Autoimmune Diseases
and
Allergy
1

Learning Objectives
To define: Inflammatory response (IR),
immunological tolerance (IT), Autoimmune
disease(AID), Allergy
To list type, C/P, practical examples of IR
To List Predisposing factors ,Classification of
HSD, C/P, Ix of (AID)
To list R/F, C/P, IX, Mx of patients with Allergy
To Give Summary
Quiz
3

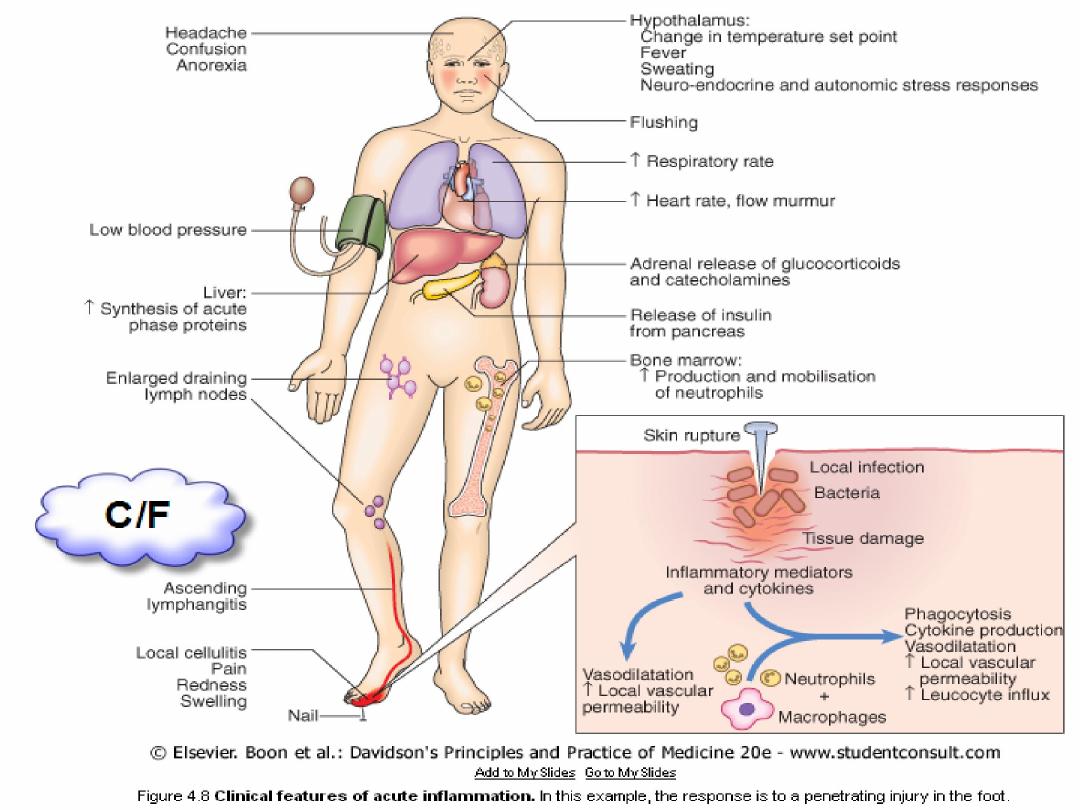
Inflammatory Response:
is response of tissues to injury or infection
Types:
1.
Acute Inflammation
Is a rapid
Classical C/F: pain, swelling, hotness, redness,
4
5

1)Acute phase proteins
:
Produced by the liver
Include: C-reactive protein (CRP)
Serum amyloid A
Fibrinogen
α
1
-antitrypsin and α
1
-antichymotrypsin
Haptoglobin (antioxidant)
Transferrin, ferritin and lactoferrin (iron-
binding proteins )
6

2)Resolution of inflammation
repair of damaged tissues
3) Sepsis and Septic shock
is C/M of severe inflammation
Most frequently caused by
Gram-negative
bacterial infection.
Multi-organ failure, and often death
7

2)chronic Inflammation
local deposition of fibrous connective tissue
(
granuloma
)
characteristic of infections such as
tuberculosis
and leprosy
8
9

