Lab.1
3
rd
-year class
Practical Pharmacology
2010-2011

Routes of Drugs
Administration

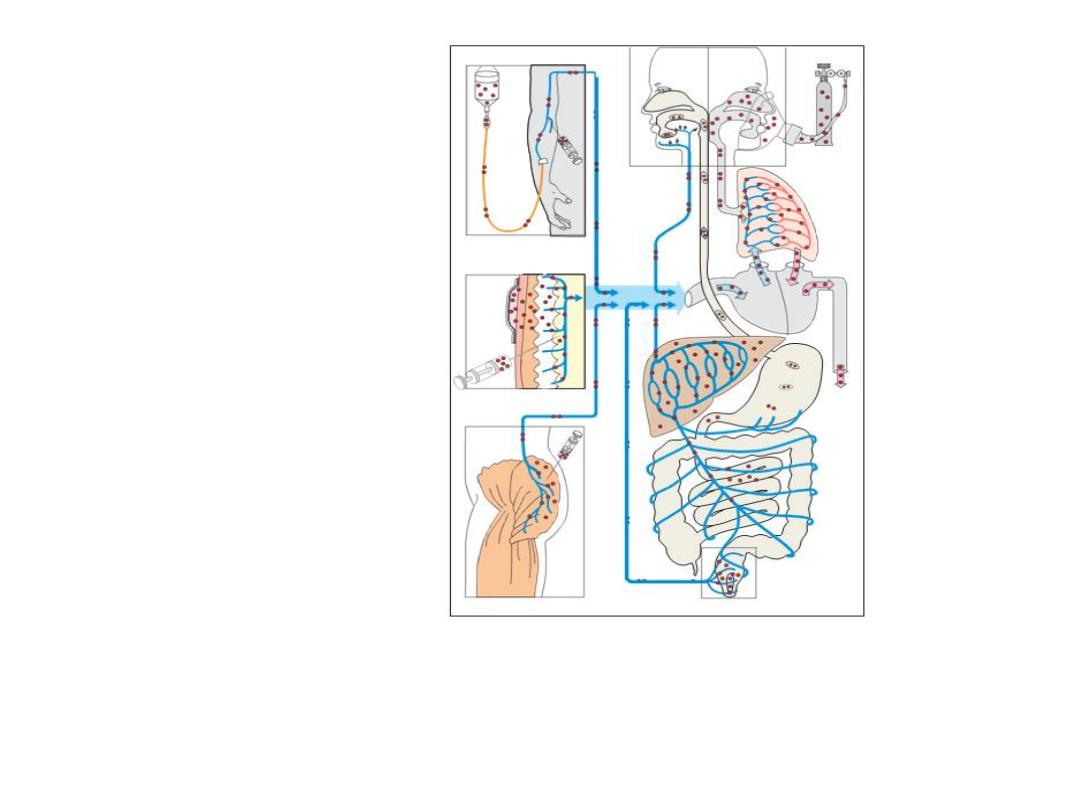
Enteral routes of
administration
1-Swallowing
2-Sublingual (buccal)
3-Rectal

Swallowing
1-For systemic effect
2-For effect in the gut

For systemic effect
:
Advantages
1. Convenience
2. Acceptability

:
Disadvantages
1.Absorption may be delayed, reduced or evenly
enhanced after food.
2.Absorption may be slow or irregular after drugs
that inhibit gut motility ( antimuscarinic,opioids,..)
3.Difference in presystemic elemination is a cause
of variation in drug effect between patients.

4.Some drugs are not absorbed ( gentamycin )and
some drugs are destroyed in the gut (insulin).
5.Tablets taken with too small quantity of liquid in
supine position, can lodge in the esophagus with
delayed absorption and may even cause
ulceration(doxycyclin,KCL)especially for elderly
and those with left a trial enlargement.

For effect in the gut
:
Advantages
1.The drug can be placed at the site of
action(neomycin,antihelmethics)
2.In non-absorbed drugs the local
cocentration can be higher than it
would be safe in the blood.

