Sunday 21 / 12 / 2014
Ali Kareem 2014-2015
©
Name
:
______________________________
Class
:
_______________________________
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
ANXIOLYTIC DRUGS
Lecture 5
Total lectures NO. 31
Dr. Mohammed Rashad

Anxiolytic & hypnotic drugs
Benzodiazepines (BDZ) :
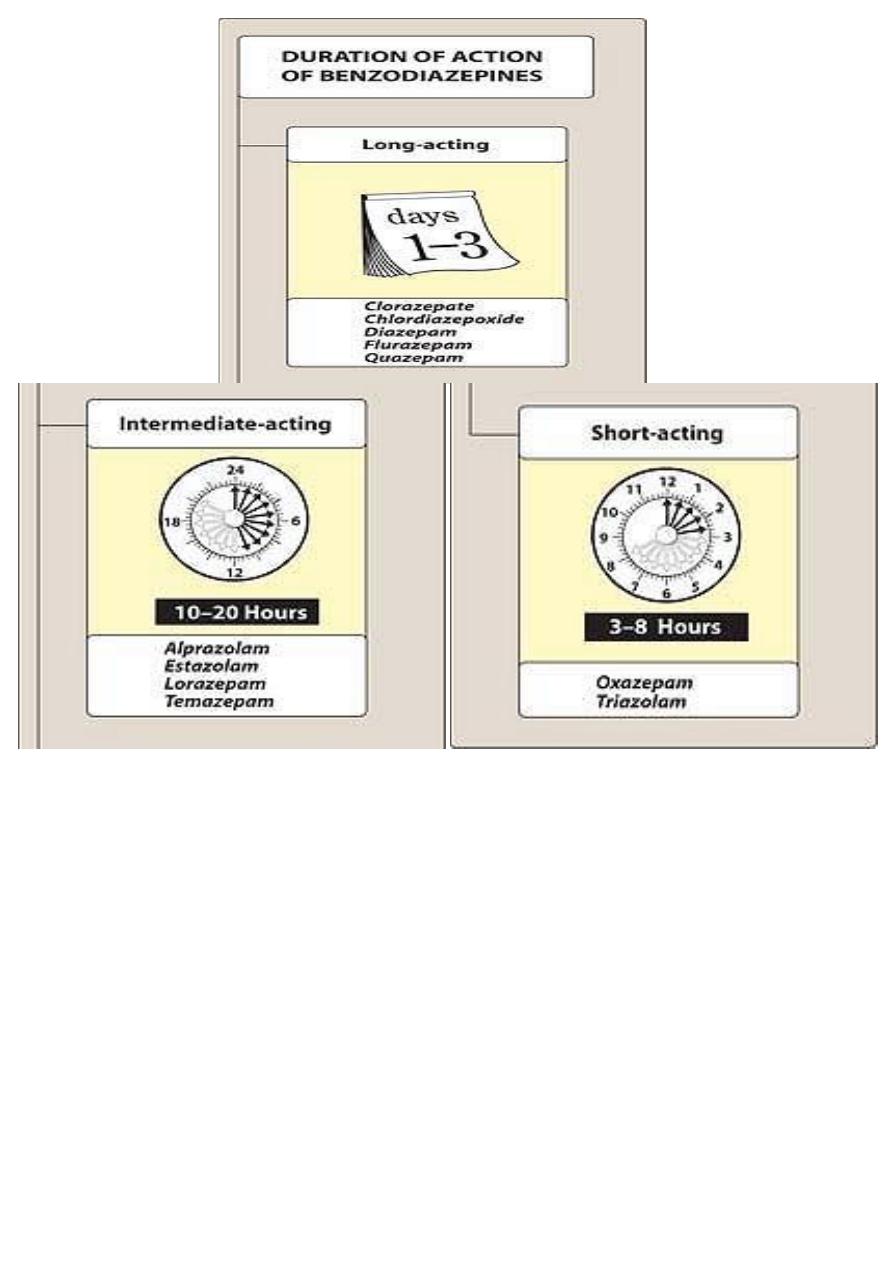
- long acting (1-3 days) , clorazepate ,chlor diazepoxide , diazepam ,
flurazepam, quazepam .
- intermediate acting (10-20 hs ) , alprazolam , lorazepam , estazolam ,
temazepam .
- short acting (3-8 hs ), medazolam , oxazepam , triazolam .
* ( benzodiazepine antagonist flumazenil ) .
* other anxiolytic drugs ( hydroxyzine , antidepressents ) .
Barbiturates :
long acting (1-2 days) : Phenobarbital . -
-short acting (3-8 hs): pentobarbital , amobarbital , secobarbital .
- ultra-short acting (20 minutes ) : thiopental .
* other hypnotic agents :
-zolpidem , zaleplon , ramelteon , eszopiclone .
-chloral hydrate .
-alcohol .
-antihistamines .
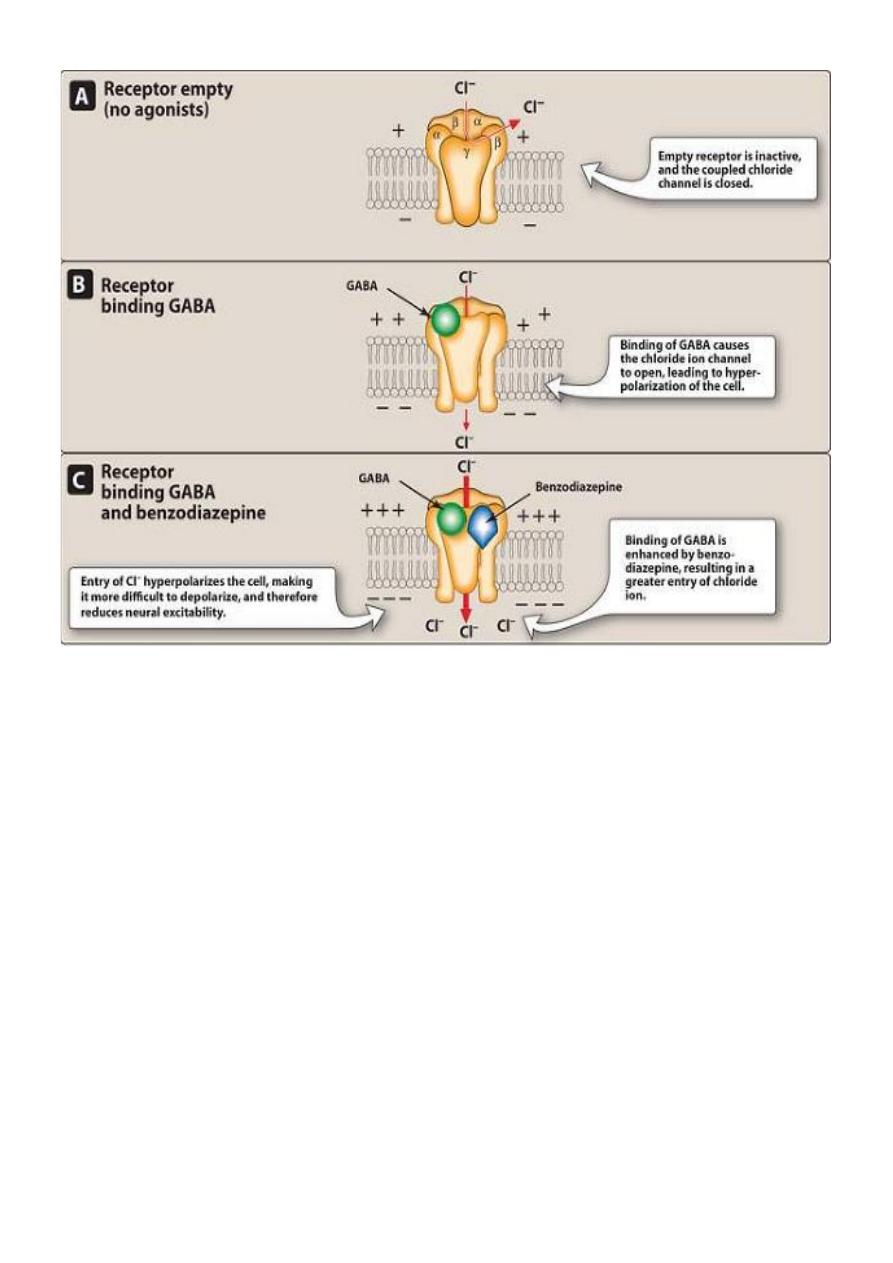
Mechanism of action of BDZs :
-
Empty receptor is inactive , & the coupled chloride channel Is
closed.

