Nutritional Therapy for GIT
Disorders

Objectives
•
Nice to know pathophysiology,
•
Must know MNT of celiac disease, lactose
intolerance, acute hepatitis.

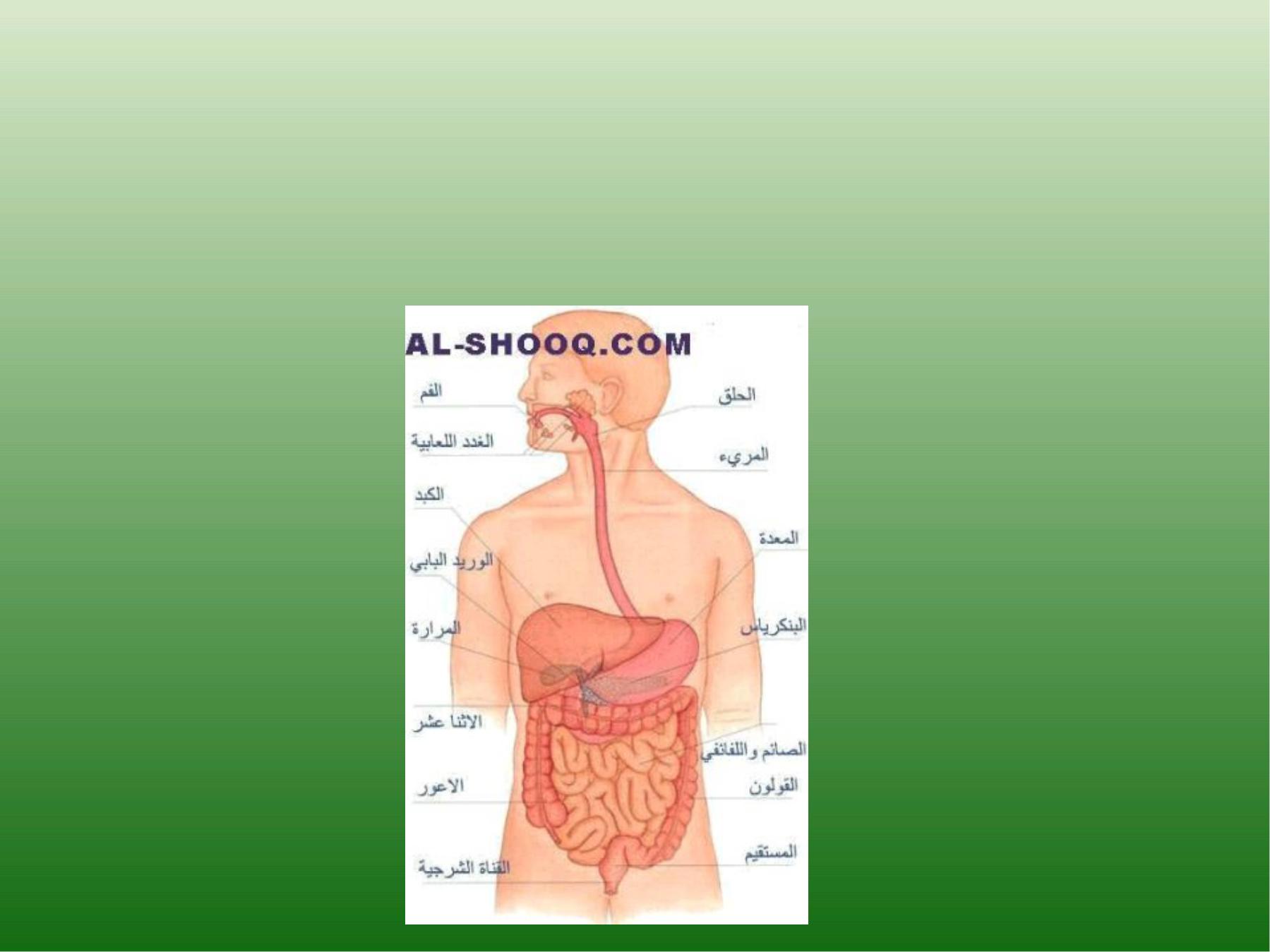
Celiac Disease (Gluten-Sensitive
Enteropathy)
Is a chronic disease that damages the mucosa
of SI, esp. duod.& proximal jejunum.
In milder disease there is damage of microvilli
on villi which decrease the absorptive surface
area by 2 folds.
In severe cases the villi become blunted or
disappear altogether.
The exact mechanism remain unknown, but
main possible cause of villi damage is by
gliadin (protein fraction of gluten) which found
in grains of wheat, oat, barley.

