Sunday 14 / 12 / 2014
©Ali Kareem 2014-2015
Name
:
______________________________
Class
:
_______________________________
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
Autocoids
Lecture 1
Total lectures NO. 30
Dr. Mohammed Qassim Mal-Allah

AUTOCOIDS
BY
Mohammed Q. Mal-Allah
Department of Pharmacology
College of Medicine

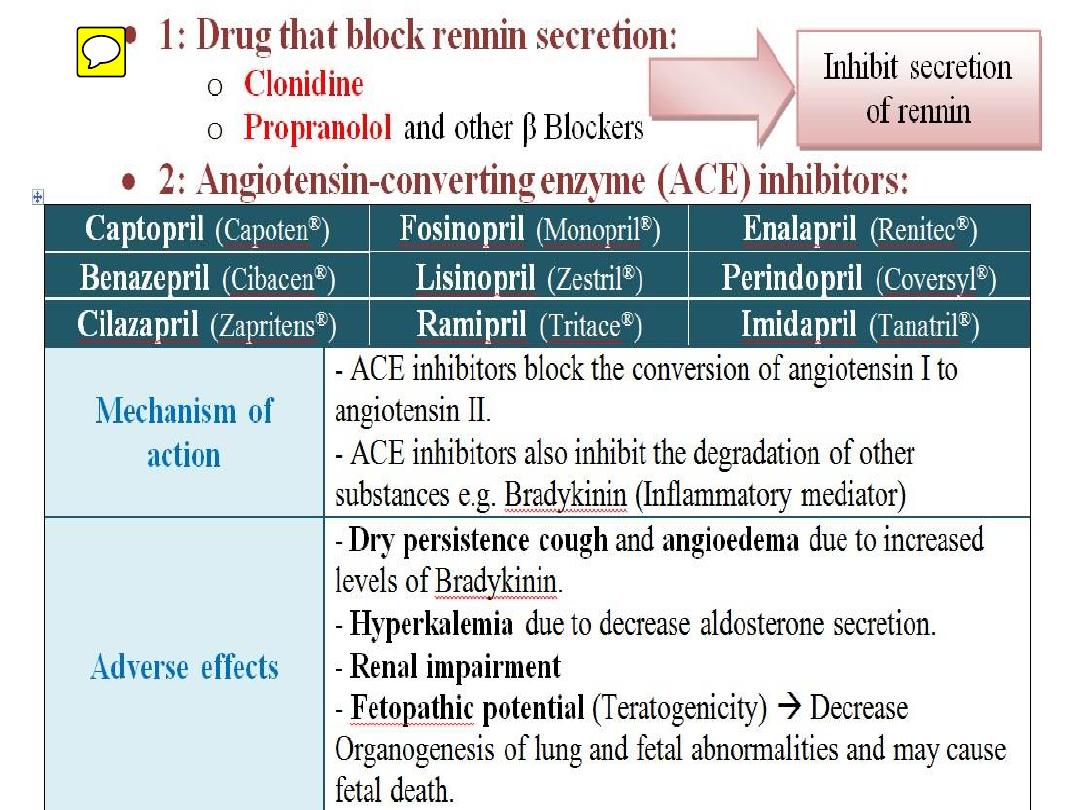
• Definition:
Auto = self Coids = Remedy
or some times called
Local Hormones
Why are they very important?

• Classifications:
A. Amine Autociods:
1.
Histamine
2.
Serotonin
B. Eicosanoids
(PGs; Thromboxane ;
Leukotriens)
C. Peptides Autociods:
1)Kinins
2) Renin; Angiotensins etc)
4.
Endogenous peptides (Kinins; Renin;
Angiotensins etc)

Serotonin
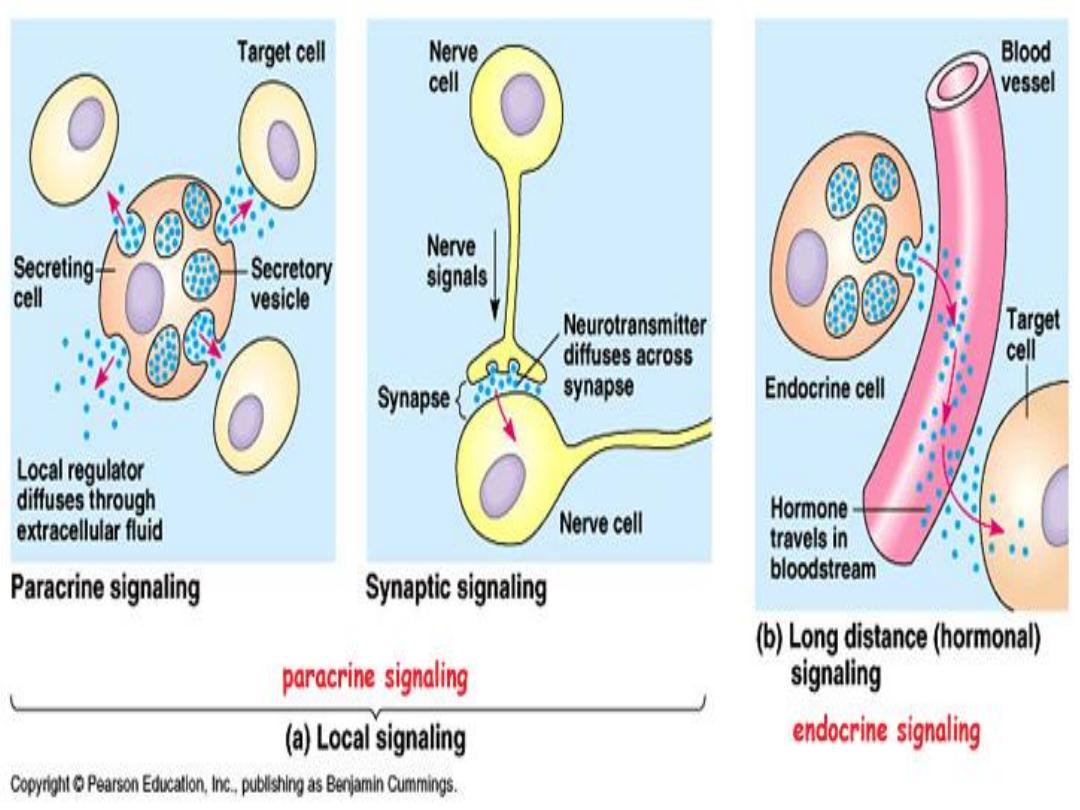
• Definition and Location:
• it is a neurotransmitter found in
enterochromaffin cells in GIT (90%) , and in
plateletes and in raphe nuclei of brain stem
.
• Is serotonin as important as N.E or
Histamine?