-
Binding of GABA causes cl ion channel to open
→hyperpolarization of the cell.
-
Binding of GABA is enhanced by BDZs →greater entry of cl ion.
-
Entry of cl ion hyperpolarizes the cell, making it more difficult to
be depolarized & therefore reduce neuronal excitability.
Ratio of safety = lethal dose ∕effective dose
BDZ : 1000 relatively safe , chlorpromazine 50 , morphine 10 .
Pharmacological actions of BDZs :
1- Reduction of anxiety: the BDZS are anxiolytics. at low doses they
inhibit neuronal circuit in limbic system .
2- Sedative and hypnotic actions : all BDZs have some sedative
properties and some of them have hypnotic properties (at high doses).
3- Anterograde amnesia: temporary impairment of memory (Alpha 1 &
GABAa receptors).
4- Anticonvulsant: for status epilepticus & seizure disorders (Alpha 1 &
GABAa receptors).
5- Muscle relaxant: at high dose
- Relax spasticity of skeletal muscle by ↑presynaptic inhibition in spinal
cord (alpha 1 & GABAa receptors).
- Baclofen (muscle relaxant affect GABAb).
Therapeutic uses of BDZ :
1- Anxiety disorders : For all types of anxiety, and not to alleviate the
normal stress of life.
- For severe anxiety and only for short periods.

