
Toxoplasmosis
Objective :
Describe the Life cycle
Mention the Infective stages
Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis
List the Lab.Diagnosis
Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis
Show the relationship between
Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy

Human
Toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasmosis is a
zoonotic disease
Caused by Coccidian
protozoan
gondii
Toxoplasma
Infectes a wide range of
animals, birds but
does not appear to
cause disease in
them

Toxoplasmosis
A disease of the blood and lymphatic system.
Cats are a critical part of the life cycle
.
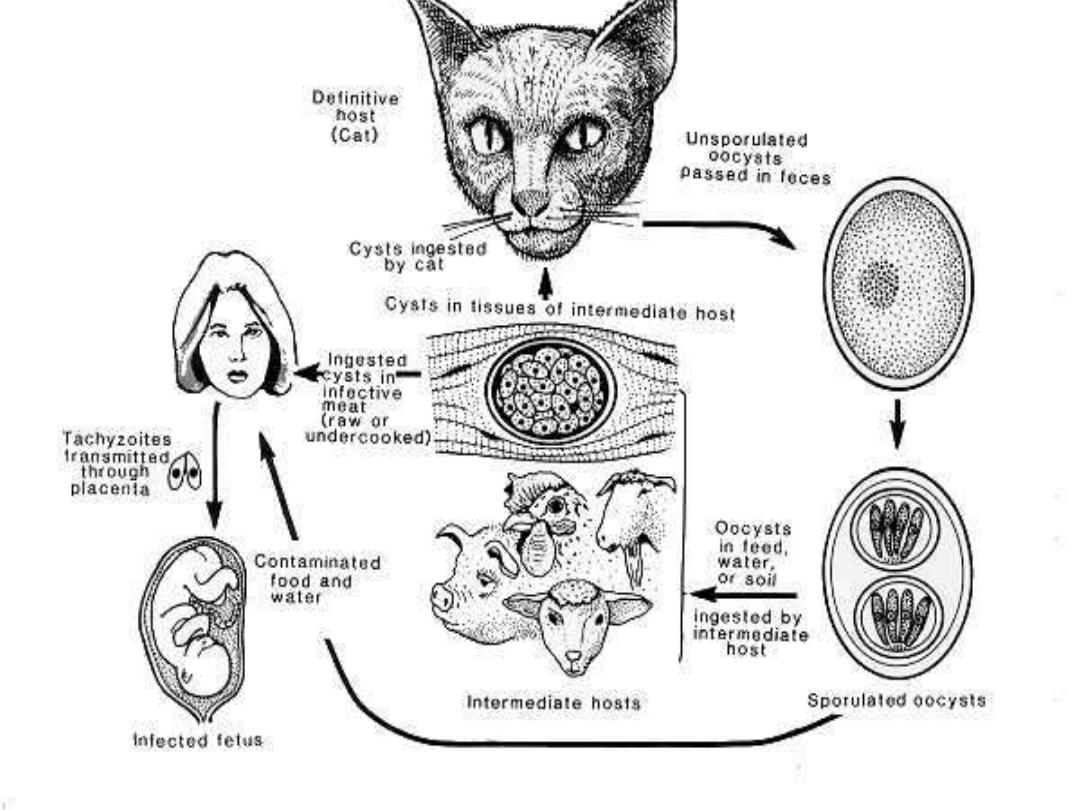
It is usually acquired by eating undercooked meats
but can also be acquired by contact with cat
feces.
Primary problem is a
congenital infection
of
fetus, resulting in either a stillbirth or a child with
severe brain damage or vision problems.

Toxoplasmosis
The normal final
host is cat and
relatives in the
family Felidae,
only hosts in
which the Oocyst
is produced & the
sexual
stage of
Toxoplasma can
be developed

Toxoplasma gondii has very low host
specificity, and it will probably infect almost
any mammal.
Non species Specific &
Non organ specific)
, and has been found
in virtually every country of the world.
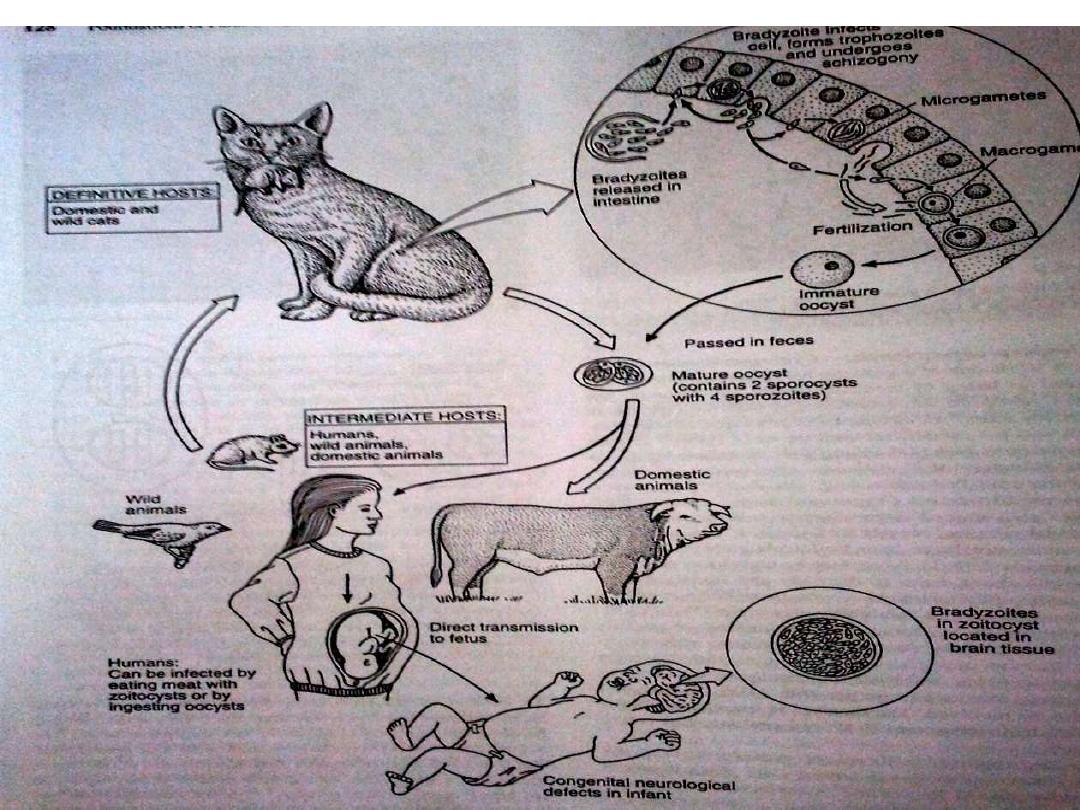
Like most of the Apicomplexa, Toxoplasma
is an obligate intracellular parasite. Its life
cycle includes two phases called the
intestinal (or enteroepithelial) and
extraintestinal phases.
Introduction

•The intestinal phase occurs in cats only (wild
as well as domesticated cats) and produces
"oocysts."
•The extraintestinal phase occurs in all infected
animals (including cats) and produces
"tachyzoites" and, eventually, "bradyzoites" or
"zoitocysts.“
•The disease toxoplasmosis can be transmitted
by ingestion of oocysts (in cat feces) or
bradyzoites (in raw or undercooked meat).
Tachyzoites are less resistant to stomach
secretions so less important sources of
infection than the other stages


Cats
• Cats are the only animal
species to
shed
the infectious
stage in their feces.
• All animals however,can disseminate
Toxoplasmosis if their
infected meat
is
eaten.
• cats get it by eating rodents,
raw meat,
cockroaches,
flies
, or by contacting
infected cats, infected cat feces, or
contaminated soil
.
Spread from Rats
– Cats to
Humans

Events on Development in man
When man ingests Oocysts with eight Sporozoites excreted in Cats
feces, can establish an infection in humans. Oocysts open in
duodenum and releases eight Sporozoites which pass through
the gut wall Circulate in body and invade various cells
In most humans infected with Toxoplasma, the
disease is
asymptomatic
. However, under
some conditions, toxoplasmosis can cause serious
pathology, including hepatitis, pneumonia,
blindness, and severe neurological disorders. This
is especially true in individuals whose
immune
systems are compromised (e.g., AIDS patients).

