
Dr. Mustafa Nema
Lec. 1
BRUCELLOSIS
Wed
18 / 2 / 2015
Done by : Ali Kareem
2014 – 2015
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
2
BRUCELLOSIS
Objectives :
At the end of this lecture, the student should be able to :
Define brucellosis.
Describe how can patient with brucellosis being presented.
Make an idea about differential diagnosis.
Outline treatment strategy.
Describe the plan of disease prevention.
INTRODUCTION
Brucellosis is a zoonotic infection transmitted to humans by contact with
animal or animal products.
The disease is rarely, if ever, transmitted between humans.
Brucellosis is also known as undulant fever and Malta fever.
MICROBIOLOGY
Caused by strains of Brucella, a small gram-negative aerobic coccobacilli.
There are four major species :
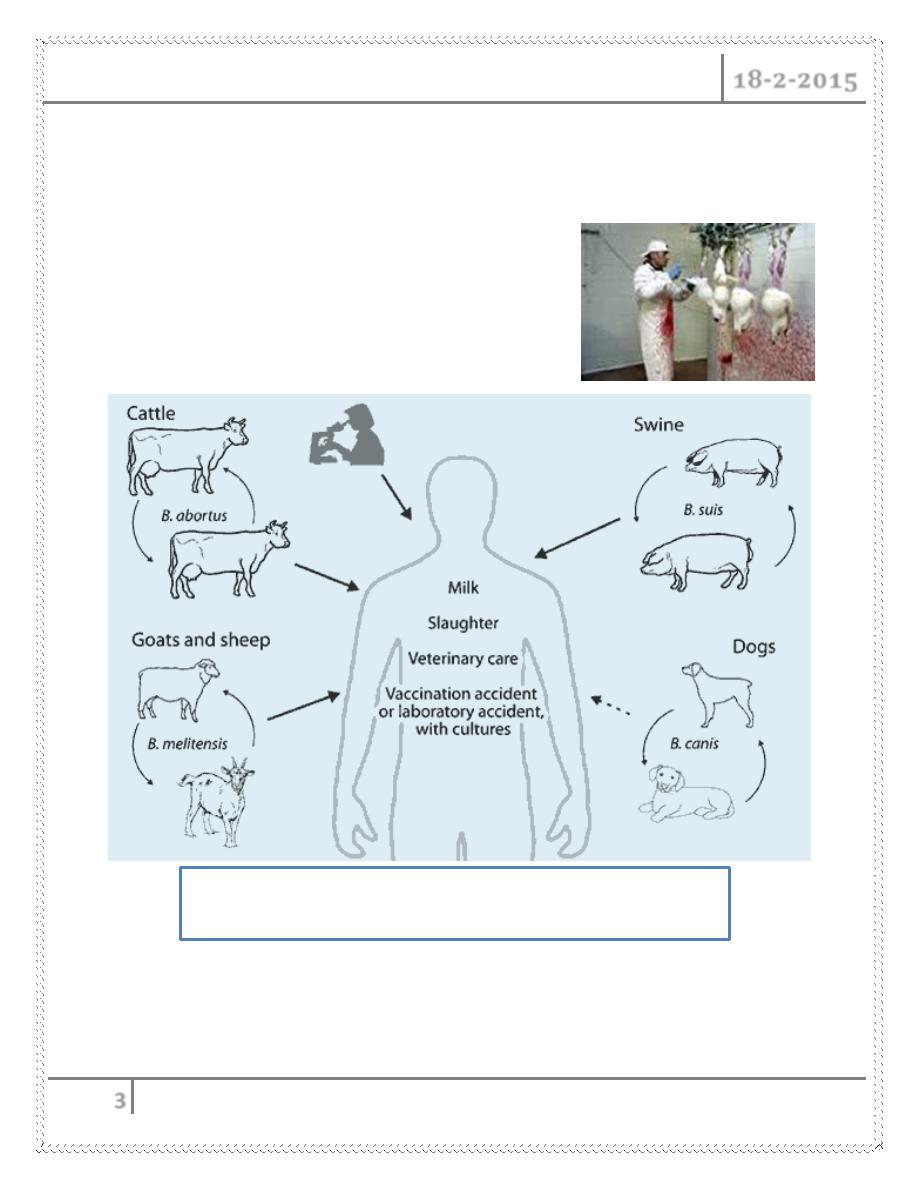
1- B. melitensis: Main sources: sheep,goats, camels. most common cause of
disease in humans.
