
Sunday 21 / 12 / 2014
Ali Kareem 2014-2015
©
Name
:
______________________________
Class
:
_______________________________
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
BARBITURATES
Lecture 6
Total lectures NO. 32
Dr. Mohammed Rashad

2
Barbiturates:
Today they have been replaced by BDZs because they induce :
- Very severe withdrawal symptoms.
- Respiratory depression.
- Enzyme induction.
Mechanism of action:
- Barbs potentiate GABA action by prolonging the duration of cl ion
channels openings .
- Block excitatory glutamate receptors .
- Block sodium channels by anesthetic concentration . All these
molecular actions decrease neuronal activity .
Pharmacological actions :
1- depression of CNS :
Sedation hypnosis anesthesia coma& death
+ ++ +++ ++++
Thus the degree of depression of CNS depends on the dose .
- they have no analgesic action & ± exacerbate pain .
- chronic use → tolerance .
2- respiratory depression : inhibition of hypoxic response to CO2 &
overdose →respiratory depression & death .
3- enzyme induction : chronic use →↓action of many drugs that utilize
p450 .

3
Therapeutic uses :
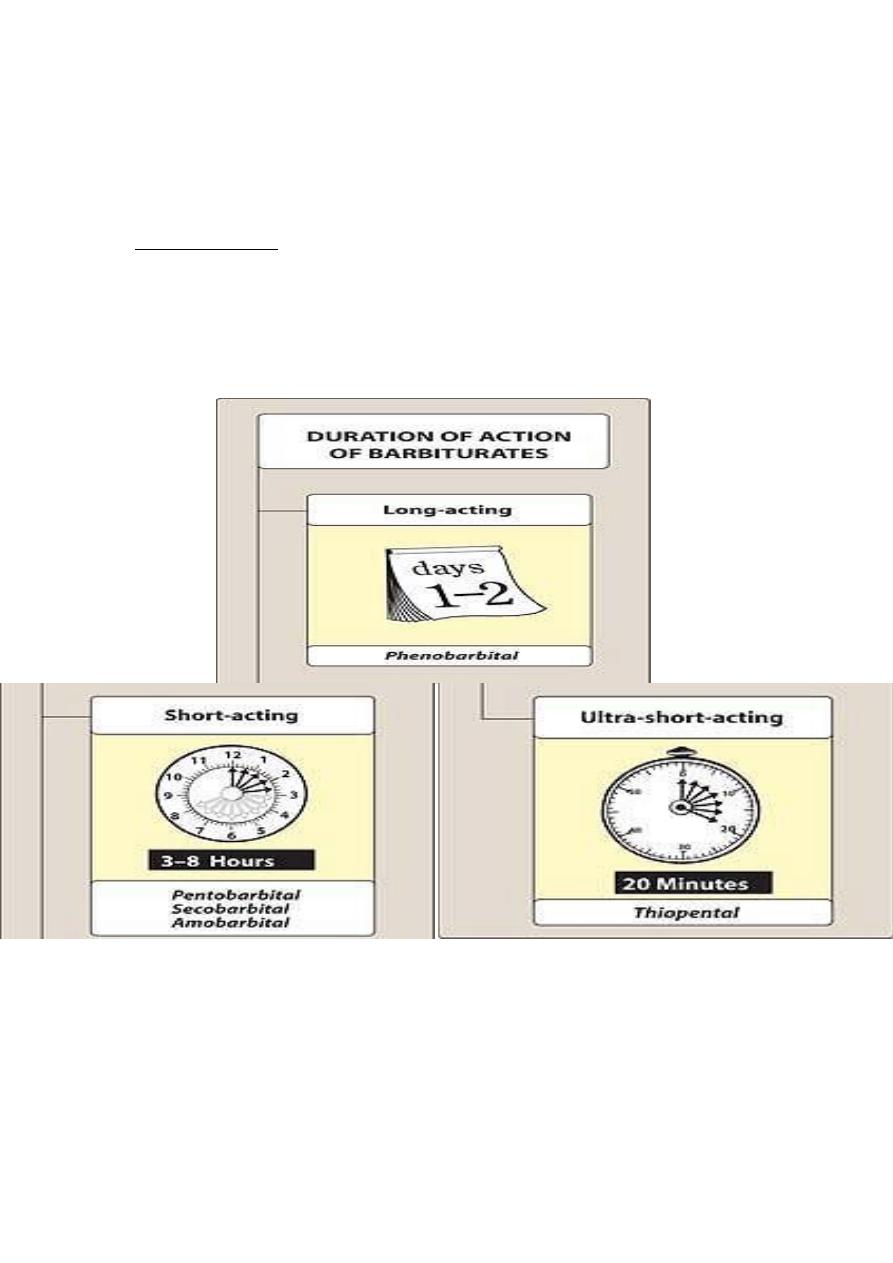
1-anesthesia : thiopental ( ultra-short acting ; i.v for induction of
anesthesia ) .
2- anticonvulsant :
- Phenobarbital for ( tonic clonic seizure , status epilepticus , eclapsia ) .
- Phenobarbital ( drug of choice ) for treatment of febrile seizure.
S\E: depress cognitive performance in children
3- anxiety:
- mild sedatives for ( anxiety , nervus tension , insomnia ) .
( replaced by bdzs )
Pharmacokinetics : oral→ absorption→ liver metabolization →wide
distribution → urine excretion .
( from brain →splanchnic area→ sk. muscle →finally to adipose tissue .
Adverse effects :
1- CNS: ( drowsiness , impaired concentration , mental & physical
sluggishness ) . This effect synergized with alcohol .
2- drug hangover : hypnotic dose .
- feeling of tiredness after waking .
- impaired ability to function normally .
- occasionally , nausea & dizziness .
3- physical dependence : abrupt withdrawal is more severe than opiates
.
- tremors , anxiety , weakness , restlessness , N&V seizures , delirium &
cardiac arrest→ death .