Toxoplasmosis can also be transmitted
transplacentally resulting in a spontaneous
abortion, a still born, or a child that is
severely handicapped mentally and/or
physically
.

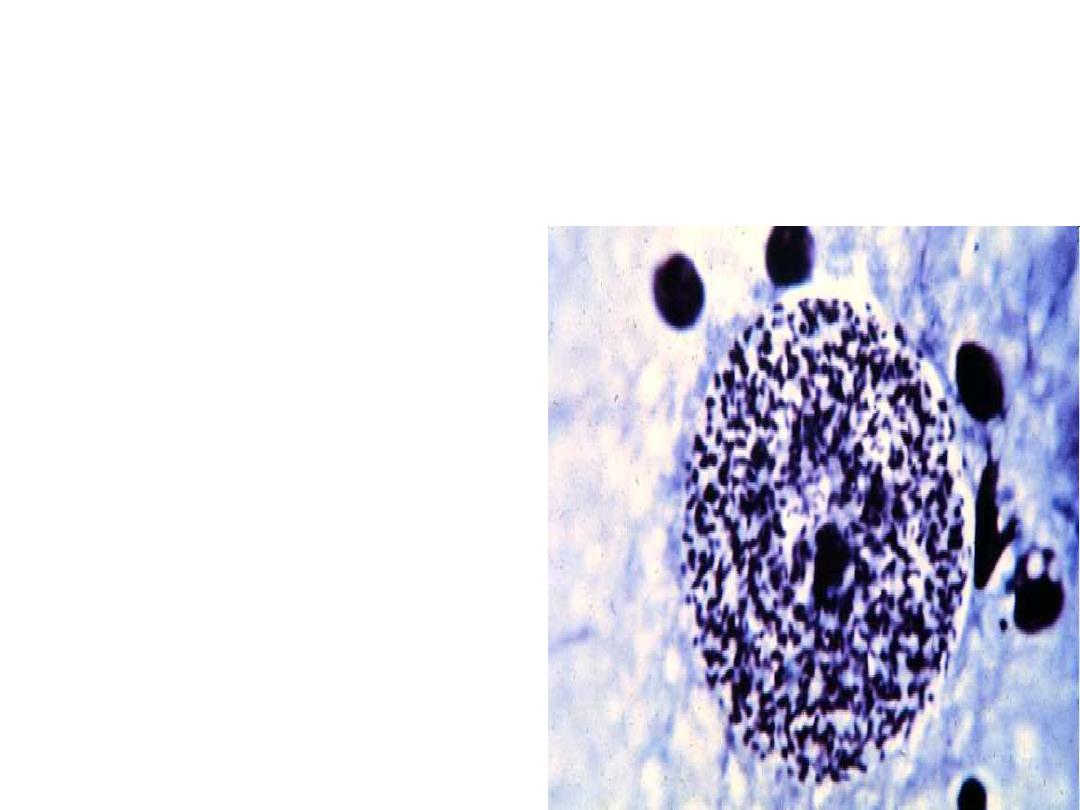
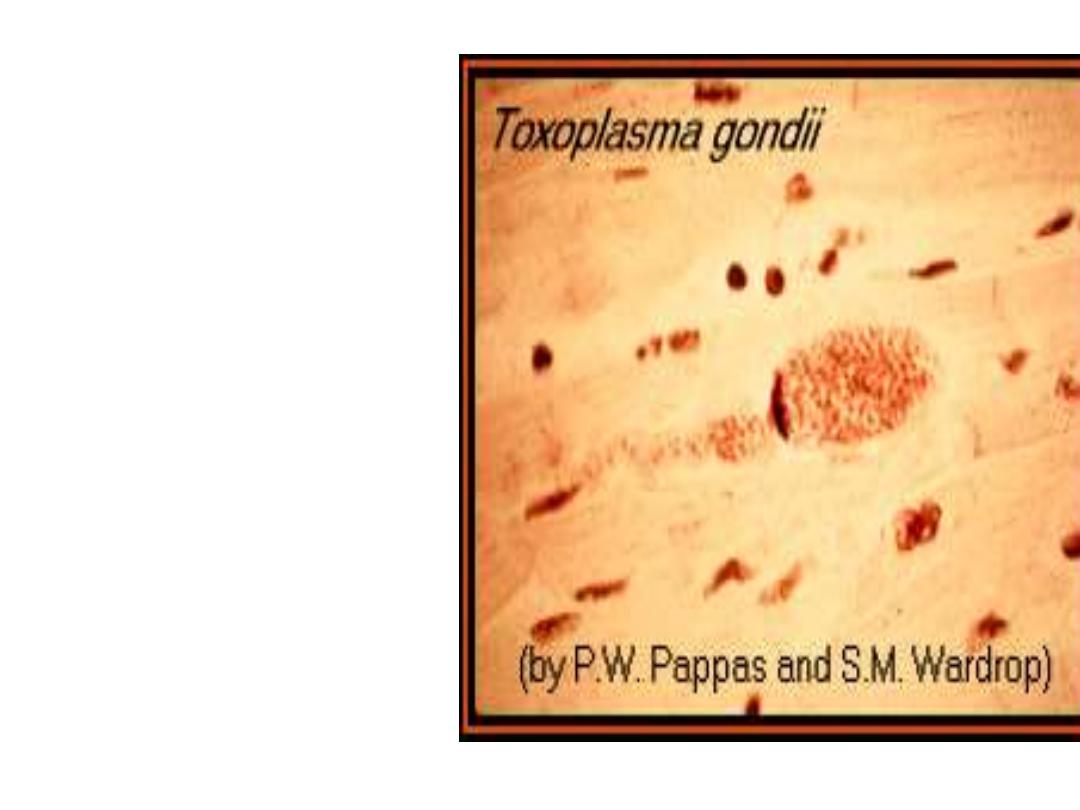
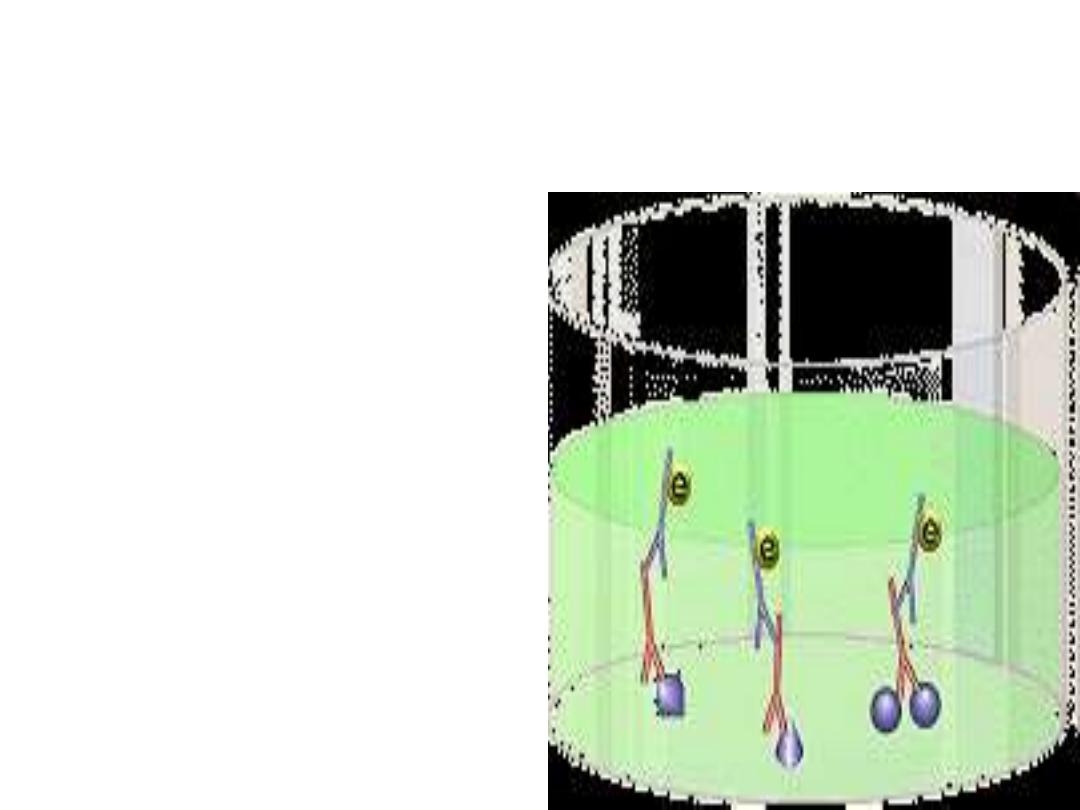
Morphology
Acute stage:
The intracellular parasites
(tachyzoite) are 3x6µ,
crescent shaped
organisms that are
enclosed in the host cells
as Macrophages to form
the Pseudocyst
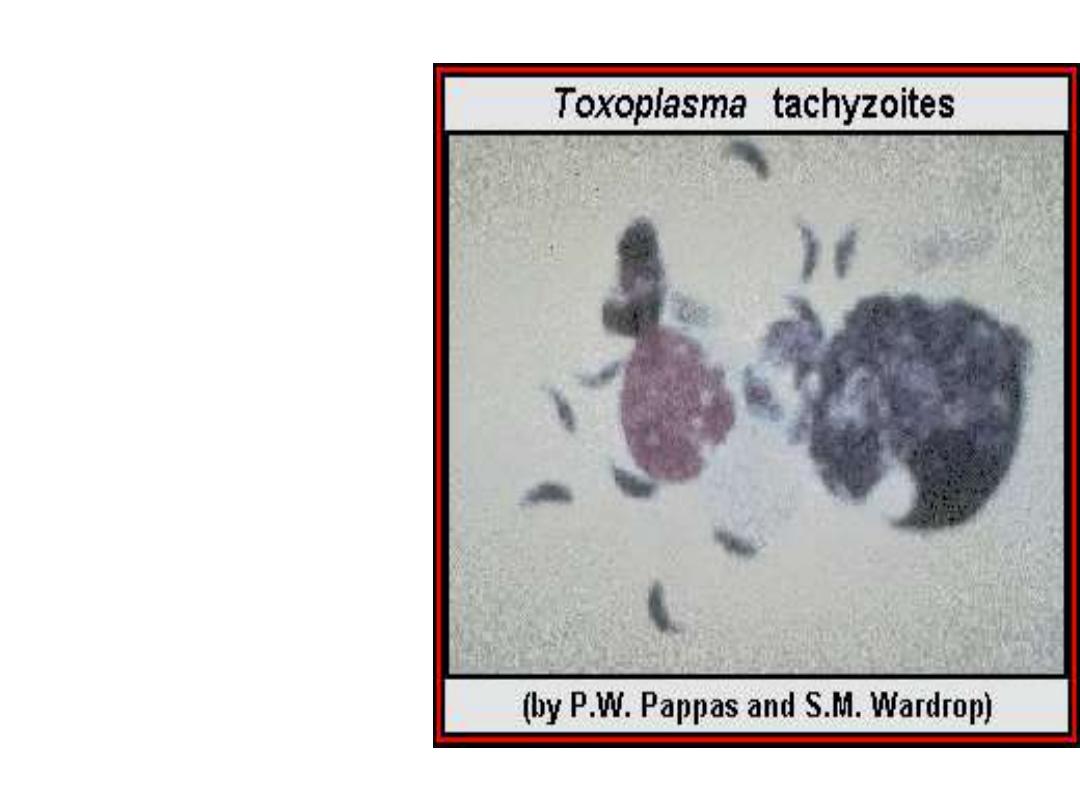
Toxoplasma gondii
tachyzoites.
Acute stage
Asymptomatic or
Flu like symptoms
Intracellular
tachyzoites of Toxoplasma
gondii.
In the psudocyst
As macrophages
Reproduction is by
Endodyogeny,
a process
of division where in 2
daughter zoites are formed
within the parent parasite,
