
1
Lec.2
Lecturer: khalidah Kareem
Dipylidium caninum (Dog Tapeworm)
It causes a disease known as dog tapeworm infection or dipylidiasis. It is a parasite of
dog and cats, humans infected accidentally.
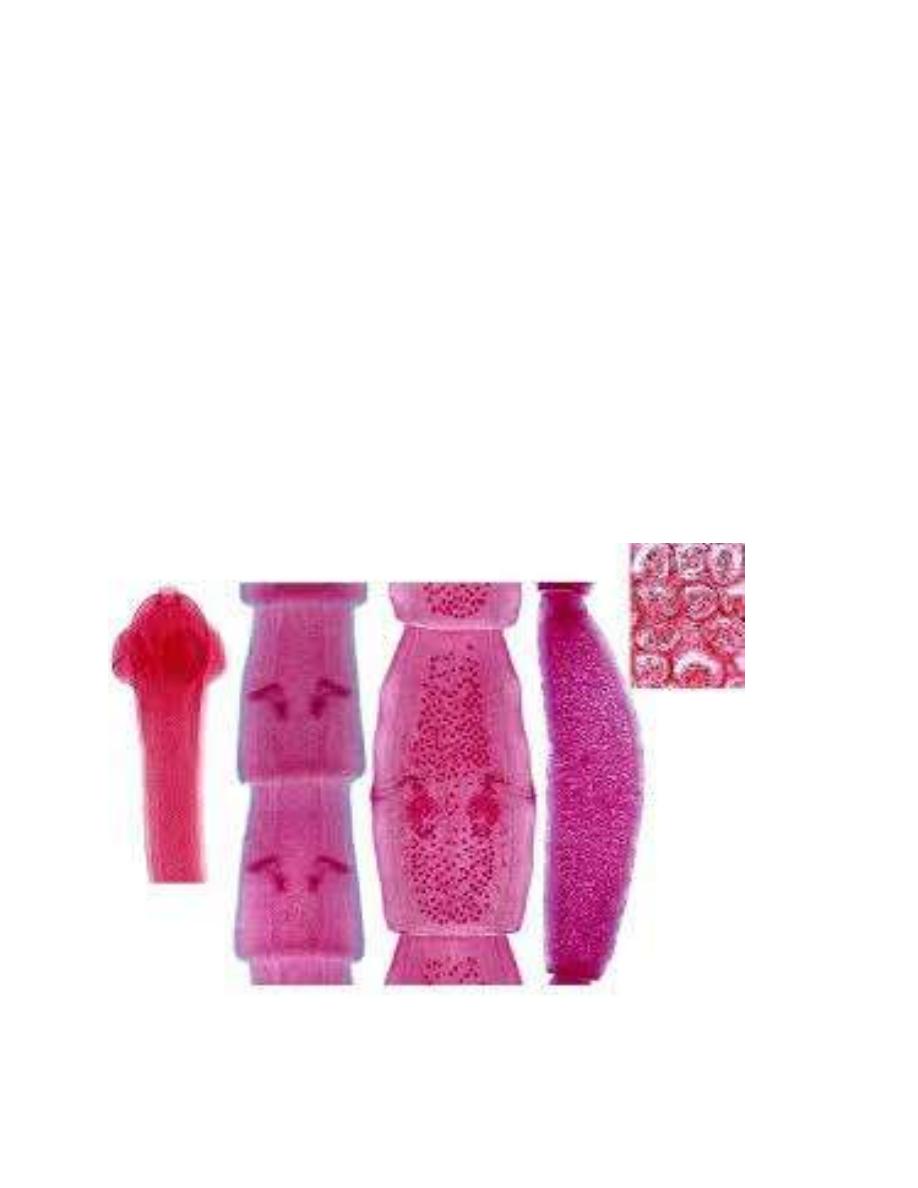
Adult measured 10-70cm in length, the segments is vas-shape; mature segment contain