Immunological tolerance
Ability of immune system to distinguish self tissue
from foreign tissue.
Failure
of
tolerance
mechanisms-----------
autoimmune disease.
10

Auto-immune disease:
Immune response against self-targets
Major cause of chronic morbidity and disability
Affecting up to 1 in 30 adults.
11

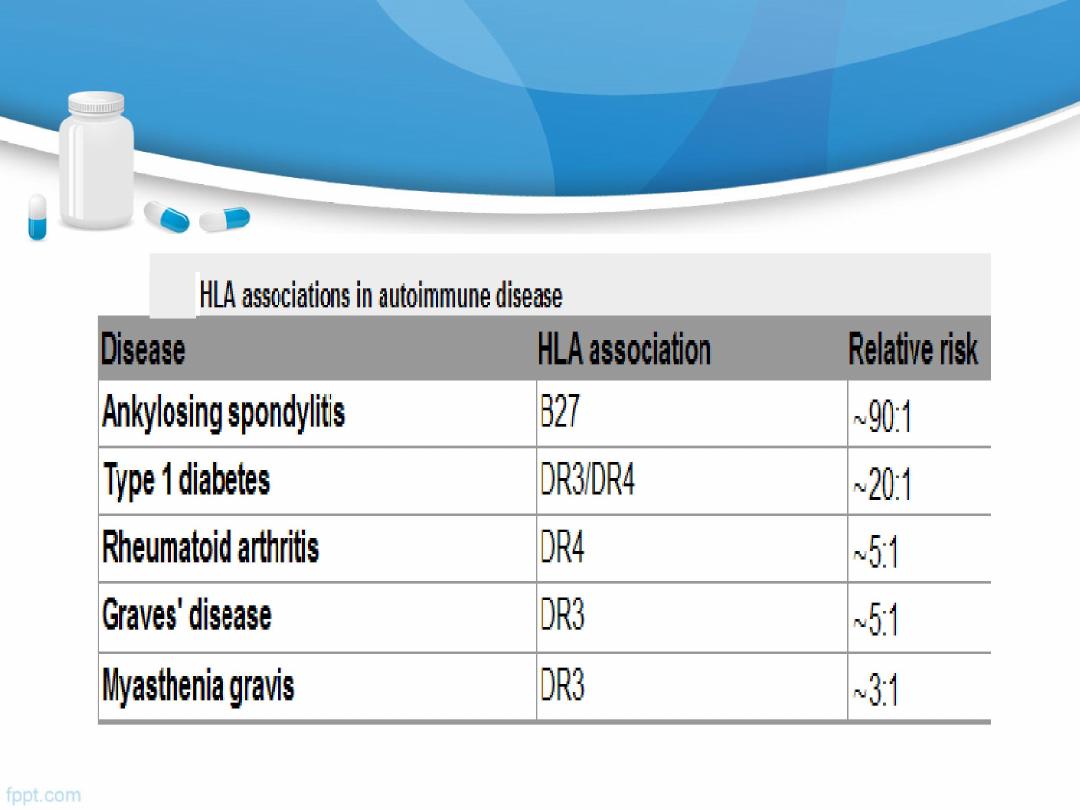
Factors predisposing to autoimmune disease
1.
Genetic :
HLA genes
2.
Environmental
:
infection- as acute rheumatic fever, reactive
arthritis
Drug: anaesthetic agent halothane
3.
Unclear
reasons: much more common in
women
than in men.
12
13
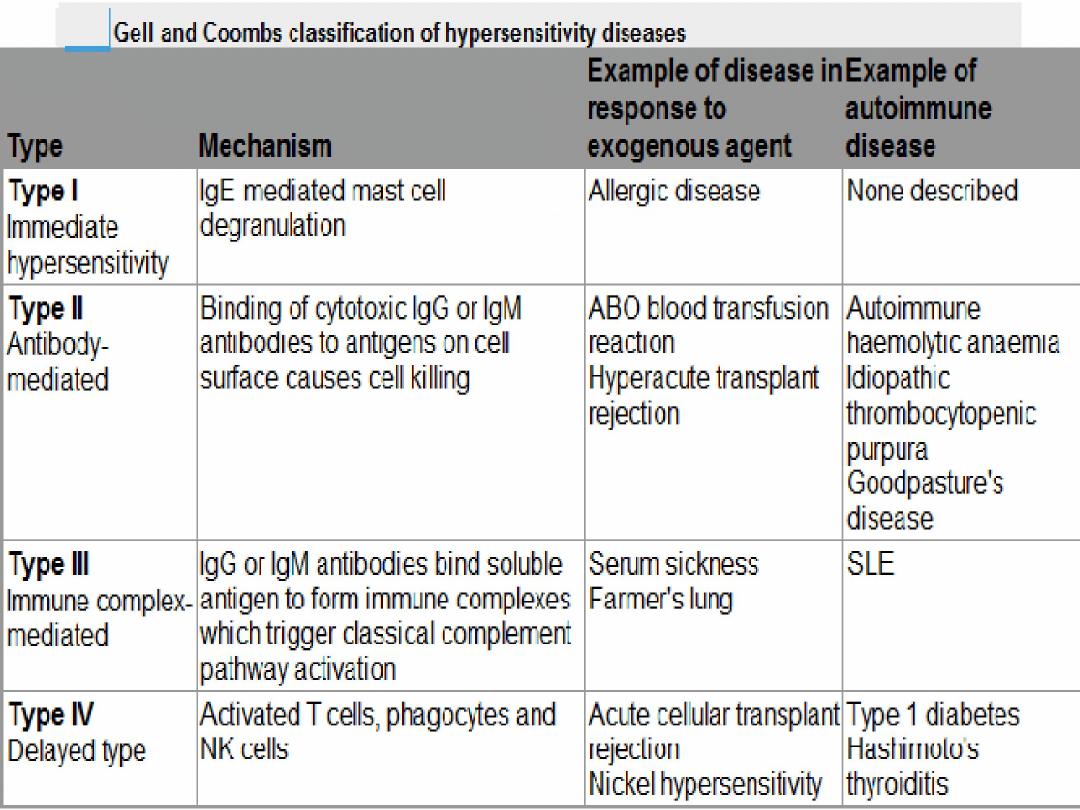
Classification Of Hypersensitivity Diseases
14

