

Population : all the people living in an
area, frequently of a country.
Common speech
In statistics
Population is any collection of individuals in which
we may interested, where these individuals may be
anything.
Population:
a set which includes all
measurements of interest
to the researcher
(The collection of all
responses, measurements,
or
counts that are of interest)
Sample:
A subset of the population

If we are interested in: population
Characteristics of Iraqi
people
All people in Iraq
Treatment of diabetics all diabetics
ics
Failure rate in 3
rd
year
of college of medicine
Height of males in 3
rd
year of college of
medicine – Baghdad
university



Imagine that we are going to make studies on:
Percentage of Iraqi population that had access to
internet.
The population we would to ask is bigger than
30 million
- Time
-Money
- at time of interview we miss some people
It is better to choose sample in appropriate way
so that we can obtain later conclusion

-
- the selection methods for elements of
population (sampling methods)
-Sample size
-- Reliability degree of the conclusions that we
can obtain, this is, an estimation of an error that
we are going to have (in term of probability).

A sample
A finite part of a statistical population whose
properties are studied to gain information
about the whole
– A set of respondents selected from a larger
population for the purpose of a survey or
experiment.

Sampling
The act, process, or technique of selecting a
suitable sample, or a representative part of a
population for the purpose of determining
parameters or characteristics of the whole
population.

-Random sampling
-Stratified sampling
-Cluster sampling
-Systematic sampling
- other types of sample technique
Probability sampling
Non- probability sampling
-Convenience sampling
- Purposive sampling
- snowball
-Quota sample

Target Population:
The population to be studied/ to which the
investigator wants to generalize his results
Sampling Unit:
smallest unit from which sample can be selected
Sampling frame
List of all the sampling units from which sample
is drawn
Sampling scheme
Method of selecting sampling units from
sampling frame

Probability of being chosen is unknown
Cheaper- but unable to generalise
potential for bias

•
Random sampling
–
Each subject has a known probability of
being selected
•
Allows application of statistical
sampling theory to results to:
–
Generalise
–
Test hypotheses