which is destroyed when
the young zoites are
released
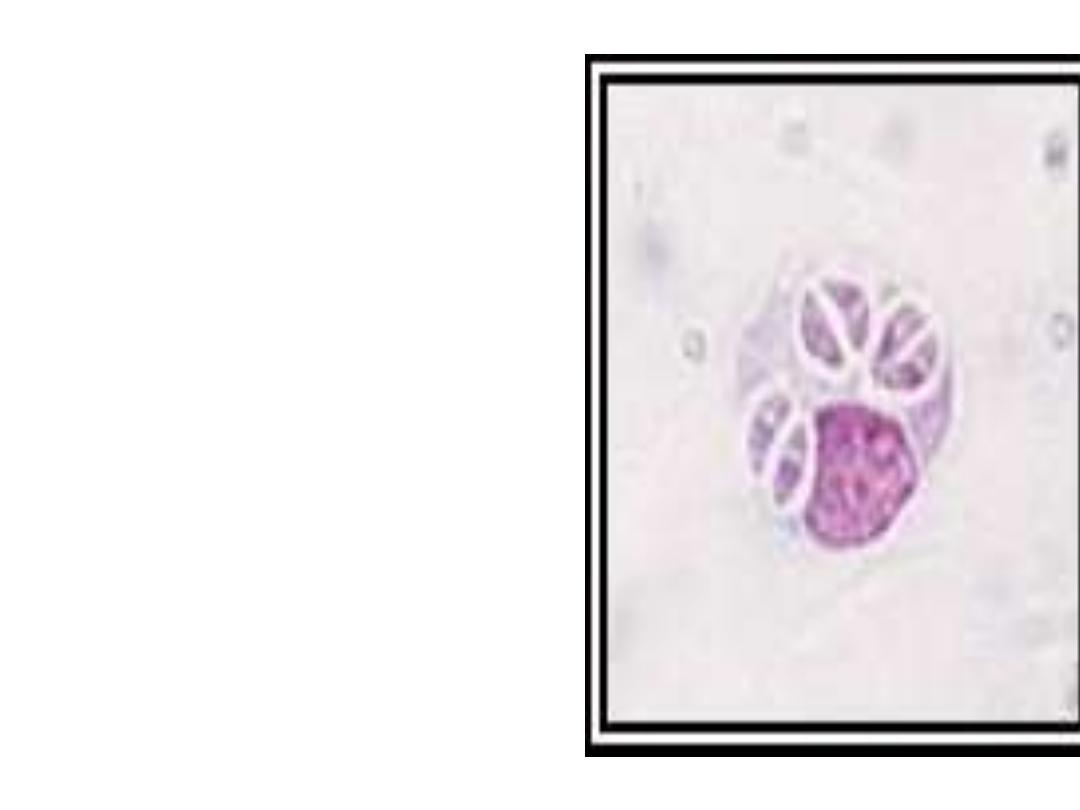
Invade Organs
In futher development they
penetrate new cells
especially Eye and Brain.
Further development slows
down in these organs
called ad
Bradyzoites
to
form a quiescent tissue
cysts
The event lead to
chronic
stage of
disease
Brain involvement carries
higher Morbidity and
Mortality if the
immunity is low
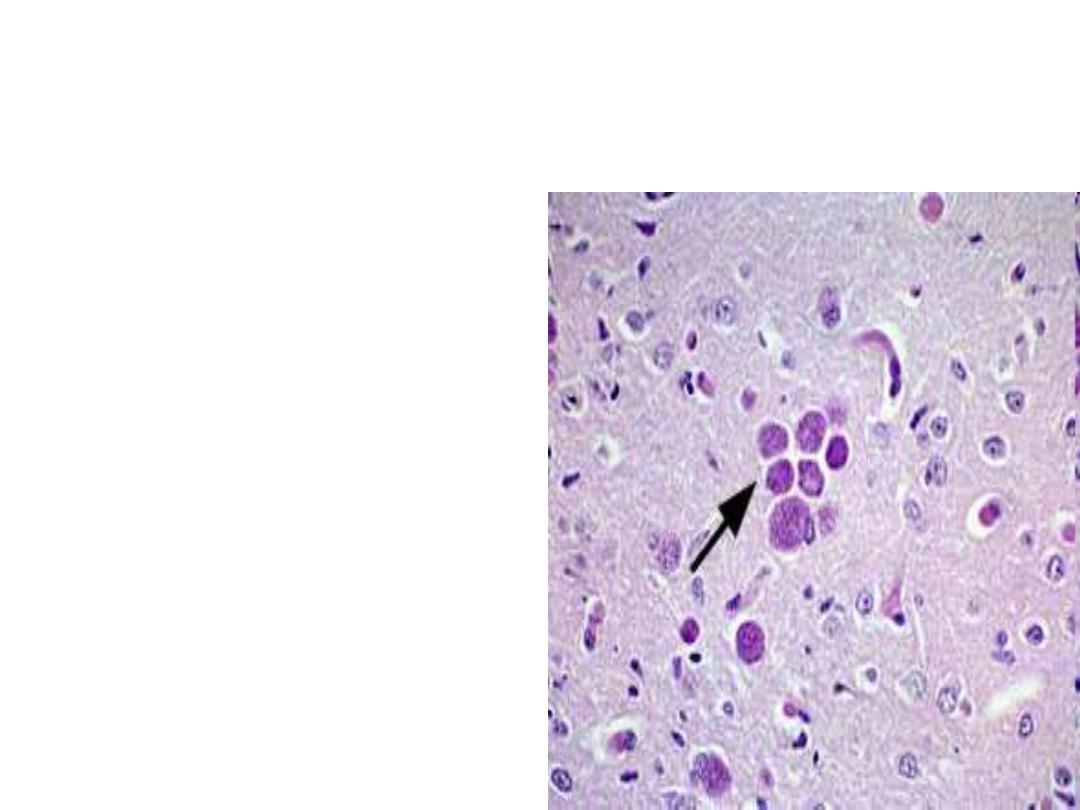
A zoitocyst of
Toxoplasma
gondii filled with
bradyzoites; this
zoitocyst (true cyst)
is in the
muscle ,eye or brain
Fate of Tissue Cysts
The tissue cysts are
infective when
ingested by cats or
eaten by other
animals.
In man it is a dead end
of disease or change
to acute stage
(tachyzoites) when
the Immunity is Low

