Phylum Nematoda
(Round worm)
General charecterstics
trichiura
Trichurs
Describe
Morphology ,life cycle, pathogenesis ,
clinical presentation
Lab. diagnosis
vermicularis
Enterobius
Morphology ,life cycle, pathogenesis ,
clinical presentation Lab. diagnosis
Learning objective

Phylum Nematoda
(Round worm)
The most abundant animals on the earth
Either free living or parasite of animals & plants
They are bilaterally symmetrical ,
unsegmented, elongated , tapering at
both ends & posses a pseudocoel (body
cavity) {
not lined with peritoneum or
mesothelium
}

The body is covered with a non cellular
cuticle
which is secreted by the underlying
hypodermis
The sex is separated ( bisexual the )
female
is longer than the male & most of them are
oviparous
,
while the male is shorter & has a
more curled tail
Size vary from less than one mm to several
centimeters

Body wall consist of
outer cutical , inner muscular
& intermediate hypodermis
The surface coat is important in evasion
of the immune response
Pseudocoel
;
The body wall enclose a fluid filled (
Hemolymph
)
cavity the pseudocoel which differs from a true
coelom in that it has no peritoneal lining

Its function as hydrostatic skeleton , the
alternation of contraction & relaxation in
dorsal & ventral muscle impels the body
into series of curves producing S shape
motion seen in nematode locomotion
Thinner & longer««»»Shorter & thicker
Hemolymph important for transport of
solute & nutrient from one tissue to
another

Digestive system is complete with mouth,
gut & anus
The anterior part consisting of mouth,
buccal cavity & esophagus, all lined
with cuticula
*
mouth
is a usually circular opening
surrounded by lips (may be fused or absent)
*
Buccal
cavity lies between mouth&
esophagus which may be supported by
teeth as hook worms
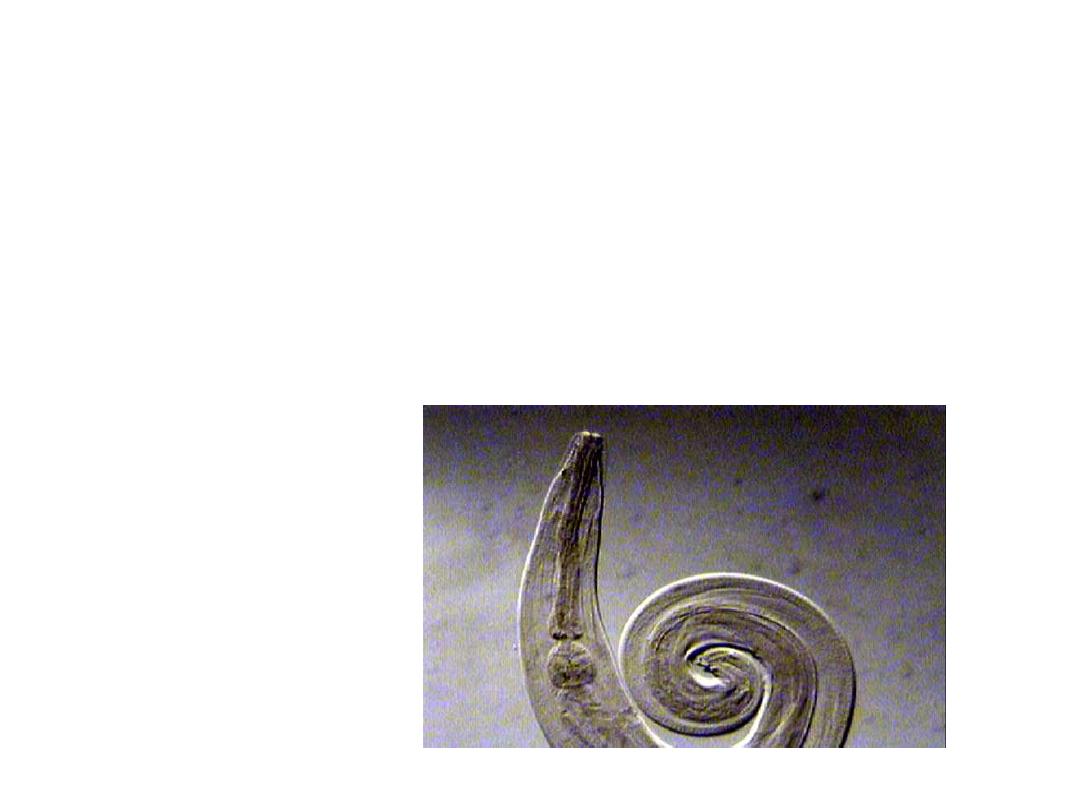
*
Esophagus
is a muscular & cylindrical
region of the digestive tract which sucks
food & forced it into the intestine ,the
esophagus often has one or more
enlargements called
bulb
s

Mid-gut)
)
Intestine ;
a
tube like structure extends from eso.-rectum
The wall of the intestine consist of simple
columnar cells with microvilli for nutrients
absorption
( the food is either blood,
tissue cells ,fluids ,intestinal contents or
combination of them)
also the
intestine serves as a primary means of
excretion of nitrogenous waste products

*
Rectum
(hind-gut)
Which is lined with cuticula & ends
in anus
in male receives the products of
reproductive system into its terminal
portion so it is a
cloaca
which
contain the copulatory specules

Nervous system
;
Is very simple, two main concentrations of
nerve elements ,one in
esophageal region
,the other in the
anal region
,connected by
longitudinal nerve trunks.