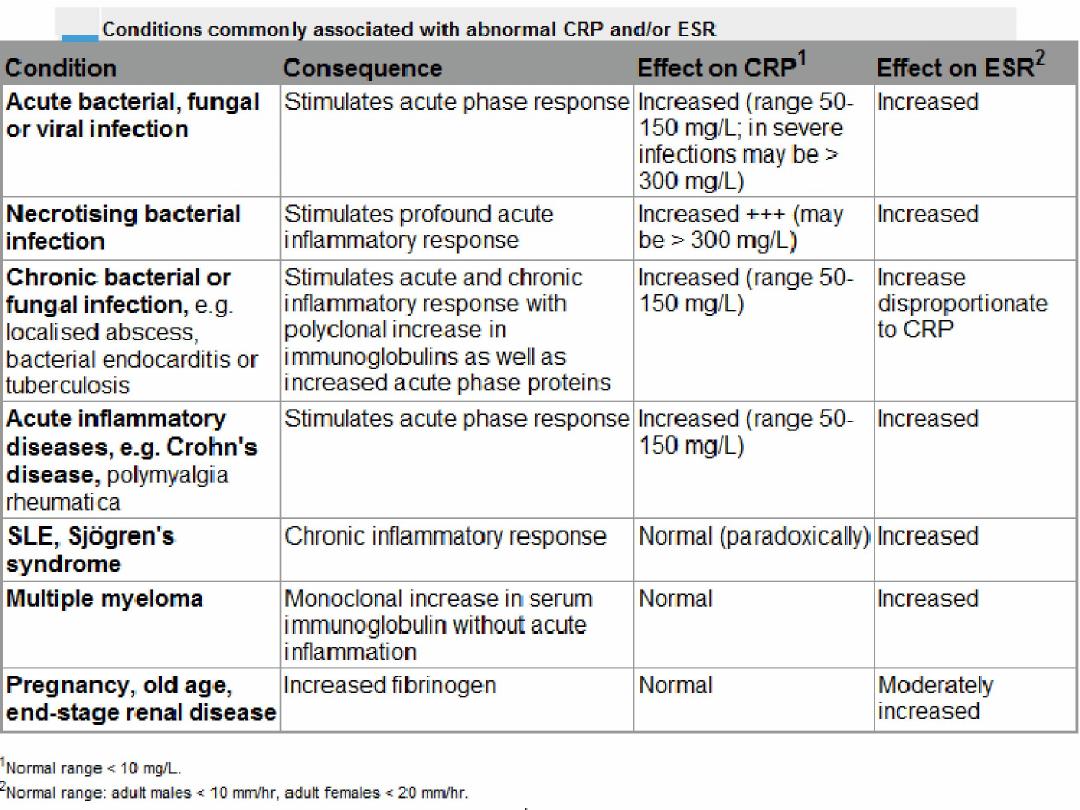
Investigations In Autoimmunity
1)AUTOANTIBODIES
1)Rheumatoid factor
2)Anti-CCP antibody
3)Antinuclear antibodies: (ANA)
4)Antibodies to extractable nuclear antigens
5)Anti-ds-DNA antibodies
6)Antiphospholipid antibodies
7)Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA
15

