
1
Parasitology
Lecture: 2
د
.
هيفاء
The genus Trichomonas
-These are common flagellates of the tropical areas,.
-They exist only in tropHozoite stage.
-They are pear-shaped body and measures 10-12 microns in length, a single
ovoid nucleus is situated at the rounded anterior end and a cleft-like
depression (mouth) lies at its side.
-There are 3-5 free flagella, a thicker flagellum passes backwards along the
side of the body forming the undulating membrane and coming out free at
the posterior end.
-The undulating membrane is supported at the base by a rod like structure
(costa).
-The axostyle runs down the middle of the body and ends in the pointed end.
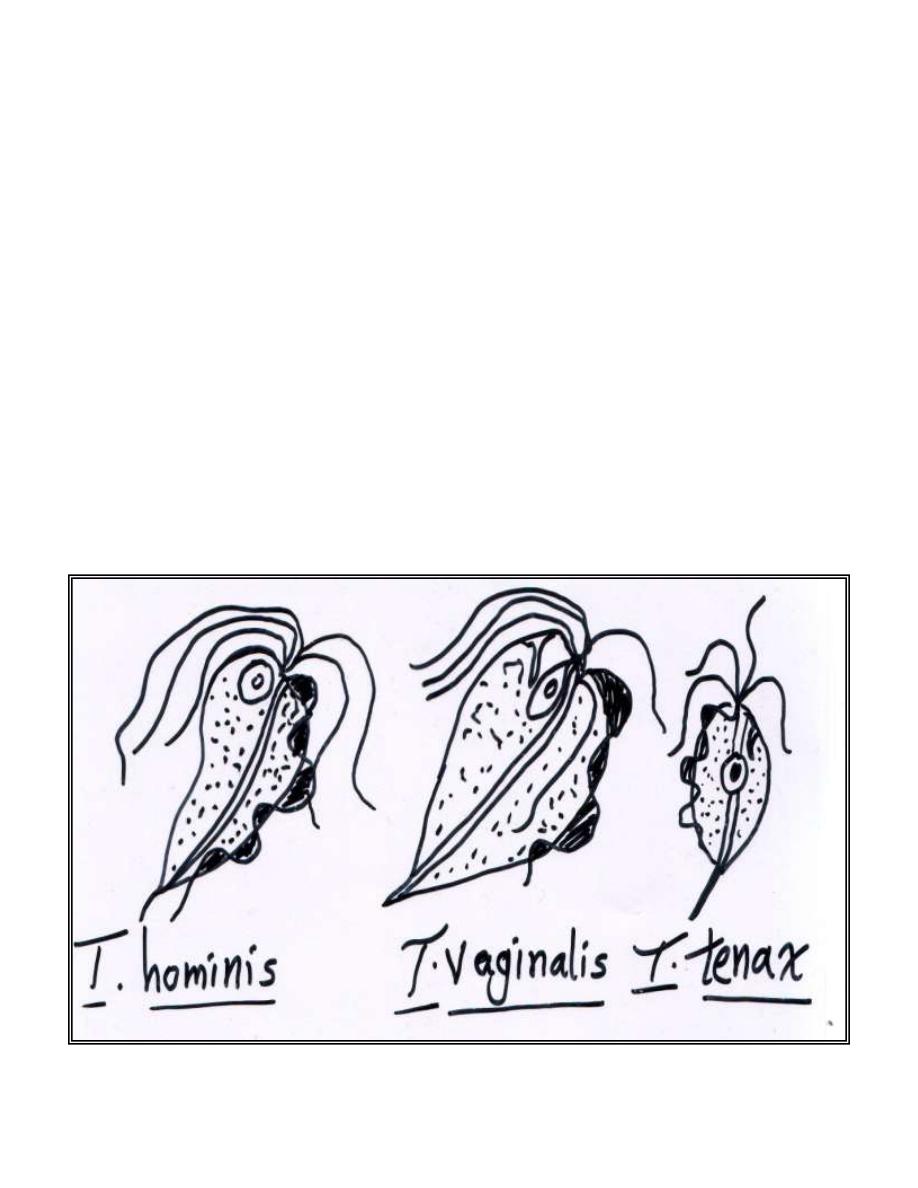
Genus Trichomonas is classified into 3 species:

2
1- T.hominis: inhabiting the ileo-caecal region.
2- T.tenax: inhabiting the oral cavity.
3- T.vaginalis: inhabiting the female genital tract, also found in the urinary
tract of both males and females.
Trichomonas hominis
-There is no proof that T.hominis is pathogenic.
-It is most commonly diagnosed in unformed stools that contain
considerable mucous.