The main sense organs are,
cephalic &
caudal papillae
( the later aids in copulation)
Predominant neurotransmitter is
acetyl choline
Several of nematocidal drugs interfere with
neural functions
as piperazine or mebandazole paralyzing the
worms →passing out of the host
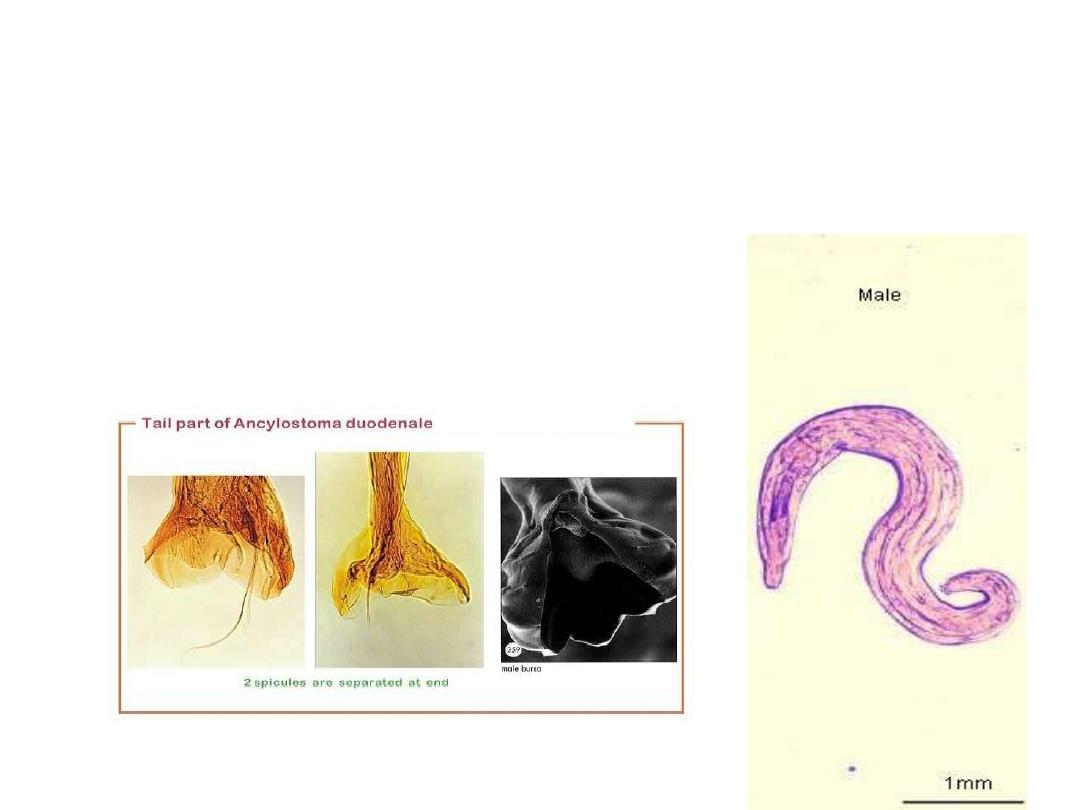
Male are smaller than Female
Male with coiled tail ,often associated with
external feature as bursae, copulatory
spicules & papillae

Female reproductive system either
single set as in Trichuris
or (mostly) paired, consist of ovary,
oviduct, uterus, vagina
& vulva which is ventral in
position

The daily production of eggs per female varies
greatly in different species ,also the stage of
development at the time of oviposition also
varies;
Eggs of Ascaris & Trichuris are
unembryonated
Those of Hookworms are in early
stages 4-8 cell
Those of
Strongyloides
are in
morula
& larva
leaves the host
Trichinella & filariae eggs develop completely &
hatch in uterus(
larviparous
)

The fundamental stages in nematode life
cycle are the
egg
,
four larval stages
, &
the
adult
In the majority of intestinal nematodes
intermediate host is not present so there
is a necessary period of development
outside the body ,frequently in
soil for
complete larval development

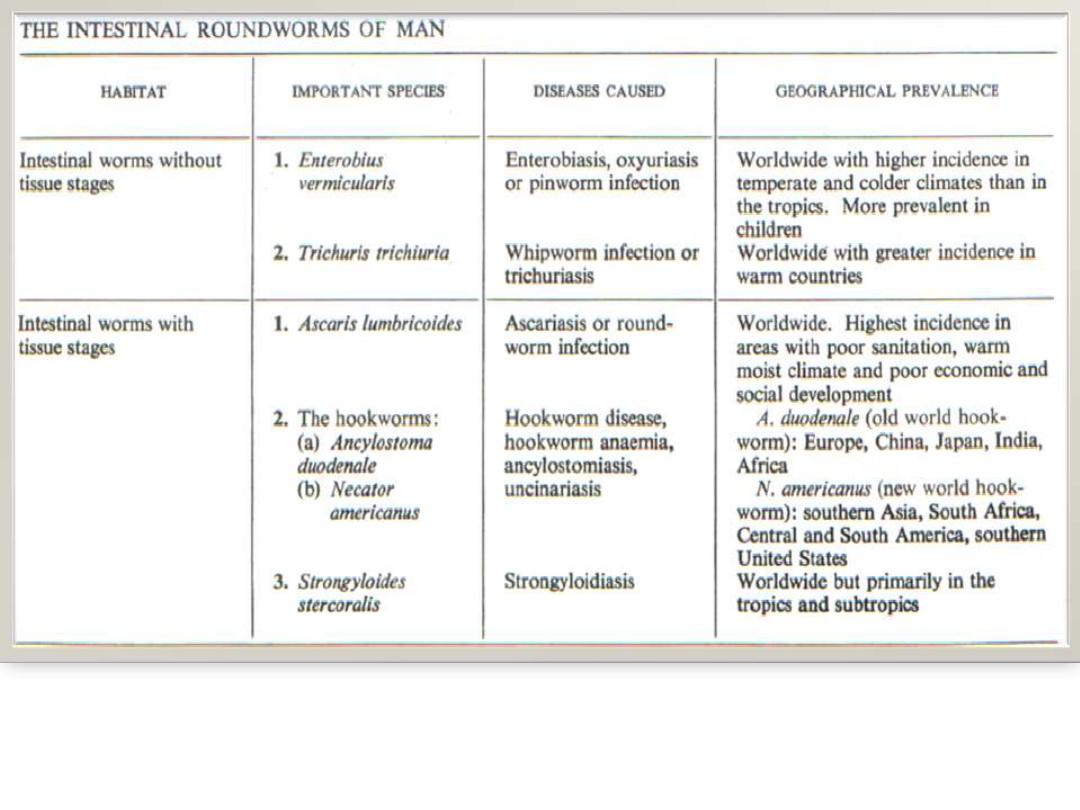
The Intestinal Nematodes found either
free in the intestinal lumen as Ascaris
or
attached to the wall of intestine as
Hookworm
or
embedded deeply in the intestinal
mucosa as strongyloides
Nematodes
With Larva
migration
Without larva
migration
trichiura
Trichurs
vermicularis
Enterobius
Large intestinal nematodes (cecum &iliocecal junction)
293

