
B
B
y
y
:
:
d
d
r
r
.
.
s
s
a
a
d
d
i
i
q
q
a
a
l
l
-
-
s
s
h
h
a
a
i
i
k
k
h
h
P
P
h
h
y
y
l
l
u
u
m
m
P
P
l
l
a
a
t
t
y
y
h
h
e
e
l
l
m
m
i
i
n
n
t
t
h
h
e
e
s
s
Class Tre m at oda
•
Subclass Digenea ( The trematodes with 2
generations in their life cycle ) indirect life cycle
.
•
Subclass monogenea (Direct life cycle with one
generation in their life cycle ex. Fish infection .

Ge n e ral charact e rs of Dige n e t ic
t re m at ode s :
1 –Leaf –like shaped unsegment, flat
worms called Flukes.
2 –Size varies from 1 MM to several
centimeters.
3 –The organs of attachment are two
suckers oral and ventral suckers the last
one known as acetabulum.

4 –Sexes are not separated , each worm is a
hermaphrodite (Monoecious ), except the
Schistosomes ( Dioecious ).
5 –Body cavity is absent.
6 – Alimentary canal is present , but
incomplete the anus is absent.
7 – Excretory and nervous system are
present .Excretory system consist of flame
cells and collecting tubules which open
posteriorly in to excretory pore.
8 –Reproductive system is highly developed.
9 –The worms are oviparous and the eggs
with operculum except that of the
Schistosoma .

FOUR KINDS OF FLUKES ARE P RESENT
THESE ARE
§
LIVER FLUKES
: ex. Fasciola hepatica
,Fasciola gigantica and Clonorchis sinensis .
§
INTESTINAL FLUKES
: EX . Fasciolopsis
buski
( Giant
intestinal fluke ) and
Heretrophyes heterophyes .
§
LUNG
FLUKES
:
ex
.
Paragonimus
westermani .
§
BLOOD FLUKES Schistosoma spp
.

L
L
I
I
V
V
E
E
R
R
F
F
L
L
U
U
K
K
E
E
S
S
Fasciola he pat ica
It is known as she e p live r flu ke . This
dise ase is world –
wide in dist ribu t ion.
The parasit e infe ct s he rbivorou s
an im als like she e p ,goat an d cat t le
and occasionally Man .

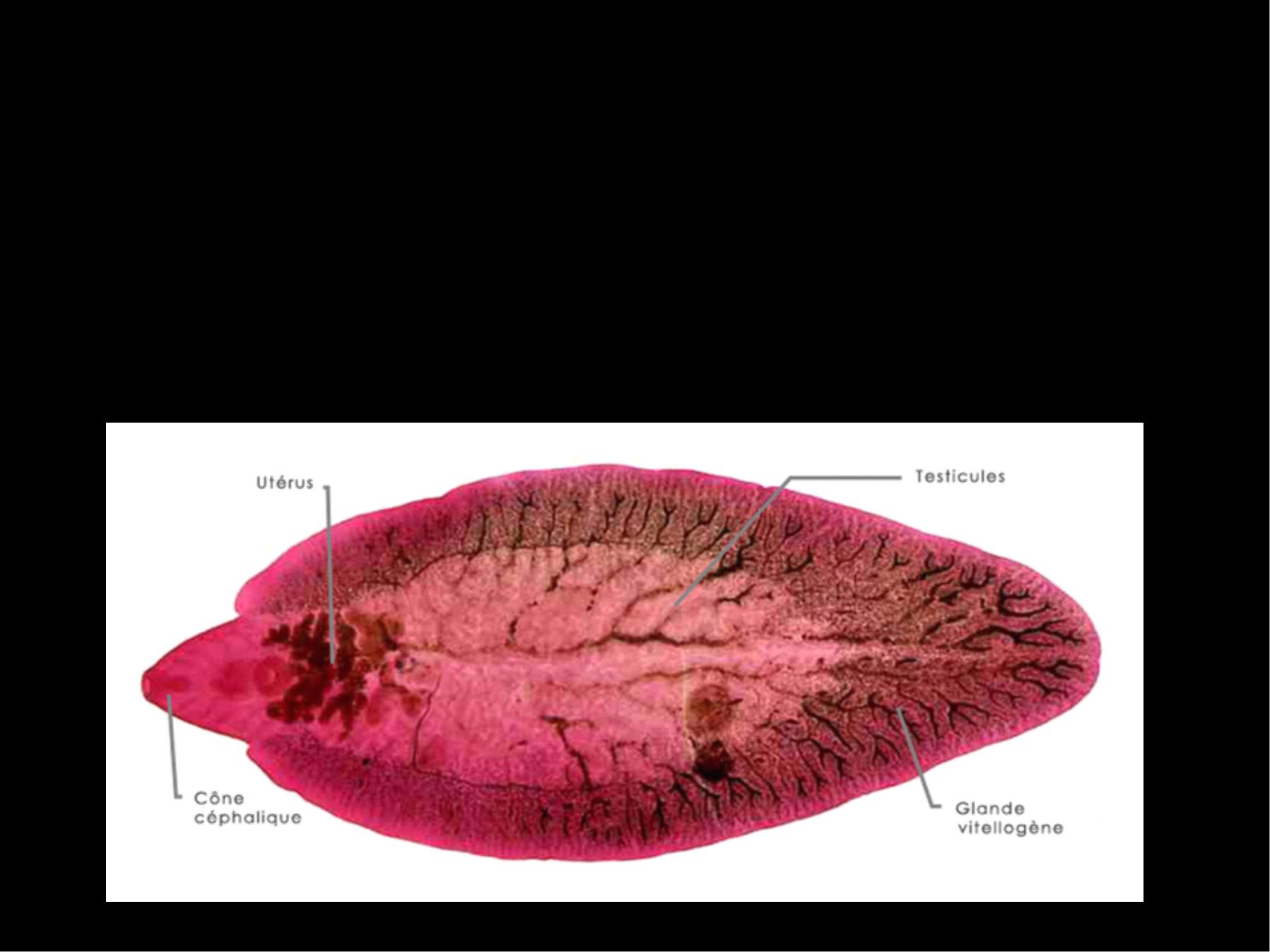
Morphology :
The
adult
worm
is
large
leaf
–like ,
unsegmented , 3 cm in length and 1.5 cm in
breadth and brown or grey in colour , there
are 2 suckers, The oral sucker is smaller than
the ventral .The intestinal caeca is highly
branched.

