
Dr. Ali A. Allawi
Lec. 4
Acid-base balance &
acid-base disturbance
Wed
3 / 12 / 2014
Published by : Ali Kareem
5102
-
5102
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ

Acid-base balance and
acid-base disturbance

I.
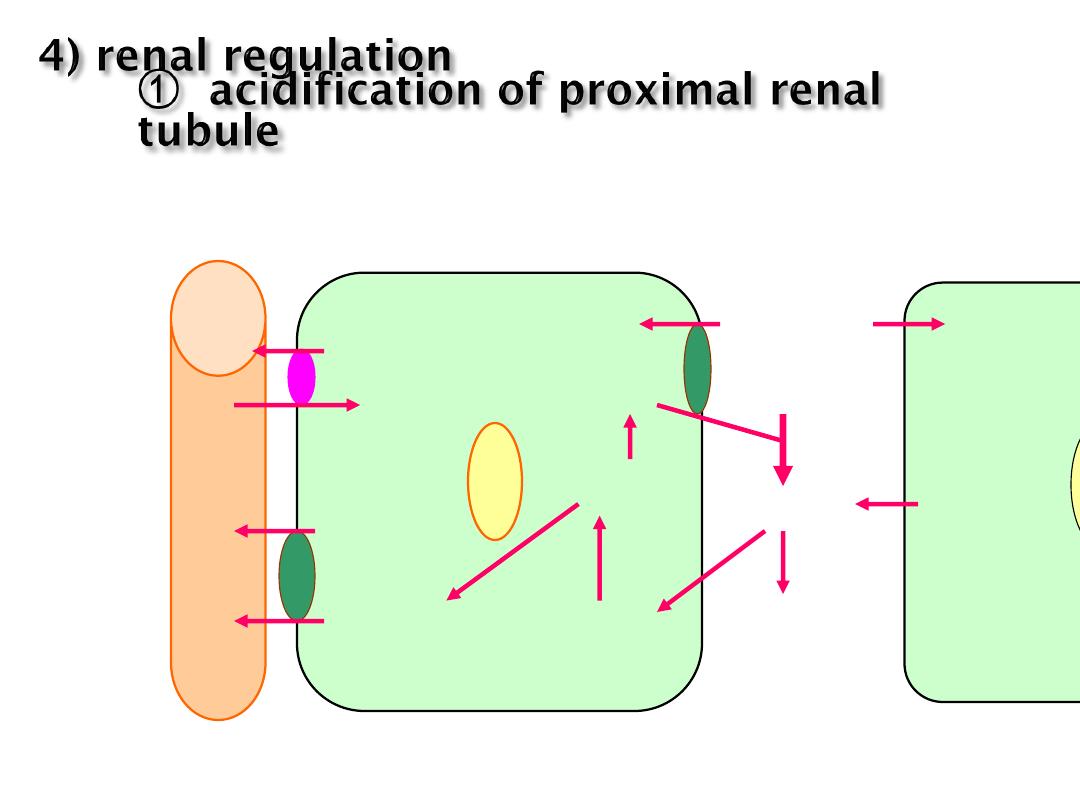
regulation of acid-base balance
1. origin of acid and base in the body
volatile acid: H
2
CO
3
(15mol/day)
sulfuric acid
1) acids phosphoric acid
fixed acid: uric acid
(90mmol/L) mesostate
2) base: salt of organic acid; NH
3
2. regulation of acid-base balance
1) role of buffer
HCO
-
3
/H
2
CO
3
53%
Hb
-
/HHb
buffer system HbO
-
2
/HHbO
2
35%
Pr
-
/HPr 7%
Phosphate 5%
Henderson-Hasselbalch
pH = pKa + lg [HCO
-
3
]/[H
2
CO
3
]
= 6.1 + lg 20/1 = 6.1 + 1.3 =7.4
buffer of fixed acid: HCO
-
3
/H
2
CO
3
buffer of volatile acid: Hb
-
/HHb
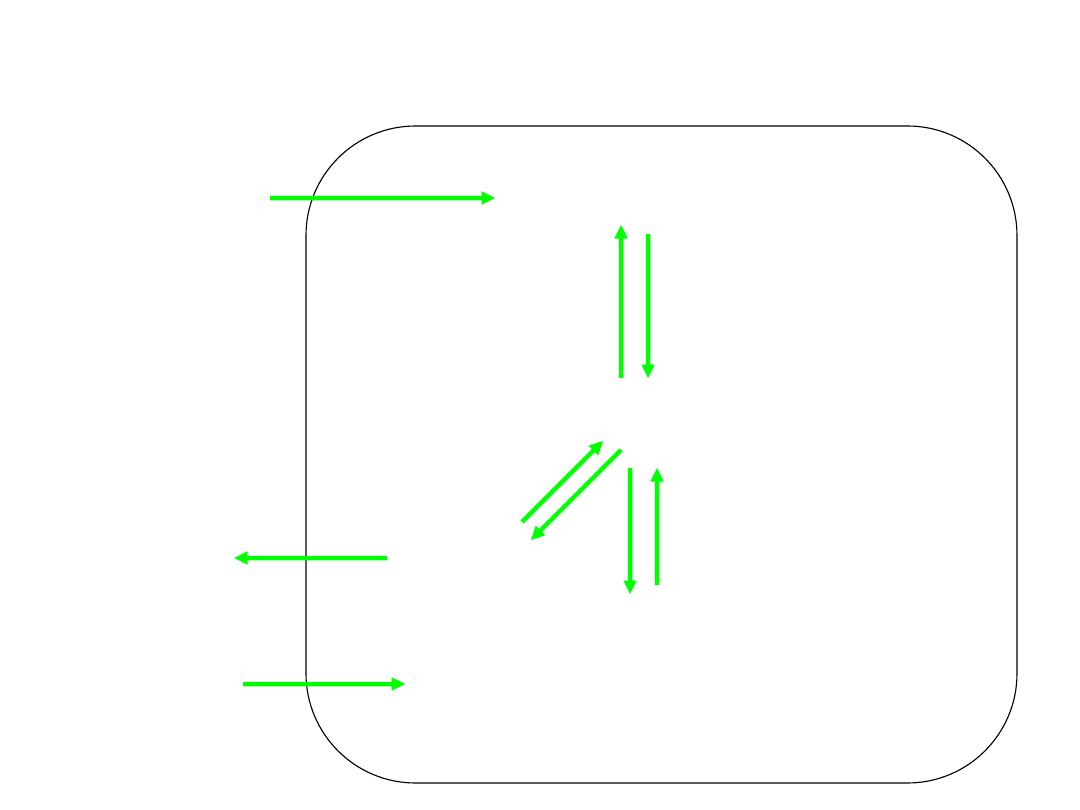
CO
2
Cl
-
CO
2
+H
2
O
C.A.
H
2
CO
3
HCO
-
3
H
+
--Hb
-
RBC
2)
respiratory regulation
alteration of ventilation
alteration of breathe out of CO
2
PaCO
2
central
[H
+
] peripheral respiration
PaO
2
(receptor)
PaCO
2
(>80mmHg)
inhibition of respiratory center