Trichurs trichiura (Whip worm)
long
mm
50
-
30
Trichurs trichiura
anterior thread or whip like structure which
Is imbedded in the intestinal mucosa
Posterior portion is fleshy & board which is free
in the intestinal lumen
Mouth lacking lips
Male is smaller with single spicule
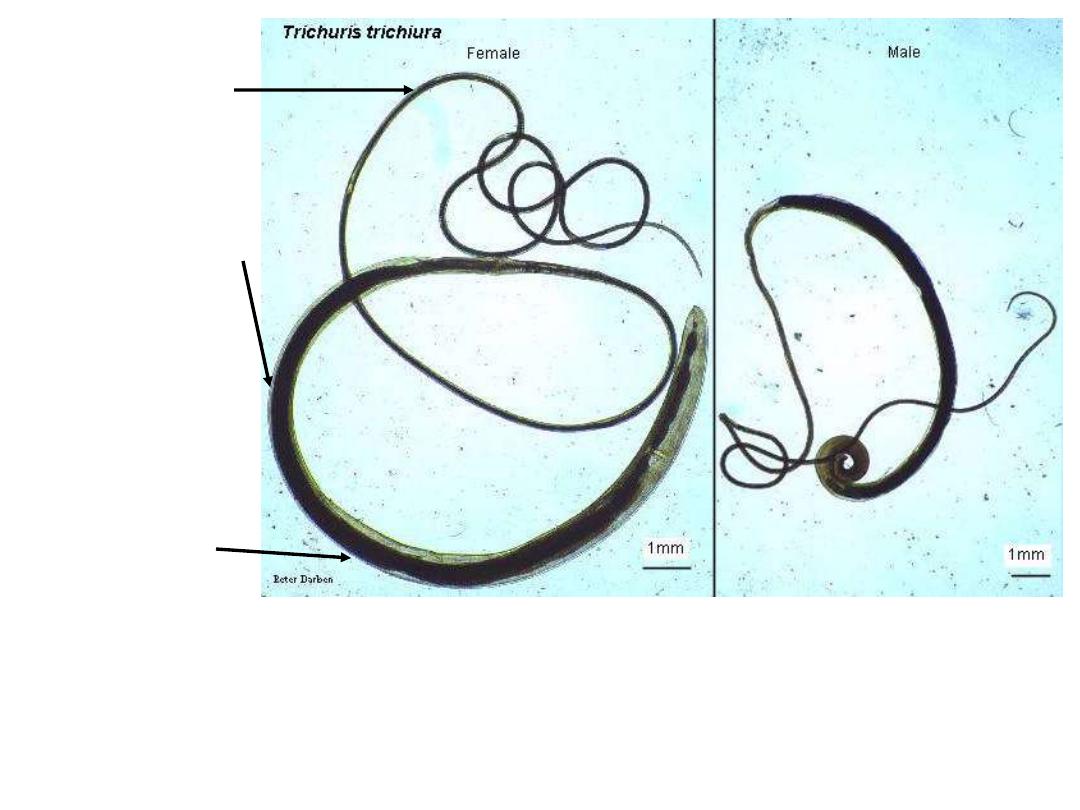
Anterior end
3/5 from the
body, thread
like for both
sexes
Posterior end
2/5 from the
body, wider and
fleshed for both
sexes
The posterior in
the female like a
comma or arc
The posterior of male caudal
extremity is coiled ventrally,
contain sheathed spicule
3
– 4 cm
4
– 5 cm
Fig 248 : Trichuris trichura male and female
Note : adult worm white or pinkish in colour
302

Each female produce 3000-20000 egg/day
Ova is a barrel shape with a prominent opercular
Plug at each end ,
unemberyonated
when passes with stool
Emberyonation is complete in about 21 days in
Soil which must be moist & shady
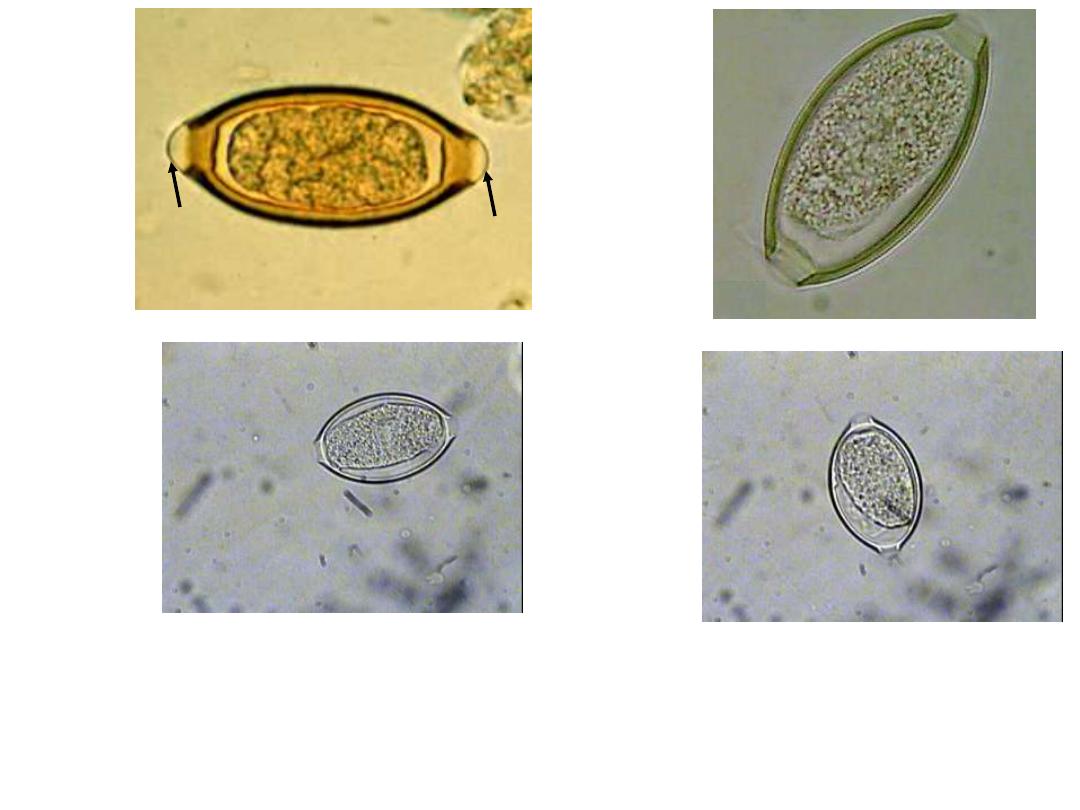
Fig 249 : Trichuris trichiura Egg 50 X 25 µm
Note : the egg barrel
– shaped, with two polar plugs yellowish brown in colour
( bile
– stained ) has a double shell, the outer one is
bile
– stained
In Iodine s.
In saline s.
Plug
Plug
303