•
Probability samples are the best
•
Ensure
–
Representativeness
–
Precision

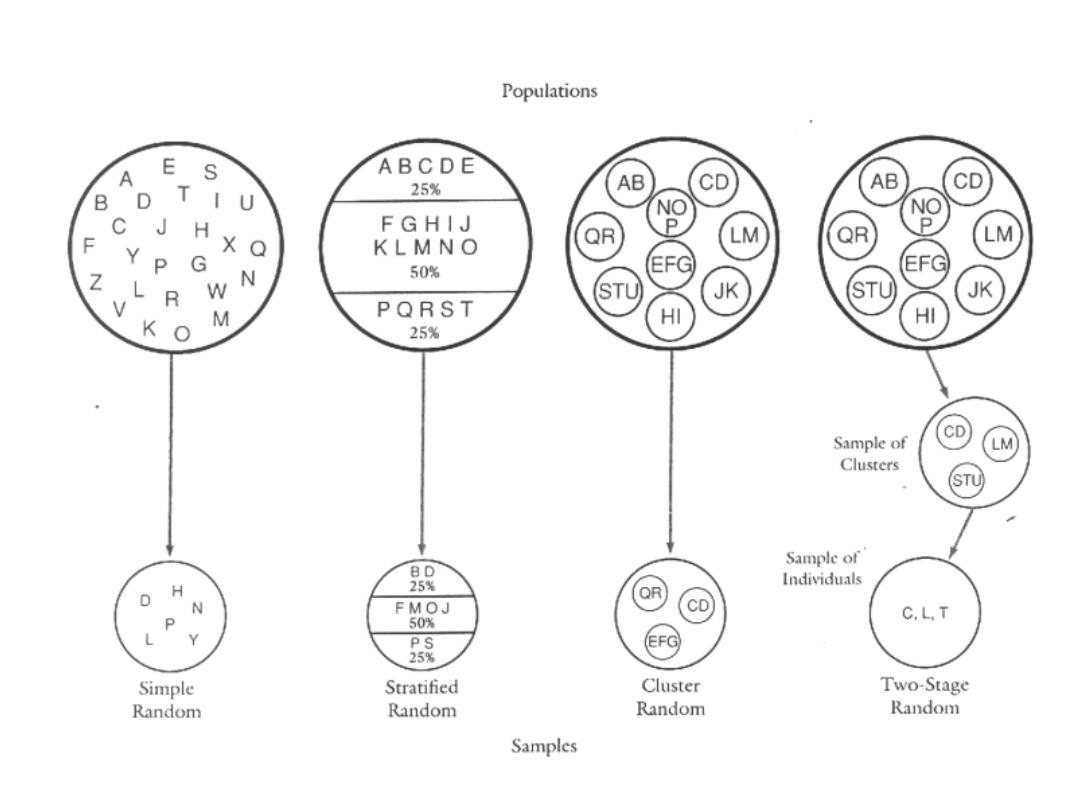
Simple random sample:
It requires:
Sample frame: a numerical list of all
observations (or units) composing the
population
Sample fraction: sample size to the total
population
Lottery method
Computer generated random sampling
Random number table (random digit)
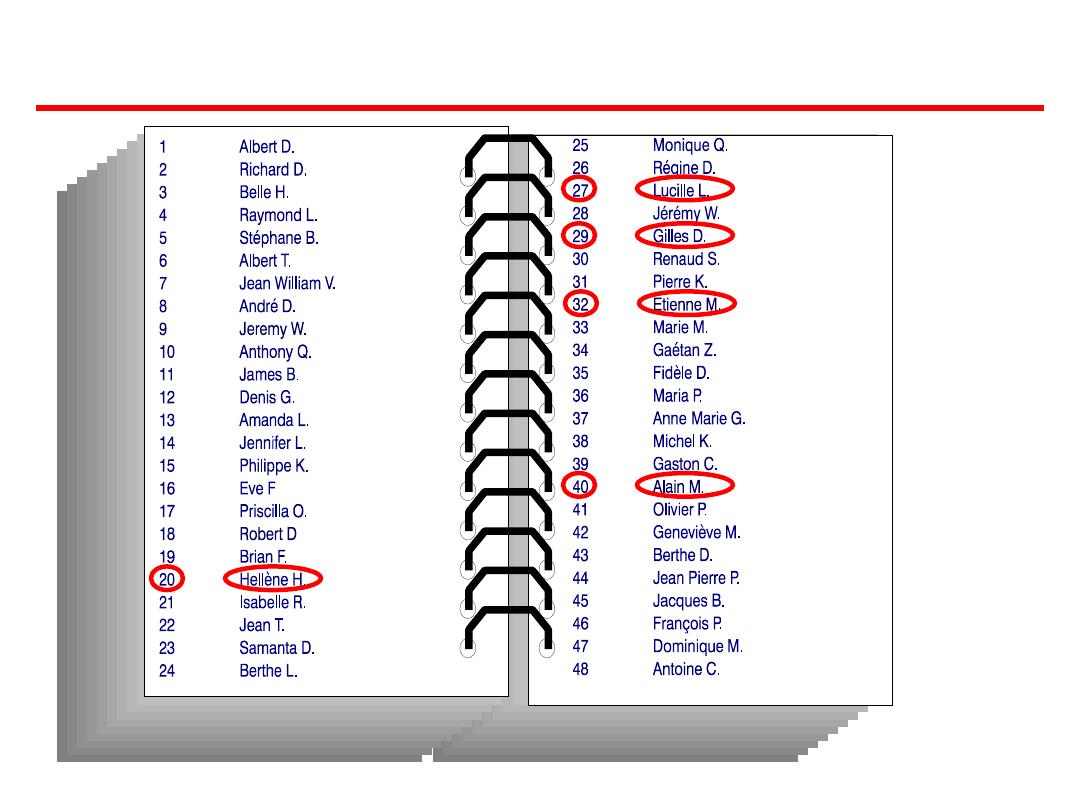
Simple random sampling