2- B. abortus: Usually acquired from cattle. known cause of animal abortion.
3- B. suis: Acquired from swine.
4- B. canis: Acquired from dogs.
Human infection
Humans are generally infected with brucellosis in one of three ways :
1- Eating undercooked meat or consuming unpasteurized/raw dairy products
BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
3
2- Breathing in the bacteria that cause brucellosis; This risk is generally
greater for people in laboratories that work with the bacteria.
3- Bacteria entering the body through skin wounds or mucous membranes
through contact with infected animals.
Slaughterhouse workers
Meat-packing workers
Veterinarians
Brucella Transmission
BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
4
Two facts..
Brucellae survive for up to 2 months in soft cheeses made from goat or
sheep milk.
Brucellae are easily killed by: Boiling and pasteurization.
PATHOGENESIS
After ingestion, Brucella invades the mucosa and is inter phagocytes.
It eventually released from the cell following induced cell necrosis.
Infection with Brucella induces antibody production by B lymphocytes.
These antibodies are important for diagnostic purposes.
Brucella spp. are intracellular organisms that survive for long periods
within the reticulo-endothelial system.
This explains many of the clinical features, including the chronicity of
disease and tendency to relapse, even after antimicrobial therapy.
CLINICAL MANIFESTATIONS
General manifestations
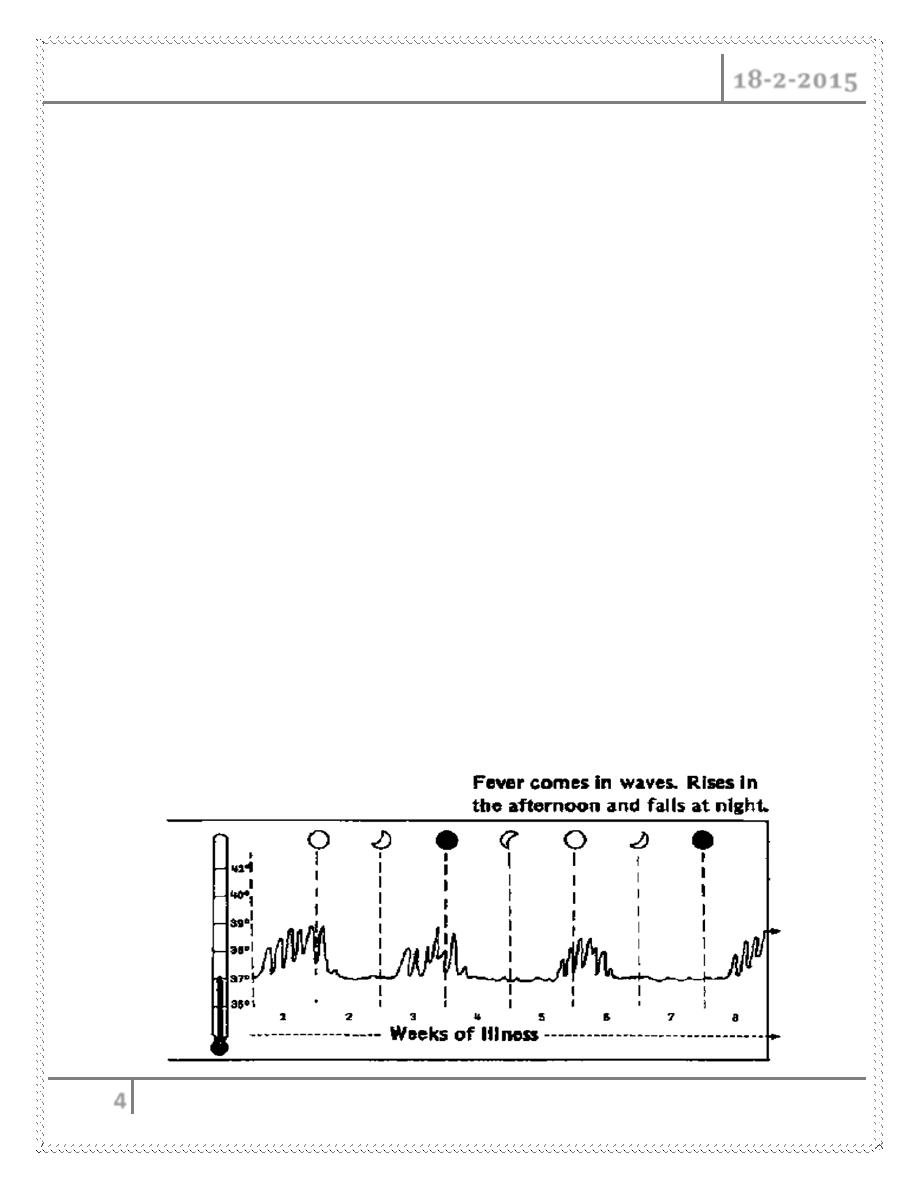
Acute illness is characterised by a high swinging (undulating ) temperature,
rigors, lethargy, headache, joint and muscle pains, and scrotal pain.
BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
5
Physical signs
Physical signs are non-specific, e.g. enlarged lymph nodes.
Enlargement of the spleen; may lead to hypersplenism and
thrombocytopenia.
Liver enlargement.
Localizing manifestations
Occurs in about 30% of patients, is more likely if diagnosis and treatment
are delayed. They include:
- Skeletal
- Neurological
- Other local diseases
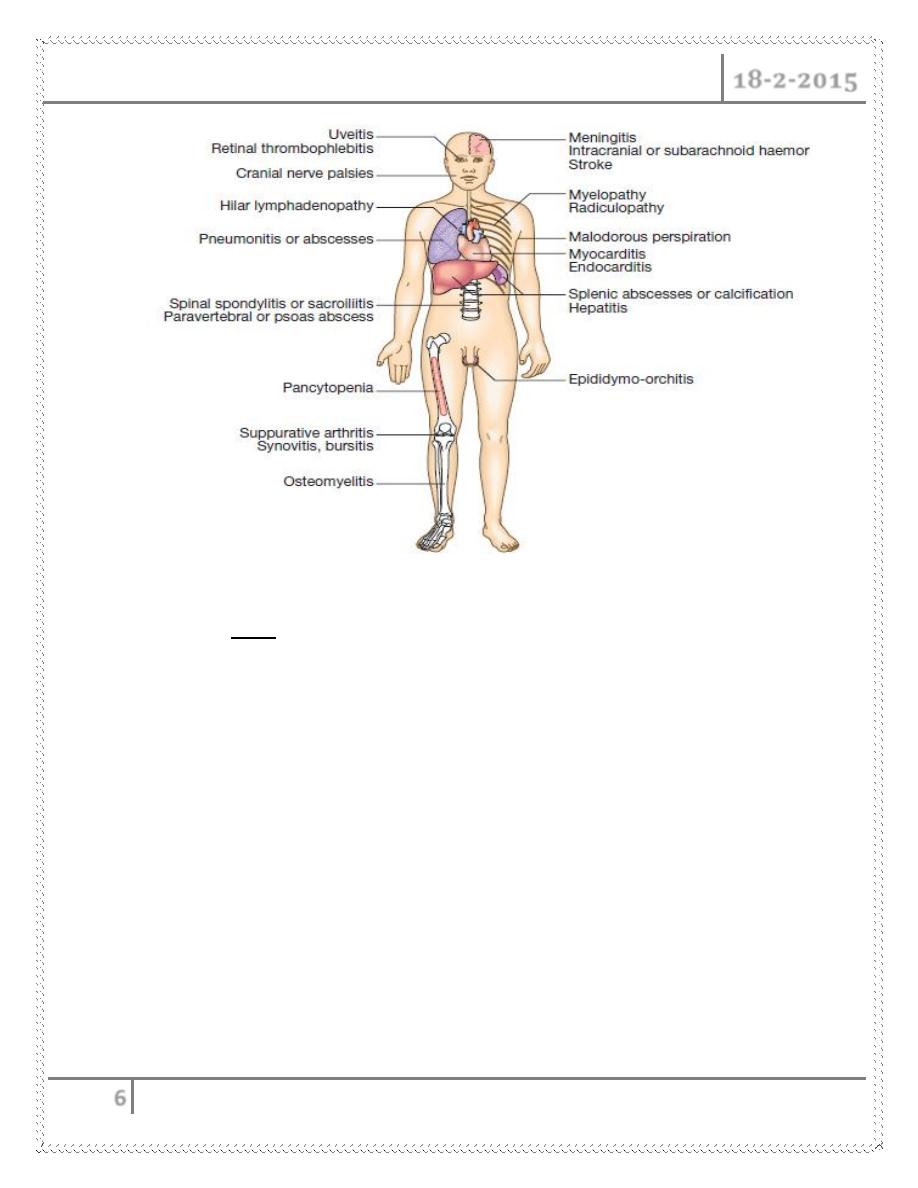
SKELETAL
o Suppurative arthritis; synovitis, bursitis
o Osteomyelitis
o Spinal spondylitis
o Paravertebral or psoas abscess .