When swallowed hatch & the larva enter crypts
of Lieberkuhn of large intestine
Worms begin to grow & tunnel within the
epithelium & break towards the luminal surface
Then the enlarging posterior portion breaks of
the epithelium & protrudes into intestinal lumen
all this requires 3 months
Anterior end remains embedded in the gut
mucosa ,so it is a tissue parasite & lives there
for several years
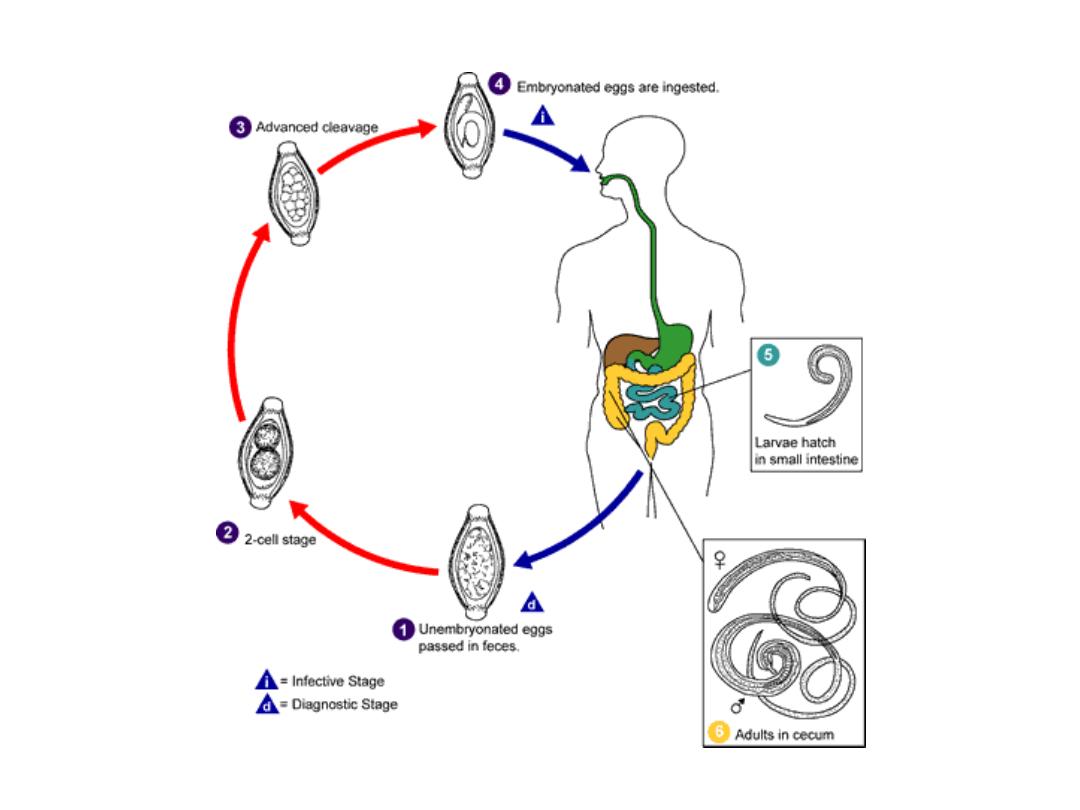
Trichuris trichiura
Life cycle
Fig 247 : life cycle of
Trichuris trichiura
301
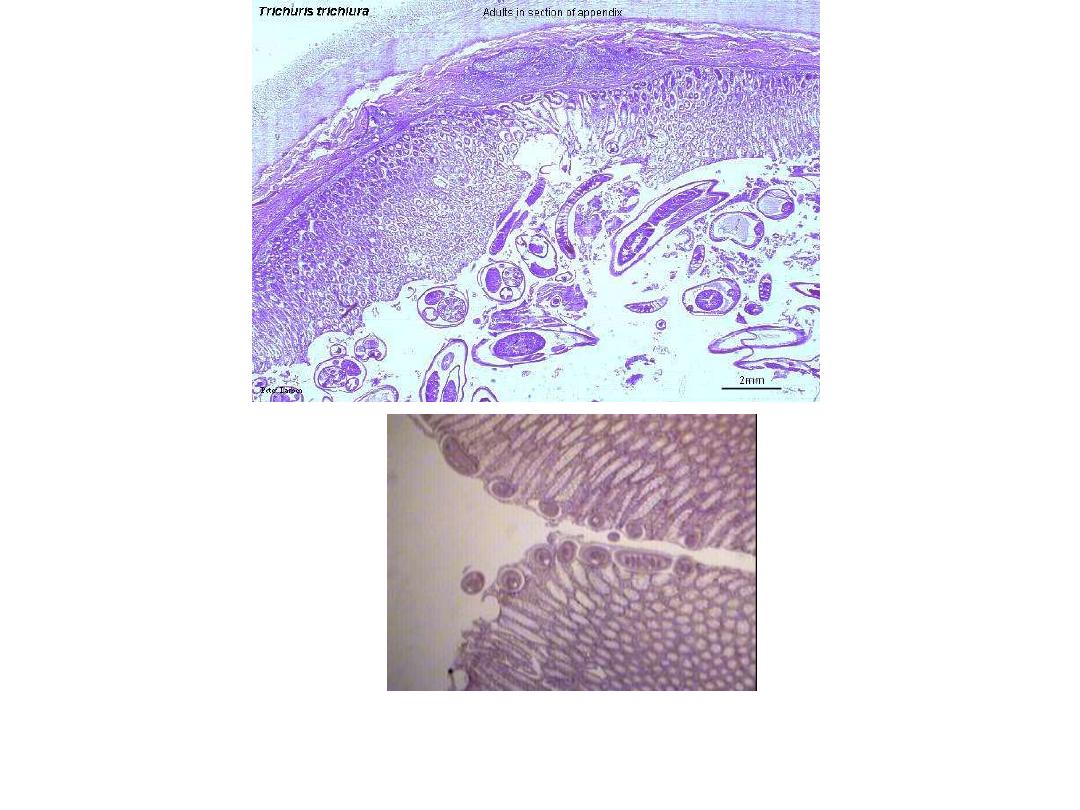
Fig 251 : Trichuris trichiura Adult Appendix Section
305
Hematoxylim - eosin s.

Epidemiology Trichurs trichiura
requires
poor standard of sanitation
in
which human feces are deposited on the soil
Associated
with worm climate high rainfall
&
Humidity (shady area)
Prevalence 1-2%especially small children
infection

The infective stage is mature ova from
contaminated soil
Geophagy eating soil ,usage of feces as fertilizer
House fly as mechanical vectors