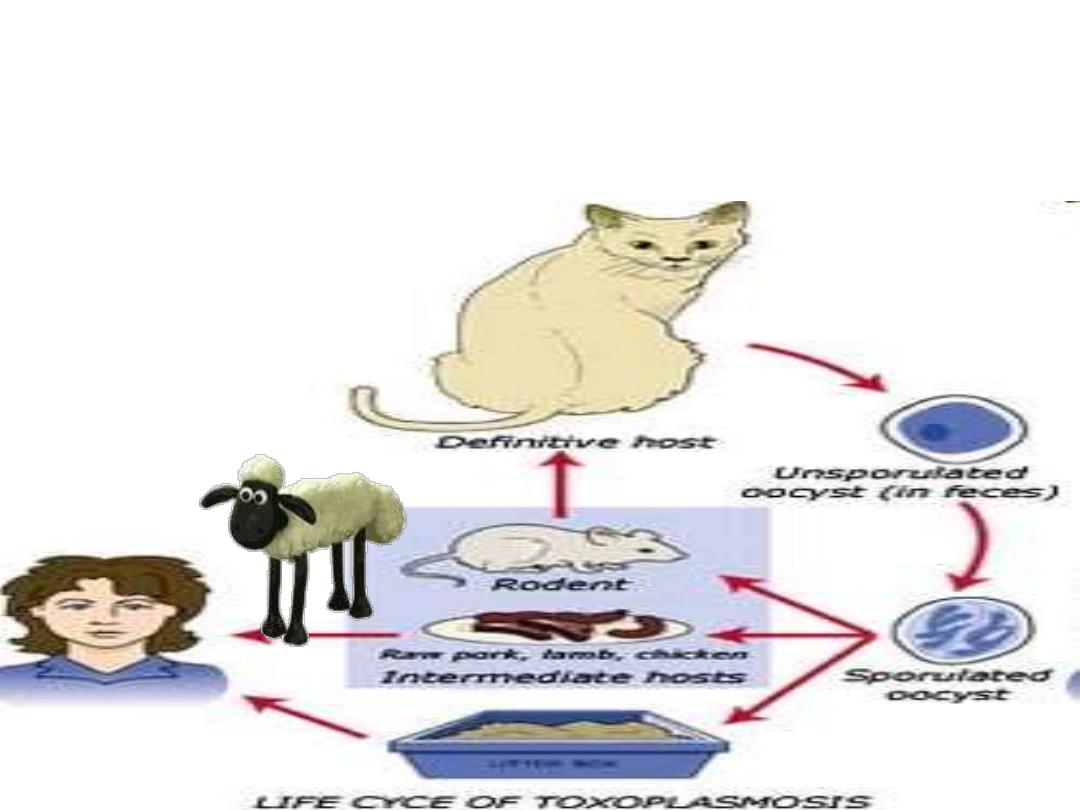
Sources of infection
• Source of all oocytes ...
– Domestic (cats) and wild (zoo) cats
(
Cats are the only known full-life-cycle host of the
protozoan) parasite
Complete host
• Persist in environment (soil) if moist > one year
– reservoir of infective oocytes
• Many intermediate hosts
– reservoir of infective tissue cysts( farm animals—
cattle,sheep,rabbit)
• Cycle in humans
(an accidental host)
– Infected
• by ingesting infective oocytes
(
in >4 day old cat feces
)
• by ingesting tachyzoites or bradyzoites
in raw meat
• by receiving
blood
or tissues
with “-zoites”
• CONGENITALLY
by transplacental tachyzoites
– Proliferative stages in humans
• tachyzoites
result from all infective stages
• bradyzoites predominate within cysts

Humans become infected in several ways:
- ingestion of oocysts through contamination of
food, water, hands, etc. with cat feces.
- ingestion of bradyzoites in uncooked meat, e.g.
lamb, pork, beef, caribou.
- transplacental when mother
develops acute
infection during pregnancy.
- blood transfusion, organ transplant.

In immunocompetent adults,
toxoplasmosis, may produce flu-like
symptoms, sometimes associated with
lymphadenopathy.
In immunocompromised individuals,
infection results in generalized
parasitemia involvement of brain, liver
lung and other organs, and often death.
•
Toxoplasmosis
produces severe
Human infections in
patient with
AIDS
The chronic infection
is altered to Acute
manifestations
Toxoplasmosis
–
Immunosupressed patients
Varying degrees of disease
may occur in
Immunosupressed
indivudals results in
Retinitis
Chorioretinits
Pneumonias
severe neurological
disorders
Other non specific
manifestions

Immunology
Both humoral and cell mediated immune
responses are stimulated in normal individuals.
Cell Mediated Immunity is protective and
humoral response is of diagnostic value.