NEUROLOGICAL
o Neurobrucellosis, usually presenting as
meningitis.
o Less common neurologic complications include stroke, and intracerebral
hemorrhage.. etc
OTHER LOCAL DISEASES
o Genitourinary disease, especially epididymo-orchitis.
o Endocarditis — 1 percent.
o Hepatic abscess.
BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
6
Presentations often fit into 1 of 3 patterns :
Febrile illness that resembles typhoid, but is less severe.
Fever and acute monarticular arthritis (typically of the hip or knee) in a
young child.
Long-lasting fever, depression, and low-back or hip pain in an older person.
DIAGNOSIS
The diagnosis of brucellosis should be considered in the setting of otherwise
unexplained chronic fever and nonspecific complaints.
The history should include details regarding possible sources of exposure to
Brucella, including contact with animal tissues or ingestion of unpasteurized
milk or cheese.
Clinical features of brucellosis

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
7
Laboratory tests
A) Specific laboratory testing:
1- Culture of blood, CSF, bone marrow, joint fluid, tissue aspirate, or biops
sample for brucella spp.
- Definitive diagnosis depends on the isolation of the organism
- Culture should be incubated for up to 6 weeks.
- Blood cultures are positive in 75–80% of infections caused by B.
melitensis and 50% of those caused by B. abortus.
- Bone marrow culture should not be used routinely but may increase the
diagnostic yield, particularly if antibiotics have been given before
specimens are taken.
- CSF culture in neurobrucellosis is positive in about 30% of cases.
2- Antibody agglutination tests
- Anti-Brucella immunoglobin :
o Ig M: useful for acute infection followed by IgG antibodies.
o IgM decreases rapidly within the first few months of illness.
- Ab agglutinin titers judged as follows :
o A single titre of 1/320 or a fourfold rise in titre is needed to
support a diagnosis of acute infection
o In nonendemic areas: > 1:160
o The test usually takes several weeks to become positive but should
eventually detect 95% of acute infections.
3- Biopsied samples (e.g., lymph node, liver) may show noncaseating
granulomas with absence of Acid Fast Bacilli.
B) Non-specific Lab Tests
BLOOD TESTS: WBC are usually normal to low; pancytopenia (low WBC,
RBC and platelets) can occur.
CEREBROSPINAL FLUID TEST: In neurobrucellosis, abnormalities of the
cerebrospinal fluid typically include a increased WBC of 10 to 200 and
elevated protein levels

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
8
RADIOLOGY: like XR of spine and echocardiography may be helpful
evaluating focal disease but do not provide a definitive diagnosis.
Novel test: Polymerase chain reaction testing
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
In endemic areas, brucellosis may be difficult to distinguish from the many
other causes of fever.
Two features were recognized to distinguish brucellosis from other causes
fevers :
1- If left untreated, fever shows an undulating pattern
2- The fever of brucellosis is associated with musculoskeletal symptoms and
signs in about one half of all patients with hepatosplenomegaly or
lymphadenopathy.