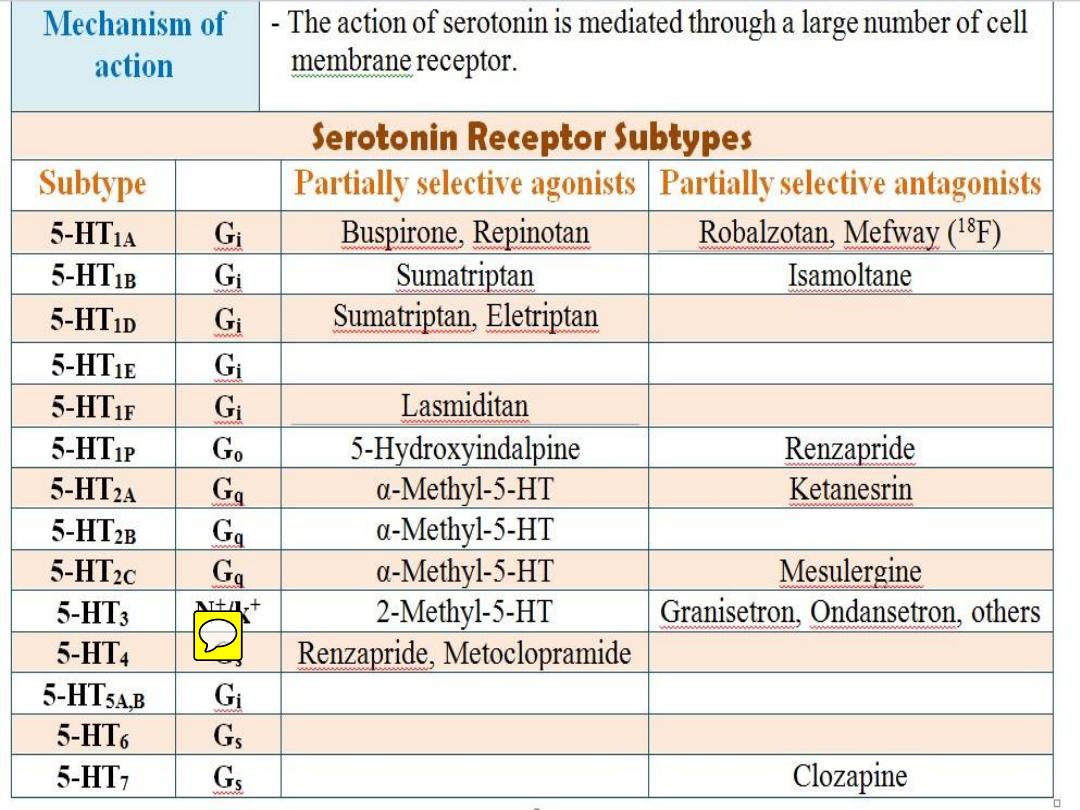
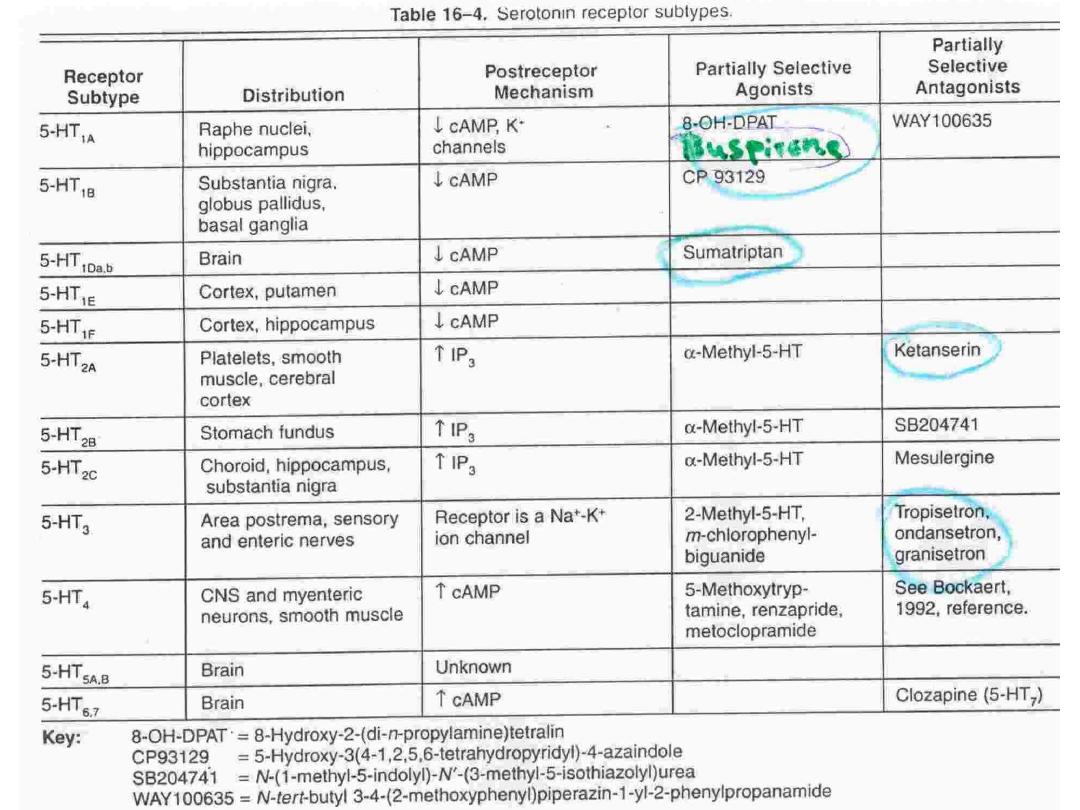
• Mechanism of action :
Interacts with
12 receptor
subtypes
• Why is 5-HT3 receptor differs from other 5-
HT receptors?