2) Cryoglobulins
3) Measures Of Complement Activation
16

Clinical presentation of Autoimmune Diseases
1)Organ-specific:
Immune response against
localized antigens
:
e.g: Graves' disease, pernicious anemia, type 1
DM
2)Multisystem
Immune response against
widespread target
antigens
: e.g: Systemic sclerosis, SLE, MCTD
17
18
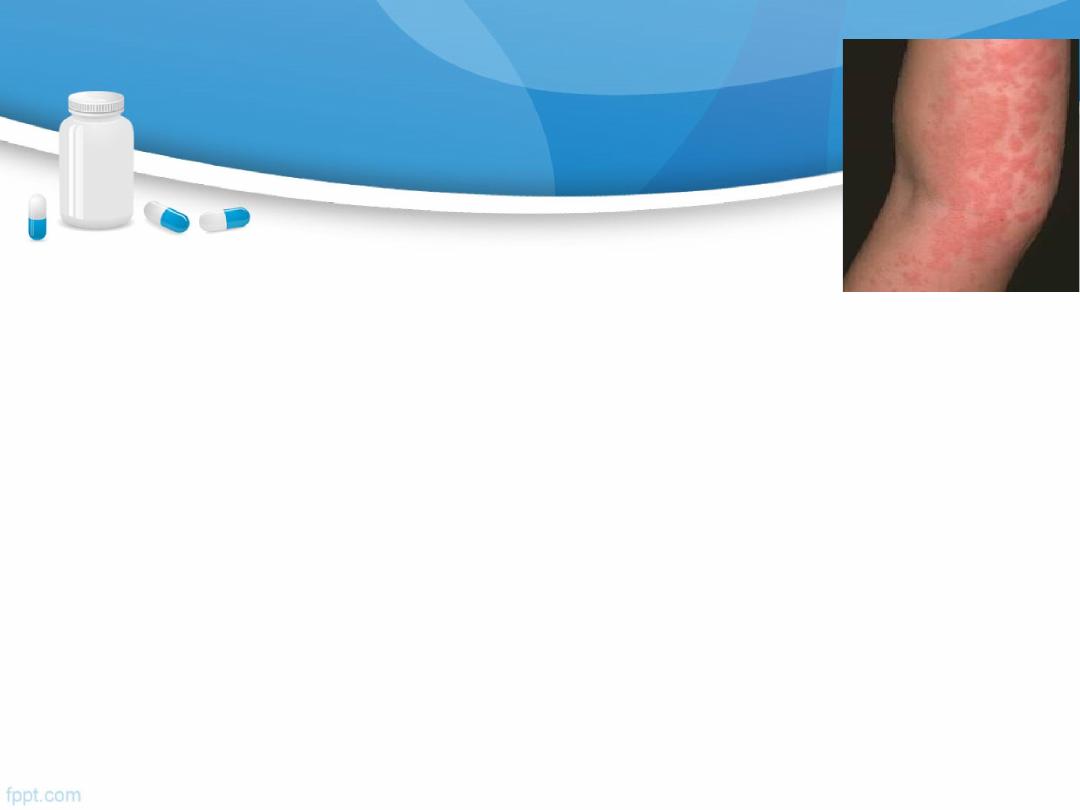