paired reproductive organs with 2 mide lateral located genital pores. [i.e. two set of male and
two set of female reproductive organs]; gravid segments resembles Pumpkin seed in its shape
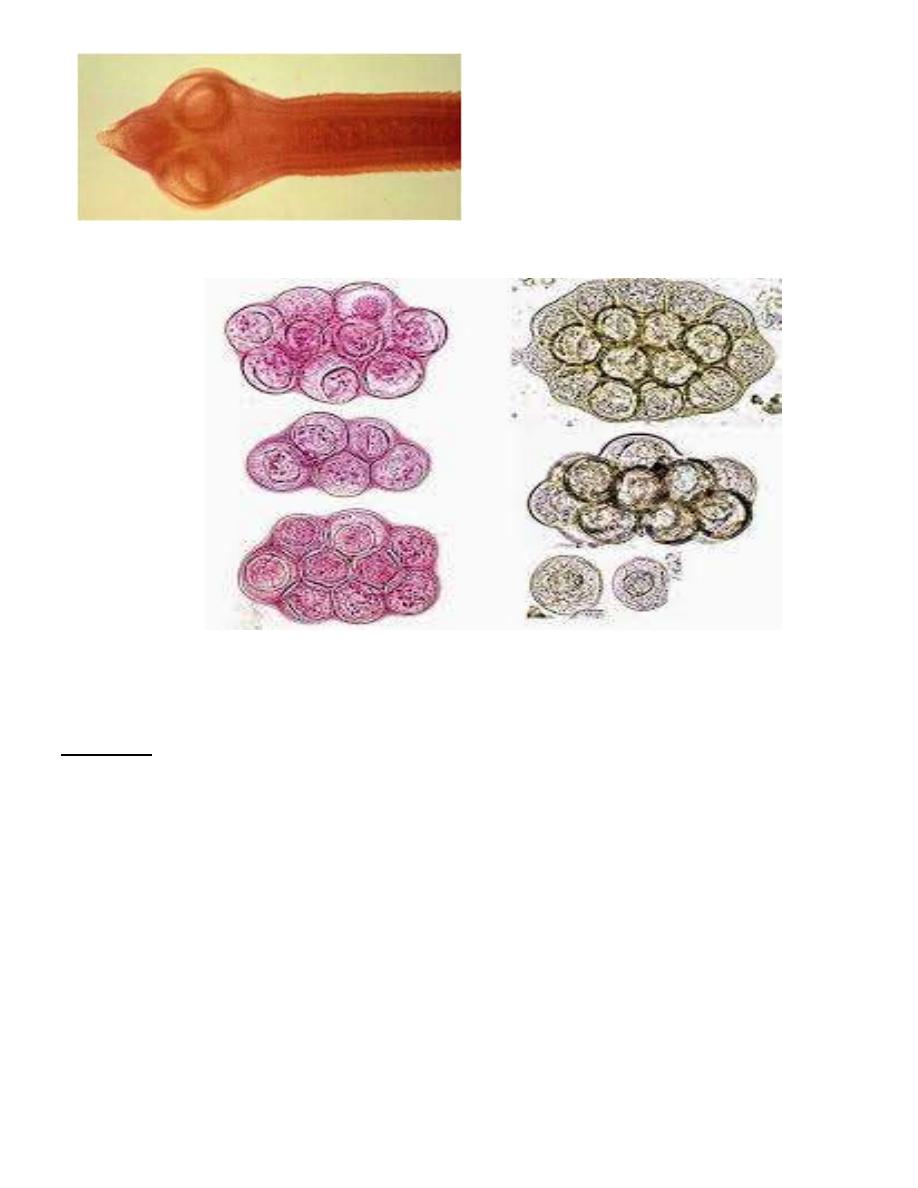
with masses of egg capsule [eggs sac] filled with 5-25 eggs. The scolex is rhomboidal in shape,
with 4suckers and retractile conical–shaped rostellum provided with 6 -7 rows of hook.
