Congenital heart diseases
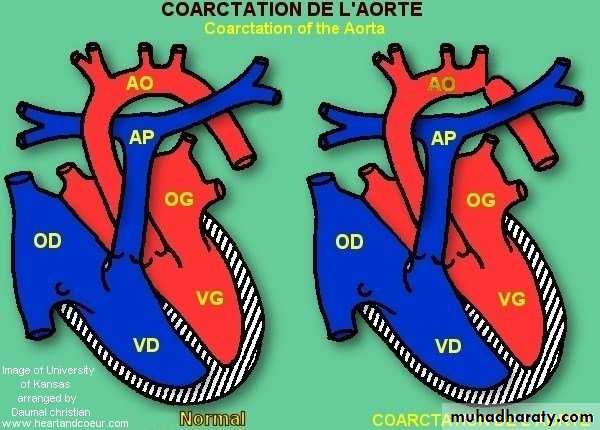
Coarctation of aorta
Constriction that occur at any portion of aorta from transverse arch to the iliac bifurication.more in male afeatures of turner synPathophysiology :
2 typesJuxtaductal ( if mild adult type) 98% just below origin of lt subclavian art.
Tubular hypoplastic ( infantile type ) .
If more severe juxtaductal or tubularhypoplastic blood pass through ductus arteriosus decsending aorta if closed diffrential cyanosis ( lower blue extremities and upper pink extremities ).
In COA:
blood pressure in area proximal to coarctation
( mechanical and hormonal )
blood pressure distal to the coarctation.
Development of collaterals from subcalvian , internal mamery , superior intercostal .
Clincal features
If mild and Dx after infancy rarely significant symptoms and most diagnosed by blood pressure with routine physical examination.Signs :
Pulses of UL and LL.
Radio-femoral delay.
Blood pressure in both UL and LL.
Blood pressure in each arm.
Ejection systolic click + thrill.
Systolic murmur in 3rd , 4th Lt sternal border .
Mid-diastolic murmur.
Systolic murmur of aortic stenosis
In neonatal period
Lt body hypoperfusion, acidosis, HF .Before ductal closure differential cynosis.
Diagnosis
• CXR
• ECG
• ECHO
• COLOR DOPPLER
• CONTINOUS AND PULSED WAVE DOPPLER
• CATHETRAIZATION + LT VENTRICULOGRAPHY
• MRI used in dx due to difficulty in infancy
Complications
• Untreated succumb at 20-40 yr.• Complications secondary to
• IE, Endarteritis
• Aneuryzms of the descending aorta or collaterals.
• Neonates : hypoperfusion + HF
• Premature coronary arterey disease
• HF
• ICH
• Hypertensive encephalopathy
Treatment
• In neonate PGE1 reopen ductus and relieve obstruction stabilize him surgery.• Older children HF antifailure surgery
• Surgery:
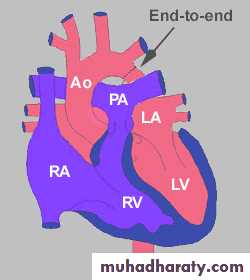
Excision and primary re-anastamosis
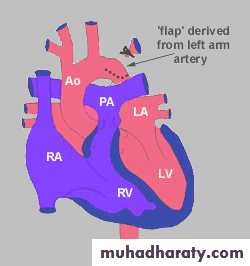
Subclavian flap.
Patch aortoplasty.
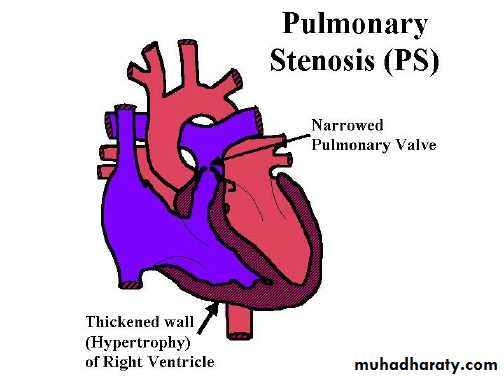
Pulmonary stenosis
Pulmonary stenosis divided anatomically into :• Vulvular ( most common ) .90%
• Supravalvular .
• Subvalvular.
Pathophysiology
Obstruction Rt. Ventricular pressure during systole wall stress severe cases RVH.Pulmonary art. Pressure normal or .
Arterial O2 normal unless VSD or ASD.
Critical pulmonic stenosis in neonate shunt at the foramen ovale
Clinical features
According to severity• Mild : asymptomatic , normal venous pressure , ejection click after 1st heart sound , 2nd heart sounds split , short ejection systolic murmur in pulmornary area .
ECG: normal or mild RVH.
CXR: poststenotic pulmonary arterial dilatation.