v Life span in sheep is 5 years and in man
about 10 years.
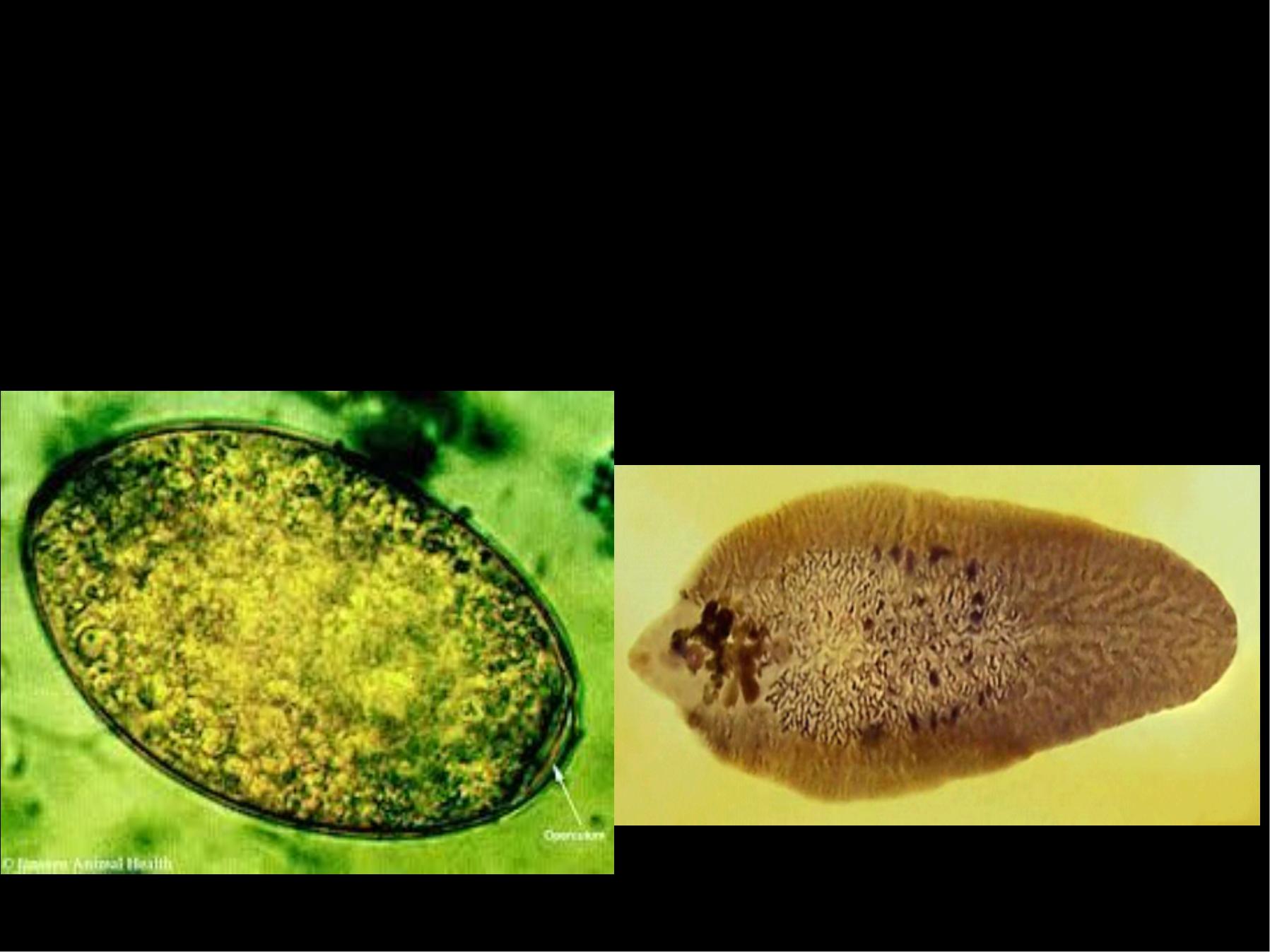
v The ova is large, ovoid in shape brownish
–yellow in colour.
v Measuring 140 M by 80 M , and it is
operculated.