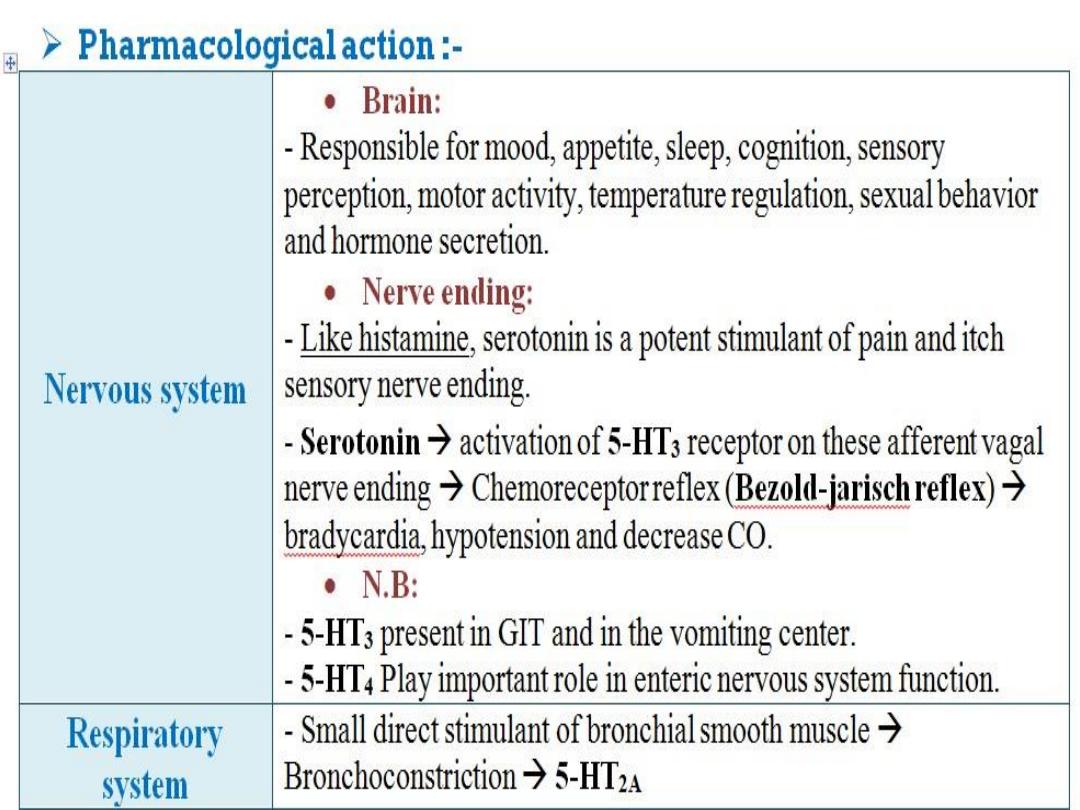
Pharmacological actions of Serotonin
• CVS:
1) Blood vessels:
Potent and direct contractions on smooth muscle (via
5-
HT
2
) EXCEPT : Skeletal Muscles and Heart blood
vessels.
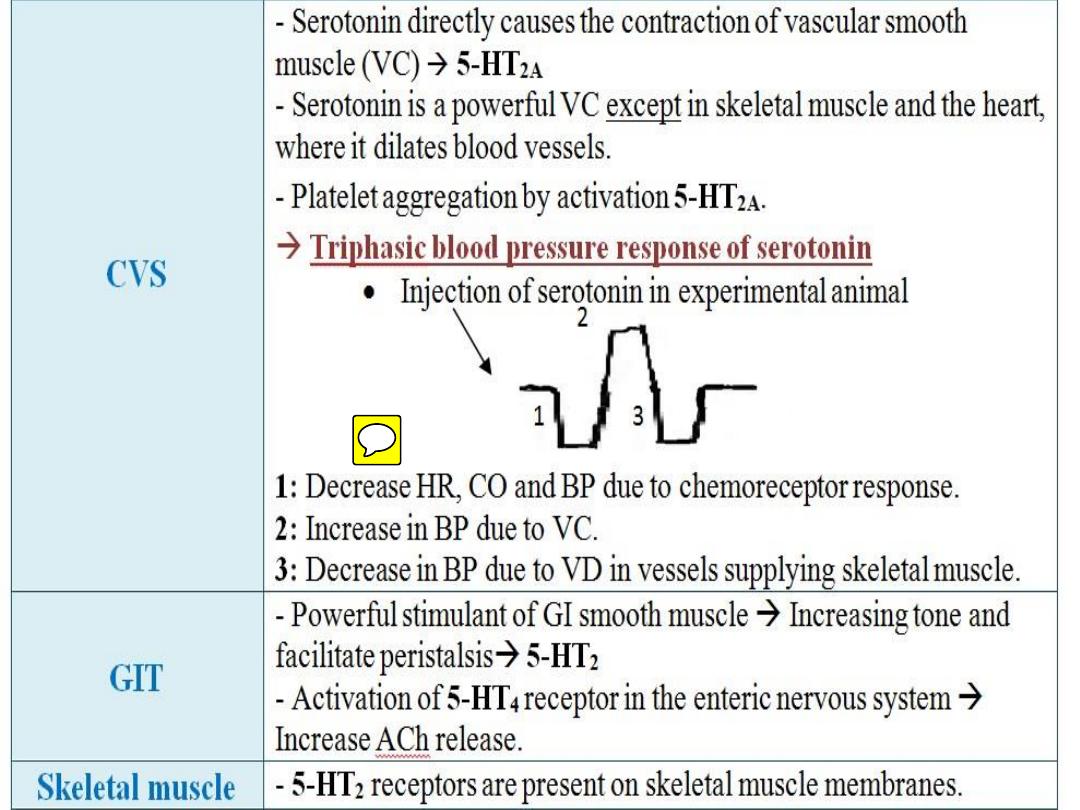
•
Note : 5- HT can give rise to triple action:
Decrease BP due to chemoreceptor
response then increase BP due to
Vasoconstriction (5-HT
2
), then decrease B.P due to
skeletal muscle V.D
2) Platelet: Increase platelet aggregation via 5-HT
2

