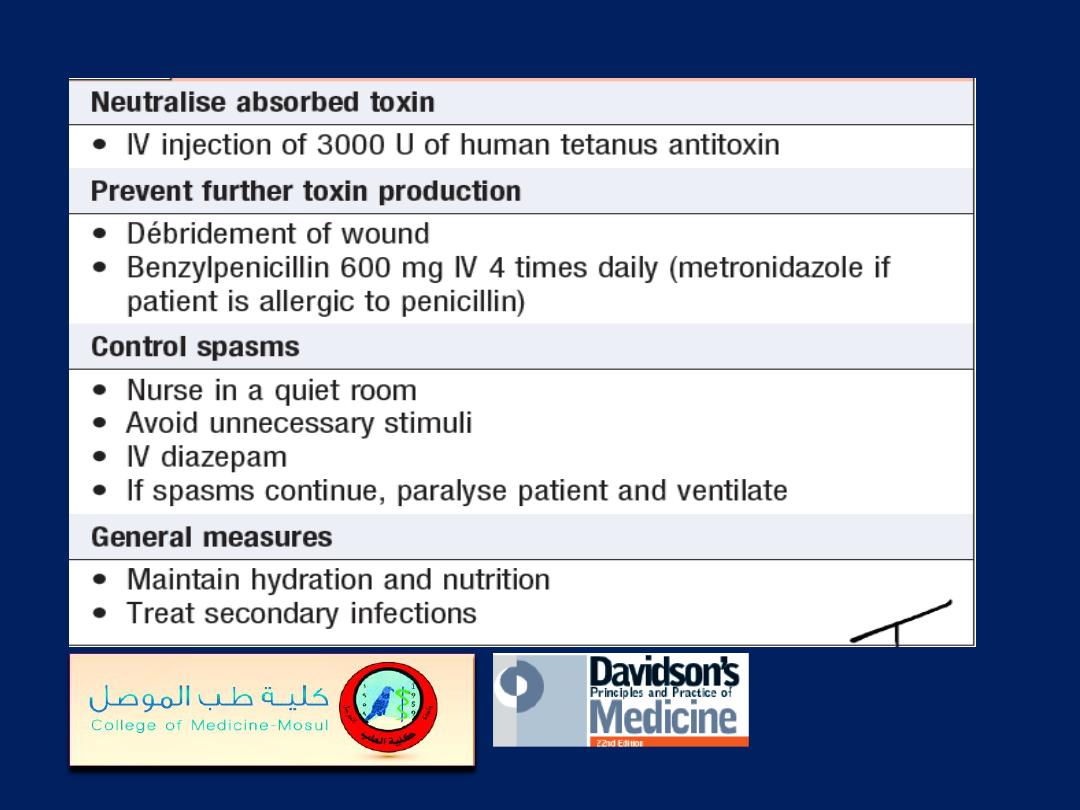
Treatment of tetanus
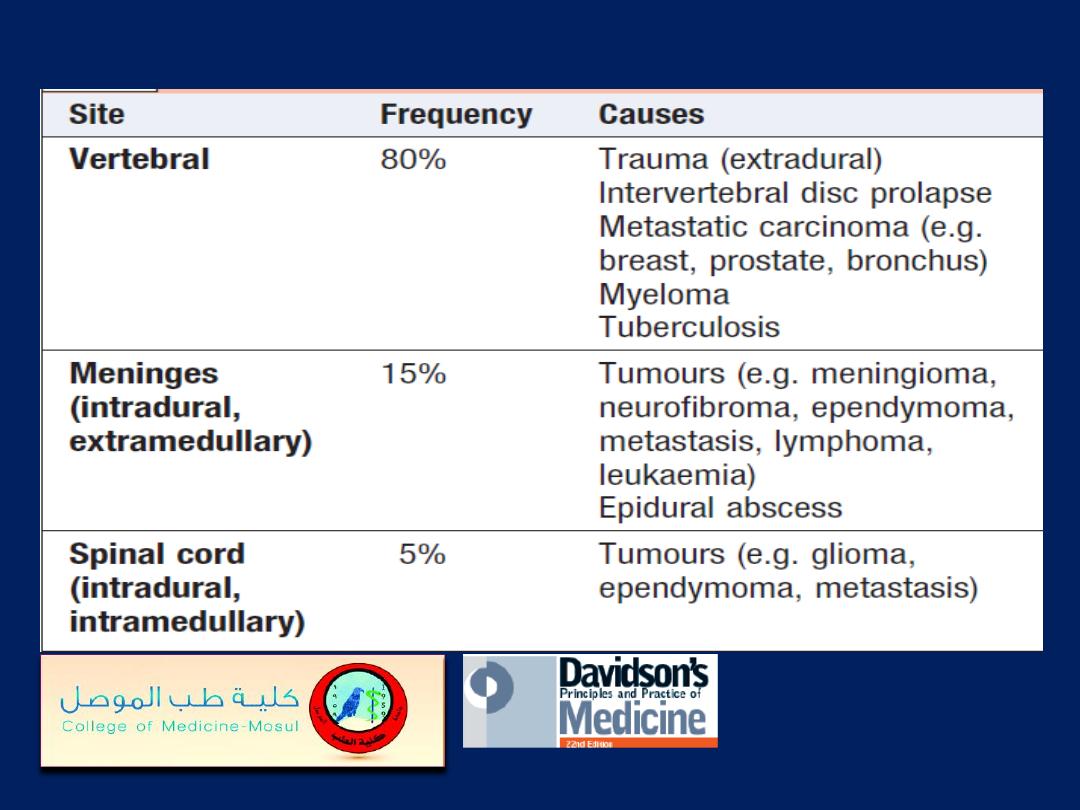
Causes of spinal cord compression