ECHO: pr.gradient usually 10-30mmHg
• Moderate : slightly elevated venous pr. , prominent a – wave in jugular pulse, 2nd heart sound split , ejection click, ejection systolic murmur
• CXR: normal or pulm.vascularity .
• ECG: RVH, spiked p-wave.
• ECHO: thickened valve , pr.gradient 30-60 mmHg.
• .
• Severe: Rt.sided failure, hepatic enlargment, periphral edema , venous pr. a-wave , heart enlarged , inaudible pulmonary component of 2nd heart sound , ejection systolic murmur and thrill , no click.
CXR: enlarged heart + pulmonary vascularity.
ECG: RVH, spiked p-wave.
ECHO: valve deformity, RVH.,pr.gradient ≥ 60 mmHg
Treatment
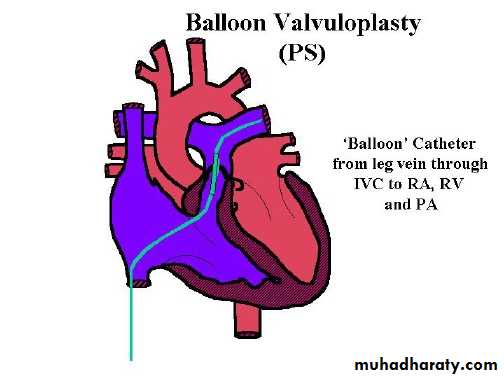
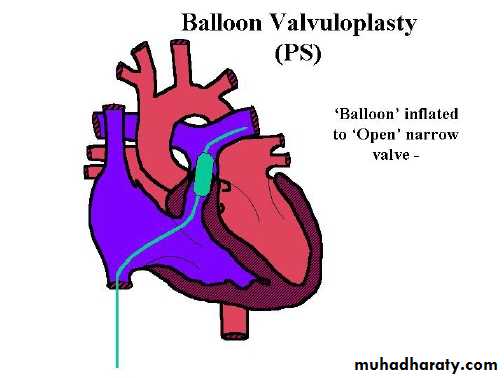
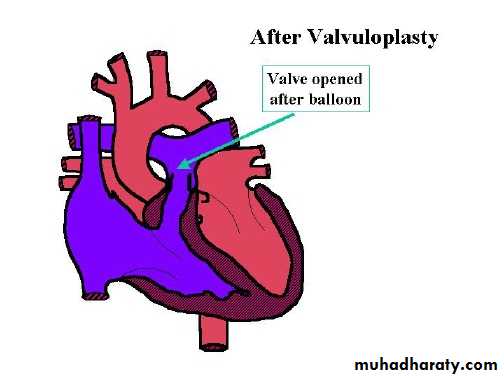
• Mild reassurance .• Moderate or severe balloon valvuloplasty .
• Critical pulmonic stenosis valvuloplasy or surgery.valvutomy
Tetralogy of Fallot
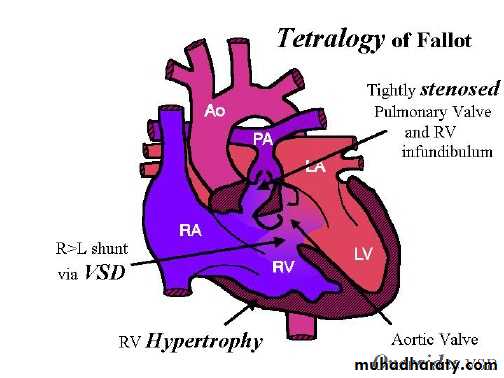
It is the commonest cyanotic heart disease in children , it’s a combination of :-
• Right ventricular outflow obstruction(pulmonary stenosis)• VSD
• Dextroposition of aorta with override of ventricular septum.
• Right ventricular hypertrophy.
RV outflow obstruction : various sites , but most common is infandibular site .
VSD large , non restrictive .Overriding of aorta ( right sided in 20% ).
Clinical featuresTime of onset of symptoms
Severity of cyanosisRV hypertrophy
Depend of the degree of right ventricular outflow obstruction
If mild initially heart failure with age , patient grows infandibular hypertrophy cyanosis develops in 1st year of life .If severe obstruction cyanosis develops immediately after birth .
In older children , long standing dusky blue skin, grey sclera, engorged blood vessels, clubing of fingers & extracardiac manifestation.
Dyspnea on exertion so they stop to take rest or have squatting position.
Growth retardation ( if severe and untreated ) .
Delayed puberty .
O/E
Pulse normalVenous and arterial pressure normal .
Heart size normal .
Lt. hemithorax bulged because of RVH.
Murmur , ejection systolic because of RV outflow obstruction .
Murmur can be holosystolic due to VSD.
The intensity of murmur during spells .
Sometimes continuous murmur due to collaterals.