• GIT:
• 1) increase contraction of smooth muscle (via
5- HT
4
).
2) Nausea and vomiting (via 5-HT
3
) therefore
5-HT
3
antagonists are used for R
X
of ?
•
Respiration :
5-HT may produce weak
bronchoconstriction.
• CNS:
very important.(Appetite; depression
and mania; Pain; Anxiety; Schizophrenia).

• Clinical Uses of Serotonergic Drugs:
• Note1:
Unlike NE or DA, serotonin its self
has no clinical uses, however, it
agonists
and
antagonists
have very important therapeutic
applications.
• Note 2:
Unlike histamine where only its
antagonists are used, serotonin agonists and
antagonists can be used.

Clin. Uses of Serotonergic Agonists:
1) Buspirone:
5-HT
1A
agonist used as anxiolytic agent.
2) Sumatriptan:
5-HT
1D
agonist for migraine (Treatment
and prophylactic).
3
) Metoclopromide (Plasil):
5-HT
4
agonist as prokinetic agent
(for Rx of gastroesophagial reflex). How does it work? And also
used for N/V
via 5-HT3 antagonistic
action.
4) Dexfenfuramine:
Acts by stim. Release and inhib. Reuptake
of serotonin.
Used as anorexic agent.
What is the effect of serotonin antagonists on appetite?