The differential diagnosis also includes :
- Typhoid fever
- Tuberculosis
- Malaria
- Epstein-Barr virus infection
- Toxoplasmosis
- Cytomegalovirus infection
- HIV infection
- And other causes of PUO
In patients with osteomyelitis or septic arthritis, the most important
differential diagnosis is tuberculosis.
TREATMENT
Adults with non-localized disease
Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily orally for 6 wks plus gentamicin 5 mg/kg IV
once daily for 7 days

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
9
or
Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily plus rifampicin 600–900 mg orally once
daily for 6 wks
Bone disease
Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily plus rifampicin 600–900 mg once daily
orally for 6 wks plus gentamicin 5 mg/kg IV once daily for 7 days
or
Ciprofloxacin 750 mg twice daily orally plus rifampicin 600–900 mg orally
once daily for 3 mths
Neurobrucellosis
Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily plus rifampicin 600–900 mg orally once
daily for 6 wks plus ceftriaxone 2 g IV twice daily until CSF is clear (though
susceptibility should be confirmed because sensitivity to third-generation
cephalosporins varies amongst strains)
Endocarditis
Almost always needs surgical intervention and antibiotics
Doxycycline 100 mg twice daily, plus rifampicin 600–900 mg orally once
daily plus co-trimoxazole 5 mg/kg of trimethoprim component for 6 mths
plus gentamicin 5 mg/kg IV once daily for 2–4 wks
Pregnancy
Rifampicin 600–900 mg orally once daily plus co-trimoxazole 5 mg/kg of
trimethoprim component for 4 wks, but caution in last week of pregnancy
due to displacement of bilirubin from albumin by drugs and risk of
kernicterus to the fetus

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
10
Follow up
Follow up of clinically cured patient by serology & blood culture every 3-
6m for 2 years .
Surgery
Some indications for surgery include :
Endocarditis
Drainage or excision of abscesses,
Spinal epidural abscess
Prophylaxis
Rifampin plus doxycycline
For 3-6 weeks after exposure (e.g., a nonspecific laboratory accident)
PREVENTION
Brucellosis may be prevented via vaccination of domesticated animals.
Other measures include the isolation of animals to decrease contact and the
slaughter of infected animals.
Protection of slaughterhouse workers includes use of protective clothing and
disinfectants, and control of air circulation.
Pasteurization of milk before processing
Summary
Brucellosis is a disease transmitted to human by animals or animal products
especially milk, cheese and meat.

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
11
It is a chronic disease characterized by long lasting fever which sometimes
affect bone, joints and other vital organs
Diagnosis need good history and brucella agglutinin test
Treatment needed for at least 6 weeks
Prevention is better than treatment
#END
Done By
Ali Kareem
Some MCQs
Q1 / Brucellosis could be distinguished from other febrile illness by :
A) hepatosplenomegaly
B) high fever
C) Undulating fever course
D) poor response to antibiotics
Q2/ On of the followings is NOT a localized manifestation of Brucellosis :
A) osteoarthritis
B) endocarditis
C) lung abscess
D) chronic diarrhea

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
12
Q3 / The brucella type that most commonly infect human is:
A) abortus
A) suis
B) melitensis
C) canis
Q4/ The main antibiotics used to treat brucellosis are:
A) cefotaxime + azithromycin
B) ampicillin + gentamicin
C) doxycyclin + rifampicin
D) meropenem + tetracyclin
Q5/ Specific investigations used for diagnosis of brucellosis is:
A) elevated WBC
B) abdominal ultrasound
C) blood culture
D) liver function tests abnormalities
Q6/ Which of the following regimen is the standard brucellosis treatment:
A) strepyomycin plus doxycycline
B) amoxcillin plus calvulonic acid
C) TMP-SMX plus amoxicillin
D) amikacine plus isoniazide

BRUCELLOSIS Dr. Mustafa Nema
18-2-2015
13
Q7/ One of the following test used in the diagnosis of brucellosis:
A) agglutination Ab
B) Widal test
C) Ig electrophoresis
D) Puel Bunnel test
Q8/ One of the following clinical senarios will fit diagnosis of brucellosis:
A) fever and rash
B) fever and acute diarrhea
C) fever and jaundice
D) fever and arthritis