v Excreted with the bile to the duodenum
and intestine and the faece.
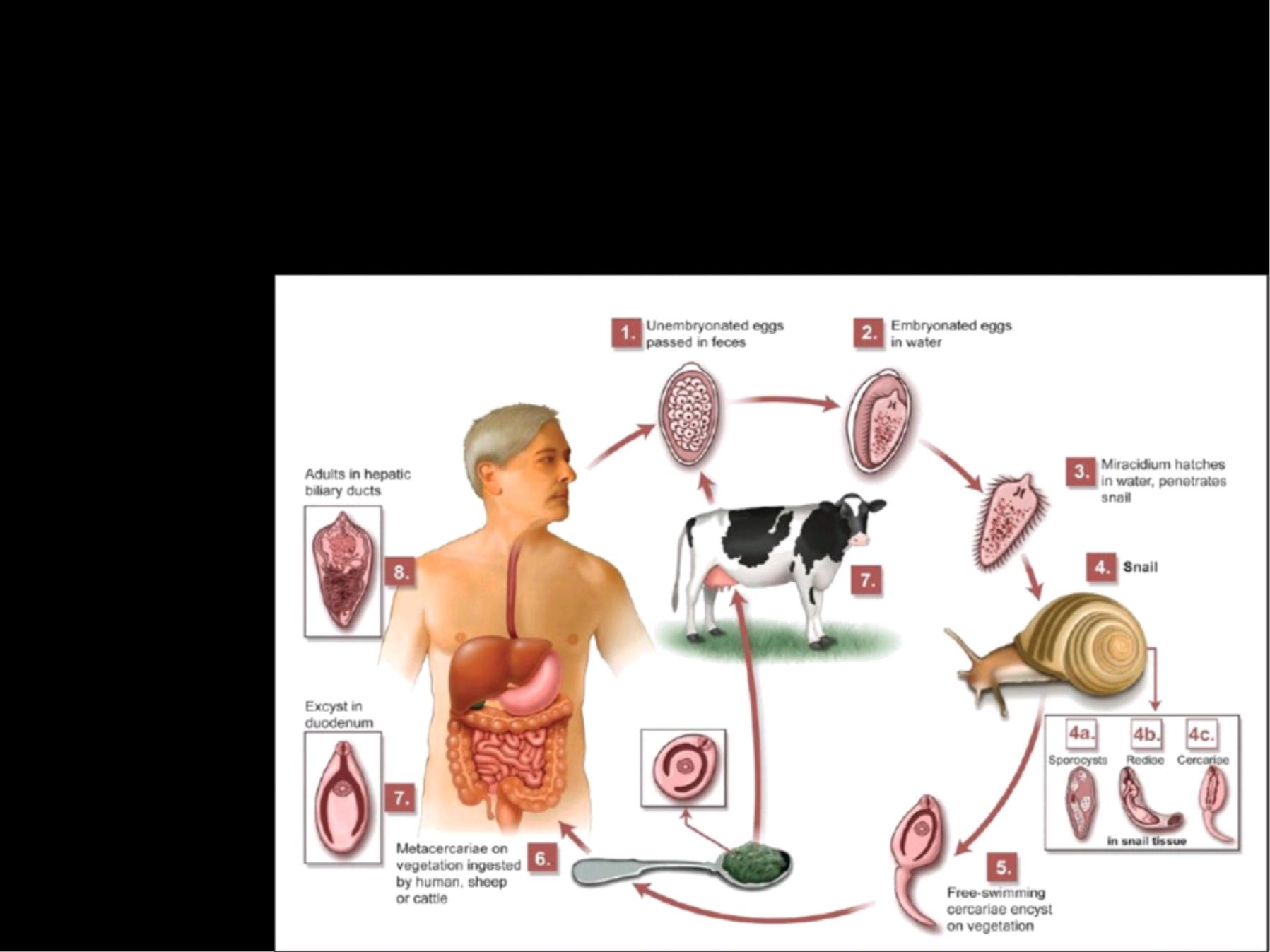
Life Cycle
Definitive host: Sheep, Goat, Cattle and Man,
Sheep is considered the reservoir host for
the infection.

