
Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
Lec. 5
Streptococcal diseases
Wed 11/ 3 / 2015
2014 – 2015
ﻣﻜﺘﺐ ﺍﺷﻮﺭ ﻟﻼﺳﺘﻨﺴﺎﺥ
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
1
Streptococcal Diseases
General characteristics
Gram-positive spherical/ovoid cocci arranged in long chains; commonly in pairs.
Non-spore-forming, non-motile.
Can form capsules and slime layers.
Do not form catalase, but have a peroxidase system.
Sensitive to drying, heat, and disinfectants.
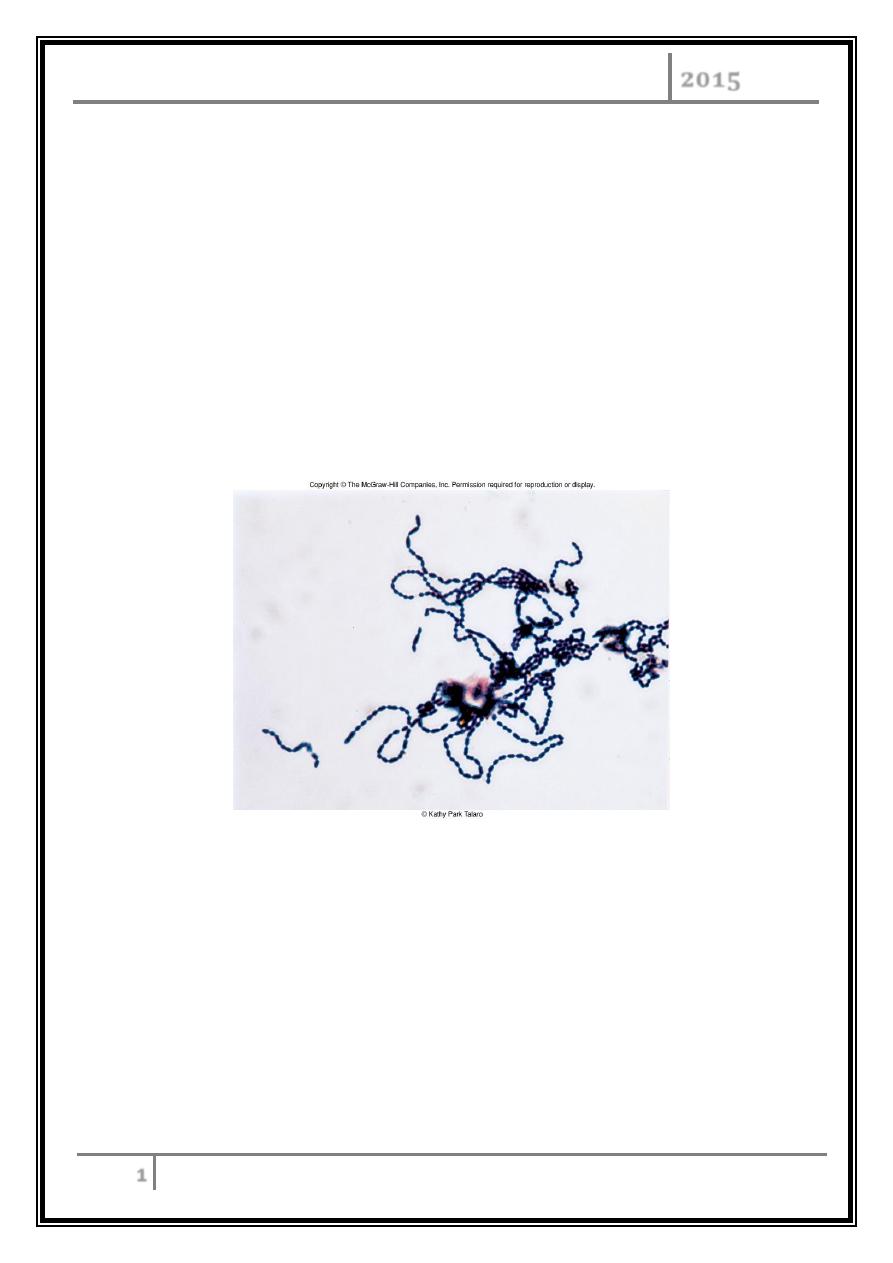
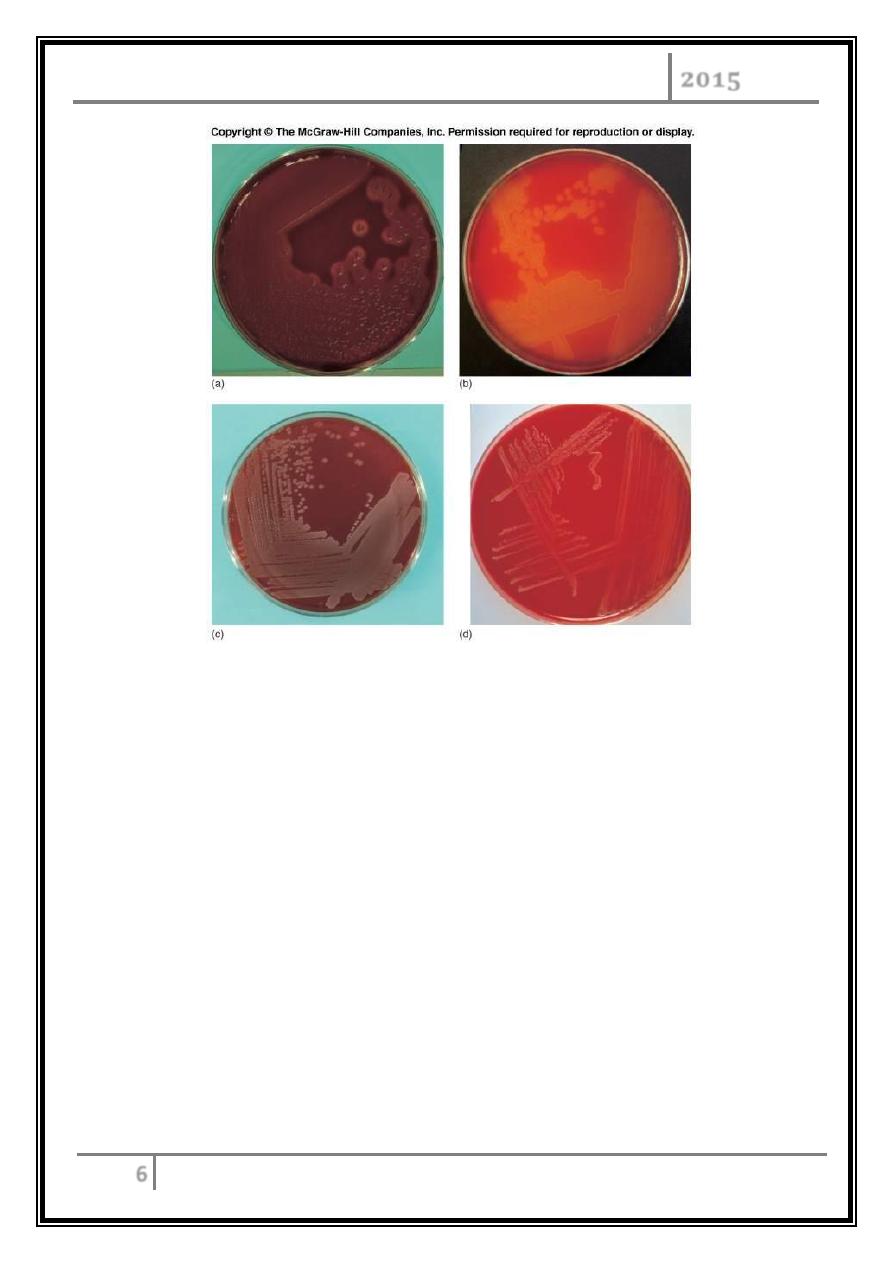
Freshly isolated Streptococcui
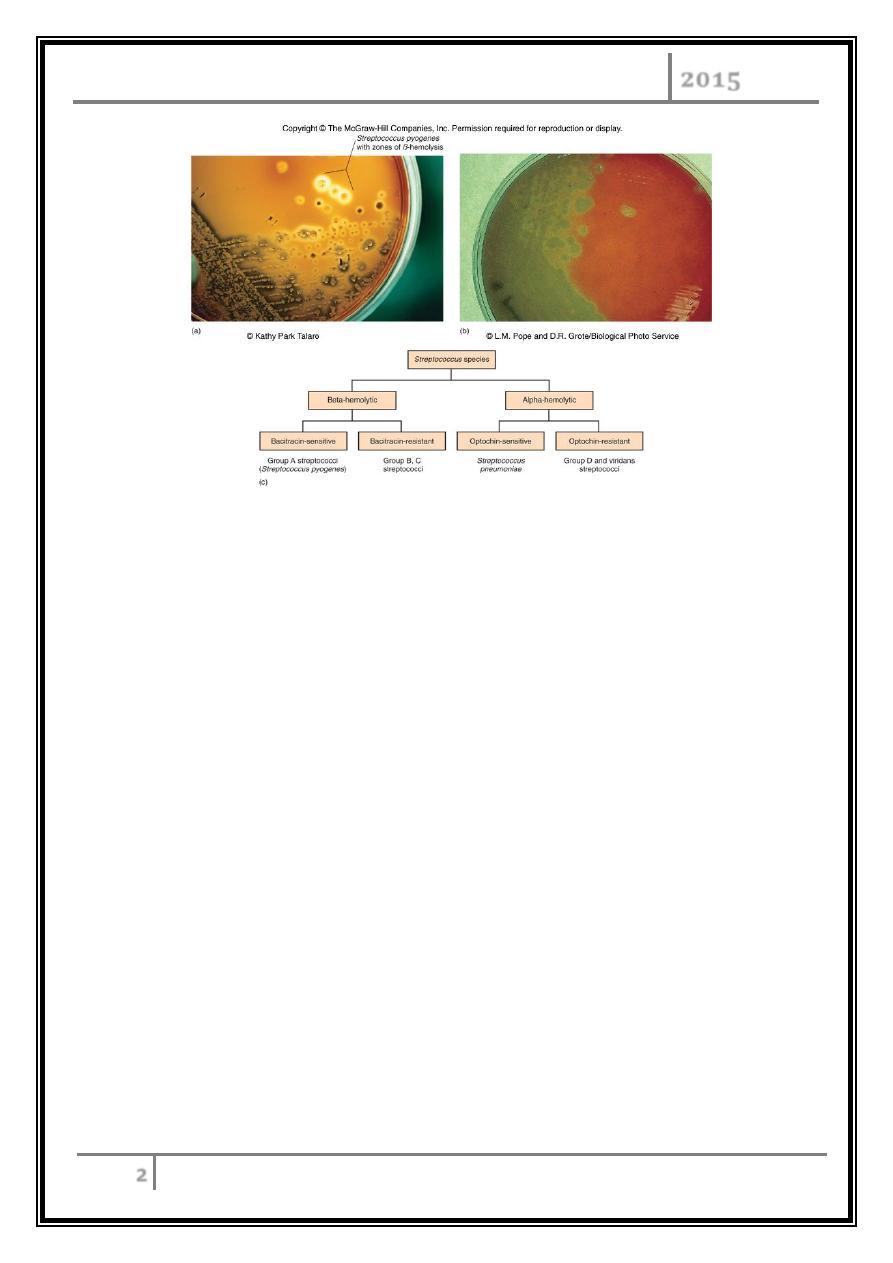
Hemolysis on Blood Agar Plates
Alpha hemolysis-organism excretes hemolysins which partially break down RBC
(incomplete hemolysis) thus a greenish zone appears around colony.