Pathology
Fewer than 100 worms rarely causes
Clinical symptoms (majority are symptom less)
Symptom of trichuriasis
→
>200
Small children are particularly prone to heavy
infection
Dysentery,
anemia
, growth retardation , finger
clubbing
(systemic nature of the effect of infection)
&
rectal prolapse
→→
Frequent location in cecum & appendix
Appendicitis
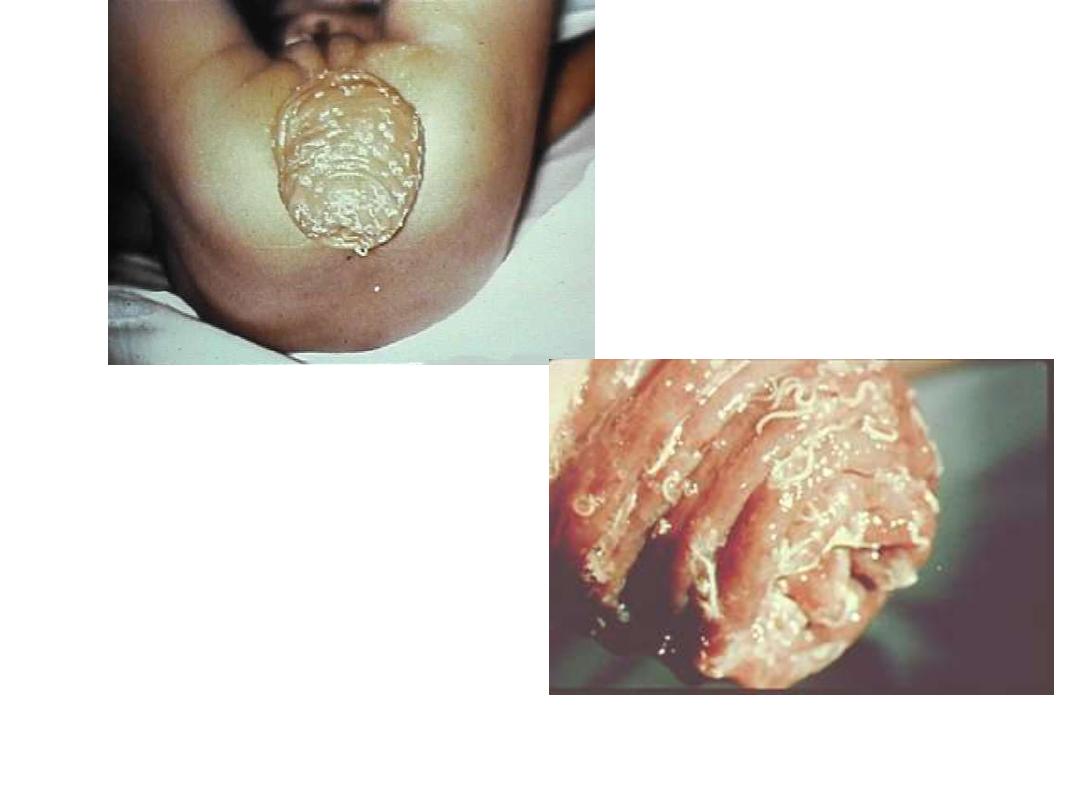
Fig 250 : symptom, with heavy infection ( prolapse of the rectum )
304

The anterior end buried in the mucosa so the
worm feeds on cell contents & blood
The inflammatory response leads to increase
macrophages in the colonic lamina properia
& increase level of TNF in mucosa & blood
also increases in IgE
Diagnosis; Demonstration of eggs & worms in
stool
Treatment; mebendazole, albendazole--------

Small children are particularly prone to heavy
Infection with Trichuriasis they may have all the followings
except
A-Dysentery& anemia
b-finger clubbing
(systemic nature of the effect of infection)
c-
rectal prolapse
D-Ulcerative colitis

Ova of T. trichura is a barrel shape with
a-aprominent opercular Plug at each end
B-unemberyonated
when passes with stool
Emberyonation is complete in about 21 days in
C-Soil
D-Have polar thickening & polar filaments
vermicularis
Enterobius