- The long acting agents preferred in anxiety that require long period of
treatment.
- Alprazolam is effective for short and long period of treatment, for panic
disorders (30% withdrawal).
2- Muscular disorders:
- Sk. Muscle spasms (as in muscle strain).
- Spasticity from degenerative disorders (m.s. & cerebral palsy).
3- Seizures :
- Clonazepam for treatment of epilepsy (p.m.)
- Diazepam & lorazepam (drug of choice) for status epilepticus and
grandmal epilepsy.
- Chlorazepam , diazepam and oxazepam for treatment of alcohol
withdrawal
- And ↓ risk of withdrawal related seizures.
4- Sleep disorders :
- All BDZs are sedatives (calming effect) and some are hypnotic agents.
- BDZs (drug of choice) for insomnia:
• ↓latency time to falling asleep.
• ↓awakening during night.
• ↑total sleeping time.
5- Amnesia:
Short acting agents for premedication & unpleasant procedures (dental ,
endoscopic, bronchoscopic and angioplasty → amnesia , conscious
sedation & anxiety ↓).
- Midazolam (injectable only) for induction of anesthesia.

A-Flurazepam ( long acting BDZ):
Pharmacological action.
-↓sleep induction time.
-↓no. of awakenings.
-↑duration of sleep.
* causes little rebound insomnia.
* maintains its effectiveness 4 weeks .
Kinetics:
The t1∕2 of flurazepam and its metabolites is 85 hs →day time sedation
& accumulation.
(residual sedation = hangover ) .
B- Temazepam ( intermediate acting BDZ ) :
- For patients (with) frequent wakening.
- Peak sedative effect 1-3 hs after oral administration, therefore, it
should be given 1-2 hs before bed time.
C-Triazolam ( short acting BDZ ) :
- It is used to induce sleep (difficulty in going) .
- Tolerance occurs within few days → withdrawal→ rebound insomnia.
NOTE: Hypnotics either intermittently or for 2-4 weeks .
Pharmacokinetics:
The BDZs are lipophilic → rapidly & completely - absorbed &
distributed throughout the body.

The longer acting agents form active metabolites with long T1∕2 ,
so clinical durations of action do not always correlate with actual
T1∕2 , this may be due to receptor dissociation rates in CNS and
subcutaneous redistribution elsewhere.
- All BDZs cross the placental barriers & appear in breast milk. → ±
depress the CNS of newborn & infant.
- Most BDZs →hepatic metabolism →to active compounds .
-urine excretion as glucuronoids or oxidized metabolites
Dependence:
- Psychological and physical dependence of BDZs occur with high dose
over a prolonged periods.
- Abrupt discontinuation → withdrawal symptoms
- ( confusion , anxiety , agitation , restlessness , tension , insomnia , &
rarely seizure ) .
- short acting BDZs →more abrupt & severe withdrawal reaction more
than long acting BDZs ( in which withdrawal symptoms may occur slowly
& last no. of days after discontinuation of therapy .
Adverse effects:
- Drowsiness and confusion ( most common side effects )
- Ataxia ( at high dose & precludes activities that require fine motor
coordination such as driving .
- cognitive impairment ( ↓long-term recall & acquisition of new
knowledge .

Triazolam:
$ most potent oral BDZs .
$ most rapid elimination .
S ∕ E : rapid development of tolerance .
- Early morning insomnia .
- Daytime anxiety .
- Amnesia confusion snd drawsiness .
Precautions:
- Liver disease.
- Acute narrow-angle glucoma .
- Alcohol & other CNS depressants ±→ lethal drug over dose .
Benzodiazepine Antagonist :
Flumazenil = GABA receptor antagonist.
-
only i.v. , rapid onset & short duration
(T1⁄ 2( 1 hs ) .
- Frequent dose may ppt. withdrawal in dependent patient or causes
seizures in patients on BDZs therapy for epilepsy.
- Most common side effects : nausea , vomiting & agitation .
Other anxiolytic agents :
Buspirone ( NBDZs anxiolytics ) : has affinity to ( 5HT1A , 5HT2A ,D2 ) .

Therapeutic advantages:
1- Useful in long term therapy for GAD & chronic anxiety with symptoms
of irritability & hostility.
2- Does not potentiate the CNS depression of alcohol.
3- Low potential for addiction
Therapeutic disadvantages :
- Slow onset of action than BDZs.
- No muscle relaxation or anticonculsant activity.
Hydroxyzine :
- Highly sedative antihistamine with antiemetic activity.
- Useful for anxiety in patients with history of drug abuse.
- Useful for sedation prior to dental procedures or surgery.