Trichomonas tenax
-This specie is slightly smaller than T.hominis .
-Its normal habitat is the mouth , particularly in diseased gums , in tartar
around the teeth and in carious teeth.
-It is not pathogenic but its presence indicates poor hygiene.
Trichomonas vaginalis
-The motile organism is larger than T.hominis and T.tenax reaching in length
27 microns and 18 microns in breadth.
-T.vaginalis is a pathogenic flagellate that infects the urogenital tracts of
males and females.

3
-It is primarily a sexually transmitted disease.
-The incidence of trichomaniasis differs depending on the population
examined, factors such as lower socio-economic state, multiple sex partners
and poor personal hygiene which linked to higher incidence of infection.
-The life cycle of T.vaginalis includes only trophozoite stage. The organism
is similar in morphology to the other trichomonas and it is characterized by
prominent axostyle and undulating membrane that stops half way down the
side of the trophozoite. It is divides by binary fission and it cannot survive
long outside the host.
Clinical significance
:
-It is a frequent inhabitant of the human vagina and of the male genital tract
localized in the prostate and urethra. It is sexually transmitted disease. The
organism is capable of surviving on dry materials for a few hours and on
moist materials for longer period. Severity of the disease depends on the
strain of the parasite ranging from symptomatic to mild to sever infection.
-Infection in male is often asymptomatic although at sometime, it is
associated with urethritis which represents the most common symptomatic
presentation in male.
- In female, the infection may also be asymptomatic (up to 50% of infected
women are asymptomatic carriers) or may produce vaginitis, cervicitis and
urethritis.

4
-Asymptomatic carriers serve as a reservoir for transmission and also remain
at risk for developing disease.
-Vaginitis may be complicated by bacterial, fungal (yeast) or spirochetal
infection. The chief complains are leukorrhea (pus cells in urine) and
dysuria, excessive discharge that is creamy yellowish to greenish and frothy
due to the gases produced vaginal bactria and sometimes the discharge may
have a bad odor (foul smell).
-The onset of symptoms, such as intense vaginal and vulvar pruritis, and
discharge is often sudden and occurs during or after menstruation.
-As above, urticaria and acute vulvulitis may also occure. It is considered
that the disease is more annoying than disabling.
-In general, it causes non-gonococcal urethritis or tetracyclin-resistant
urethritis in male.
-The organism dose not infect the epithelium, it is found loose in the vaginal
cavity or adherent to the epithelium.
-There are certain factors that play a role in the pathogenesis of the parasite
which include; age, sex, glycogen contents, pH, pregnancy, seminal fluid
and number of parasites needed for infection.
-The essential factors for growth of T.vaginalis are:
1- Presence of glycogen in vaginal cells.
2- pH of vagina (optimal pH for growth of T.vaginalis is 5.5).
5
*Why the incidence of T.vaginalis infection is high among mature females?
This explained by the changes in the pH and glycogen amount of vagina.
-In mature female (15-40 years), the normal vaginal pH is acidic (4-4.5),
this acidity maintains by certain type of bacteria called Dauder lein’s
lactobacillus which lives on expence of the high amount of glycogen in the
vaginal cells, and as a biproducts, it produces lactic acid which makes
vaginal medium acidic (4-4.5) in the mature females. Also, there is a highest
peak of sexual activity, so, the seminal fluid can elevate the acidity of
vagina to 5.5 (optimal pH).
-Female of this age (15-40 years) need less than 10
parasites to become
infected, whereas the male need 10
parasites to become infected.