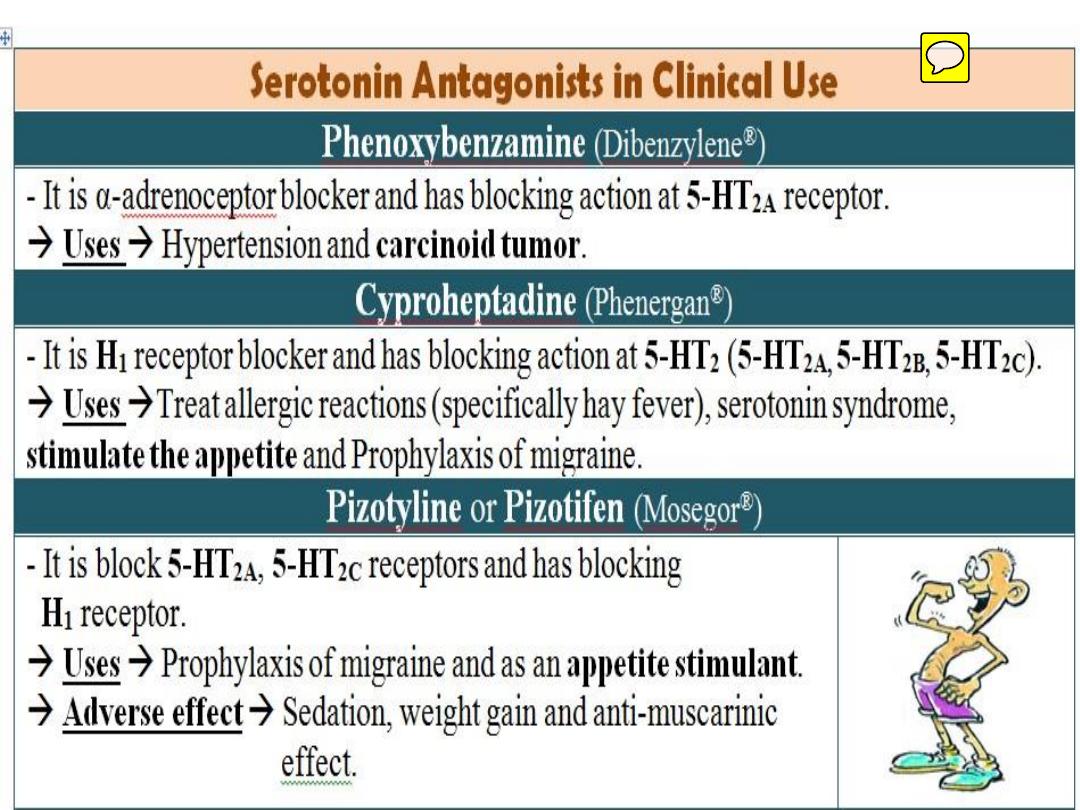
Clinical Uses of Serotonergic Antagonists:
1
) Ondan
s
etron
& Grani
setron
:
5-HT3 antagonists Common
used for
Rx of N/V induced by cytotoxic
(chemotherapy) drugs.
2
) Cyproheptadine
: Both H1, 5-HT1,2 and cholinergic antagonist
used for
Rx carcinoid tumor
(significant increases in serotonin)