D.caninum
Scolex immature mature Gravid Egg-sac
2
D.caninum: [scolex]
D.caninum: Egg capsules
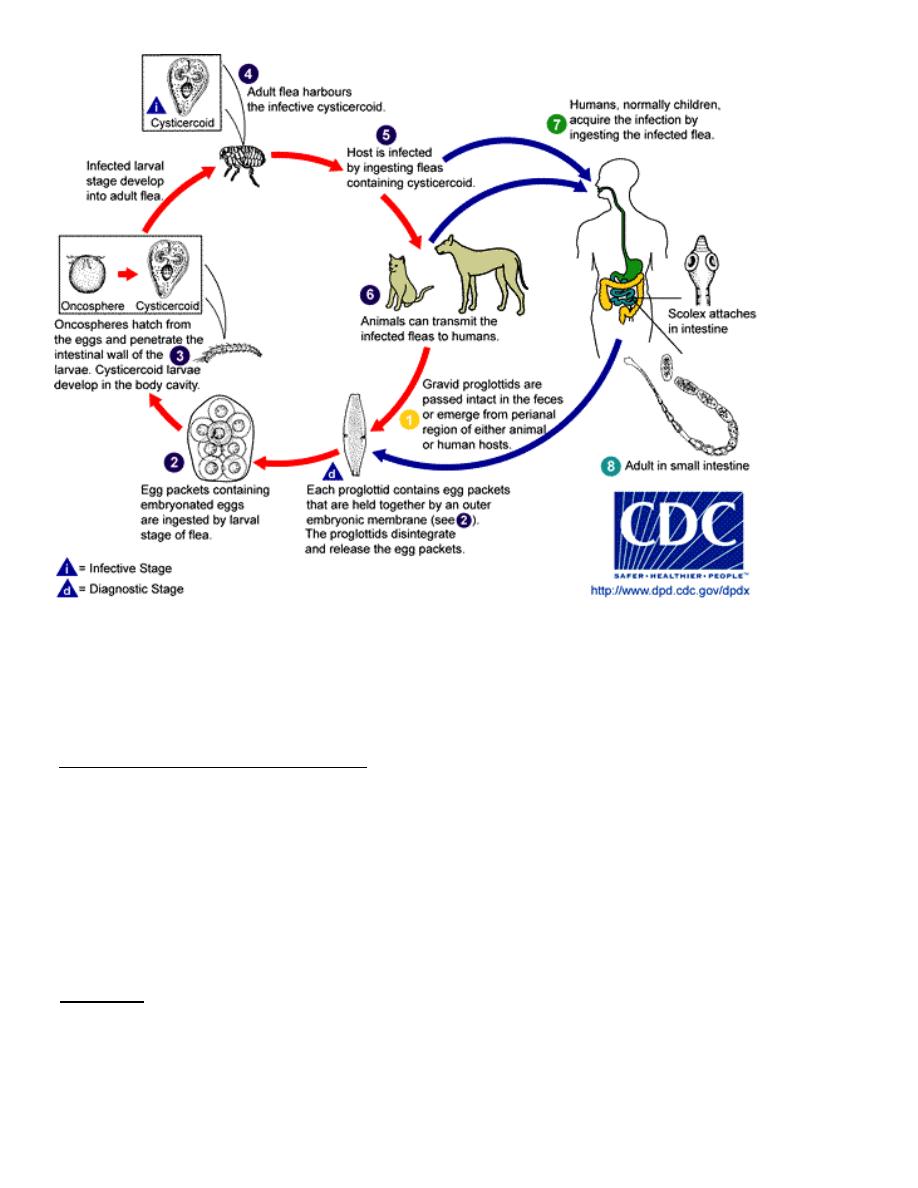
-Life cycle: when larvae of dog fleas or cat fleas ingested the egg capsule,
hatching occurs and the liberated embryos transform to cysticercoids larvae.
The definitive host becomes infected by ingesting the infected insect.
3
D.caninum: Life cycle
-Pathogenesis and Symptomatology:
. Asymptomatic in light infection
In children, it may produce diarrhea and occasionally there may be sever sensitization
reaction, e.g. urticaria, fever and eosinophilia. Patients with heavy infection may
develop appetite loss, diarrhea, abdominal discomfort, indigestion and anal pruritus
caused by gravid proglottid migrating out of the anus.
-Diagnosis: by recovery of characteristic gravid segments evacuated in the stool or migrating
from the anus and by observing the egg capsules in the stool.

4
Diphyllobothrium latum (fish tapeworm or broad tapeworm)
It causes a disease known as diphyllobothriasis or fish tapeworm infection.