4
Precautions :
- barbs ( enzyme inducer) →↓ effect of drugs that are metabolized by
p450 hepatic enzyme .
- barbs increase porphyrins synthesis → C\I in patients with acute
intermittent porphyria .
Barbs poisoning : over dose → death from ;
( respiratory & central cardiovascular depression ) →shock .
- treatment : no specific antagonist .
- artificial respiration .
- GI evacuation .
-hemodialysis .
- alkalinization of urine .
Other hypnotic agents : ( non bdzs hypnotics ) :
- zaleplon .
- zolpidem : few residual effects .
Therapeutic advantages :
- show minimal withdrawal effects .
- exhibit minimal rebound insomnia .
- little or no tolerance occur with prolonged use .
Therapeutic disadvantages :
- have no anticonvulsant or muscle relaxing properties .
- adverse effects : nightmares , agitation , headache , GI upset , dizziness
, day time drowsiness ,)

5
Eszopiclone : effective for up to 6 months .
Ramelteon : selective agonist at MT1 , MT2 ( melatonine ) .
Light ++ retina → signal to SCN ( hypothalamus ) →signal to pineal gland
→inhibits melatonine release →dark → ++ melatonin→ sleep .
Therapeutic advantages :
1- the potential for abuse is minimal with minimal dependence or
withdrawal effects .
2- the drug can be administered long-term .
3- for patients with increased sleep latency .
Therapeutic disadvantages :
1- dizziness , somnolence & fatigue .
2- increased prolactin levels .
Chloral hydrate
( trichloroacetaldehyde )
- acetaldehyde CL3 →( liver ) ethanol CL3 .
- The onset of sleep induction is 30 minutes & the duration 6 hs .
- irritant to GIT → epigastric distress & unpleasant taste sensation .
-
it synthesized with ethanol .
Antihistamines : non prescription sedative antihistamines as doxylamine
are effective in mild insomnia .
S\E : anticholinergic side effects .
Ethanol ( ethyl alcohol ) : has anxiolytic & sedative effects but its toxic
potential outweigh its benefits .

6
- alcoholism is a serious medical & social problem , CNS depressant
→sedation →hypnosis ( if large dose ) .
- thus a shallow dose – response curve
( wide dose range → sedation ) .
- oral absorption & total body H2O is volume of distribution ; liver
metabolism ; kidneys & lung execretion .
- it produce severe CNS depression with bdzs , antihistamines , barbs .
- chronic consumption : 1- severe liver disease . 2- gastritis . 3-
cardiomyopathy . 4- nutritional deficiency .
Treatment of alcohol withdrawal :-
1- bdzs ( treatment of choice ) .
2- carbamazepine : for convulsion episodes during withdrawal .
1- disulfiram :
Ethanol → ( by alcohol dehydrogenase )→ acetaldehyde →
( by aldehyde dehydrogenase ) → Acetate .
-(disulfiram ) inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase → accumulatiom of
acetaldehyde in blood → flushing , hypoventilation , tachycardia &
nausea .
- some use in patient serioudly desiring to stop alcohol ingestion .
- the patient abstains from alcohol to prevent unpleasant effect of
disufiram .
- induced acetaldehyde accumulation
2-Naltrexone :
long acting opiate antagonist ( oral ,injectable)
7
- FDA approved for alcohol dependence conjunction with supportive
psychotherapy
( better tolerated than disulfiram ) .
3- Acamprosate:
yet poorly understood mechanism .
- it is utilized in alcohol dependence treatment programs in conjunction
with supportive psychotherapy .