Intermediate host : Snail of the genus
Lymnaea
1-
The eggs pass out in the faeces of the
definitive host , mature in water and from
each egg a ciliated miracedium
will be
developed in 2 –3 weeks .
2-
The miracedia enter the body of the
intermediate host ( Snail of the genus
Lymnaea ) .

3-
Inside this host the miracedia pass
through the stages of Sporocyst , 2
generations of Redia and finally to Cercaria.
The whole cycle takes from 1 –2 month.
4-
The cercaria after leaving the snail swim
in the water and encyst on grasses and
water plants forming Metacercaria .

5-
The Metacercaria will be swallowed with
the grass by the definitive host: sheep , goat ,
cattle and occasionally Man .
6-
On entering the digestive tract , the
Metacercaria excysts in the duodenum and
migrate
through
intestinal wall
to
the
peritoneal cavity and enter the liver capsule
and settle in the bile ducts of the liver and
develop to adult worms .This takes about 3
months .

P at hoge n icit y
Infection of the liver with F. hepatica is
known
( liver Rot )
Fascioliasis is prevalent
in sheep ,goat and cattle in the middle and
south parts of Iraq and to less extent in the
north , heavy infection now a day in man
reported in Iraq .
The
infection
causes
great
loss
and
mortality
especially among sheep, goat and
less in cattle.