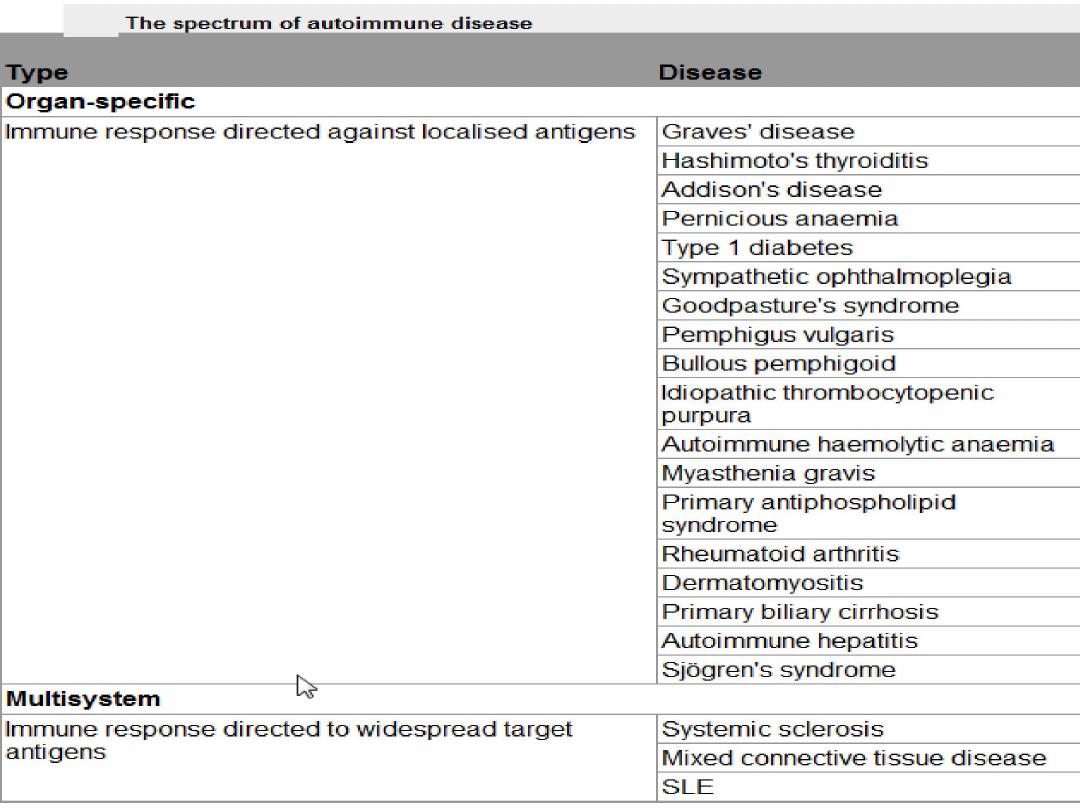
Allergy
is C/M of inappropriate IgE immune response to
harmless environmental substances .
Risk Factors
1.
Genetic:
A family history (the strongest factor).
2.
Environmental
factors :pollutants, cigarette
smoke, infection
3.
Unexplained
19
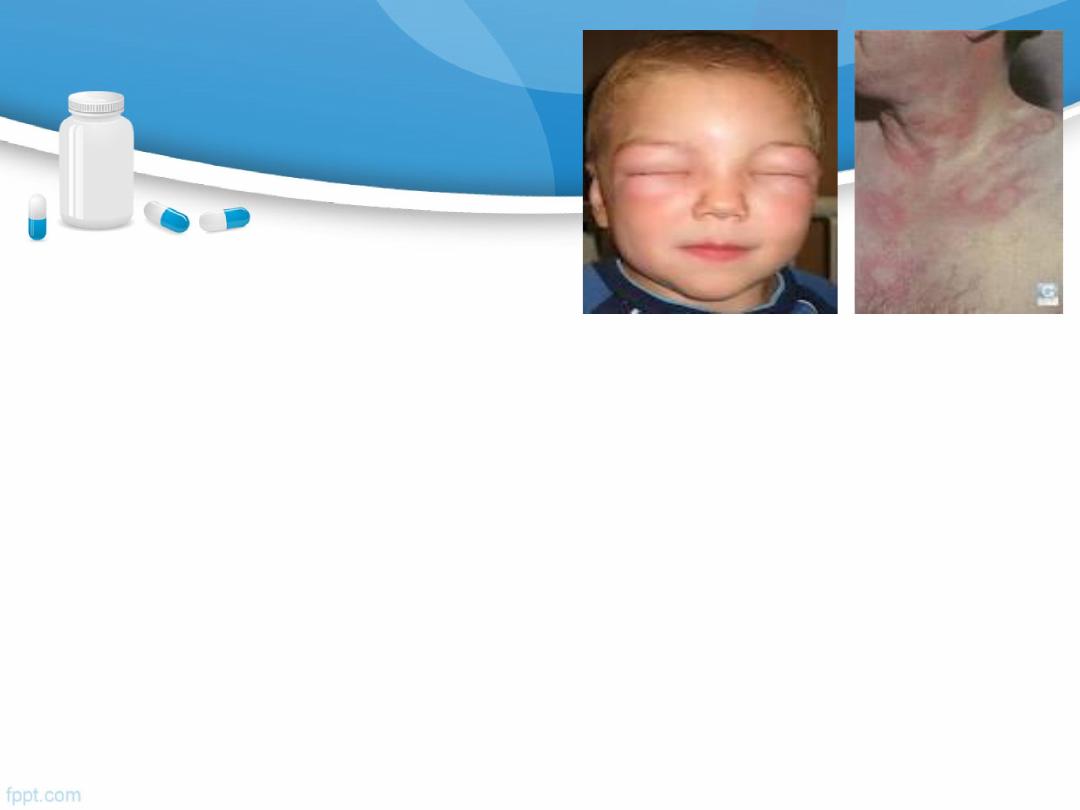