Beta hemolysis-organisms excrete potent hemoysins which completely lyse RBC
(complete hemolysis) thus a clear zone appears around colony.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
2
Hemolysis patterns on blood agar
Types of Infection
Primary infections invade healthy tissue and most often affect the throat.
Secondary strep infections invade tissue already weakened by injury or illness.
They frequently affect the bones, ears, eyes, joints, or
Both primary and secondary strep infections can travel from affected tissues to
, and spread throughout the body.
Classification
Lancefield classification system based on cell wall Ag – 17 groups (A, B, C … etc).
Classification based on hemolysis:
α- hemolysis – A, B, C, G and some D.
β- hemolysis – S. pneumoniae and others collectively called viridians.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
3
GROUP A (GAS),
responsible for:
o Necrotizing fasciitis
o Toxic shock syndrome.
o Strep throat.
View of group A Streptococcus
GROUP B (GBS) -
S. Agalactiae, S.pyogenes.
Most often affects pregnant women, infants, elderly, and chronically ill
adults.
Most prevalent cause of neonatal pneumonia, sepsis, and meningitis.
Endocarditis in debilitated people.
GROUP C (GCS)
It is a common source of infection in animals. It rarely causes human illness.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
4
GROUP D (GDS) -
Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium, and E. durans.
Wound infections in hospital patients. It is also associated with the following:
Abnormal growth of tissue in the gastrointestinal tract.
UTI.
Infections in women who have just given birth.
GROUP G (GGS)
Normally present on the skin, mouth, throat, in the intestines and genital
tract.
Lead to infection in alcoholics and in people who have cancer, diabetes
mellitus, and rheumatoid arthritis.
Infections caused by GGS:
- Endocarditis.
- Osteomyelitis.
- Peritonitis.
Human Streptococcal Pathogens
S. pyogenes.
S. agalactiae.
Viridans streptococci.
S. pneumonia.
Enterococcus faecalis.

STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
5
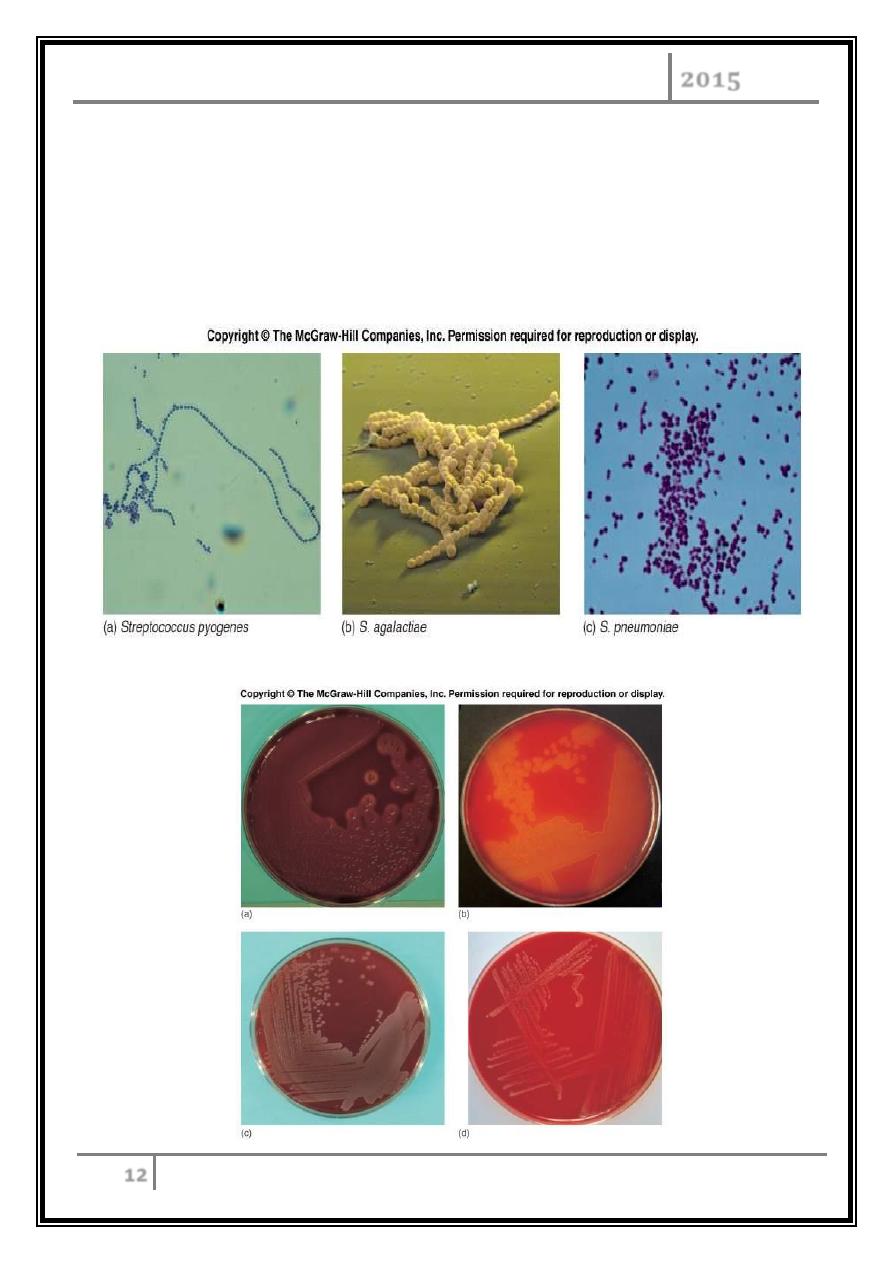
Streptococcus pyogenes
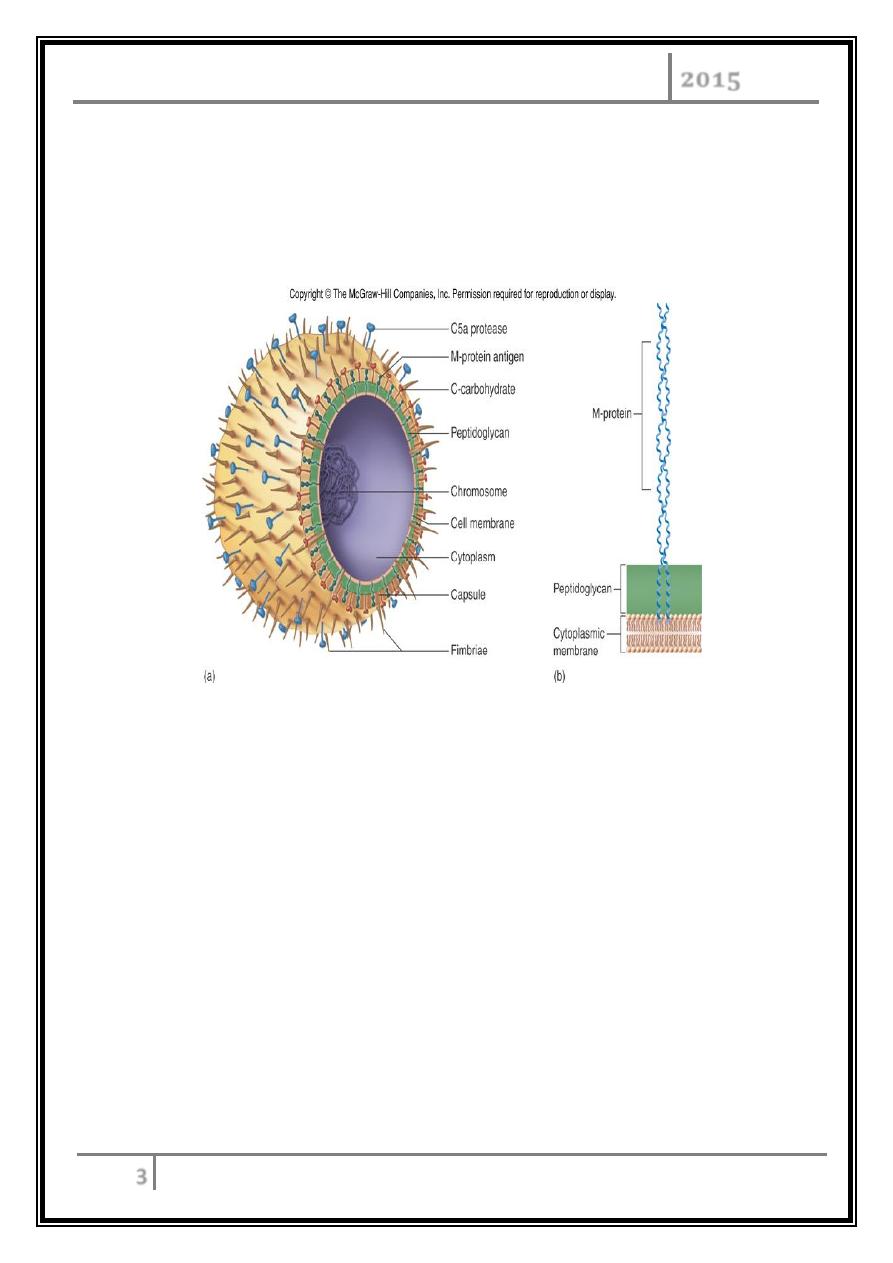
Beta Hemolytic Group A Gram positive cocci in chains.