and to
increase appetite
..
3) Ketanserin:
5-HT2/1c antagonist and
a
1-adrenergic blocker.
(used as antihypertensive agent)
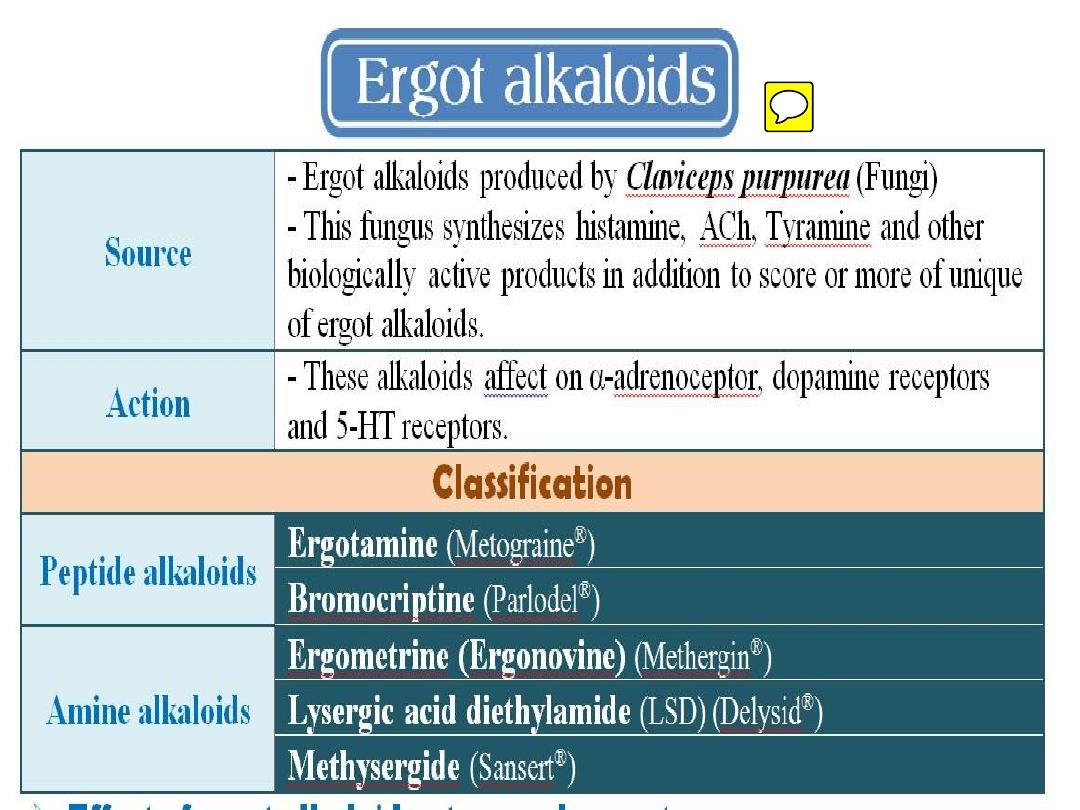
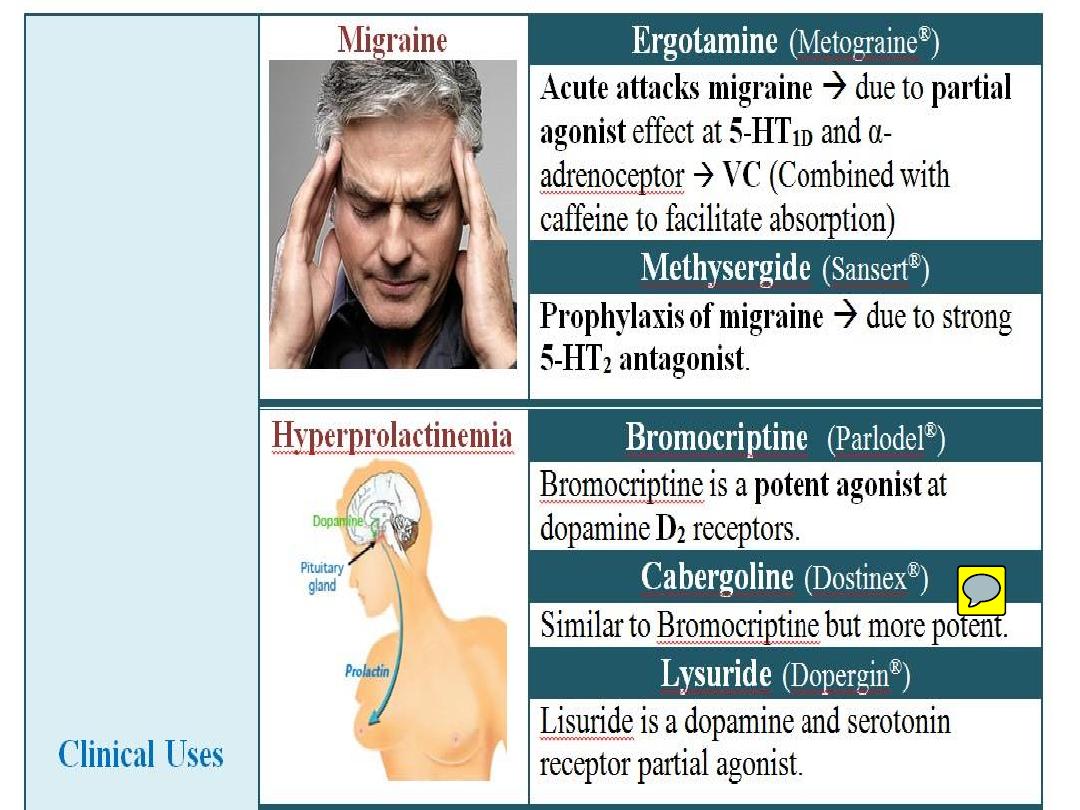
4) Methysergide:
This is an ergot alkaloid acts as 5-HT1,2
antagonist used for Rx of migraine.
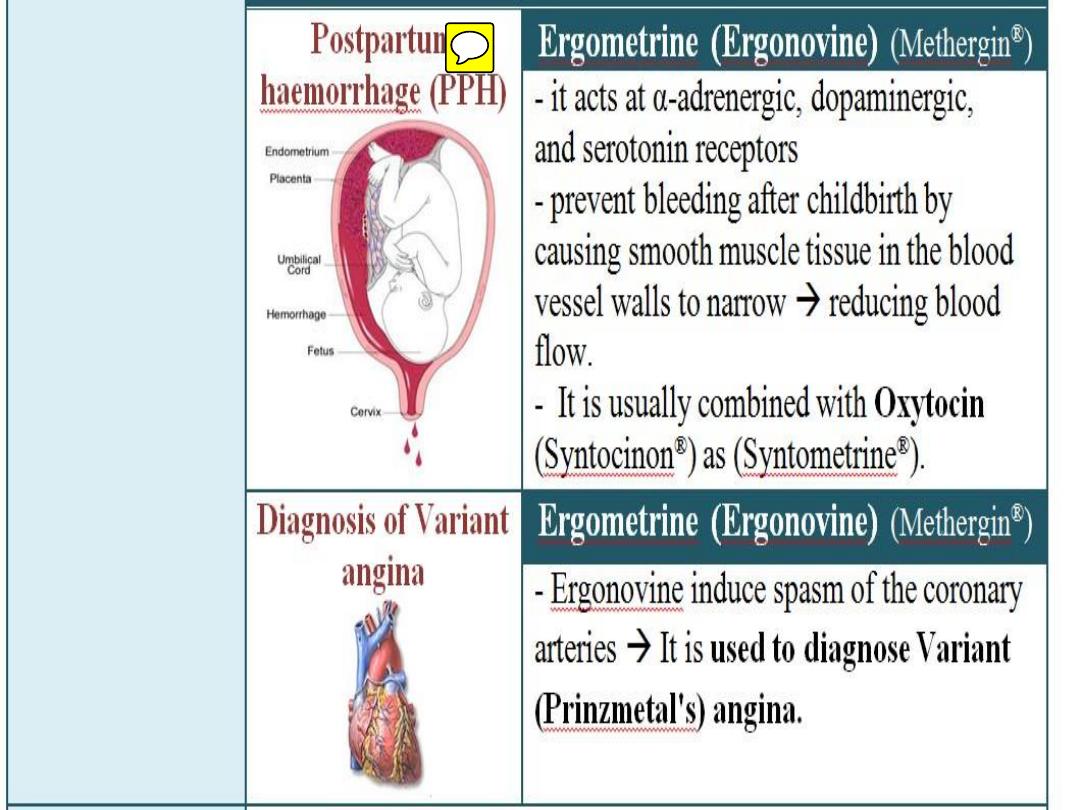

