Sunday 16 / 11 / 2104
@Ali Kareem 2014-2015
ANTI-COAGULANTS
Lecture 3
Total lectures NO. 17
Dr. Naseer Al-Harchan
"Pharmacology
Name
:
______________________________
Class
:
______________________________
مكتب اشور لالستنساخ
1
xa
t
+ +
+
brio
r
gula
++
(ant
ANTICOAGULANTS
Formation of thrombus:
Prothrombin hrombin (II a)
+
Fibrinogen (I) Fibrin (Ia)
Plasminogen plasmin
- - Fi nlysis
1. Heparin: (Direct anticoagulants)
Strong acid, -ve charged mucopolysaccharide.
Various ++ elease from liver and lung mast cell into circulation.
Mechanism of Action: act in vitro and in vivo:
1. Antithrombin III (heparin cofactor) + IX, X, XI, XII
Heparin
Complex (anticoa nt action)
2. Antithrombin III + thrombin
Heparin
30- time
complex icoagulant action)
(+ +) means stimulation while (- -) means inhibition.
2
+ +
_ _
cleaning factor "lipoprotein lipase”
f
h
Thrombin
1. Platelets Platelets aggregation
Heparin
2. Heparin intake by endothelial cells
Pharmacological Actions:
1. Anticoagulant action.
2. Lipemia clearing factors production:
Triglyceride ree fatty acid
3. Suppresses aldosterone production.
4. Increase free plasma thyroxin.
Inhibits antifibrinolytic drugs and antifibrinolysis
Kinetics:
- S.C, LV (not orally because it will be destroyed in the stomach).
- I.M ematoma.
- Infusion with glucose or saline.
- Low molecular wt. heparin (once daily), safe, not required daily control
(Dalteparen, Enoxaparin, Tineaparin ).