Immunity
Acquired immunity in women is
particularly protective to the fetus.
In Immunosupressed and AIDS patients
changes the host resitance and
causes the chronic infection becomes
fulminating acute
Toxoplasmosis

Premunition: a host may
recover clinically & be
resistant to specific challenge
but some parasites may
remain and reproduce slowly

Toxoplasmosis in Pregnancy
In 1 st Trimester
may lead to still birth
major central nervous system anomalies
In 2
nd
Trimester
Less severe complications
Transmission to the fetus is more frequent if the
maternal infection occurs in the 3
rd
trimester
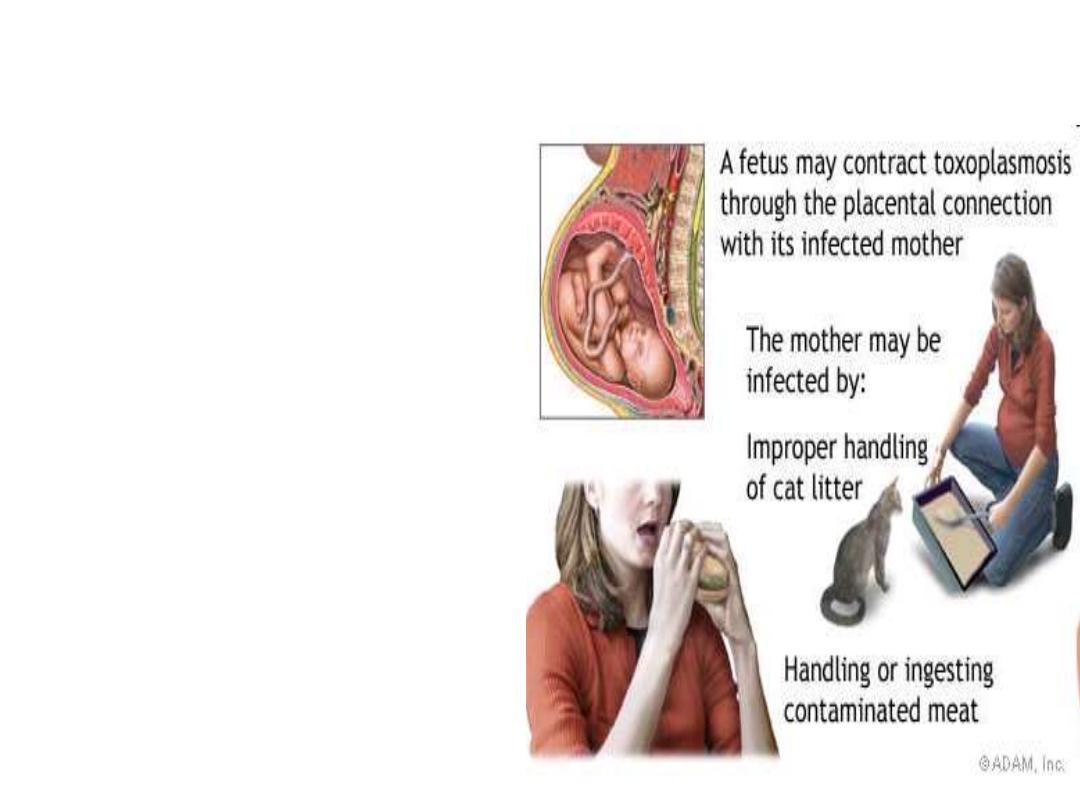
Congenital Toxoplasmosis
Congenital infection
develop in fetus only
when non immune
mothers are infected
during pregnancy

Congenital infections occur in about 1-5
per 1000 pregnancies of which 5-
10
%
result in miscarriage,
8-
10
% result in serious brain and eye
damage to the fetus,
10
-13% of the babies will have visual
handicaps.
Although 58-
70
% of infected women will
give a normal birth, a
small
proportion of
babies will develop active retino-
chorditis or mental retardation in
childhood or young adulthood
( Post natal
Toxoplasmosis is less severe)
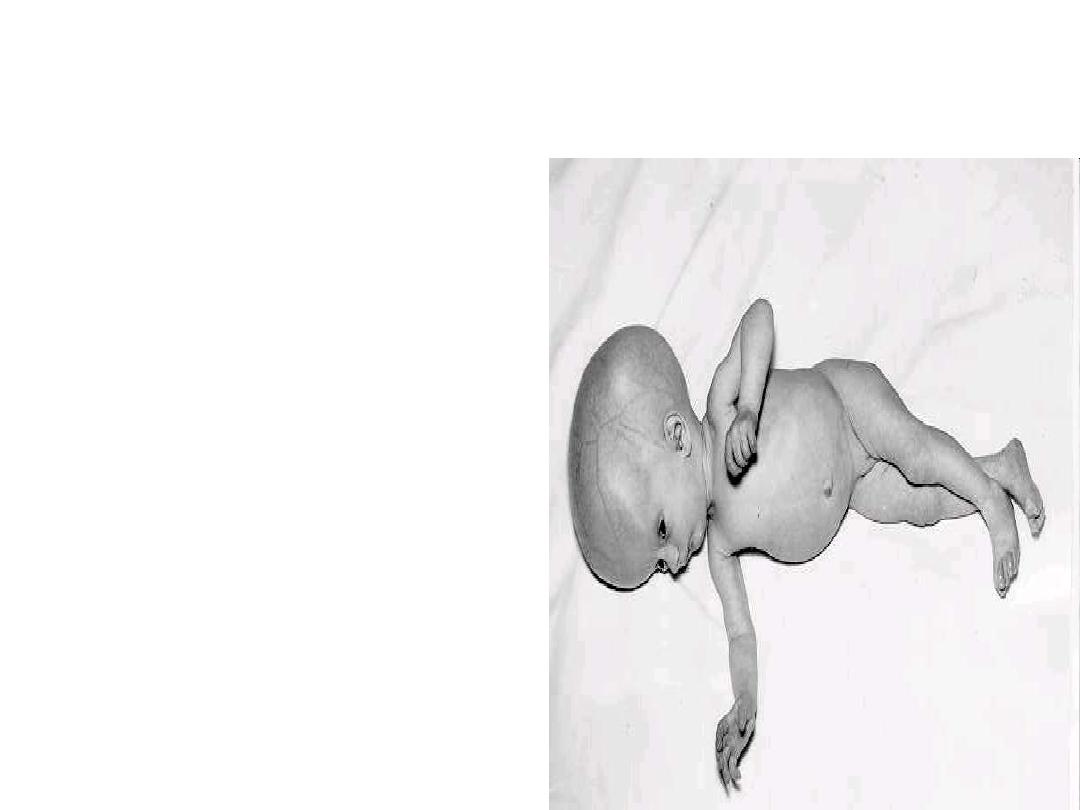
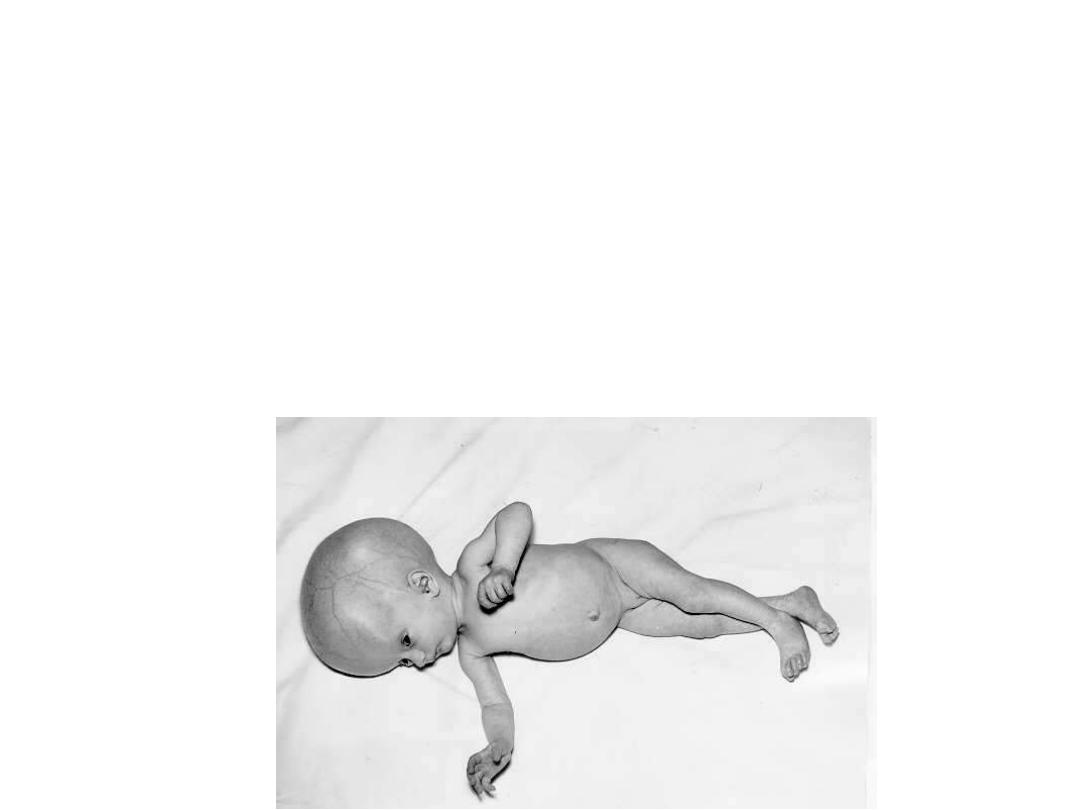
Congenital Infection
Prenatal toxoplasmosis
Lead to
Still Birth
Or
Sabin`s tetrad
:
Chorioretinits
Intracerebal calcification
Psychomotor disturbances
Hydrocephaly
or
Microcephaly
Prenatal toxoplasmosis may
manifest with blindness apart
from congenital defects