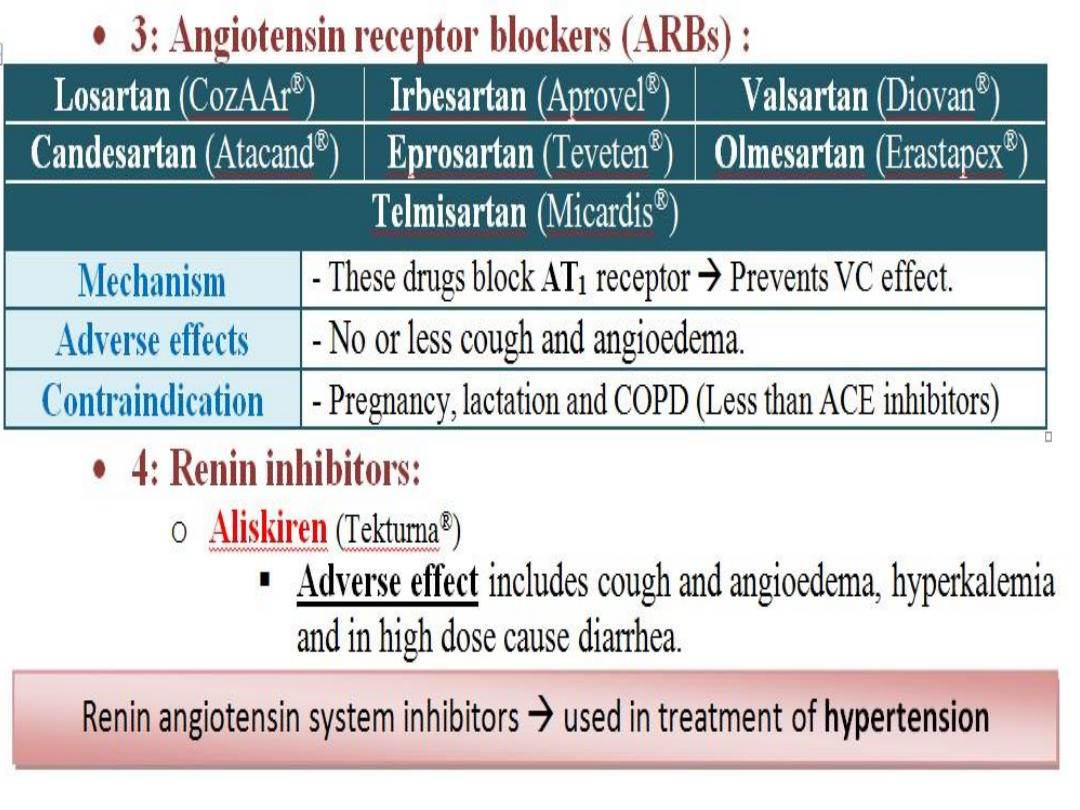
C. Vasoactive Peptides
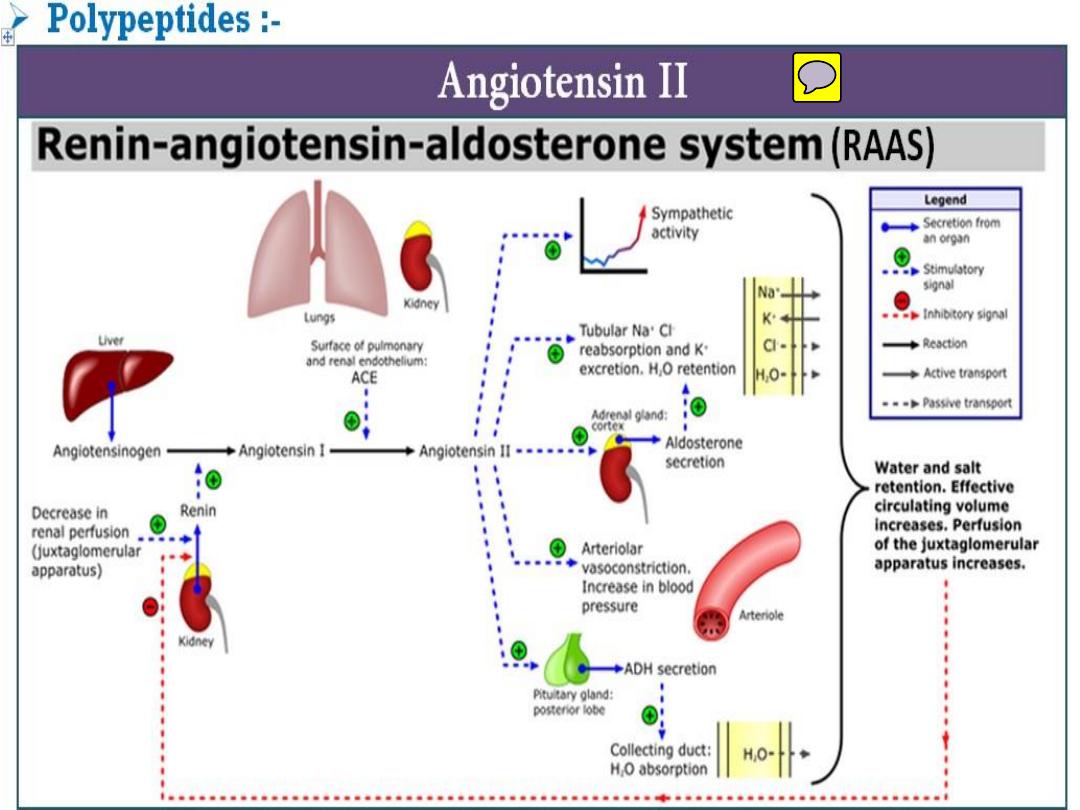
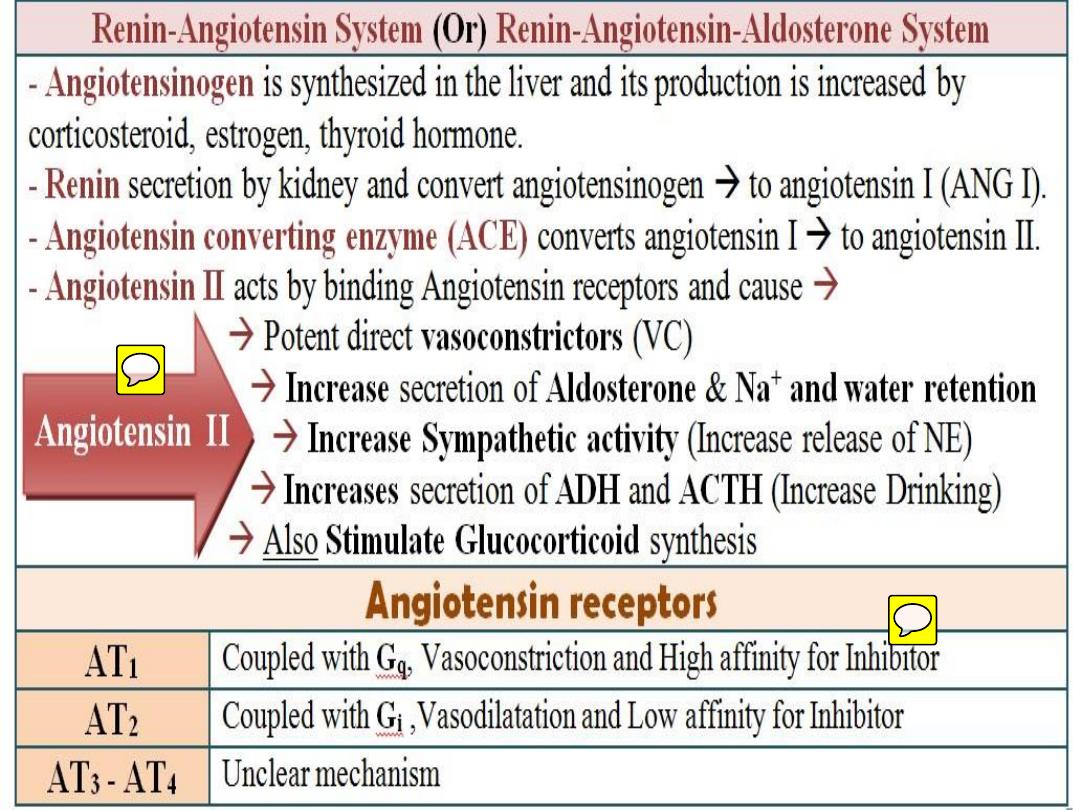
• A. Vasoconstrictors
(angiotensin II;
vasopressin; endothelins and
neuropeptide Y.
• B. Vasodilators
(Bradykinin and related
Kinins; Natriuretic Pepties; Vasoactive
Intestinal Peptide; substance P;
Neurotensin)