Extracellular products are responsible for virulence:
Pyrogenic exotoxin A
Acts as a superantigen and causes STSS.
Exotoxin B
Causes protein breakdown.
Virulence factors of
β
- haemolytic S.pyogenes
Extracellular toxins:
Streptolysins – hemolysins; streptolysin O (SLO) and streptolysin S (SLS) –
both cause cell and tissue injury.
Erythrogenic toxin (pyrogenic) – induces fever and typical red rash.
Superantigens – strong monocyte and lymphocyte stimulants; cause the
release of tissue necrotic factor.
Extracellular enzymes:
Streptokinase – digests fibrin clots.
Hyaluronidase – breaks down connective tissue.
DNase – hydrolyzes DNA.
Gram Stain of S. pyogenes
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
6
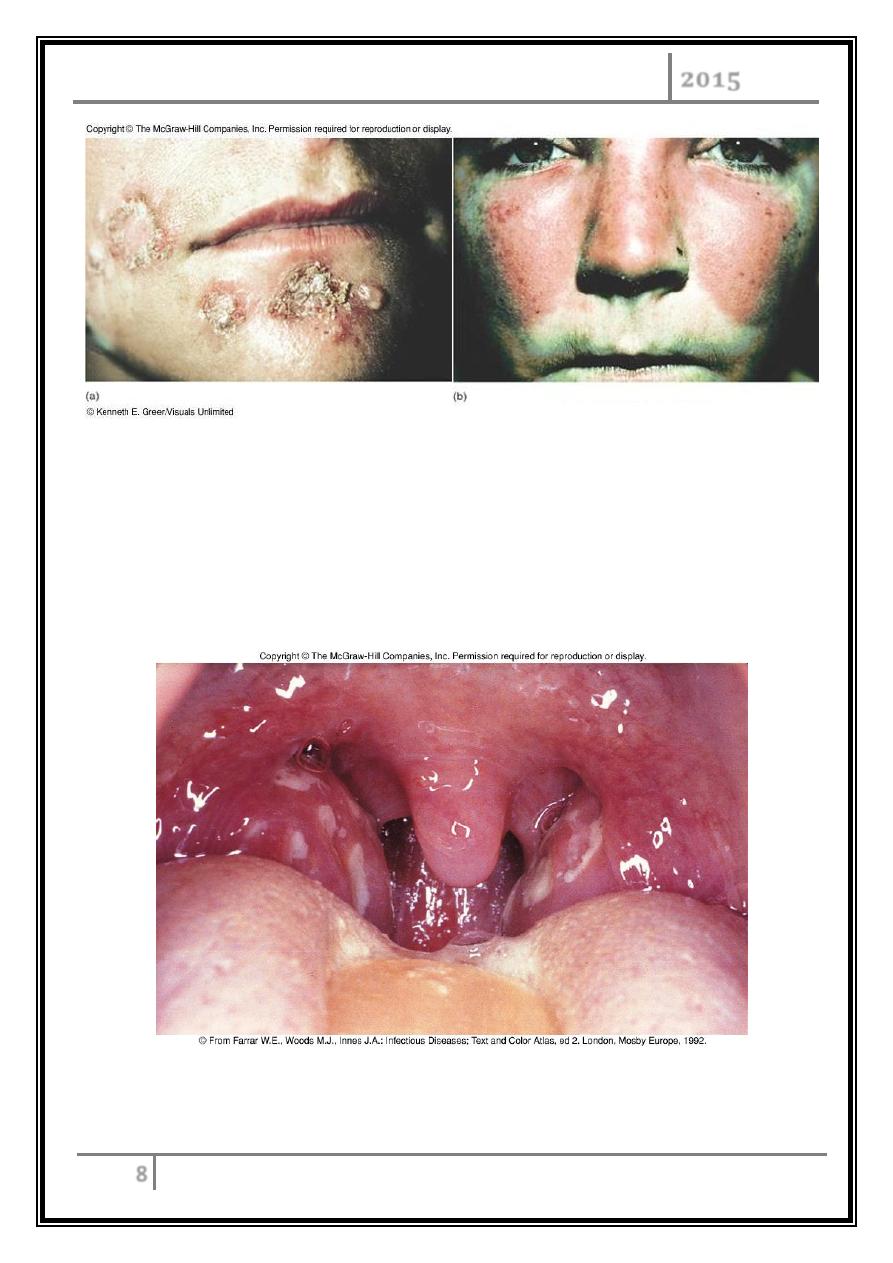
Diseases caused by S. pyogenes
Strep throat.
Impetigo.