Systematic random sampling – samples
according to a rule
E.g., every fifth person is chosen
Problems: same as simple random. Rule
must not lead to bias.
Systematic sampling
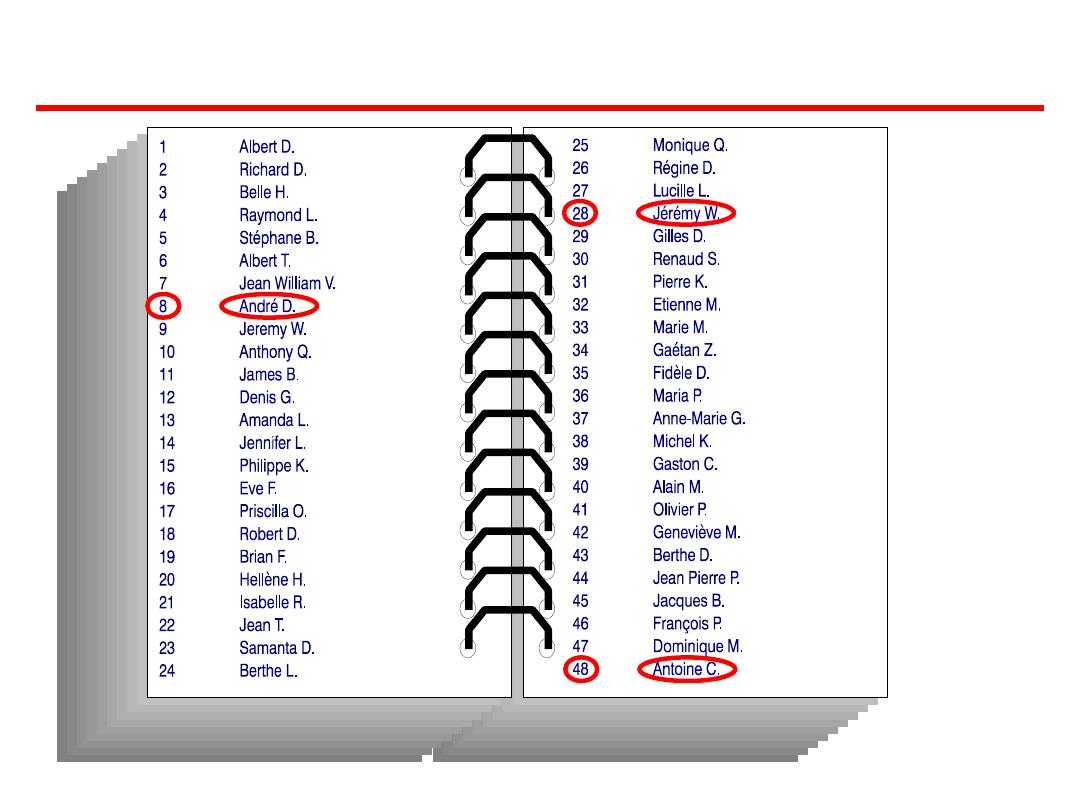
Systematic sampling