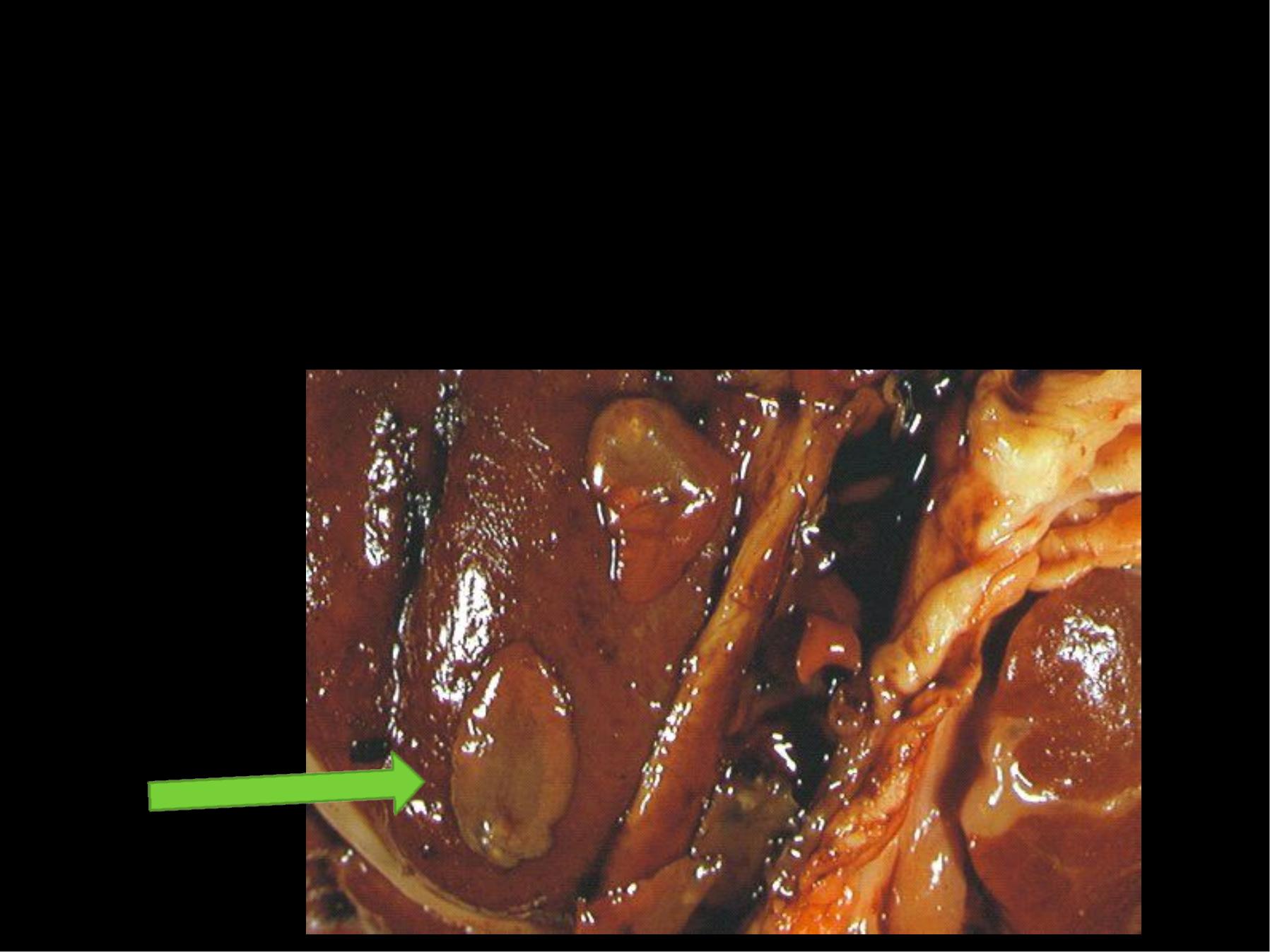
He avy in fe ct ion of t he live r cau se s
live r cirrhosis an d dam age t o t he live r
t issu e .
It was once prim arily t hou ght of, as
Ve t e rinary proble m bu t it has be e n
e st im at e d t hat 17 m illion pe ople are
infe ct e d and t hat 180 m illion are at
t he risk of infe ct ion .
The pat hoge n is wide spre ad, all ove r
t he world. Infe ct ion be gin s wit h
consu m pt ion of wat e r plant s or bad or
n ot washe d ve ge t able s.

Dise ase signs an d sym pt om s in m an
Fascioliasis occurs in two stages:
The first stage:
larval period is marked
clinically by
abdominal pain
,
fever
,
weight
loss and articaria
.
Eosinophilia
and
elevations
in liver transaminase
. This stage can last for
several months. Egg production during this
stage is minimal.

The second stage : refers
to biliary period
,
represents the maturation of larvae in to
adult flukes that pass in to the biliary ducts.
Symptoms during this phase are often subtle,
vague and even asymptomatic
. Patients may
develop
intermittent right upper quadrant
pain
, which can mimic cholecystitis . Ova are
released.