Enterobius vermicularis (pin worm)
Most common nematode of man
Female is slender with sharp , pointed
Tail (8-12 mm)
Male posterior end curved ventrally with
Single spicule(2-4 mm)
Have 3 lips surrounding the mouth,
Followed by cuticular inflation of the head
Cuticular expansion
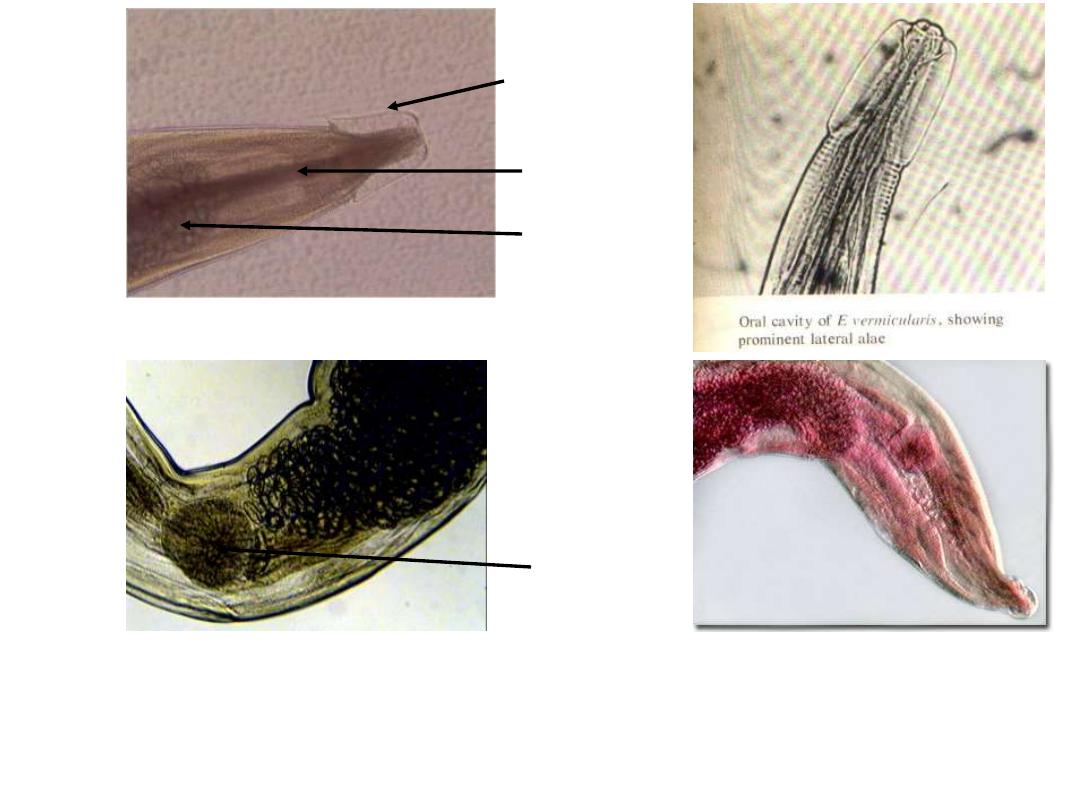
Fig 241 : Enterobius vermicularis Adult Anterior end
Note : the cuticular cervical expansions ( alae ) and the double
– bulb muscular
oesophagus ( similar in both sexes )
Cervical alae
Oesophagus
Bulb
Globular bulb
295
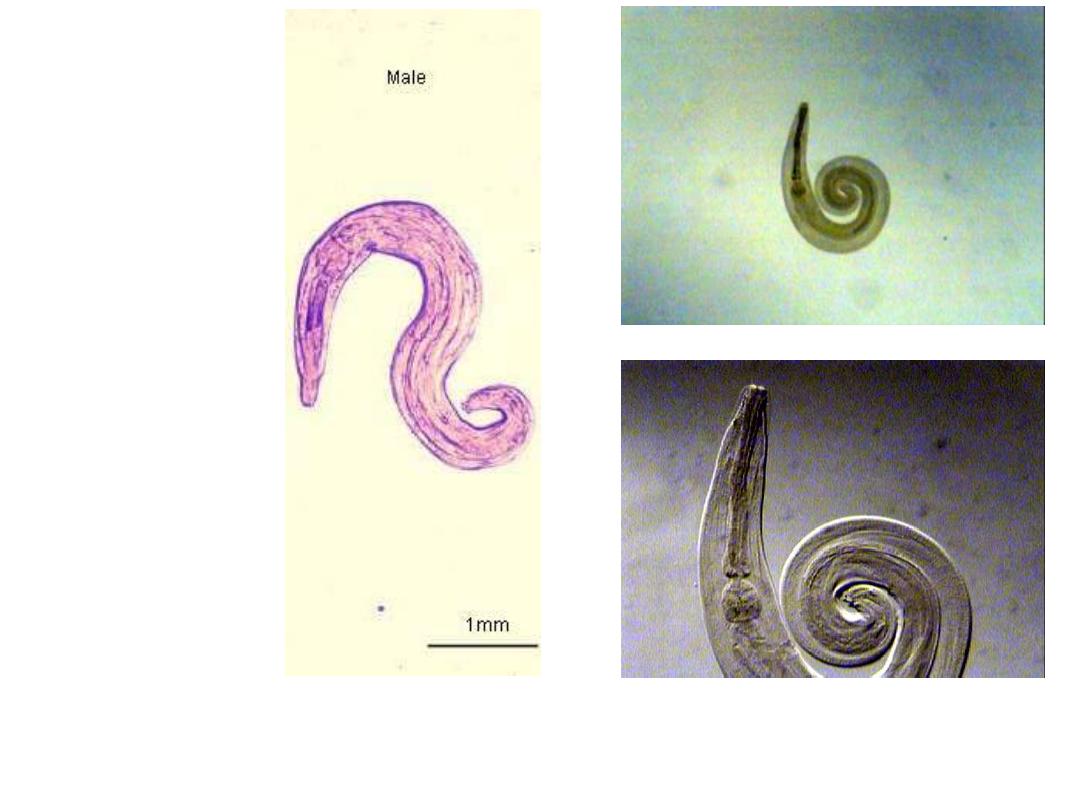
Fig 242 : Enterobius vermicularis Adult Male 2
– 4 mm X 0.1 – 0.2 mm
posterior end is curved with one spicule, rarely seen in stool
296
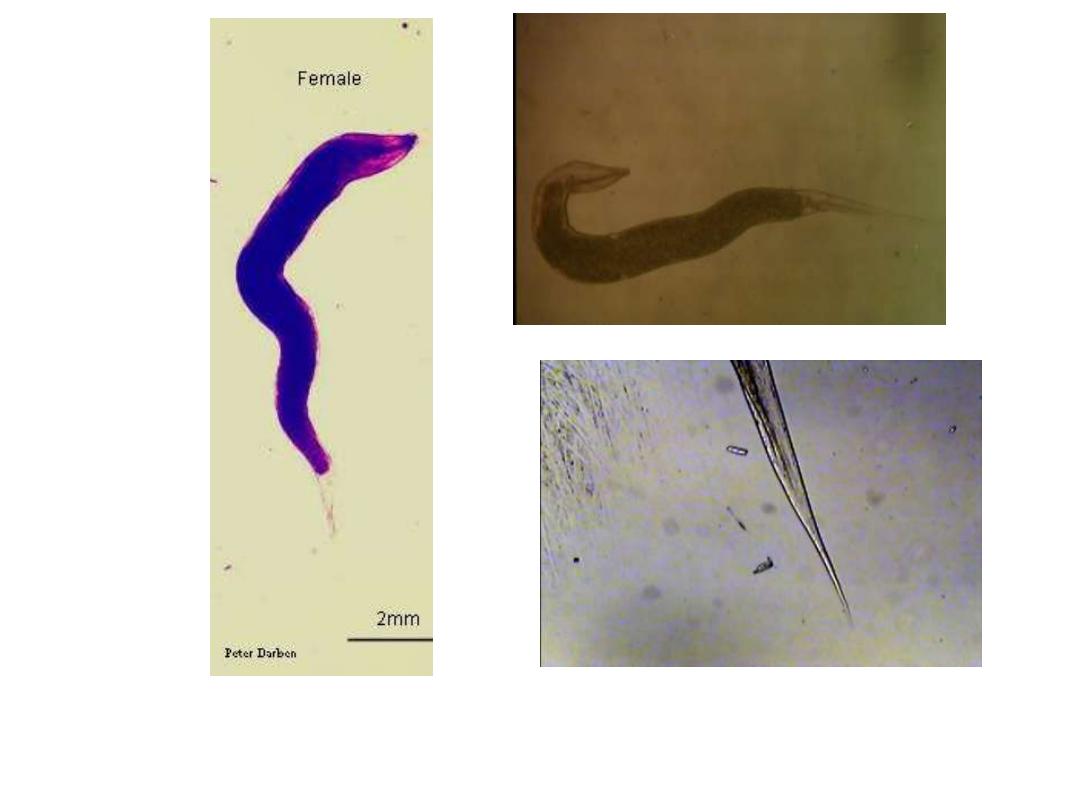
Fig 243 : Enterobius vermicularis Adult Female ( 8
– 12 mm X 0.3 – 0.5 mm )
Note : white in colour, spindle shaped and resembles a short piece of thread, pointed
tail macroscopically seen in stool
Enterobius vermicularis Adult
Female Posterior End
297