3
P 2
Lab. control:
1. Activated Partial thromboplastin Time (APTT).
2. Kaolin Cephalin Clotting Time (KCCT).
Adverse effects:
1. Bleeding (may be cerebral hemorrhage).
2. Acute thrombocytopenia (reversible).
3. Osteoporosis and spontaneous fractures.
4. Hypersensitivity as severe asthma, urticaria, ± anaphylaxis.
5. Diarrhea (rare).
Alopecia = boldness (transient).
Heparin Antagonist: Protamine SO4 :
Basic drug from fish ± : - 1.sudden B .Flushing 3.Dyspnea
Contraindication:
1. Active bleeding or bleeding tendency e.g. Pu, SBE, sever HPT
2. Heparin hypersensitivity.
3. Eye, Brain & spinal cord surgery (closed chamber surgery).
2. Warfarin: (Indirect oral anticoagulants)
Mechanism:
It INHIBITS activation of factors:
1. II (prothrombin)
2. VII, IX,X (vit.K dependent factors)
4
poxid
activ
e
Inactive II, VII, IX, X Inactive II, VII, IX, X
carboxylase
Vit. K ( e) Vito K e e (inactive)
reductase
onset of action: 72 hrs, this delayed time because the conc. of factor II must
nough to show their effects, so we start with heparin (which acts immediately).
Side effects
1. GIT upset.
2. Cutaneous lesion as purpura and other bleeding.
3. Teratogenic abnormality.
Control:
Prothrombin time: normal
INR, PT control: during therapy 2-3 times of normal
Contraindication:
1. bleeding or bleeding tendency e.g. Pu.
2. Severe renal, liver diseases.
3. HPT and increase risk of cerebral hemorrhage.
Warfarin Antagonists
1. Whole blood transfusion.
2. K1 = Phytomenadione.
Side effects: Anaphylaxix (I.V.) and Haemolysis (in G6PD deficiency)
5
++
Fibr
thrombin ++
Fi
brin
+
+
F
s
Uses of Anticoagulants:
Prophylactic (stop formation of Fibrin) .
Treatment (prevent propagation of thrombus).
1. Deep venous thrombosis, DVT (treatment & prophylactic).
2. Arterial thrombosis (valuable in prophylactic).
3. Thromboembolic pulmonary HPT (lifesaving).
4. Acute myocardial infarction.
5. Unstable angina.
6. Rheumatic mitral valve disease.
7. Cerebro Vascular Accident (CVA) : thrombosis, infarction.
8. Transient ischemic attacks (TIA), aspirin usually used.
9. Disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
10.Dialysis (heparin to maintain blood fluidity).
Fibrinolytics *and antifibrinolytics
**:
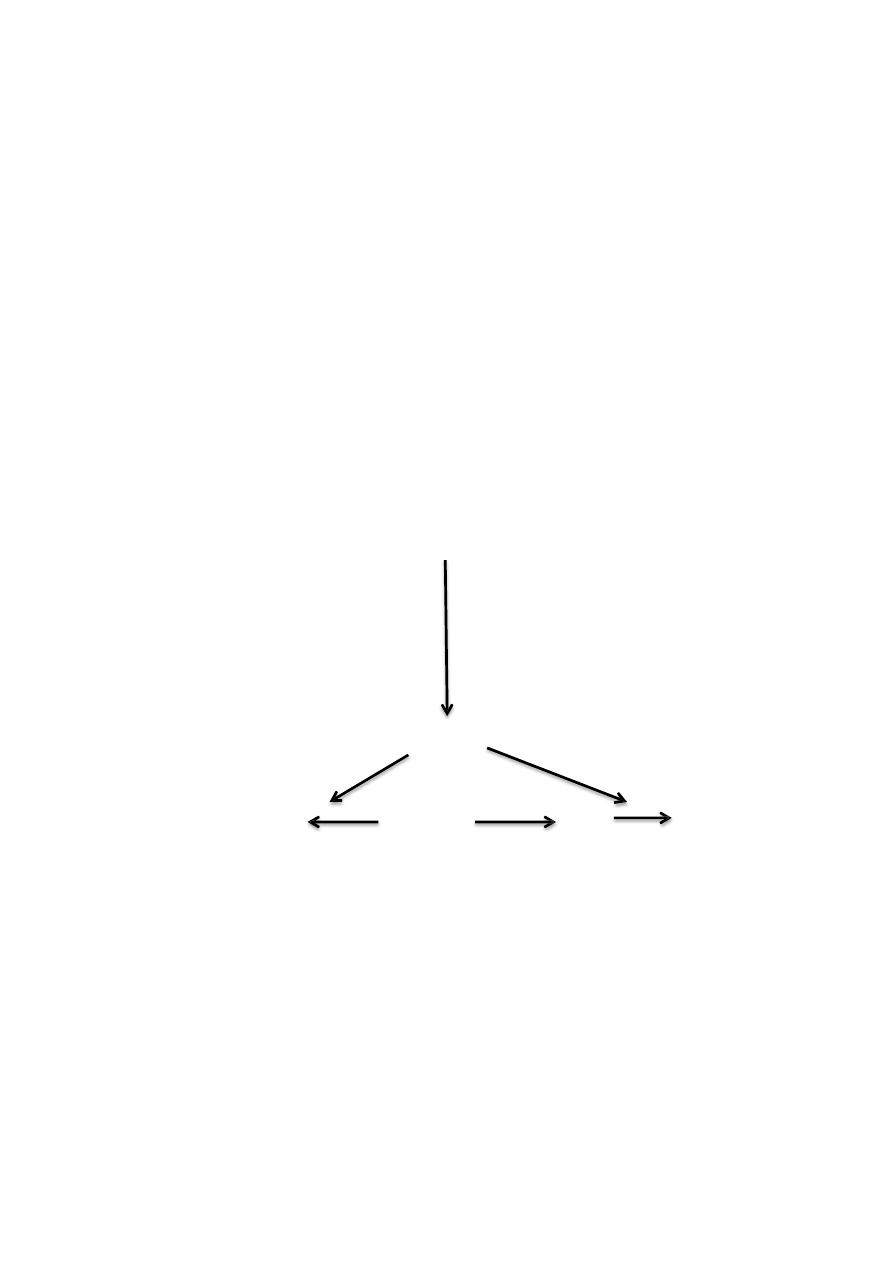
Plasminogen
Activation Inhibition
Fibrynolytics(thrombolytics): Antifibrynolytics
Streptokinase & Urokinase Amino caproic acid
Antistreplase Tranexamic acid
Alteplase (TPA = tissue
Plasminogen activator)
Plasmin
Degradation product inogen ibrin salt
products
* also called plasminogen activators or thrombolytics. ** also called plasminogen inhibitors.
6
re
in
in
s c
Plasminogen activator
Plasminogen inhibitor
Clinical Uses:
1.Coronary thrombosis (emergency)
[major application]
1-3 hrs canalization
2.Multiple pulmonary emboli
3.DVT.
Clinical uses:
1. Acute episode in hemophilia.
2. Other bleeding disorders.
Side effects:
1. Bleeding as cerebral hemorrhage.
2. Allergic reaction (streptokinase)
Intra-arterial or I.V.
Orally active
Property
Heparin
warfarin
Structure
large polymer, acidic
small, lipid soluble
Route of Admn.
parenteral
oral
Site of action
blood
liver
Onset of action
Rapid (seconds)
slow, depend on t 1/2 of
factors being replaced
Mechanism
activate Antithrombin III
impairs synthesis of II,
VII, IX, X
Antidote
protamine
vit. K, plasma
uses
acute, over days
chronic, over weeks or
months
Antiplatelet drugs:
Aspirin:
Mechanism : Inhibits cyclooxgenase (irreversible) hibits thrombaxans
(TX) synthesis.
Uses: 1. Myocardial infarction (MI).
2. transient ischemic attacks (TIAs), other thrombotic events.
Dipyridamole:
Mechanism: inhibits phosphodiesterase hibit AMP in platelets.
Uses: prevent thrombosis of artificial valve (limited uses).

7
Ticlopidine:
Mechanism: inhibits ADP (powerful stimulator of platelets aggregation).
Uses: effective in preventing TIAs (particularly valuable for patient who can't
tolerate aspirin).
Side effects:
1. GIT upset.
2. Bleeding in 5 %.
3. Leucopenia in 1 %.
Clopidogril:
Less side effects and the leucopenia is negligible.
Drugs used in clotting Disorders
A. To reduce clotting:
1) Anticoagulants:
• Heparin, Enoxaparin (LMW), Lepirudin, Danaparoid
• Warfarin (oral)
2) Antiplatelet drugs:
• Aspirin, Dipyridamole, Eptifibatide, Tirofiban
• Ticlopidine, clopidogril

8
B. To facilitate clotting:
1) Plaminogen inhibitors:
• Amino caproic acid
• Tranexamic acid
2) Replacement factors:
• Factor VIII
• Factor IX
3) thrombolytics or Fibrinolytics or Plasmingen activators
• Streptokinase, Urokinase
• Antistreplase Alteplase
3) Vit. K:
• Kl = phytonadione
• K2= menadione