Ø Complications from chronic disease
include
ane m ia, cholan git is, biliary
obst ru ct ion, jau ndice an d live r
cirrhosis.
Subcapsular liver hematomas
and hemoperitoneum are also reported.
Ø
Ectopic sites include
inguinal lymph
nodes, subcutaneous skin , brain and eyes
infection , no potential for malignancy of
the biliary tract
.
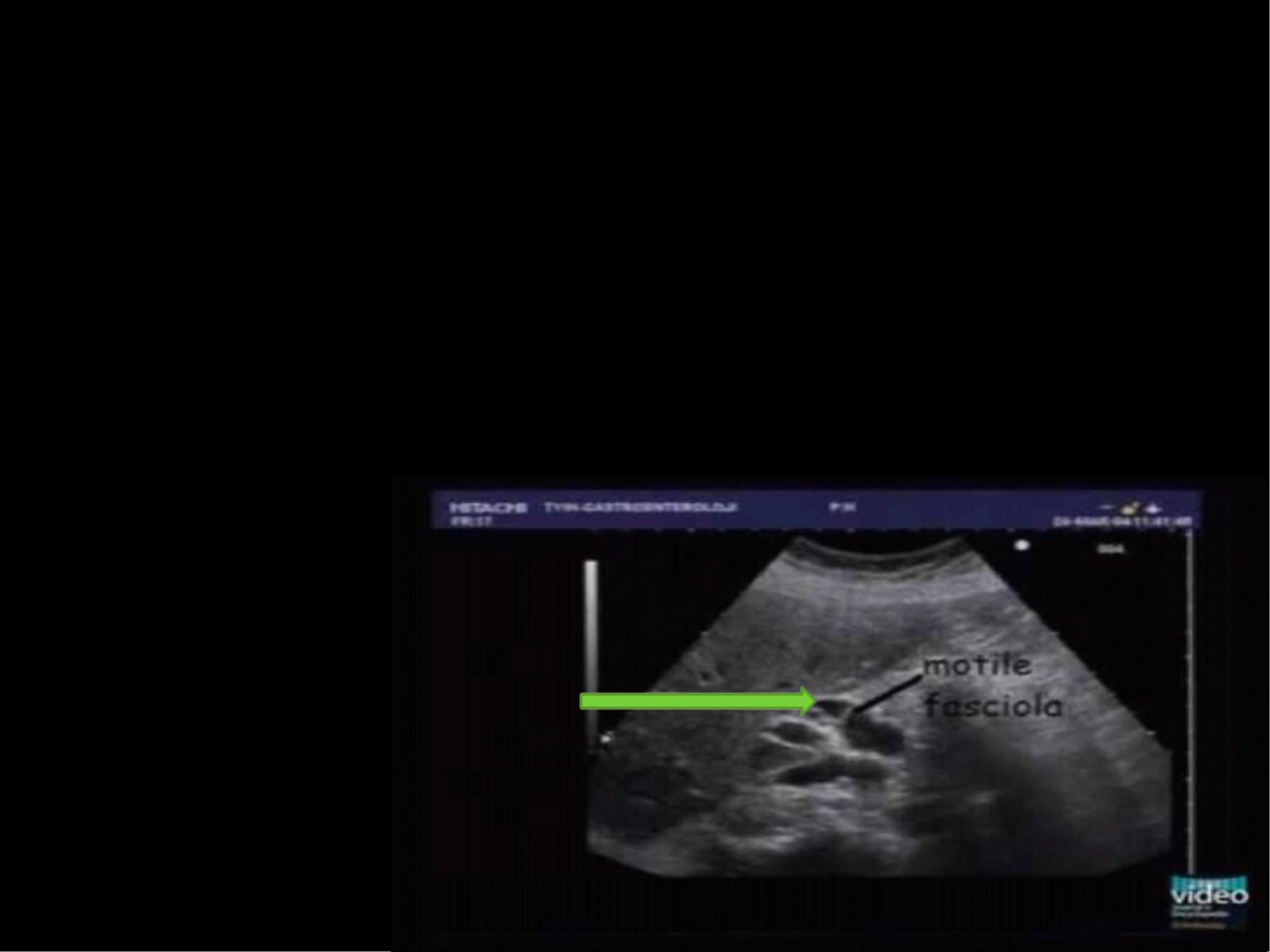
Di a gnos i s
•
General stool examination by finding the
eggs.
•
Radiological examination X –
Ray.
•
Ultrasound ,and CT scan .
•
ELISA.

Tre a t m e n t
Triclabe ndazole , abe n zim idazole is
t he first lin e t re at m e nt 10 m g / kg
B.W. as a single dose . For m ore
se ve re dise ase , an addit ion al dose
can be t ake n 12 hou rs lat e r.

P re ve nt ion and P rophylaxis
-
Early de t e ct ion of t he in fe ct ion.
-
P u blic he alt h m e asu re s and he alt h
care worke rs.
-
Im proving sanit at ion, de cre asin g
ou t door de fe cat ion .
-
Im prove m e nt of inspe ct ion an d
t ran sport of ve ge t at ion.

-She dding of viable e ggs.
-Cont rol snail popu lat ions.
-Rou t in e t re at m e n t of live st ock .

Fasciola gigant ica
•
Another species of Fascioliasis prevalent
in Iraq .
•
Life cycle and hosts similar to that of F.
hepatica.