Disadvantages:
1.The drug distribution may be uneven
2.In some diseases of the gut the whole
thickness of the wall is affected and
effective blood concentration may be
needed(bacillary dysentry,typhoid
)

2-sublingual or buccal sulcus for
systemic effect
Advantages
1. Quick effect is obtained (glycerol trinitrate ,
nifidipine) especially if the tablet is chewed
,giving a greater surface area for solution .
2. The effect can be terminated by spitting
out the tablet .
Disadvantages:
1. The inconvenience if use has to be
frequent.
2. Irritation of the mucous membrane.
3. Excessive salivation which promote
swallowing ,so losing the advantages
of
bypassing presystemic elimination .

3- rectal administration
• A-for systemic effect
• B-for local effect

A-for systemic effect (suppositories
or solution )
Advantages
1. A drug that is irritant to the stomach can
be given by suppository
(aminophylline,indomethacin)
2. The route is suitable in vomitting
,migraine,morning sickness or when the
patient cannot swallow.
3. When cooperation is lacking (sedation in
children).

:
Disadvantages
1. Psychological :the patient may be
embarrassed or may like the route too
much .
2. Rectal inflammation may occur with
repeated use.
3. Absorption may be unreliable (especially
if rectum is full of feces).

B-for local effect
e.g. in proctitis or colitis

Parenteral routes of administration
1. Intravenous (bolus or infusion)
Advantages:
1. It gives swift, effective and highly predictable
blood concentration .
2. It allows rapid modification of dose ,i.e.
immediate cessation of administration is
possible if unwanted effects occur during
administration.
3. The route is suitable for administration of drags
that are not absorbed from the gut or too
irritant to be given by other routes (anti
cancer).

Disadvantages
1. Local venous thrombosis is liable to occur with
prolonged infusion and with bolus doses of
irritant formulations .(diazepam , micro
particulate components of infusion fluids)
2. Infection of intravenous catheter and the small
thrombi on its tip are risky during prolonged
infusions .
3. Plasma concentrations may rise at such a rate
that normal mechanisms of distribution and
elimination are outpaced. So, hazard if a drug
is given too quickly.

intramuscular injection
-
2
:
Advantages
1.
Reliable route.
2.
Depot preparations (penicillin, neuroleptics ) can be
used at monthly or longer intervals.
3.
Suitable for irritant drugs.
4.
Absorption is more rapid than following subcutaneous
injection ( soluble preparations are absorbed in 10-30
min. )
Disadvantages
:
1.
The route is not acceptable for self-administration.
2.
It may be painful .
3.
If any adverse effect may occur to a depot formulation ,
it can not be removed.

subcutaneous injection
-
3
:
Advantages
1. Reliable route
.
2. Acceptable for self
– administration .
Disadvantages
:
1. Poor absorption in peripheral circulatory failure
.
2. Repeated injections at one site may cause
lipoatrophy , resulting in erratic absorption .

inhalation
-
4
A-as a gas : volatile anaesthetics .
B-as an aerosol : these are particles
dispersed in a gas , the particles are
small enough to remain in suspension for
a long time instead of sedimenting
rapidly under gravity . These particles
may be liquid (fog) or solid (smoke) e.g.
salbutamol .
C-as a powder : sodium cromoglycate .

Advantages:
1-Can be rapidly taken up or eliminated
giving the close control that has marked
the use of this route in general anesthesia.
2-Self administration is practicable.
3-Aerosol&powder provide high local
concentration for action on bronchi,
minimizing systemic effect.
4-Aerosol can be used for systemic effect
(ergotamine in migraine).

:
Disadvantages
1-Special apparatus is needed.
2-Drug must be non-irritant if the patient is
concious.
3-Obstructed bronchi may cause therapy to
fail (mucus plug).

5-Topical application
1-For local effect
2-For systemic effect

For local effect
(skin ,eye ,lung ,anal canal ,vagina)
:
Advantages
Provision of high local concentration without
systemic effects.

Disadvantages:
1-Absorption can occur, especially when
there is tissue destruction so that systemic
effects result.
2-Occular administration of
β- adrenoceptor
blocker may cause systemic effect(1
st
-
pass elimination is bypassed) and such
eye drops are contraindicated to patients
with asthma or COAD.

For systemic effect
Transdermal delivery system (TDS) release drug
through a rate controlling membrane into the
skin and so into the systemic circulation.
Fluctuations in plasma concentrations associated
with other routes are largely avoided, as is 1
st
-
pass elimination in the liver.
-
GTN in angina and ERT in post
:
Examples
menapause can be given as sticking plaster to
skin or as an ointment.