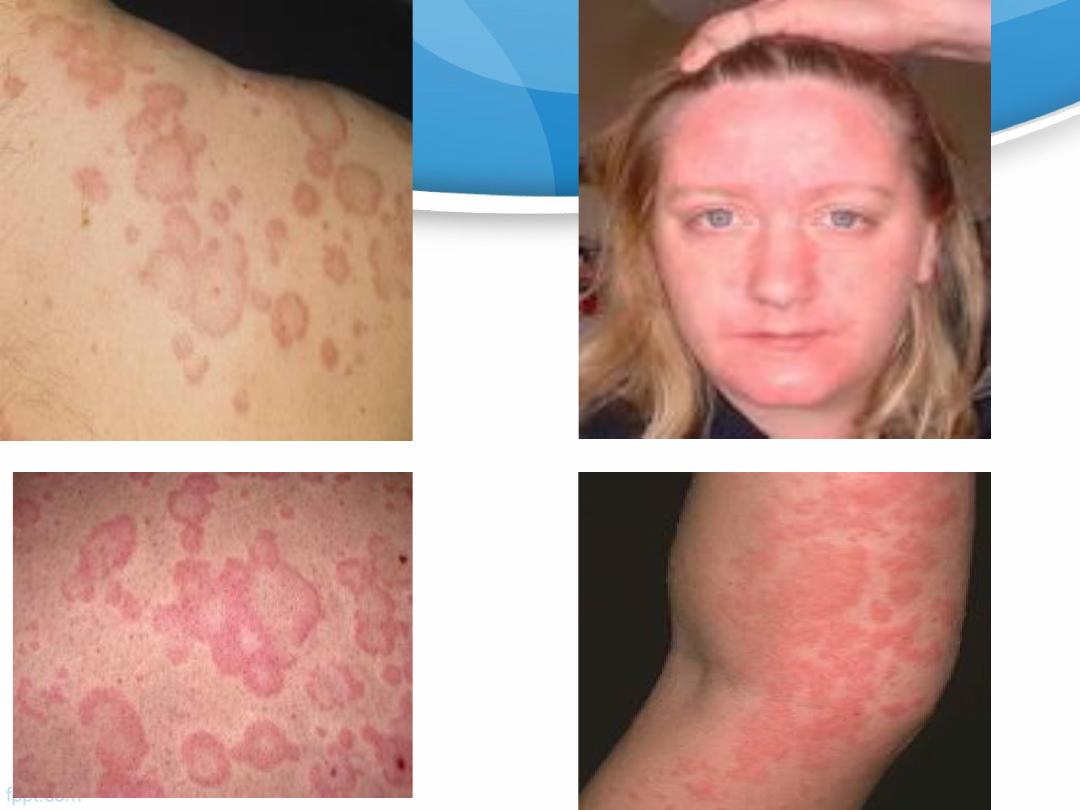
C/P of allergy
Symptoms (angioedema, urticaria, wheezing ….).
Other allergic symptoms
usually occurs within minutes of exposure to allergen
R/F –HX of allergic disease.
-Hx of potential allergens in the home and
workplace
-DHx:Hx of drug intake: Sulfa, penicillin,---
20
21