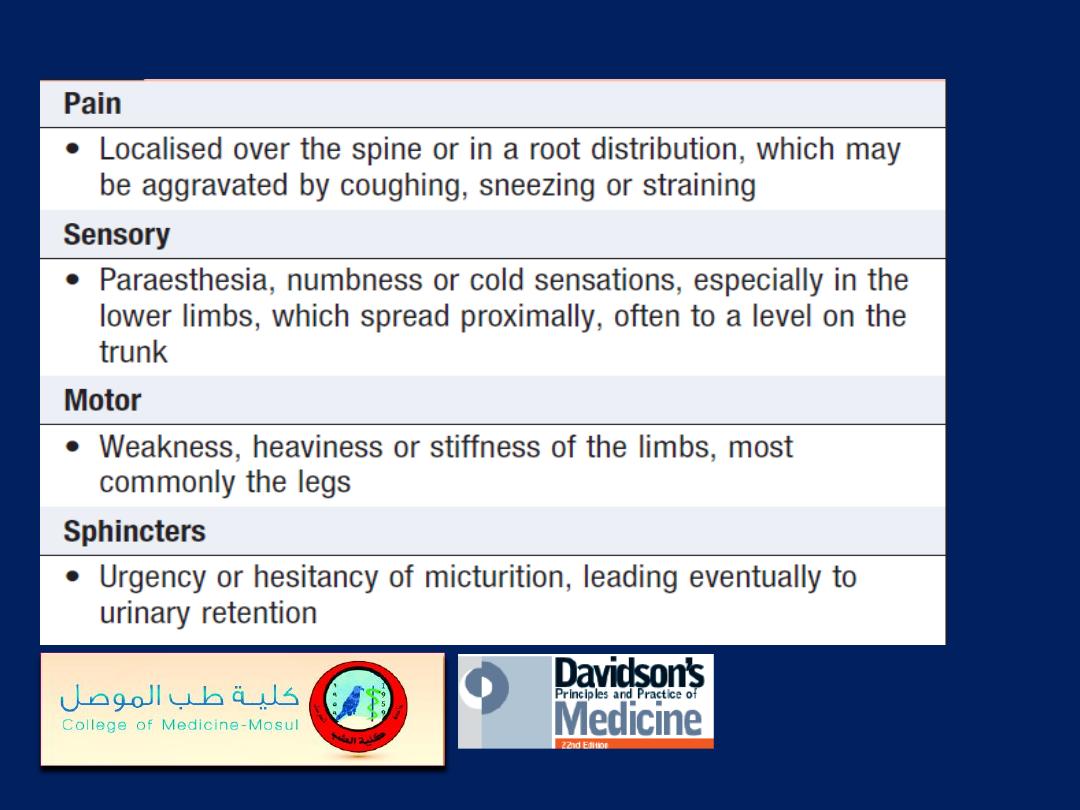
Symptoms of spinal cord compression

Signs of spinal cord compression