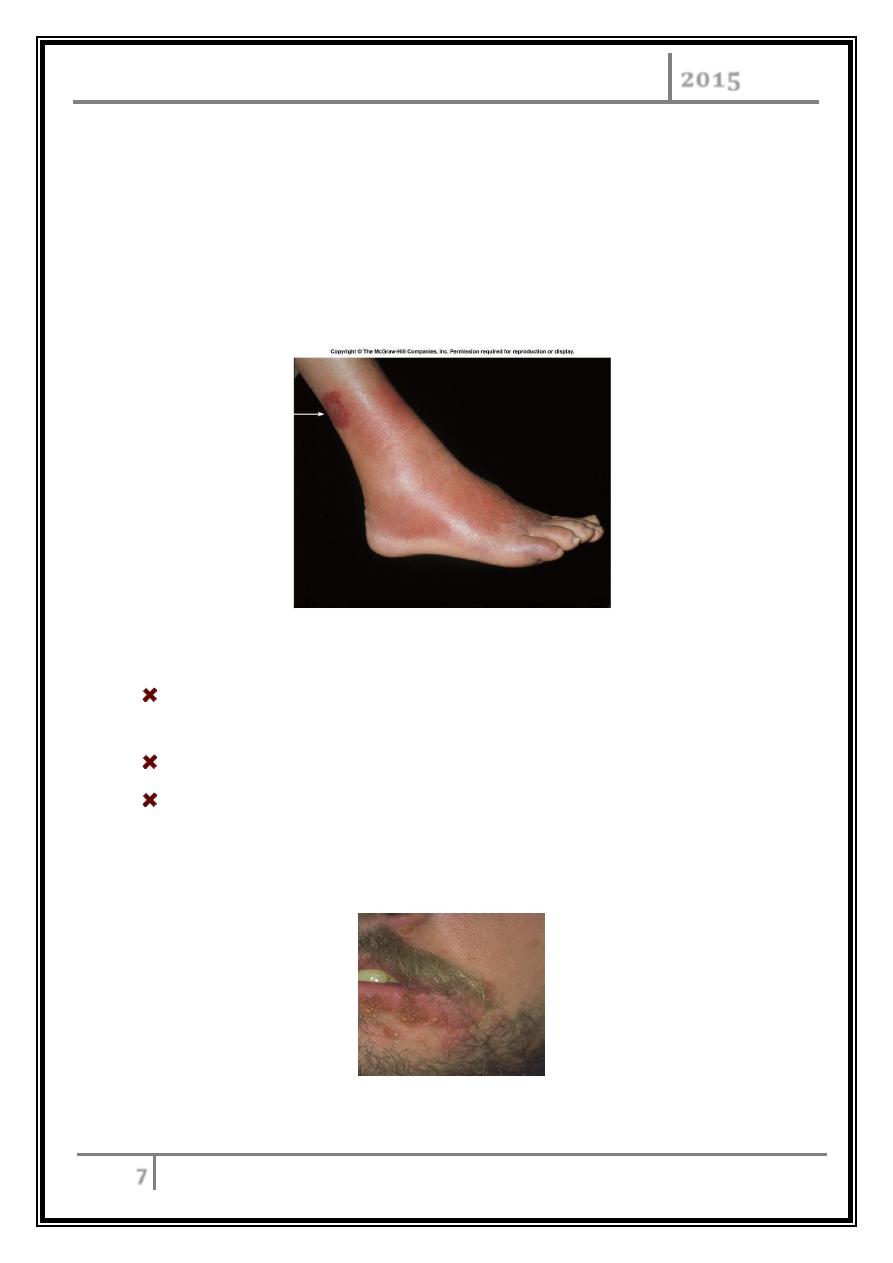
Erysipelas.
Cellulitis.
Invasive Strep A infections:
o Necrotizing fasciitis.
o Myositis.
o Toxic shock-like syndrome.
Beta hemolysis
S.pyogenes
S. pneumonia
Alpha
hemolysis
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
7
Erysipelas
Acute infection and imflammation of the dermal layer of skin.
Bacteremia common.
Painful red patches which enlarge and thicken.
Treatment - penicillin or erythromycin.
Impetigo
Often occurs in epidemics in school children; also associated with insect
bites, poor hygiene, and crowded living conditions.
Friable, golden crusts over erythematous skin.
Treatment:
- Topical fucidin or mupirocin 7-10 d.
- Oral flucloxacillin or erythromycin if widespread or unresponsive
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
8
Streptococcal skin infections
Strep throat (Streptococcal pharyngitis)
Most common of all Strep diseases.
Spread by saliva or nasal secretions.
Incubation period 2-4 days.
Pharyngitis and tonsillitis
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
9
Diagnosis
Usual symptoms are slight fever associated with sore throat and visual of
pus in back of throat.
Throat swab for microscopical examination and growth on blood agar (beta
hemolysis).