Investigations
1)Skin prick test:
is the
'gold standard'
of allergy testing
A droplet of diluted standardized allergen solution
is placed on the forearm, and the skin is
superficially punctured through the droplet with a
sterile lancet.
22

• After 15 minutes
, a positive response is
indicated by a
local weal and flare
response ≥ 2 mm
larger than the negative
control.
The results clearly seen.
24

Disadvantages
: remote risk of a
severe allergic
reaction, so
resuscitation tools
should be available.
Antihistamines inhibit the amount of response and
should be stopped at least 2 days before testing.
25

2) Specific IgE test
An alternative to skin prick testing
very useful if skin testing is inappropriate
26

3)Supervised exposure to allergen (challenge test)
Placebo-controlled allergen challenges
usually performed in specialist centers
e.g. food challenge
May
be
useful
in
the
investigation
of
occupational asthma or food allergy.
27

4)Mast cell tryptase
useful in investigating a possible anaphylactic
event
5) Non-specific markers of atopic disease:
-
↑total serum IgE
- eosinophilia (up to 20%, = 1.5 × 10
9
/l )
28

Management
1.Education:
Avoidance of the allergen
2.Drugs:
-Antihistamines
-Corticosteroids,
-Sodium cromoglicate,
-Antigen-specific immunotherapy
-Omalizumab(a monoclonal antibody against IgE)
-Preloaded self-injectable adrenaline (epinephrine)
29

Summary
30
• IR: tissue response to injury or infection, acute &
chronic.
• IT: immune system distinguishing self tissue from
foreign tissue
• AD:
Immune
response
against
self-targets,
predisposed
by
genetic,
environmental,&
unkown. Screened by certain Ab.
• HSD: 4types.

31
Allergy:↑↑IgE response to painless env. Stimuli. ,
gentic-env-unkn, has spcial Cf & Rx

Quiz ???
32

Q1
/
In acute phase reactant, which one is correct?
A.C-reactive protein
B.Serum amyloid A
C.Transferrin
D.α
1
-antitrypsin
E. All of the above
33

Q1
/
In acute phase reactant, which one is correct?
A.C-reactive protein
B.Serum amyloid A
C.Transferrin
D.α
1
-antitrypsin
E. All of the above
34

Q2/
Regarding autoimmune diseases, which one is
correct?
A.Immune responses against foreign targets
B. chronic morbidity and disability have not been
reported
C.Intact tolerance mechanism
D.Much more common in women than in men.
E.All of the above
35

Q3/
The gold standard test for allergy is
A.Specific IgE test
B.challenge test
C.Skin prick test
D.Mast cell tryptase
E.None of the above
37

• Next lecture: Anaphylaxis, angioedema,
transplantation and graft
rejection
39

