
Dr. Ali A. Allawi
Lec. 1
Fluid and Electrolyte
Imbalances
Thurs 20 / 11 / 2014
Published by : Ali Kareem
5102
-
5102
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
2
Fluid & electrolyte imbalances
Objectives :
1. Body fluid compartment
2. Fluid balance or homeostasis
3. Movements of fluid
4. Regulation of body water
Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
3
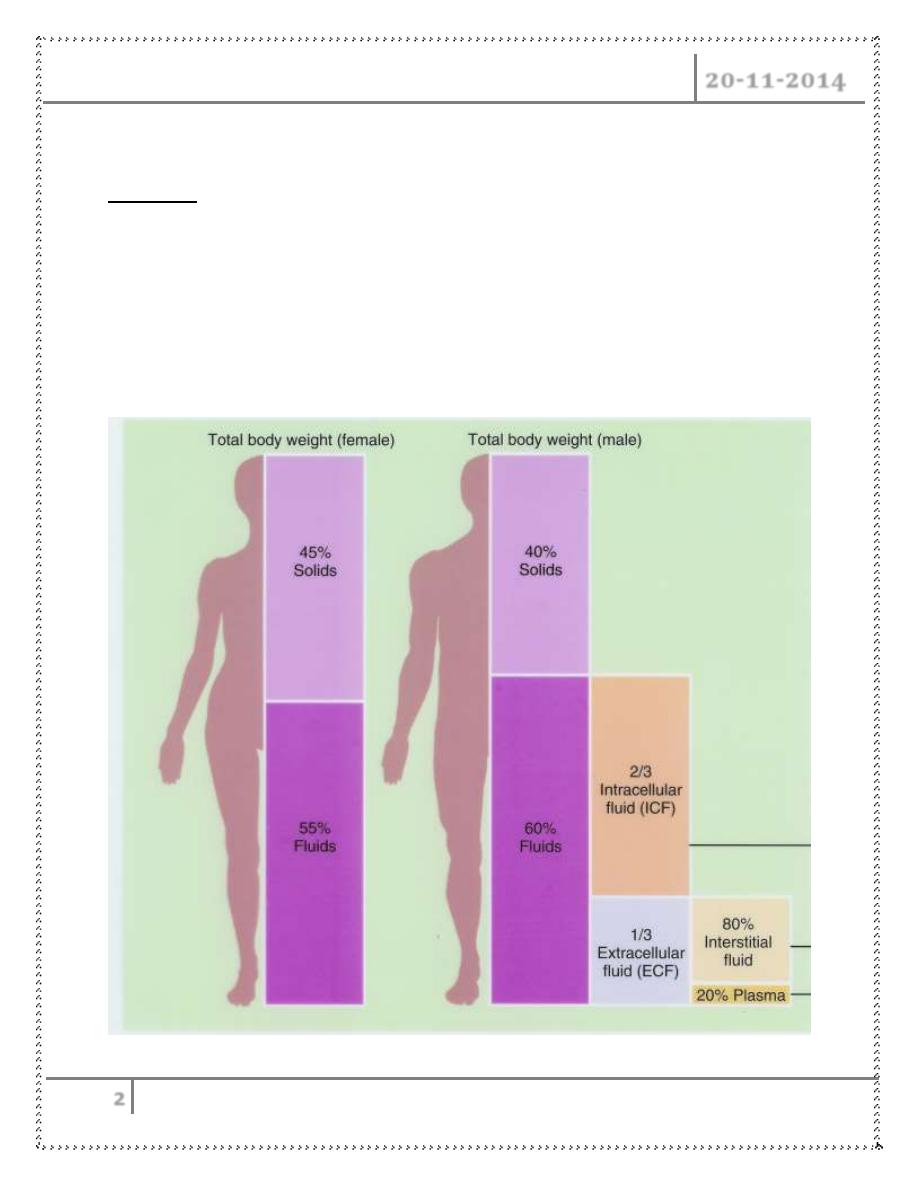
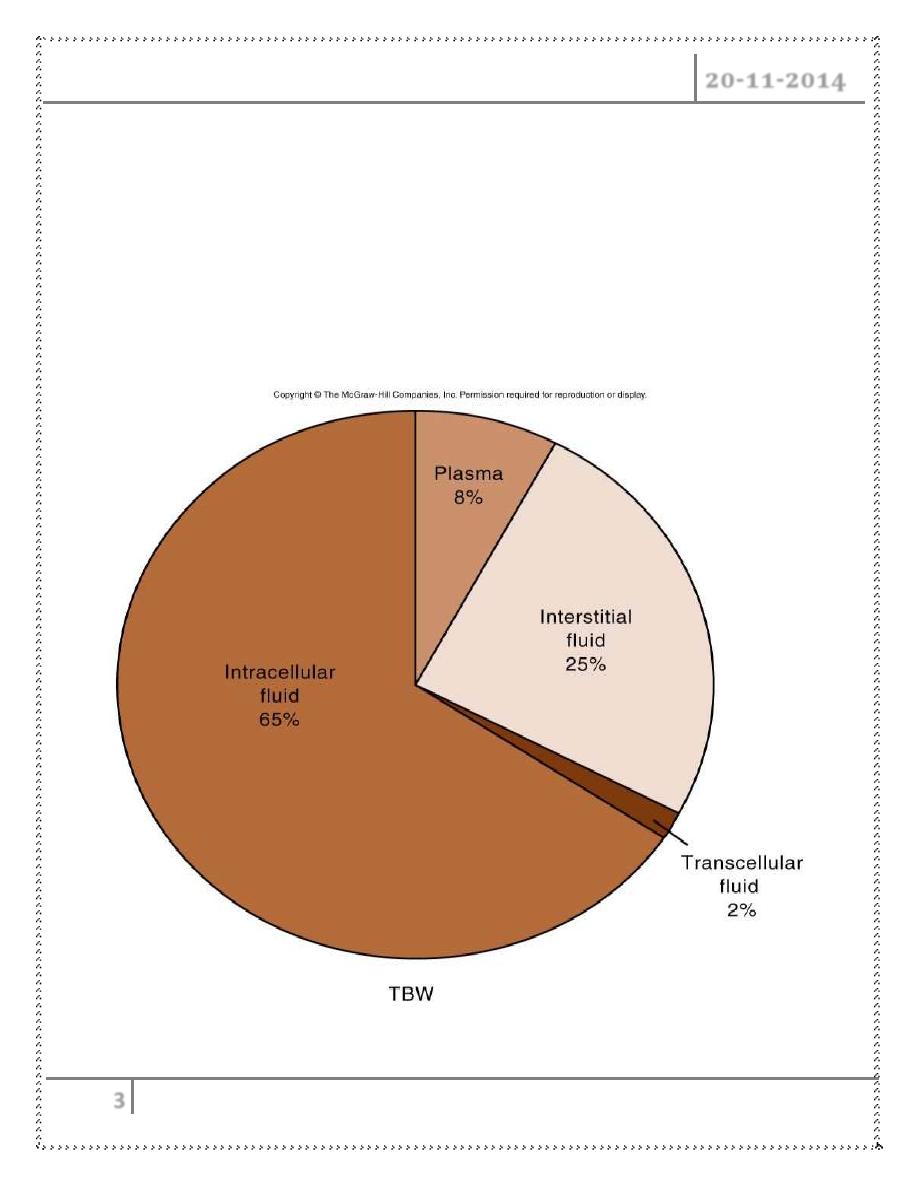
Body Fluid Compartments :
• 2/3 (65%) of TBW is intracellular (ICF)
• 1/3 extracellular water
– 25 % interstitial fluid (ISF)
– 5- 8 % in plasma (IVF intravascular fluid)
– 1- 2 % in transcellular fluids – CSF, intraocular fluids, serous
membranes, and in GI, respiratory and urinary tracts (third space)
Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
4
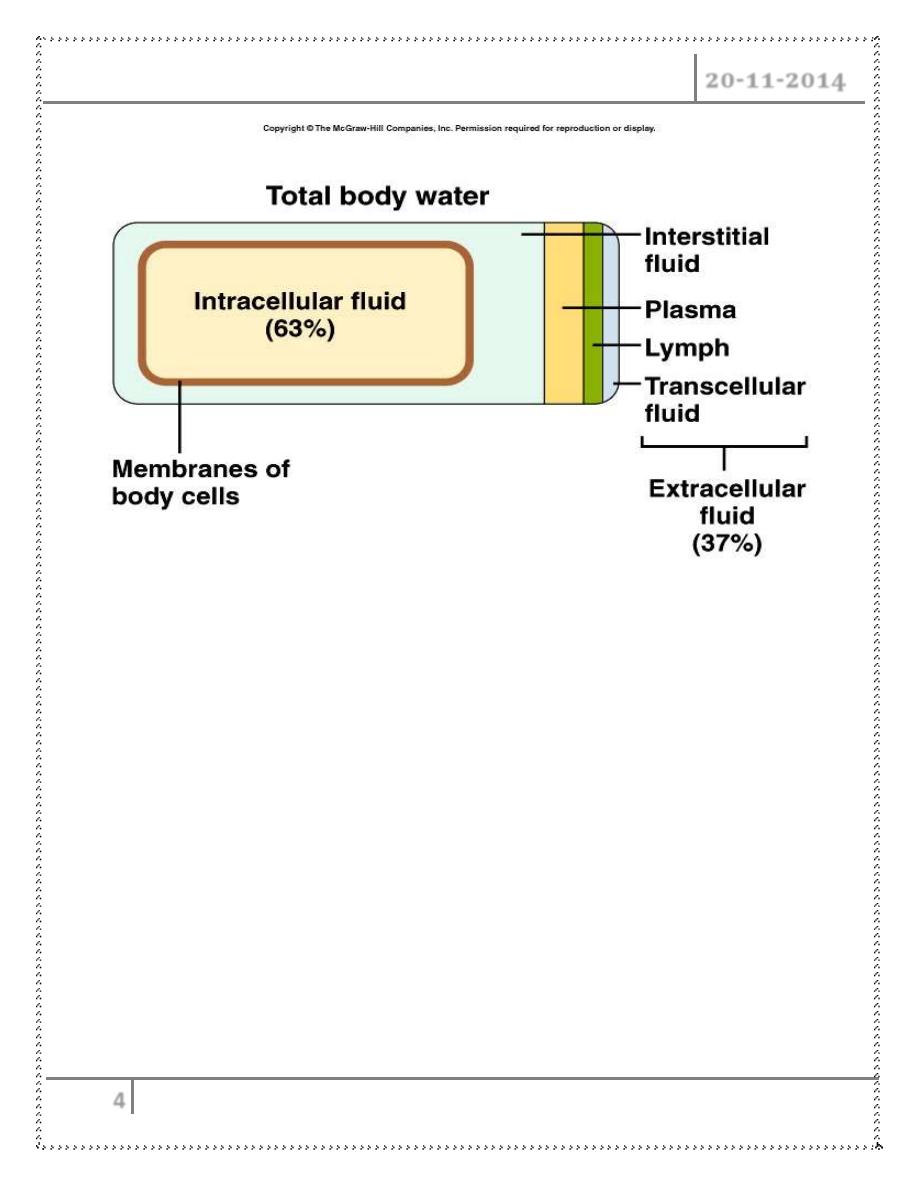
• Fluid compartments are separated by membranes that are freely permeable
to water.
• Movement of fluids due to :
– hydrostatic pressure
– osmotic pressure
• Capillary filtration (hydrostatic) pressure
• Capillary colloid osmotic pressure
• Interstitial hydrostatic pressure