•
It result in diarrhea, steatorrhea, flatulence,
abdominal distention, wt. loss & weakness.
•
In early stage; fat mal absorption is more typical
( idiopathic steatorrhea).
•
In more severe cases the digestion &
absorption of protein, CHO, Ca, vit.K, folate, B
12
&other nutrients becomes impaired.
•
Result in severe nutritional deficiencies, wt. loss,
osteomalacia, inadequate blood coagulation,
macrocytic anemia of pernicious anemia (B
12
&
folate mal absorption).

MNT of CD:
Ø
Avoid gluten containing foods & products
made from these foods; bread, crackers,
cereals, pastas, malt flavoring, bargala
ﺑﺮﻏﻞ
,
commercial white cream sauce, cake,
pastries, commercial ice cream, chocolates,
ketchup,& other processed foods (check
ingredients on the label) ----.
Ø
The allowed foods; rice, potatoes, soy
protein, meat substitutes, fresh meats, fish
and eggs, fresh milk ,fresh fruits&
vegetables, tea, coffee, sugar.
Ø
All foods should be made at home.

Lactose Intolerance
•
The most common disaccharidase disorder
is lactase deficiency (intestinal brush border
enzyme that hydrolyzes lactose to glucose & galactose).
•
Undigested lactose remaining in intestine will draw
water into digestive tract causing abdominal cramps,
flatulence, & diarrhea.
•
The severity of the symptoms depends on; amount of
lactose ingested & the degree of intolerance.
•
It affect more than half of adults around the world.
•
S.t. it is secondary to or accompanies acute or
chronic diseases that damage the intestine; gluten-
sensitive enteropathy ,Crohn’
s disease, or patient
have small bowel or gastric surgery or excessive use
of parenteral nutrition (atrophy of SI).

MNT of lactose intolerance;
•
Suspected case of lactose intolerance needs to
establish patient tolerance by gradual adding of small
amount of lactose containing foods to a lactose free
diet.
•
Most people can tolerate 5-8gm lactose (1-2 cups of
milk). Better tolerated if given with other foods &
distributed throughout the day.
•
Yogurt, cocoa & chocolate milk may be better
tolerated than milk.
•
Lactase enz. is available as lactaid, lactrase, &dairy
Ease may be added to milk 24h before ingestion.

•
Tablet contains lactase is available can be
ingested just before eating a meal (1/2 -3
tab.) depending on the degree of intolerance.
•
Restricting lactose containing foods place the
person at risk of Ca, riboflavin, &V.D def.
These nutrients can be provided at RDA by
use lactase enz. –treated milk &milk products,
with supplementation.
Nutritional Therapy In Liver Diseases
For patient with acute &
chronic liver dis.
There is –ve NB, which
lead to muscle wasting.
Acute hepatitis:
Infectious mononucleosis,
cirrhosis, toxic chemicals, viral Infection(nausea,
fever, liver
tenderness& enlargement,
jaundice, anorexia, coma).

MNT for Acute Hepatitis:
No medication to treat hepatitis,
bed rest & proper nutrition are the major therapy;
ü
Hydration (i.v.), then initiate oral feeding& liquid diet.
ü
Fluid 2500-3000ml/d.
ü
Small frequent meals.
ü
High in calories(3000-4000Kcal).
ü
High quality protein(100-150gm=1.5-2g/kg).
ü
CHO not <40% of total calories to promote glycogen
synthesis& spare protein.
ü
Fat: not limited (as tolerated).
ü
Multivitamin supplementation; V.B. comp.(B
1
&B
12
),V.K
( to normalize bleeding tendency), V.C, zinc for poor
appetite.