If the strain of S. pyogenes is lysogenic for a particular phage which
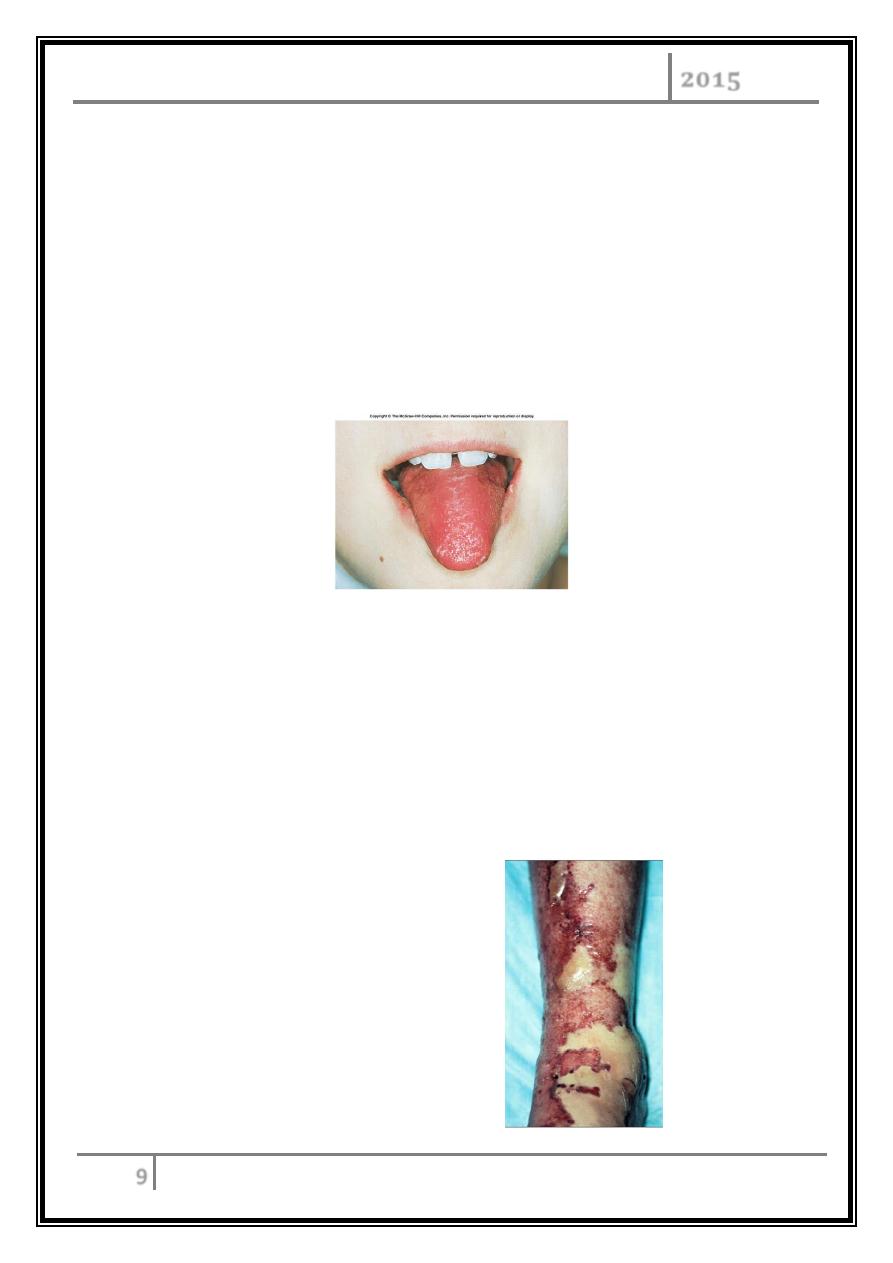
expresses an erythrogenic toxin the result is Scarlet fever.
Rash appears and characteristic is the strawberry colored tongue.
Strawberry tongue
Treatment of Strep throat
Penicillin G or Erythromycin are drugs of choice.
Although the disease is self-limiting it is important to treat immediately to
avoid post strep complications.
Necrotizing fasciitis
Also known as “flesh eaters”.
Can cause rapidly
deteriorating disease and
death.
Common cause of wound
infections.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
10
Symptoms
Acute pain at the site of the wound.
Swelling.
Fever and confusion.
Overlying skin tightens and becomes discolored.
Shock and death.
Pathogenesis
o Wound colonization enhanced through tissue binding proteins.
o Subcutaneous fascia is destroyed in necrotizing fasciitis.
o Muscle tissue is also destroyed by bacterial penetration.
o Organisms multiply and produce toxic products.
o Organisms and toxic products enter bloodstream.
Prevention and Treatment
No proven prevention measures.
Penicillin is still an effective treatment, must be given early.
Urgent surgery required due to rapidity of toxin spread.
Amputation is sometimes required.
Poststreptococcal diseases
Rheumatic Fever - autoimmune disease follows a strep throat.
Acute glomerulonehritis or Bright’s Disease - inflamatory disease of renal
glomeruli and structures involved in blood filter of kidney. Due to deposition
of Ag/Ab complexes.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
11
α -
Hemolytic Streptococci: Viridans Group
- Streptococcus mutans, S. oralis, S. salivarus, S. sanguis, S. milleri, S. mitis.
- Widespread residents of the gums and teeth, oral cavity, and also found in
nasopharynx, genital tract, skin.
- Not very invasive; dental or surgical procedures facilitate entrance.
- Bacteremia, meningitis, abdominal infection, tooth abscesses.
- Subacute endocarditis – Blood-borne bacteria settle and grow on heart
lining or valves.
- Persons with preexisting heart disease are at high risk.
- Colonization of heart by forming biofilms .
- S. mutans produce slime layers that adhere to teeth, basis for plaque.
- Involved in dental caries.
- Persons with preexisting heart conditions should receive prophylactic
antibiotics before surgery or dental procedures.
Group D Enterococci and Groups C and G Streptococci
Group D:
Enterococcus faecalis, E. faecium, E. durans.