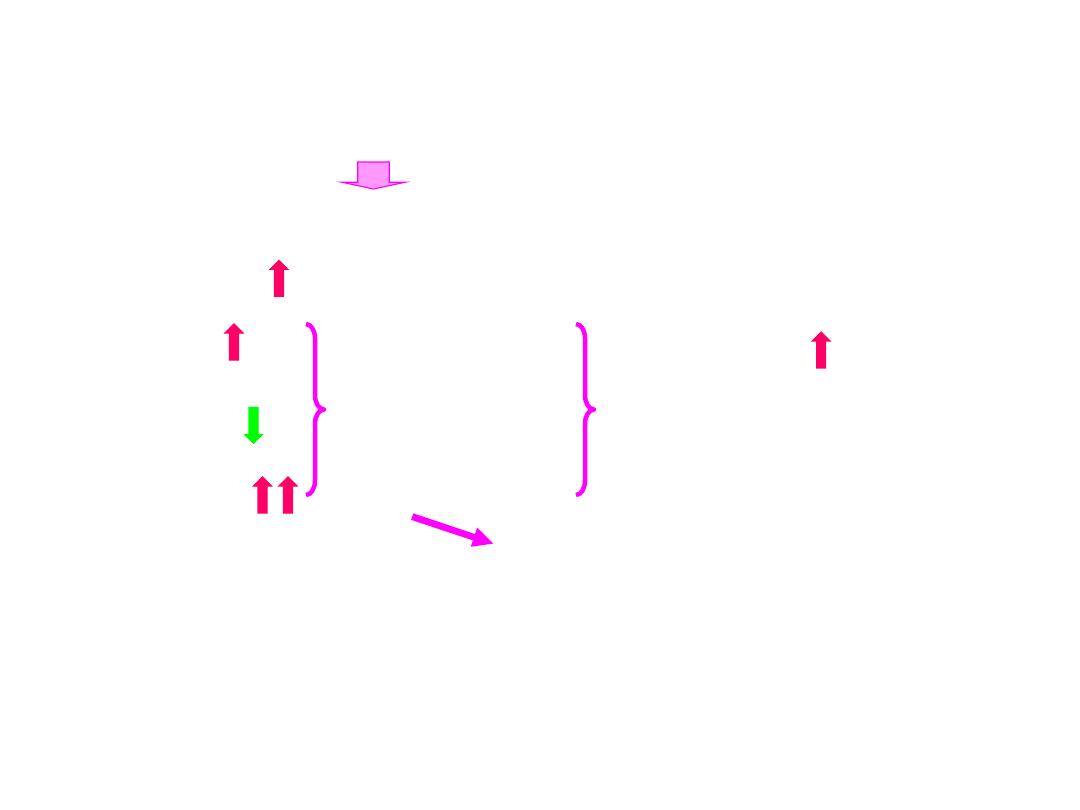
3) cellular action exchanges of H
+
and K
+
Na
+
Cl
-
HCO-
3
H
2
CO
3
H
2
0
K
+
NH
3
Na
+
H
+
H
2
CO
3
Na
+
C.A
.
HCO
-
3
H
2
O+CO
2
②
acidification of distal renal tubule
H
+
-pump
NH
+4
H
2
CO
3
H
+
NH
3
HCO
-
3
H
2
O+CO
2
K
+
Ⅱ.
parameters of acid-base
1. pH important and inexact parameter
normal range: 7.35~7.45
2. PaCO
2
partial pressure of CO
2
of dissolved
in arterial plasma (respiratory parameter)
normal range: 4.4~6.25kPa(33~46mmHg)
primary change:
respiratory acidosis PaCO
2
respiratory alkalosis PaCO
2
secondary change:
metabolic acidosis PaCO
2
metabolic alkalosis PaCO
2

3. standard bicarbonate(SB)
and actual bicarbonate(AB)
SB: [HCO
-
3
] in plasma under standard condition
(38℃; PO
2
=150mmHg; PCO
2
=40mmHg)
AB: [HCO
-
3
] in plasma under actual condition
Normal range: 22~27mmol/L ; AB=SB
4. buffer base(BB)
sum of all buffer base in blood
normal range: 45 ~ 55mmol/L
5. base excess(BE)
normal range: ±3mmol/L
6. anion gap (AG)
+
-
Normal range: 12 ± 2 mmol/L
Na
+
Cl
-
AG
HCO
-
3
Ⅲ
. simple acid-base disturbance
1. metabolic acidosis