Female when gravid the 2 uteri contain
Thousands of eggs
Egg is enlongated oval & flattened on one
side
( D shape)
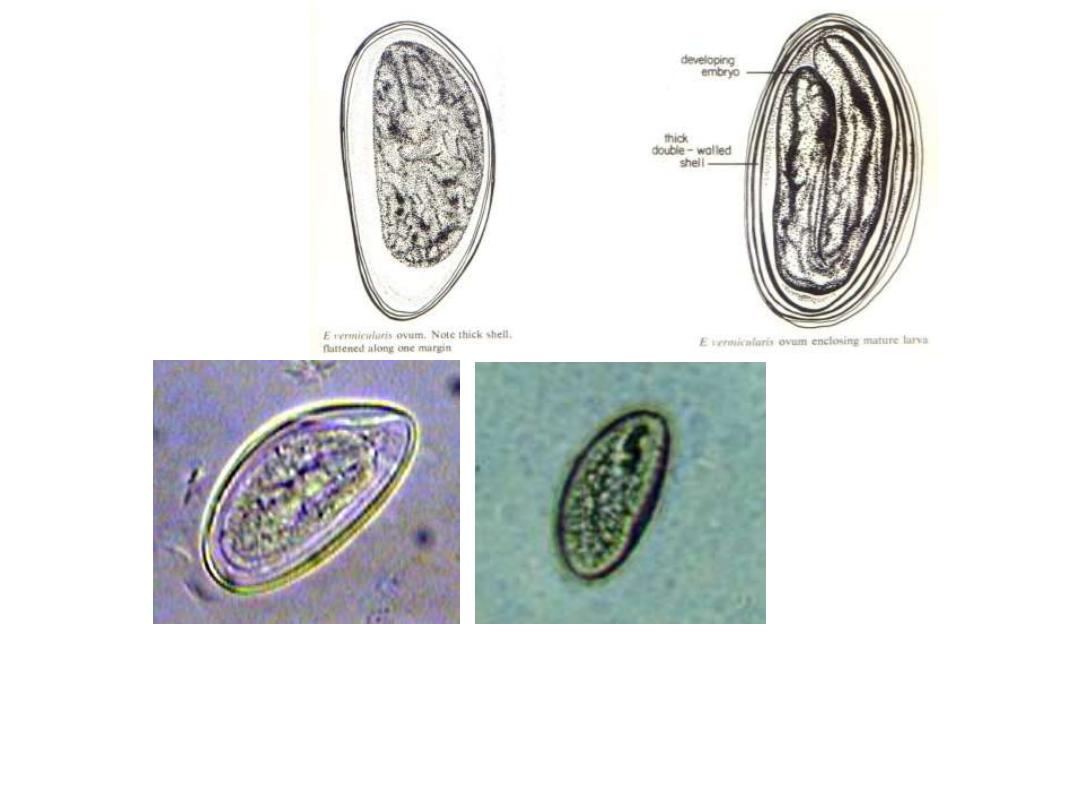
Fig 244: Enterobius vermicularis Egg 50
– 60 X 30 µm
Note : colourless D
– shape ( flattened on one side and convex on the other, thick
double
– walled shell )
rarely seen in stool smear
In Iodine s.
298

Adult worm habited mainly iliocecal region
Although the worm can wonder through out
The GIT from the stomach to the anus
They attached themselves to the mucosa
Where they presumably feed on epithelial cells
& bacteria

The gravid female begins migrating within the
lumen of intestine , passing out of the anus on
to perianal skin where they crawl about on the
outer skin , where they leave their eggs.
One worm may deposits about 5000—15000
eggs , female soon die after oviposition
While the male die soon after copulation
So in intestine female > male

Ova when laid it contains a partially developed
larva which will be developed to infectivity
within 6 hr. at body temperature
So
re-infection or auto-infection
is very
common
Auto-infection can occur by two routs

Egg swallowed then hatched in the duodenum ,
the larva slowly move down in the intestine ,
molting twice to become adult by the time
they arrived to the iliocecol junction ,the total
time from ingestion →sexually mature worm
about 15-45 days
Or if the perianal folds are uncleaned for a long
period , the attached ova hatches and the
released larva wonders into the anus & hence
to the
intestine
(retro-infection)

Epidemiology
Ova remain viable for weeks
Ova are very light so air born Clothing ,
towels & bedding rapidly become
seeded with eggs even the carpets
Most common means of infection is
through insertion of fingers & objects in
the mouth
Human can inhale then swallow the air
borne ova
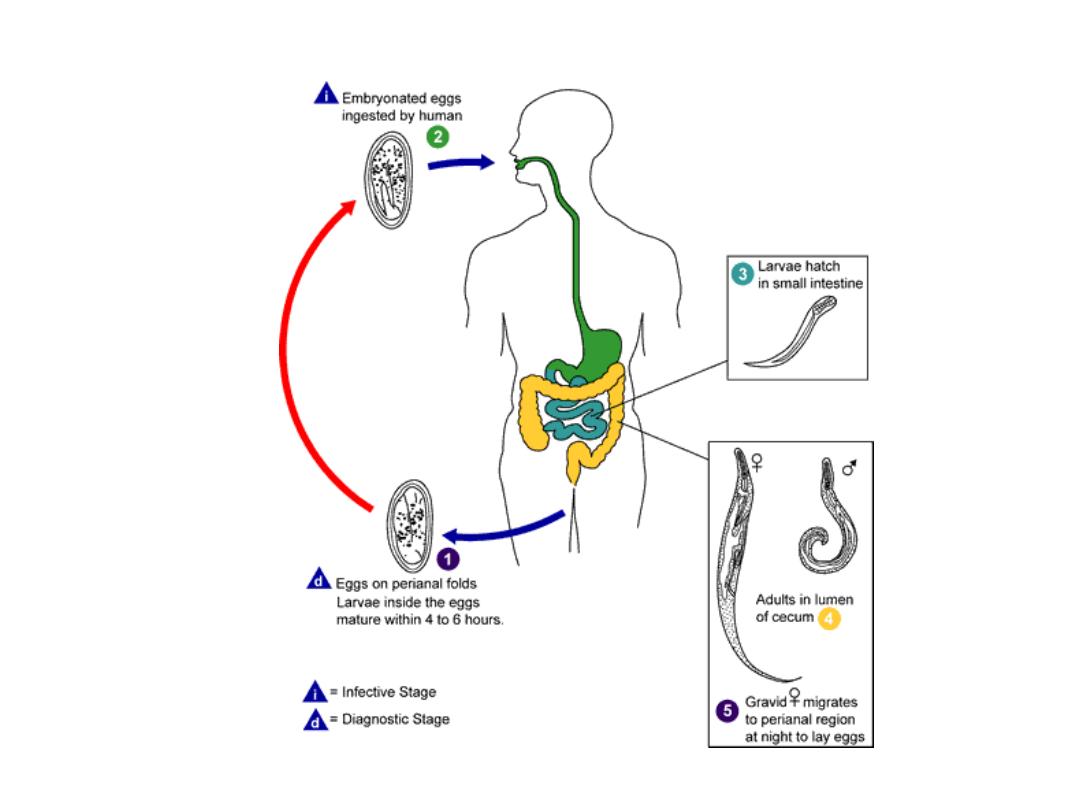
Enterobius vermicularis
Life Cycle
: life cycle of
Enterobius vermicularis ( Oxyuris vermicularis )
294

Pathogenesis;
It has 2 aspects
1-damage caused by worms within the intestine,
because of the attachment to the mucosa
results in mild inflammation with or without
secondary bacterial infection
2-damage resulting from movement of female
out the anus &eggs deposition around the
anus leads to tickling sensation& scraching of
perianal area