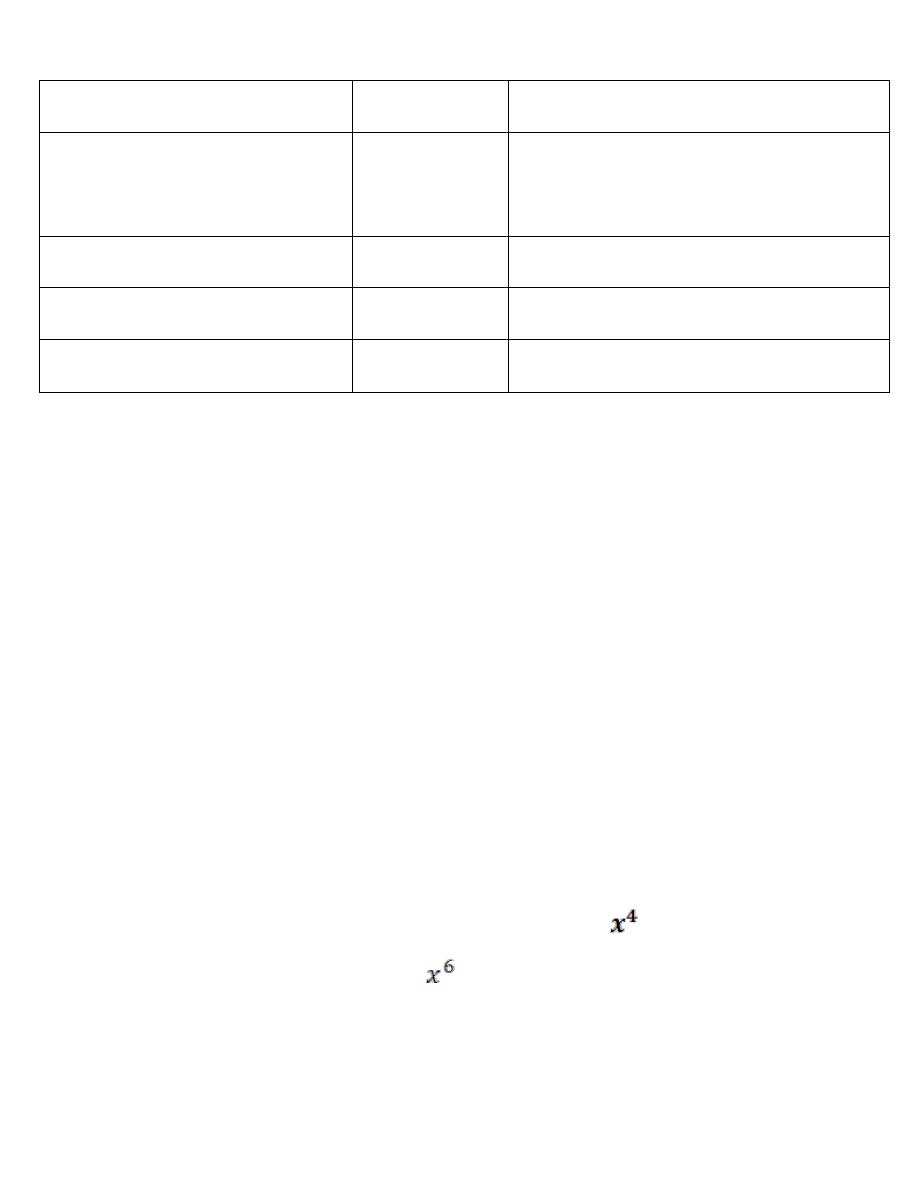
Sex / age (year)
pH
Glycogen content in epithelium
Mature female/15-40 yr.
4-4.5
++ prevelant
+++ during pregnancy
Immature female/ < 15 yr. 7
scanty
Menapouse female/ >40yr. 7
no glycogen
Male
7(of urethra) scanty

6
-Beacuse of both T.vaginalis and bacterial flora (lactobacilli) live on
glycogen and acidic pH, therefore, during infection with T.vaginalis , no
chance for bacteria to live and the pH of vagina rise to 5.5 (optimal pH for
T.vaginalis growth) beacuse no lactic acid production.
-The glycogen content of the epithelium is high and increases during
pregnancy, thus pregnant female is more liable for infection.
-Using of antibiotics and presence of other infection will elevate the pH of
vagina or urethra to 5.5 and can help in producing infection.
-In other groups (immature female , menapouse and male) because of scanty
or no glycogen due to the hormonal changes, this bacteria (lactobacillus) can
not live. Therefore, the pH will rise and be high (about 7) and whole
bacterial flora changes to other flora, and because of this high pH (7) and
scanty glycogen, T.vaginalis loses its viability and can not live in this
environment (T.vaginalis loses its viability below the pH of 3.8 and above
pH of 7.5).
-Infection has also been associated with premature rupture of ameniotic
membrane, premature birth and post-hysterectomy cuff infection. More
recently, it has been implicated as a factor in transmission of HIV.
-Neonate can acquire the organism during passage through infected birth
canal. It is estimated that 2-7% of female babies acquire trichomoniasis by
directed vulvovaginal contamination. Reports have been also documented
T.vaginalis as a cause of neonatal pneumonia.
7
Laboratory diagnosis
The diagnosis for this organism is commonly based on the examination of
wet preparation of vaginal and urethral discharges , prostatic secretions and
urine sediments. The presence of actively motile organism with jerky
motility is diagnostic.
Treatment
The treatment of choice for T.vaginalis infection is metronidazole . All
sexual partners of infected individuals should also receive treatment. This
medication should not be used during pregnancy unless the benefits of
treatment outweigh the risks to the fetus.