concept: the primary disturbance is a decrease
of [HCO
-
3
] in the arterial plasma
1) cause and pathogenesis
lactic acidosis: hypoxia, diabetes
liver disease
ketoacidosis: diabetes, starvation
①
metabolic
acidosis in severe renal failure: fixed acids
increased AG
salicylic acid acid
poisoning: intake food
diarrhea;
GI: intestinal suction
(loss of intestinal fistula
HCO
-
3
) biliary fistula
② metabolic
acidosis in early renal failure:
normal AG NH
3
secretion
H
+
secretion
Renaltubular acidosis:
H
+
secretion
kidney: depressant of C.A.
(loss of acetazolamide
HCO
-
3
) intake of Cl
-
NaCl, NH
4
Cl
Hyperkalemia
2) compensatory regulation
① buffer:
② respiratory compensation
③ cellular compensation
④ renal compensation
[H
+
] : C.A. H
+
secretion
NH
3
secretion
[HCO
-
3
] / [H
2
CO
3
] = 20:1 compensation
acidosis
[HCO
-
3
] / [H
2
CO
3
] < 20:1 decompensation
acidosis
3) effect on body
①
cardiovascular system
hyperkalemia arrhythmia
[H
+
] : contractility
peripheral resistance
②
central nervous system
[H
+
] ATP , γ-amino butyric acid
(somnolence, coma)
4) principles of treatment