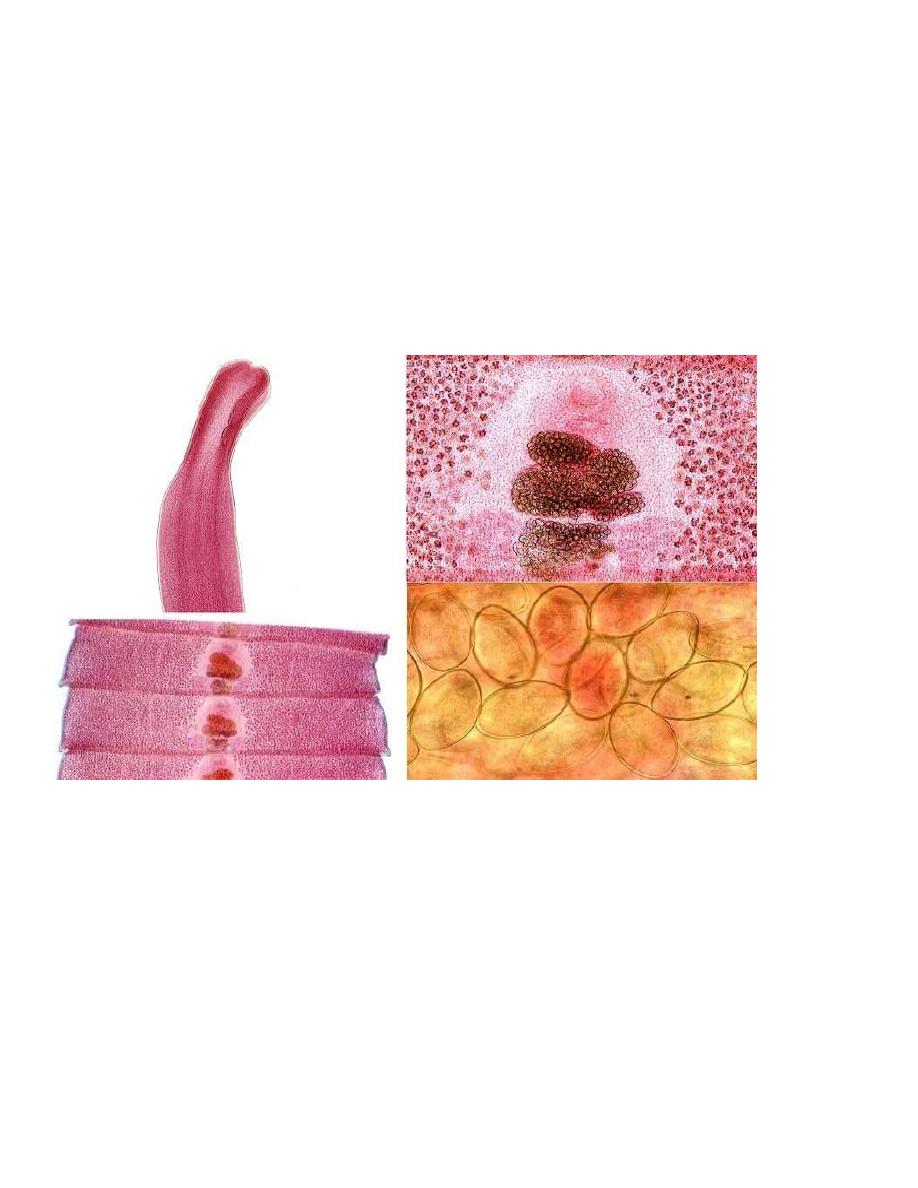
Adult worm is up to 10meters or more in size, adults live in small intestine. The scolex is
almond shape provided with 2 suctorial grooves or bothria.
D.latum progllotids are wider than they are long , mature progllotid compose of one set of
both male and female reproductive organ and centrally located genitale pore.G ravid
progllotid contain acentrally located coiled uteiane which frequntly assumes a rosette shape
filled with eggs .