Summery of Clinical presentations :
1. majority are asymptomatic
2. acute toxoplasmosis: fever, lymphadenopathy (much like
infectious mononucleosis - EBV); can rarely cause specific
organ inflammation, e.g. encephalitis, myocarditis.
3. reactivation toxoplasmosis: occurs in immunosuppressed
such as AIDS, transplant and cancer patients: presents with
specific organ involvement e.g. encephalitis, pneumonitis.
4. choreoretinitis: occurs later in life in individuals who
acquired toxoplasmosis congenitally
Post natal toxoplasmosis
;
focal lesion in retina presenting as decreased visual acuity;
rarely occurs during acute toxoplasmosis.
5. congenital toxoplasmosis: transmission from mother to
fetus when mother has developed acute toxoplasmosis during
pregnancy - increased transmission rate in third trimester, but
increased severity of fetal disease in first trimester. Presents as
hydrocephalus, hepatomegaly, cerebral calcifications, mental
retardation with death at one end of spectrum and mental
retardation or just later choreoretinitis at the other end of
spectrum.
Diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis
Desired specimens,
Blood ( serum)
Sputum
CSF
Lymphnodes
Tonsil tissues
Striated muscle biopsy
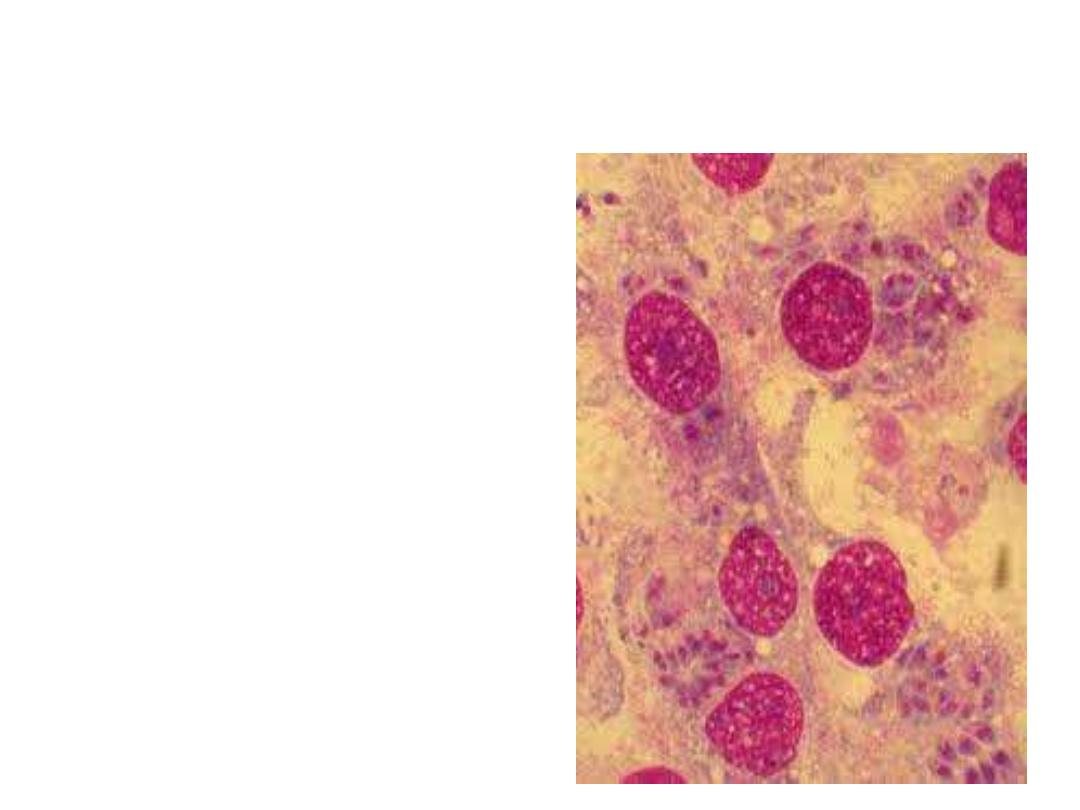
Diagnosis
Suspected toxoplasmosis
can be confirmed by
finding the organism
from tonsil or lymph
gland biopsy.
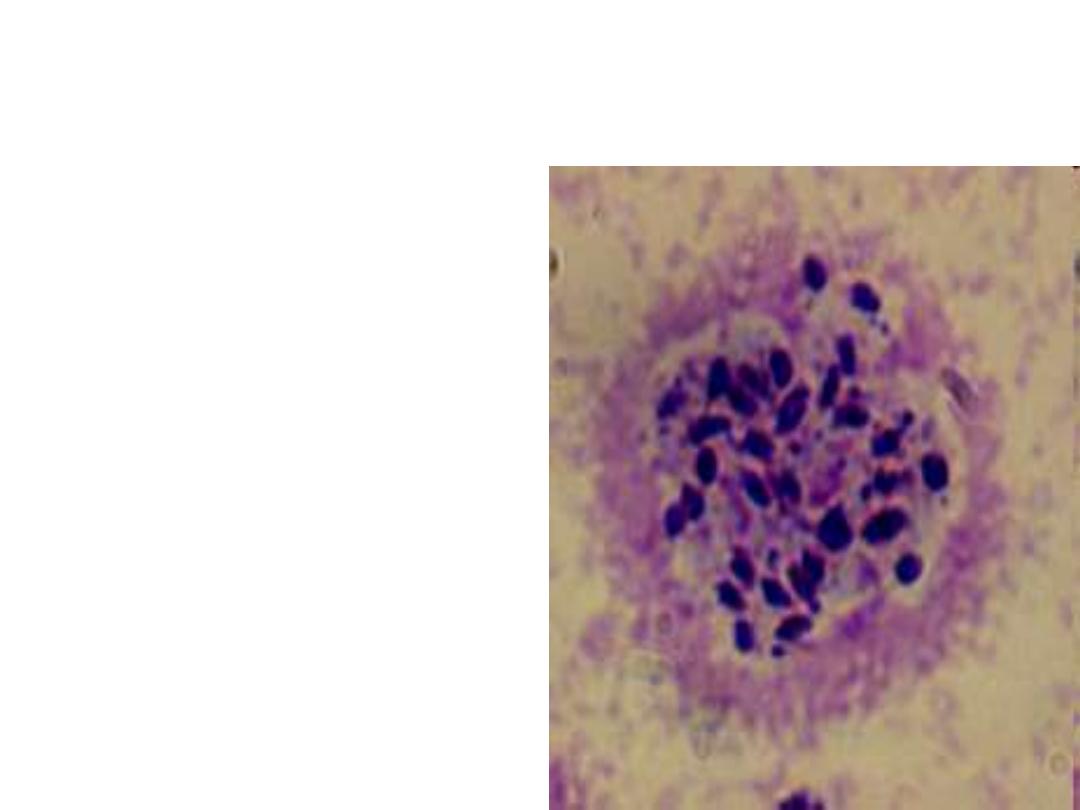
Microscopic Examination of
Tissues
Smears and sections
stained with Giemsa’s
stain
Periodic acid Schiff method
preferred
Pseudocyst seen in the
acute stage.
The densely packed cysts
seen in the brain or other
parts of nervous system
suggest chronic infection