• Tissue colloid osmotic pressure
Balance
• Fluid and electrolyte homeostasis is maintained in the body
Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
5
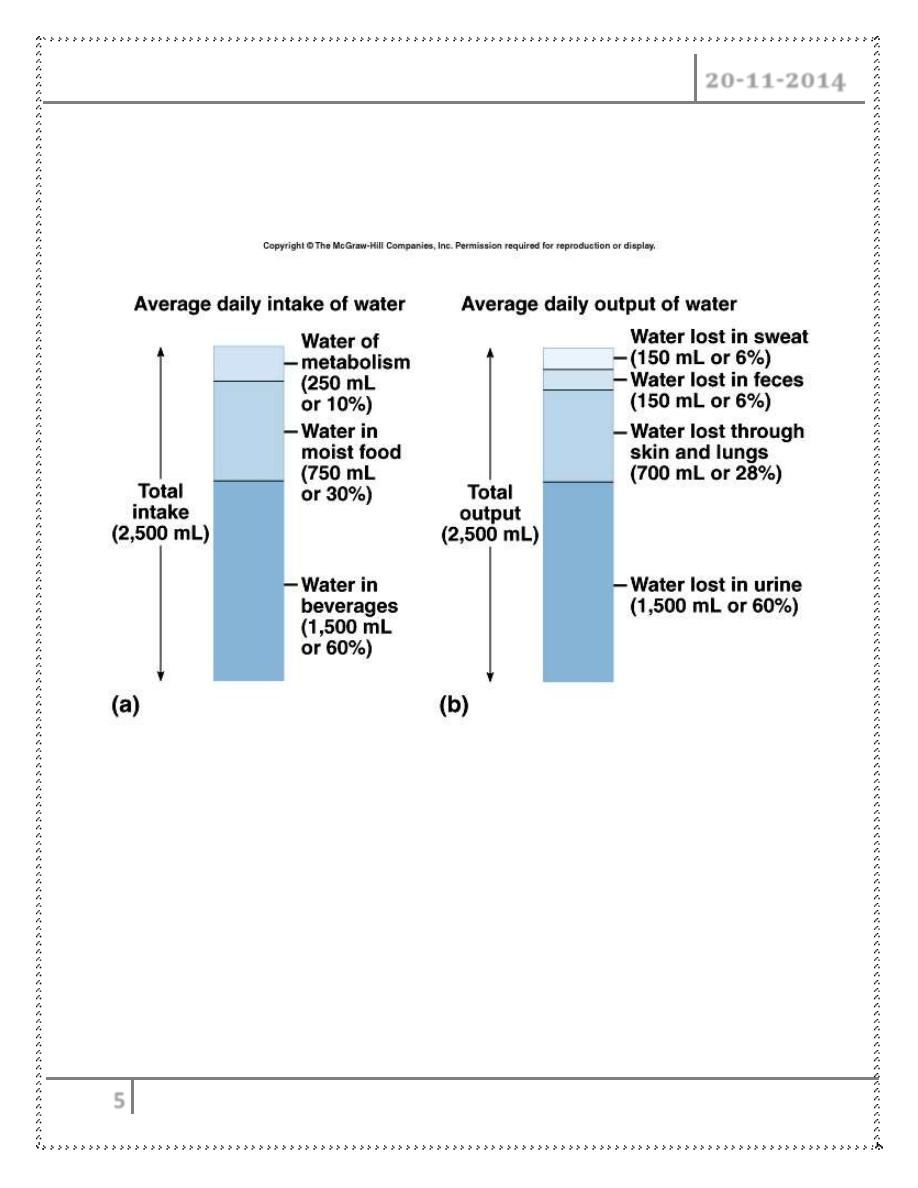
• Neutral balance: input = output
• Positive balance: input > output
• Negative balance: input < output
Solutes – dissolved particles
• Electrolytes – charged particles
– Cations – positively charged ions
• Na
+
, K
+
, Ca
++
, H
+
– Anions – negatively charged ions
• Cl
-
, HCO
3
-
, PO
4
3-
• Non-electrolytes - Uncharged

Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
6
• Proteins, urea, glucose, O
2
, CO
2
Body fluids are :
– Electrically neutral
– Osmotically maintained
Specific number of particles per volume of fluid
Homeostasis maintained by :
• Ion transport
• Water movement
• Kidney function
MW (Molecular Weight) = sum of the weights of
atoms in a molecule
mEq (milliequivalents) = MW (in mg)/ valence
mOsm (milliosmoles) = number of particles in a
solution
Tonicity
- Isotonic - Hypertonic - Hypotonic
Movement of body fluids
“ Where sodium goes, water follows.”
Diffusion : movement of particles down a concentration gradient.