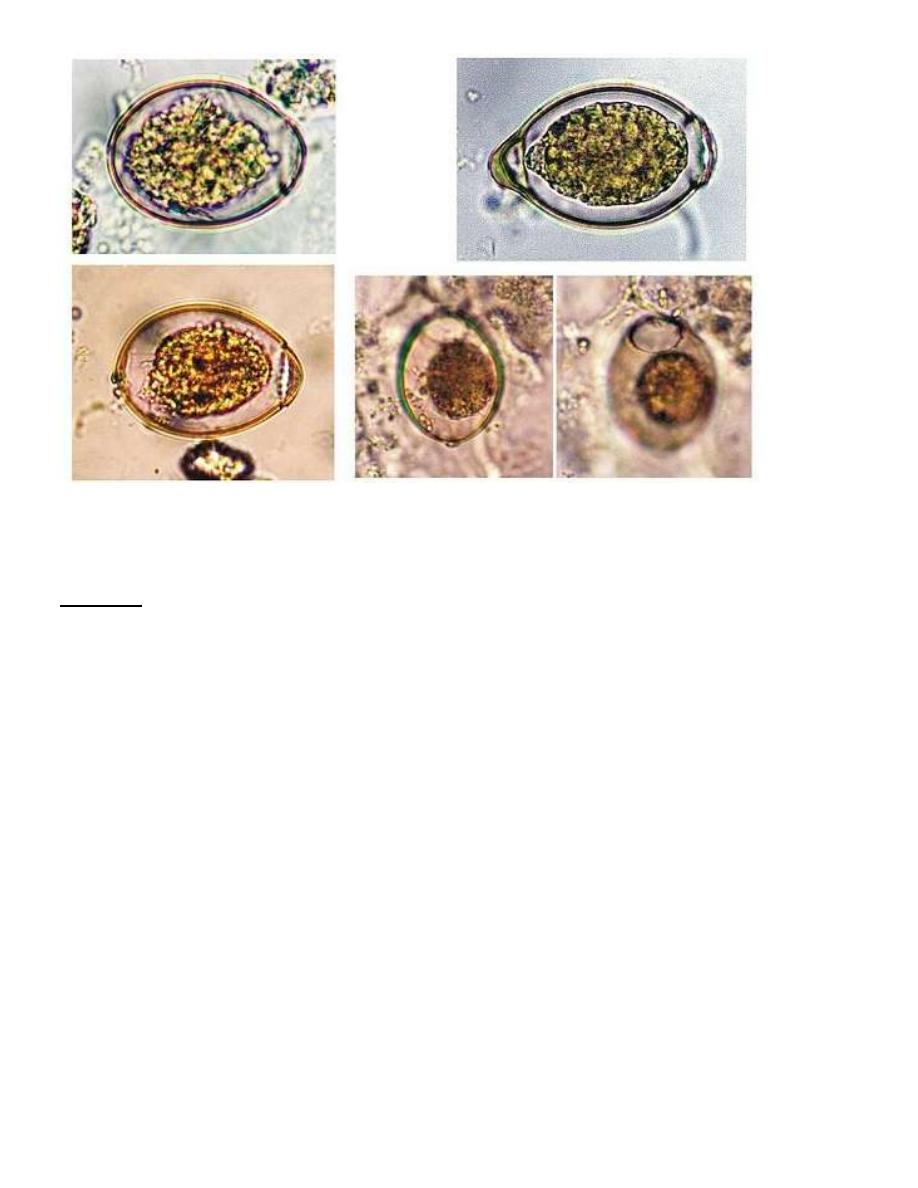
D.latum: sclex, segment and egg.
Eggs: broadly ovoid, light golden-yellow in color, have an operculum at one end and a small
inconspicuous thickening of the shell at the opposite end.