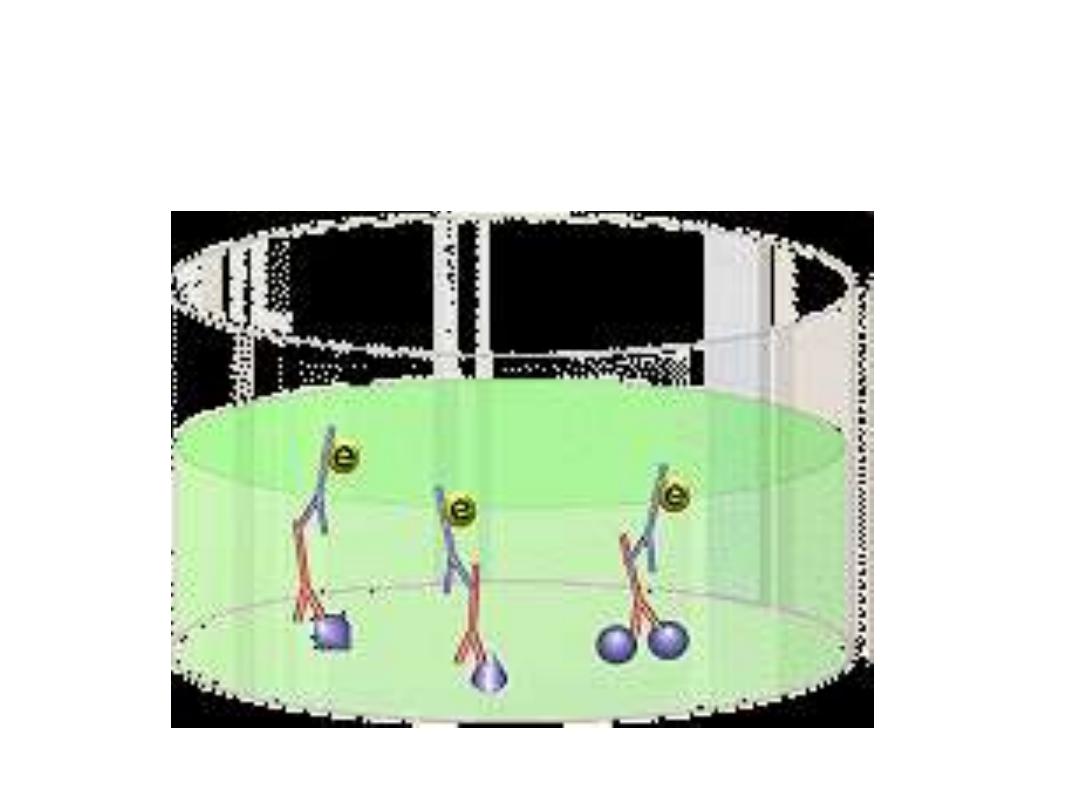
Immunological tests:
Tests which employ whole parasites include
• the
dye
test (Sabin-Feldman Dye Test (DT)
,
direct
agglutination and the
fluorescent
antibody test,
• whilst tests that use disrupted parasites as
an antigen source include
ELISA
,
latex
agglutination
,
indirect haemagglutination
and complement fixation.
Serology
Sabin Feldman dye
test
based on principle that
Antibodies to Toxoplasma
appear in 2-3 weeks that
will render the membrane
of the laboratory cultured
T.gondii
living
impermeable to Alkaline
methylene
blue
,So the
organism are unstained in the
presence of serum with antibodies
Newer Methods in Diagnosis
-Immuno florescent
assay method.
-ELISA for IgM and
IgG detection
-PCR
Frankel’s intracutaneous
test (Toxoplasmin skin
test )useful for
epidemiologcal purpose
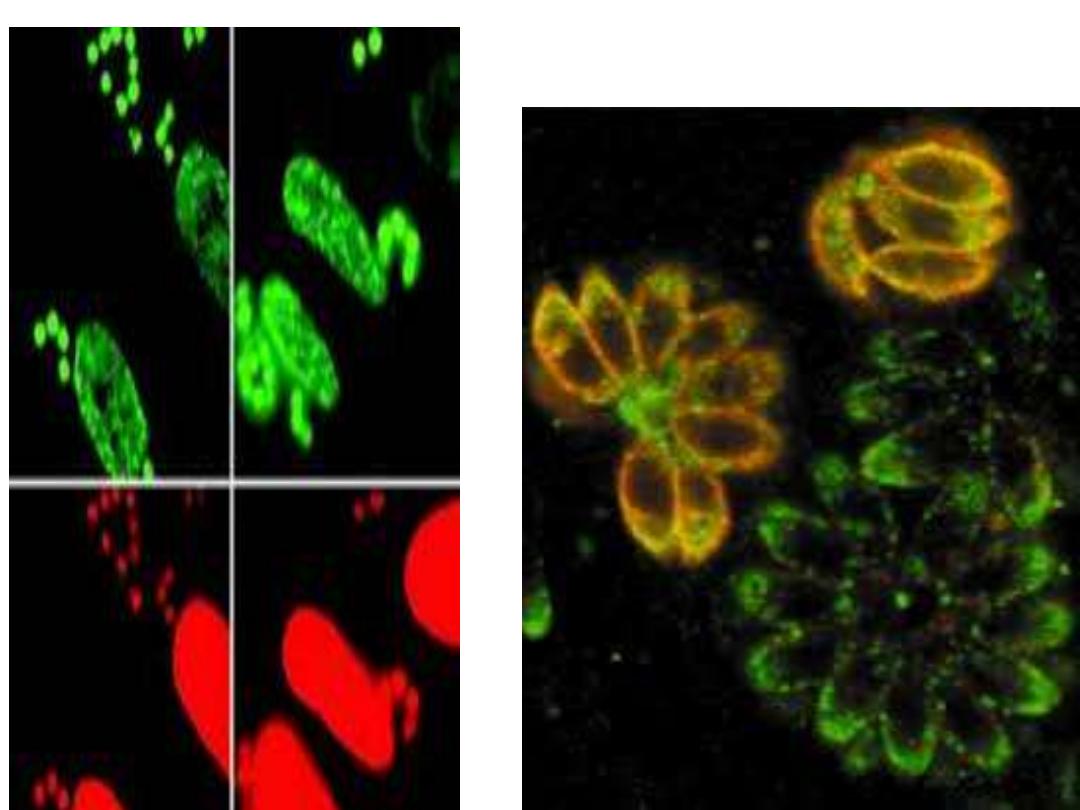
fluorescent antibody test
,
ELISA Test
Acute infection

• Detectable levels of IgM antibody appear
immediately before or soon after the onset of
symptoms. IgM levels normally
decline within
4 to 6 months,
but may persist at low levels
for up to a year
• IgG levels begin to rise 1 or 2 weeks after
infection. Peak levels are reached in 6 to 8
weeks, then gradually decline over a period of
months or even years.
Low levels of IgG are
generally detectable for life
.
• immunocompromised individuals may not
produce any IgM. Antibody levels do not
correlate with severity of illness