Clinical features;
One third of infections are asymptomatic
Tickling sensation , pruritis &scratching of
perianal region leading to viscous circular
bleeding & bacterial infection
Patient feelings of nervousness, discomfort ,
restlessness, irritability, loss of appetite ,
nausea , vomiting, perianal pain, insomnia,
bed wetting & nightmare
Sometimes the worms wonders into appendix,
vulva , vagina ,uterus or peritoneum
→inflammation
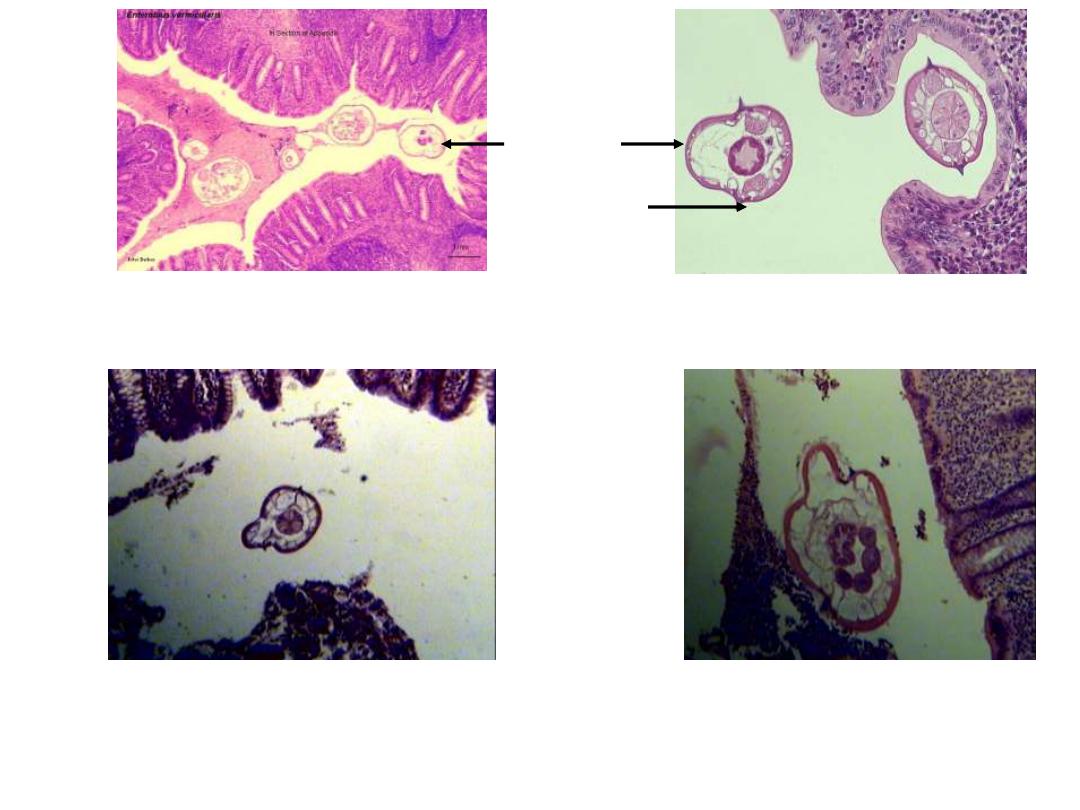
: Enterobius vermicularis Adult in Appendix Section
Note : cuticular lateral alae like spine in cross section of adult worm
Lateral alae or
Lateral crest
Section of
adult worm
300
Hematoxylim - eosin s.

Diagnosis
By finding ova or adult worm
General stool exam is not helpful very few are
passing in stool
Sometime during night or early morning can see
the worm in the perianal area
Scotch (Cellophane) tape technique is
the method of choice for diagnosis

Scotch tape is held against a flat wooden
applicator with the sticky side out , pressed to
anal canal
At morning the tape is reversed & stuck on
microscopic slide
Sometimes egg recovered from under the nail or
swabbing the perianal region
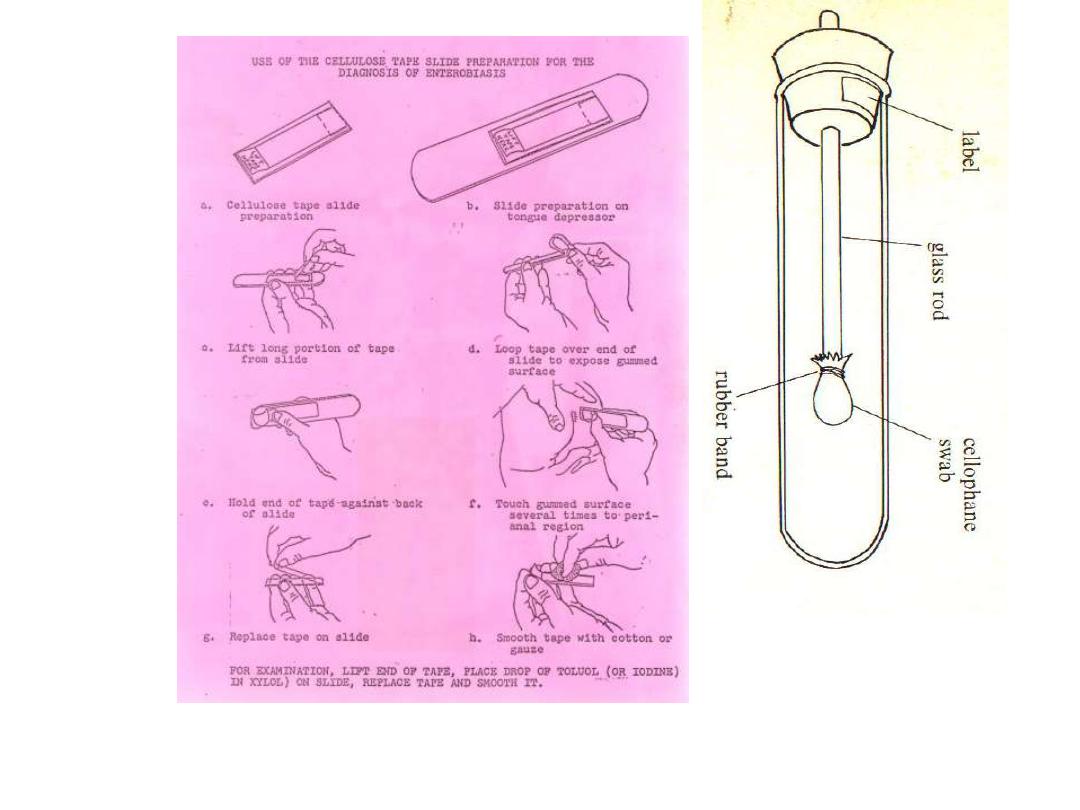
The NIH swab. The
cellophane is now usually
replaced with sticky tape
Scotch tape technique ( graham swab )
: The techniques which used for detected the eggs of E. vermicularis from perianal
skin, eggs are rarely recovered in stool
Note :
eggs can also be recovered from under the finger nails
299

Treatment;
Mebendazole (vermox) repeated after 7-10
days
All family must be treated
All bed lines & towels washed in hot water &
the home must be cleaned