Normal colonists of human large intestine.
Opportunistic urinary, wound, and skin infections, particularly in
debilitated persons.
Groups C and G:
Common animal flora, frequently isolated from upper respiratory;
pharyngitis, glomerulonephritis, bacteremia.
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
12
Streptococcus Pneumonia
Caused by infection with Streptococcus pneumonia.
Gram positive, alpha hemolytic, Lancefield serotype A.
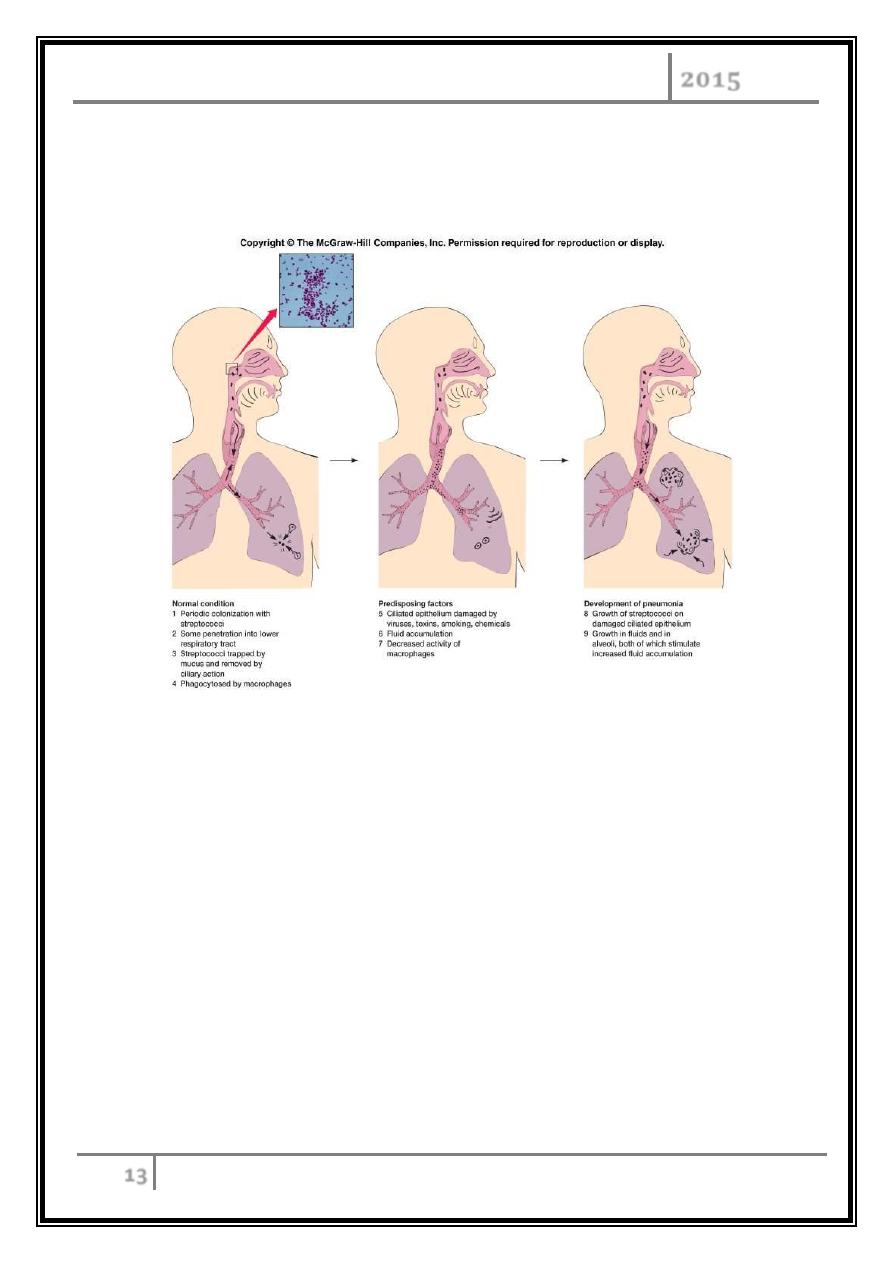
Often part of normal flora of respiratory track and becomes infective once
hosts resistance is lowered. Classified as an endogenous infection.
Strep Pneumoniae
S. pneumoniae
Alpha hemolysis
STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
13
Predisposing factors: upper respiratory viral infection, diabetes, alcoholism.
60-80% of all pneumonias.
Strep pneumonia
Cause of strep pneumonia
Primary virulence factor is the capsular polysaccharide which protects the
organism against phagocytosis.
Pathogenesis is due to rapid growth of bacteria in alveolar spaces.
Symptoms of strep pneumonia
Onset abrupt.
Chest pains.
Chills.
Labored breathing.

STREPTOCOCCAL DISEASES Dr. Mohammed Waheeb
2015
14
Diagnosis of strep pneumonia
o Chest X-ray.
o Culture and staining.
o Biochemical tests of isolated organism.
Treatment of strep pneumonia
Typically treated with Penicillin G, cefotaxime, oflaxacin or for those allergic
to penicillins can be treated with erythromycin or tetracycline.
Pneumococcal vaccine (Pneumovax 23 or Pnu-immune 23) is available for
the elderly.
… End …