Diagnosis
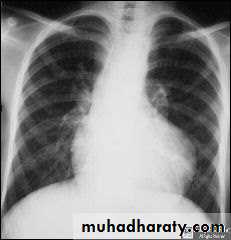
• CXR : boat shaped heart , clear lung field , 20 % right sided aorta .• ECG : RVH , right axis deviation .
• ECHO
• Cardiac cathetarization .
• Selective right ventriculography : important for child as surgical candidate .
• Lt. ventriculography .
• Coronary angiography .
Complications
• Cyanotic spells• Cerebral thrombosis
• Brain abcess
• Infective endocarditis
• Heart failure
Cyanotic spell
Usually at 4-6 mo.Patient restless , cyanosed , gasping , syncop follows .
Mainly after awakening or vigorous exercise .
intensity of the murmur.
Continued for few min.-few hrs .
Followed by generalized weakness , sleep.
Treatment of spell
• Put him on abdomen , knee-chest position.• O2 .
• Morphine ( 0.2mg/kg s.c ) relaxe pulmonary infandibulum and sedate child .
• If severe NaHCO3 to correct acidosis .
• If still resistant phenylephrine or methoxantheme to systemic vascular resistance and Rt. Lt shunt .
Treatment
Medical :
• If severe obstruction medical Rx until surgical intervention.
• Include
• Provide O2 , maintain body temperature .
• Treat and prevent hypoglycemia .
• Start PGE1 infusion
• If less severe obstruction and while await for the surgery observe for the following:
Rx dehydration.
Rx iron deficiency anemia .Inderal 0.5-1 mg/kg 6hr.
Phlebotomy if symptomatic patient and hematocrite > 65%.
Surgical Rx.
2 options : palliativecorrective
Time : 4-12 mo.
Palliative surgery
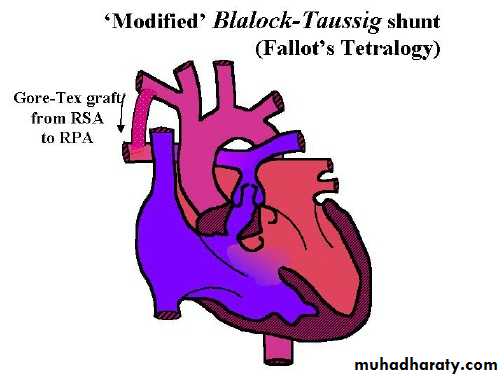
Modified Blalock – Taussing shunt , which a conduit from subclavian artery to homolateral branch of pulmonary art. or directly from ascending art. To main pulmonary artery .
.
With increasing age need for more pulmonary blood flow do corrective surgery or reanastomose on the opposite site
Transposition of great vessels
CCHD with pulmonary blood flow .Either d-TGA or l-TGA.
Either with intact VS or VSD.
Male > female .
50% with VSD .
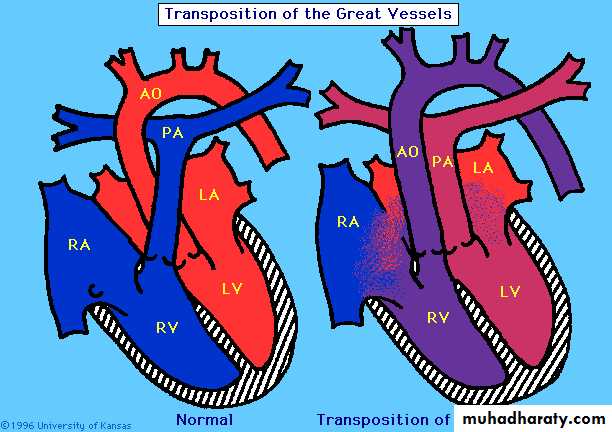
For d- TGA aorta arises from RV and pulmonary art. From LV .
Aorta anterior and to the right of pulmonary art.
C/F: cyanosis & tachycardia .
HF less commonif untreated not survive neonatal period .
Dx
ECG Rt. Sided dominance pattern.
CXR mild cardiomegaly.
Hyperoxia test.
ECHO.
CATHETRIZATION.
Treatment
Infusion of PGE1Protect against hypothermia , Rx acidosis & hypoglycemia .
If no response Rashkind Balloon septostomy then arterial switch operation ( Jantene operation ) within 2 wks.
If TGA&VSD do Rashkind operation.
Extracardiac manifestation of CCHD.
• Polycythemia .• Relative anemia .
• CNS abcess.
• CNS thromboembolic stroke.
• Low grade DIC , thrombocytopenia.
• Hemoptysis .
• Gum disease .
• Gout .
• Arthropathy , COF.
• Infection .
• Pregnancy complications .
• FTT.
• Psychosicial problems .