Cluster: a group of sampling units close to each
other i.e. crowding together in the same area or
neighborhood
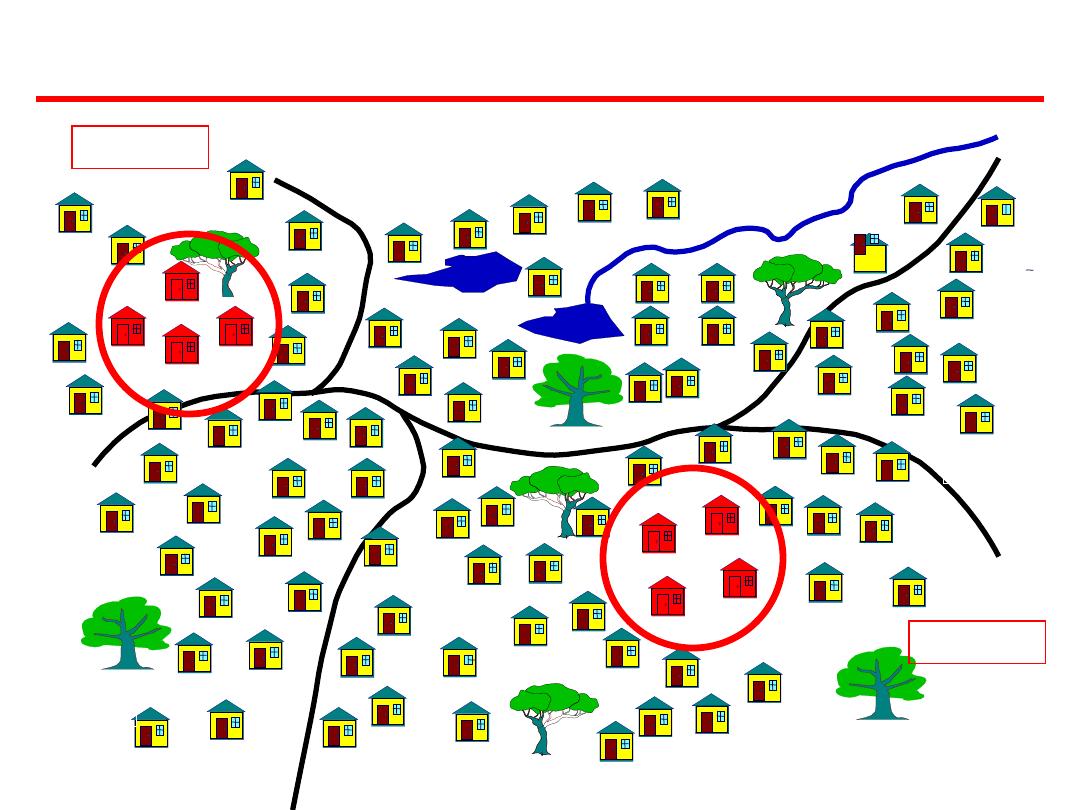
Section
4
Section 5
Section 3
Section 2
Section 1
Cluster sampling

Stratified sampling
Multi-stage
sampling
Stratified sampling
– break the sample
into various subgroups or strata and
sample from them.
Must have good knowledge of strata

Qualitative researchers are not as concerned
about representativeness
Relevance to the research topic
Importance of context
Sample size does not have to be determined
in advance.
Selection of cases gradually over time
Important: many statistics assume random
sampling

Types of nonprobability sampling
Convenience sampling (haphazard,
accidental) – sample whoever is available.
Used by both quantitative and qualitative
researchers
Problems
no representativeness
It is haphazard, can be very biased
Not random (avoid using word)

Purposive sampling - Use judgment and
deliberate effort to pick individuals who
meet a specific criteria.
Especially good for exploratory or field
research.
Appropriate for at least 3 situations.
1. select cases that are especially informative.
E.g., college coaches and championships
2. desired population for the study is rare or
very difficult to locate.
E.g., prostitutes
3. case studies analysis – find important
individuals and study them in depth.

Purposive sampling - Use judgment and
deliberate effort to pick individuals who
meet a specific criteria.
Especially good for exploratory or field
research.
Appropriate for at least 3 situations.
1. select cases that are especially informative.
E.g., college coaches and championships
2. desired population for the study is rare or
very difficult to locate.
E.g., prostitutes
3. case studies analysis – find important
individuals and study them in depth.

Systematic error (or bias)
Inaccurate response (information bias)
Selection bias
Sampling error (random error)
Errors in sample