Osmosis : diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane.
Active transport : movement of particles up a concentration gradient ;
requires energy.

Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
7
ICF to ECF – osmolality changes in ICF not rapid
IVF → ISF → IVF happens constantly due to changes in fluid pressures and
osmotic forces at the arterial and venous ends of capillaries
Regulation of body water :
• ADH – antidiuretic hormone + thirst
– Decreased amount of water in body
– Increased amount of Na+ in the body
– Increased blood osmolality
– Decreased circulating blood volume
• Stimulate osmoreceptors in hypothalamus
ADH released from posterior pituitary → Increased thirst
Result :
increased water consumption
increased water conservation
Increased water in body → increased volume and decreased Na+
concentration
Dysfunction or trauma can cause :
Decreased amount of water in body
Increased amount of Na
+
in the body
Increased blood osmolality
Decreased circulating blood volume
Edema : is the accumulation of fluid within the interstitial spaces.

Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
8
Causes :
Increased hydrostatic pressure
Lowered plasma osmotic pressure
Increased capillary membrane permeability
Lymphatic channel obstruction
Hydrostatic pressure increases due to :
Venous obstruction :
– Thrombophlebitis (inflammation of veins)
– Hepatic obstruction
– Tight clothing on extremities
– Prolonged standing
Salt or water retention
– congestive heart failure
– renal failure
Decreased plasma osmotic pressure :
↓ plasma albumin (liver disease or protein malnutrition)
plasma proteins lost in :
– Glomerular diseases of kidney
– Hemorrhage, burns, open wounds and cirrhosis of liver
Increased capillary permeability :
Inflammation
Immune responses
Lymphatic channels blocked :
Surgical removal
Infection involving lymphatics
Lymphedema

Fluid & Electrolyte Imbalances Dr. Ali A. Allawi
20-11-2014
9
Fluid accumulation :
Increases distance for diffusion
May impair blood flow
= slower healing
increased risk of infection
pressure sores over bony prominences
Psychological effects
Edema of specific organs can be life threatening (larynx, brain, lung)
Water is trapped, unavailable for metabolic processes , can result in dehydration
and shoc. (severe burns)
Done by
Ali Kareem