5
ss
Egg of D. latum
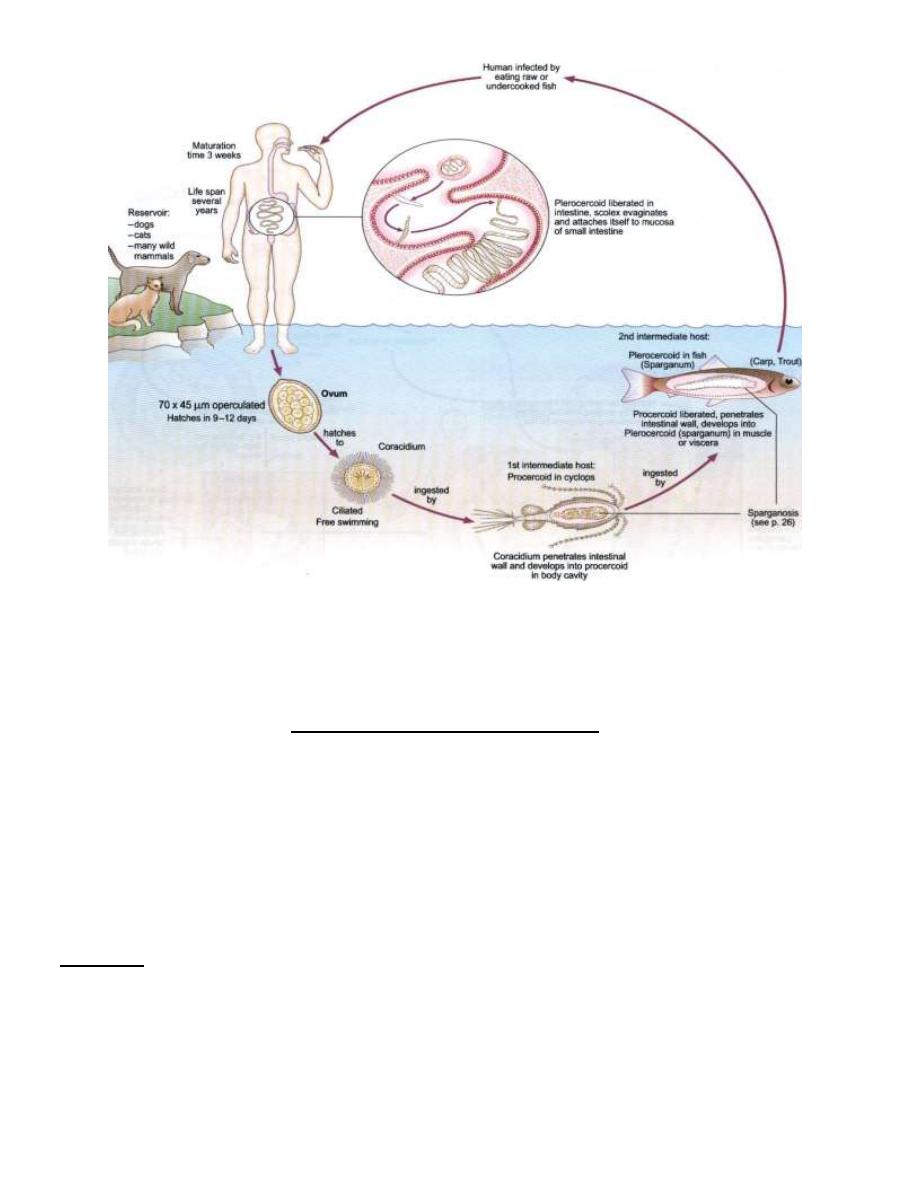
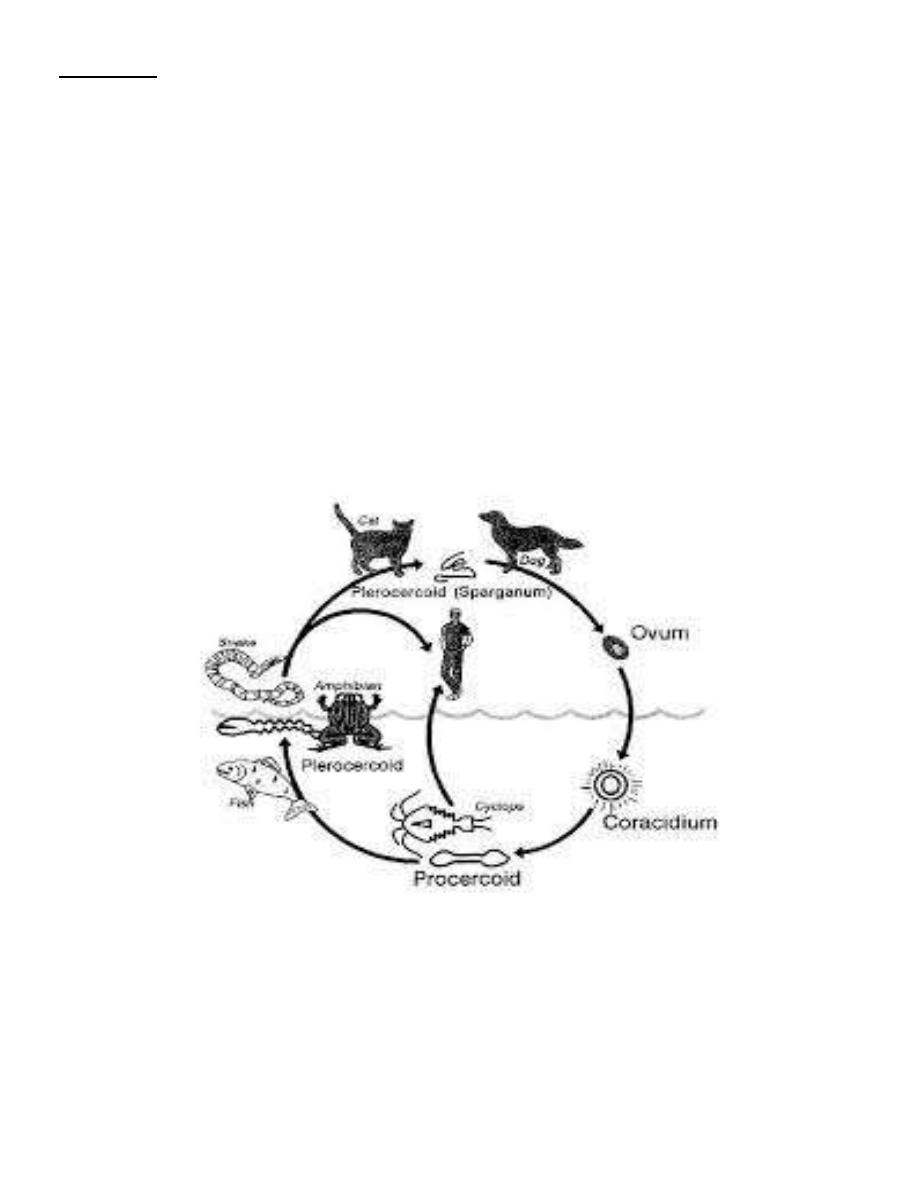
-Life Cycle: Embryonation of eggs takes place in fresh water lead to the formation of ciliated
oncosphere (coracidium).
Coracidium escapes through the operculum and swims in water. If this embryo eaten
by suitable species of copepod or Cyclops it will transforms to Procercoid larva. If the
infected Cyclops is then eaten by a fresh water fish [Crap 0rTrout], the larva is transforms
into a Plerocercoid larva (sparganum). When the infected fish is eaten row or uncooked by
definitive host, the worm develops to maturity and begins laying eggs in about 4 weeks.
6
D.latum
life cycle
-
Pathogenesis and Symptomatology;
It may produce on symptoms but infections often cause digestive disturbances, including
diarrhea, hunger pains or loss of appetite, anorexia, nausea and vomiting. Sudden vomiting
of a portion of the worm may occur, accompanied by symptoms suggesting peptic ulcer or
appendicitis. In heavily infected individuals, vitamin B12 deficiency and megaloblastic
anemia develops.
-Diagnosis: depends on finding the characteristic eggs or strands of proglottids in stool [GSE
and direct microscopic examination], or occasionally vomited proglottids.
-biopsy in case of spargnosis.
7
Treatment:
Niclosamide is drug of choice or Praziquantal.
Surgical removal used for spargnosis or spargunum.
Spargnosis
Spargnosis: is a human tissue infection with (sparganum) Plerocercoid larva of spirometra
spp.
Several spp. of Spirometra are intestinal parasites of canine and feline hosts. Cyclops
is the first intermediate host; second intermediate hosts are fishes, frogs, snacks and birds.
Human infection can be acquired by swallowing a Procercoid in a copepod or a
Plerocercoid in a second intermediate host or applying Plerocercoid-infected flesh of frogs and
snakes as poultices on an inflamed eye or finger.
Spirometra spp. Life cycle
ا
لصور
ة دورة
الحياة
Spirometra spp.
ل
لطالع
.فقط