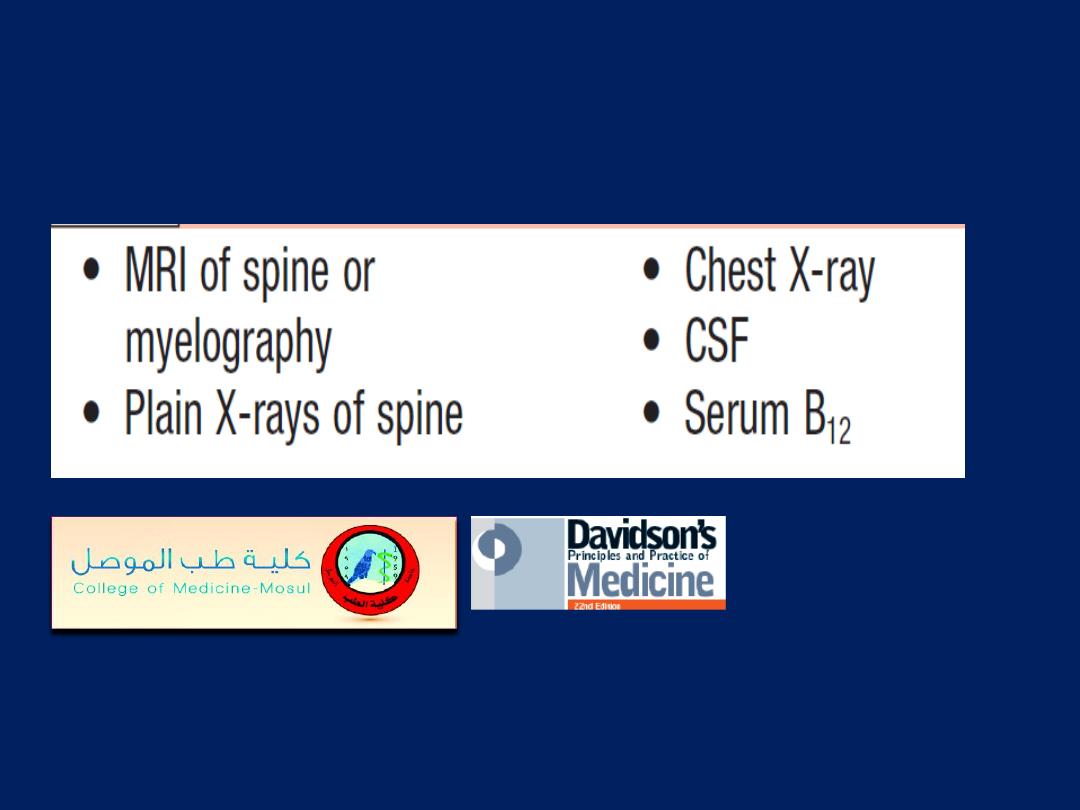
Investigation of acute spinal cord syndrome

Indications for emergency