kinin
A group of vasodilator peptides formed by
the action of kallikreins (enzymes) on protein
substrates known as kininogens.

Kinins receptors & Mechanisms of action:
• Their biological effects are thought to be
mediated by specific receptors( membrane
receptors at target cells).
• -Two types of receptors (ß1&ß2)-bradykinin
recep.-
• - Some of their actions mediated by generation of
PGs, others may involve changes in intracellular
conc. of Ca
++
.
• -Metabolism of Kinins: rapid (t
1/2
less than 15
seconds) by Kininases.
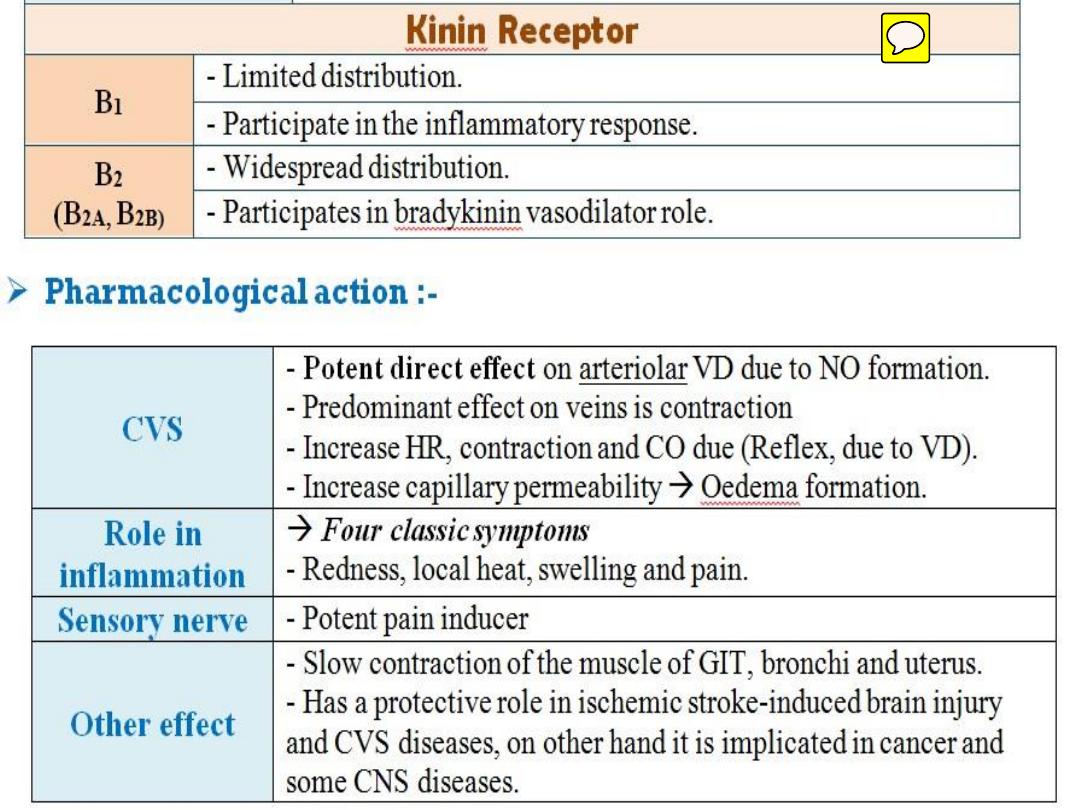

Vasodialtion may be due to:
I. A direct inhibitory effect of kinins on the
arteriolar smooth m.
II. May be mediated by the release of
vasodilator PGS(E2 & I2).

b. The predominant effect of kinins on veins is
contraction & may be due to:
1-direct stimulation of venous smooth m .. or
2- due to the release of vasoconstrictor PGs(F2
α).

2- Effects on the endocrine & exocrine glands:
I. Kinins may modulate the tone of salivary &
pancreatic ducts & help to regulate GIT
motility(due to effect on smooth m.).
II. They influence transepithelium transport of
H2O,electrolytes, glucose & amino asids & may
regulate their transport in the GIT & kidney.
III. May play a role in the physiologic activation
of various prohormones (proinsulin).
Ergotamine (Metograine
®
)

Bromocriptine (Parlodel
®
)
Cabergoline (Dostinex
®
)
Lysuride (Dopergin
®
)
Ergometrine (Ergonovine) (Methergin
®
)
Sumatriptan (Imigran
®
)
Captopril (Capoten
®
)

Losartan (CozAAr
®
)
Buspirone (Buspar
®
)
Tegaserod (Zelmac
®
)
Cyproheptadine (Phenergan
®
)
Pizotyline or Pizotifen (Mosegor
®
)
Ondansetron
(Zofran
®
)
Granisetron (Kytril
®
)