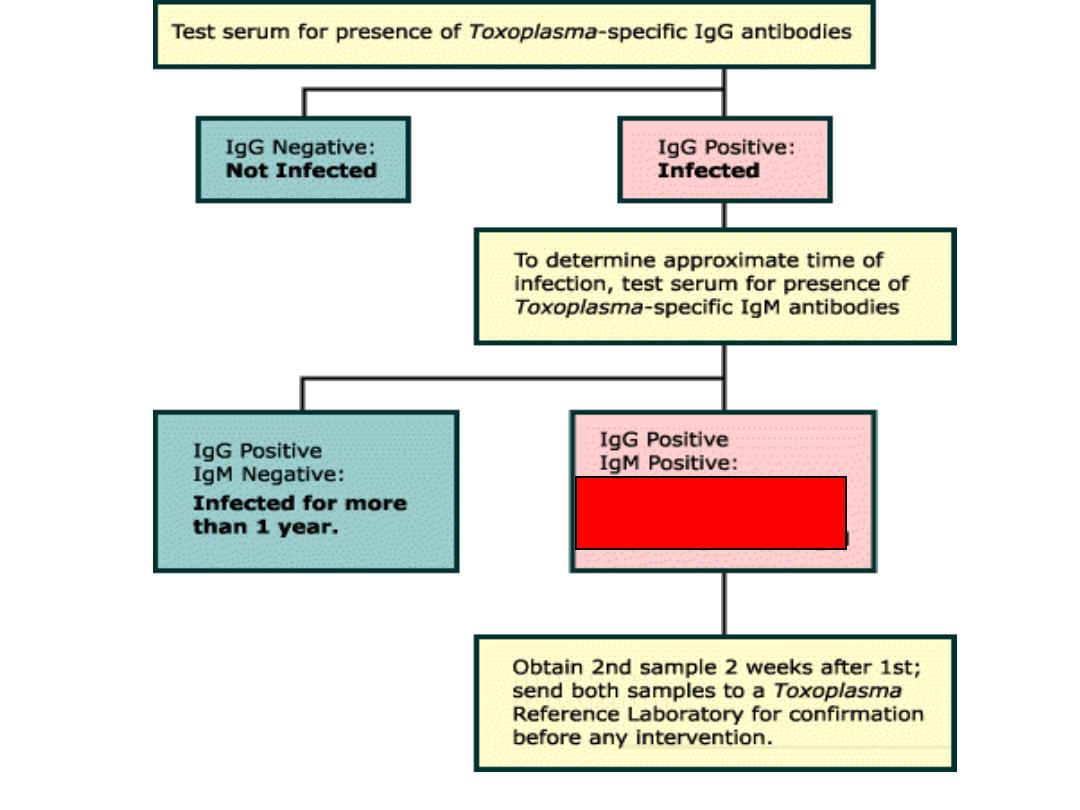
Serologic Diagnosis of Toxo
• unreliable in immunodeficient (AIDS) pts
• normally IgM and IgG rise simultaneously
– IgG - persists for years
– IgM - undetectable after “cure”
• elevated IgM titer is diagnostic of recent infection in
persons with normal immunity
• A negative IgG or IgM test excludes Diagnosis
– a + IgM test confirms acute toxoplasmosis or current
Toxoplasma infection
(
measure IgM
antibodies, have low specificity )
• in the United States,
most
pregnant women are
not screened routinely
for toxoplasmosis
Only those with a
high risk.

Polymerase Chain Reaction
(PCR)
• PCR amplification is used to detect T. gondii DNA in
body fluids and tissues.
• It has been successfully used to diagnose
congenital,
ocular, cerebral and disseminated toxoplasmosis
.
• PCR performed on
amniotic fluid
has revolutionized
the diagnosis of fetal T. gondii infection by enabling an
early diagnosis to be made,
• PCR has allowed detection of T. gondii DNA in brain
tissue, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), vitreous and aqueous
fluid, bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, urine, amniotic
fluid and peripheral blood.

incidence
• Seroconversion rate -----7.5% in Egypt
• 30% in canada
----- 50 % in USA
-----
>
60% in France
Very common throughout the world; up to 50+% in
other developed or developing countries.

Care of the Meat
Avoid eating raw or
undercooked meat.
Freezing < -20
0
c
Heating at 50
0
c for 4-6
minutes destroys the
cysts and sterilizes
the meat.

Immunity to TG
• Active infection normally occurs
only once
in a lifetime.
• Although the parasite remains in the body indefinitely
latent infections usually persist for life
(
the immune system
reacts against the parasite, causing the parasite to hide in an
inactive form (cyst) in tissues throughout the body (usually the
skeletal muscles and the brain).
. ,
• True cyst generally is harmless and inactive
unless
the
immune system is not functioning properly in immuno-
compromised host -- the parasite can reactivate and
cause serious illness, characterized by inflammation of
the brain
• If a woman develops immunity to the infection at least
six to nine months before pregnancy, there is a very
rarely
any danger of passing it on to her baby because
immunity is developed to it

Widespread phobia
Toxoplasmosis is a part of TORCH syndrome
It is not a cause of habitual abortion
Only pregnant with primary active infection with
toxoplasmosis during pregnancy leads to congenital tox
and after primary infection there is persistence of cysts of
tox BUT development of active immunity protect
subsequent pregnancy
Very rarely
reactivation of previously latent T. gondii
infection induced
by severe
decrease of
immunity(People on chemotherapy , People with
congenital immune deficiencies , People with AIDS/HIV ,
long administration of corticosteroid drugs in the case of
transplant patients)
Many doctors believe that is the case which has created
a widespread phobia
among pregnant women and has
given some sort of satisfaction among some doctors by
treatment their pregnant women by chemotherapy which
is in fact unnecessary

Toxoplasmosis TTT
• Drugs of choice for pregnant women or
immunocompromised persons:
Spiramycin or Pyrimethamine plus
Sulfadiazine
• Prophylaxis –in the primary prevention of
toxoplasmosis in persons with HIV who have
dormant or latent infection
- trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
• pyrimethamine plus folinic acid
• dapsone + pyrimethamine
Treatment of Infected Newborns
• Infected babies should be treated as soon
as possible after birth with pyrimethamine
and sulfadiazine which, as mentioned
earlier, can help prevent or reduce the
disabilities associated with toxoplasmosis.
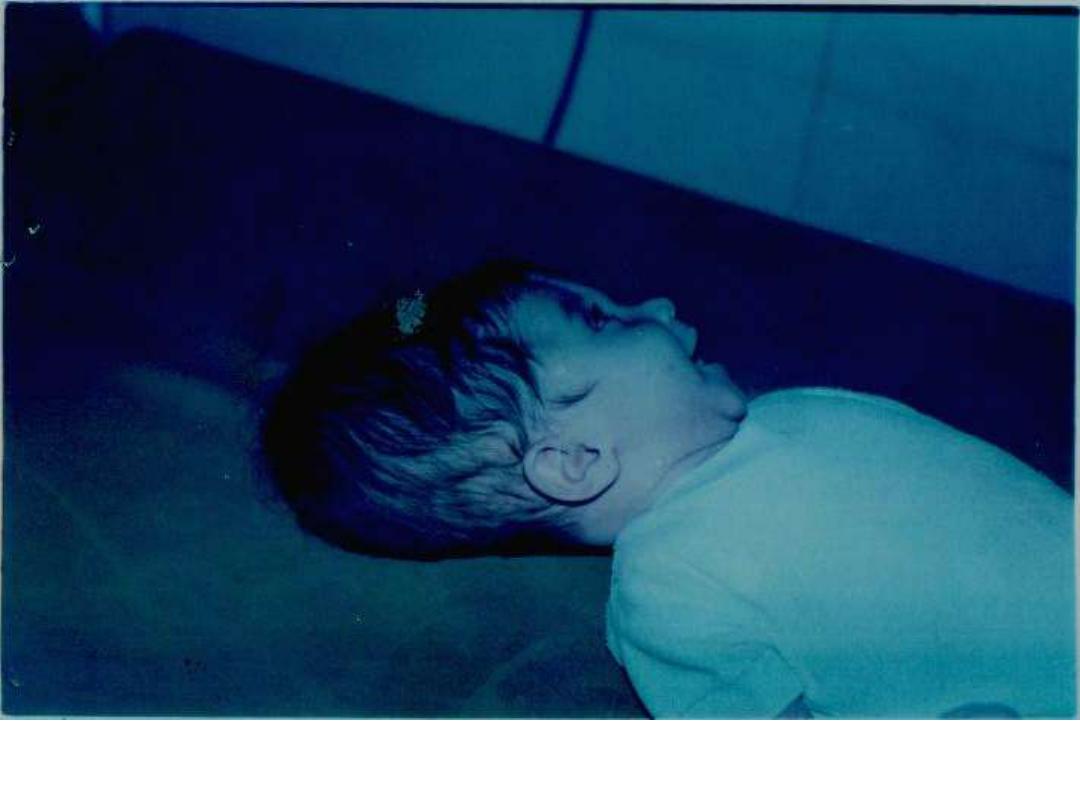
Figure-5- Girl with hydrocephalus due to congenital toxoplasmosis.

Under research
• developing vaccines against Toxoplasma
gondii .

Thank You