CT/MRI in acute stroke
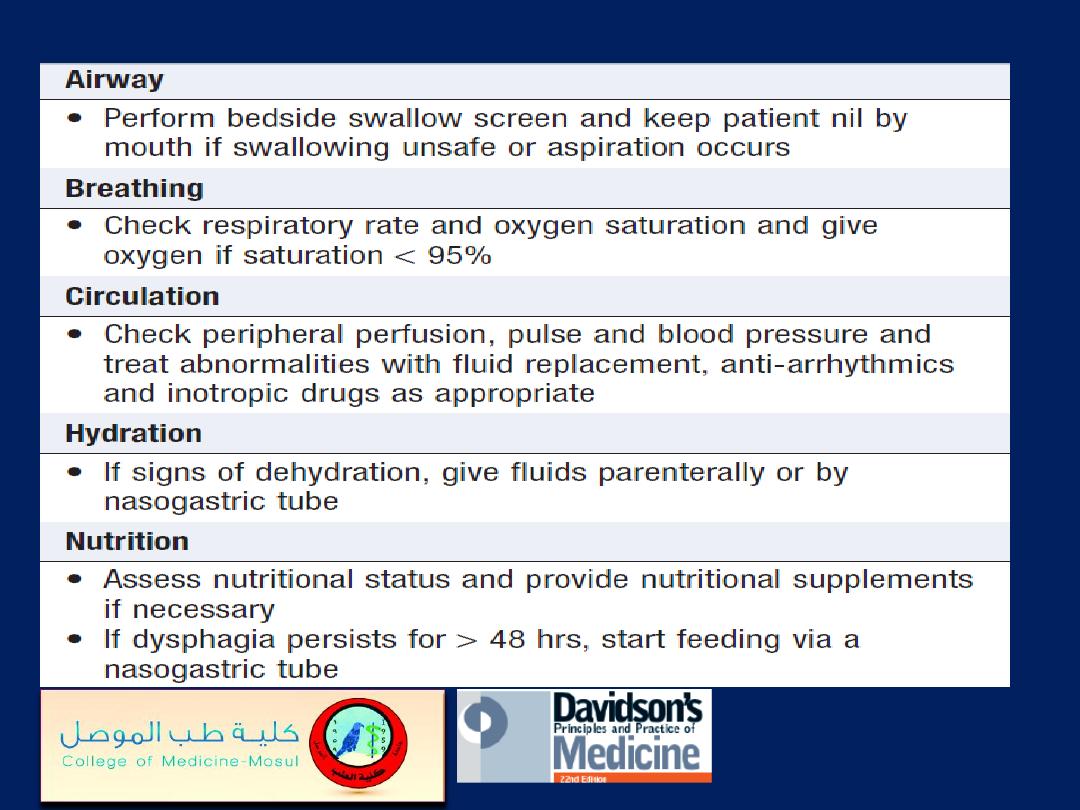
Management of acute stroke
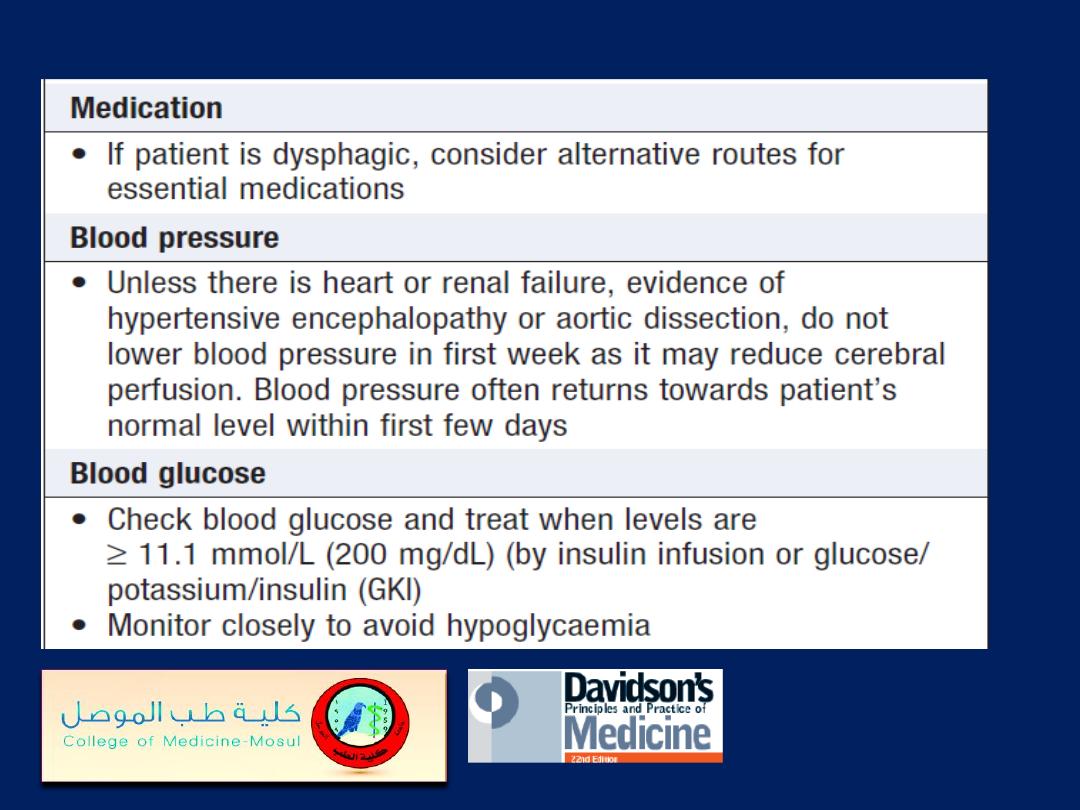
Management of acute stroke'cont'd
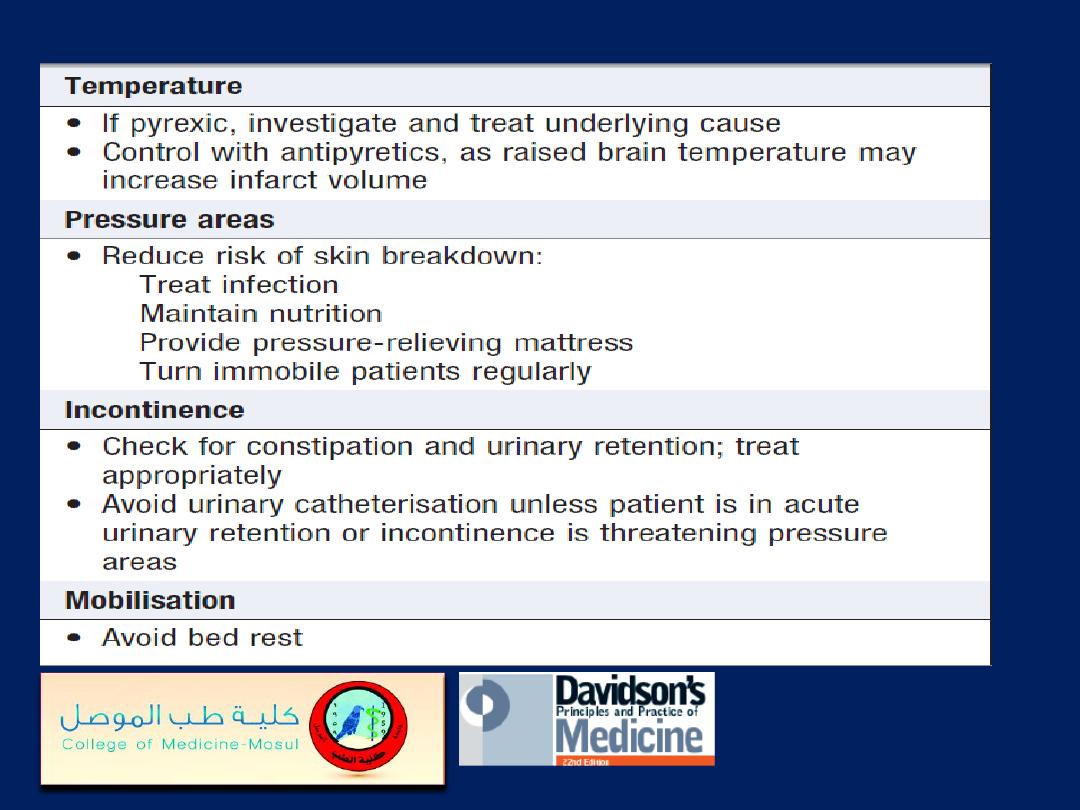
Management of acute stroke'cont'd
