
Tissue specimens received in the
surgical pathology laboratory have a
request form that lists the patient
information and history along with a
description of the site of origin. The
specimens are accessioned by giving
them a number that will identify
each specimen for each patient.
Next
Specimen accessioning
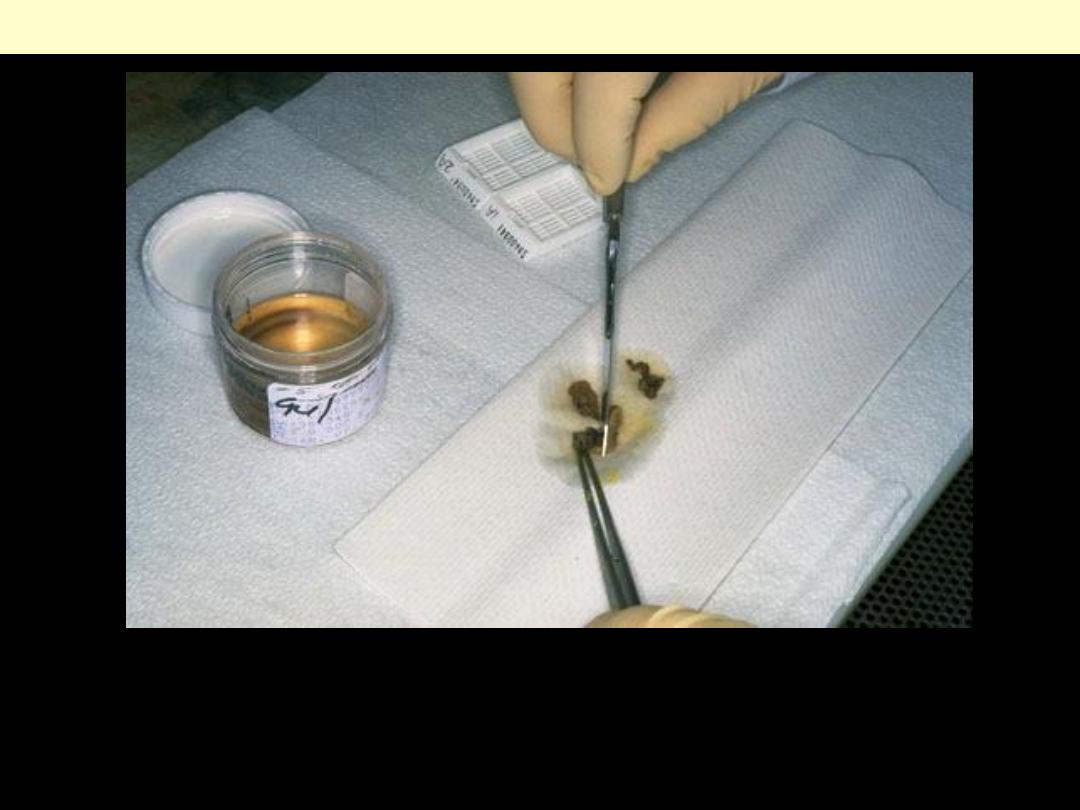
Tissues removed from the body for diagnosis arrive in the Pathology Department and are examined by
a pathologist, pathology assistant, or pathology resident. Gross examination consists of describing the
specimen and placing all or parts of it into a small plastic cassette which holds the tissue while it is
being processed to a paraffin block. Initially, the cassettes are placed into a fixative.
Next
Gross examination
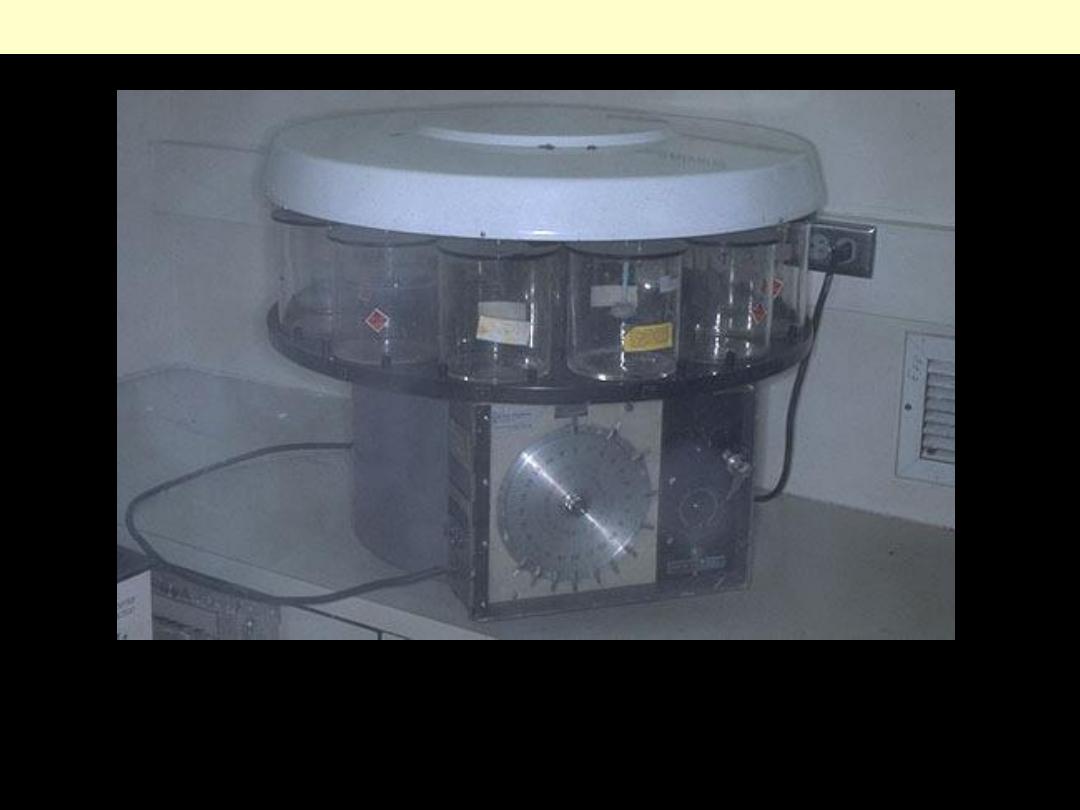

Once the tissue has been fixed, it must be processed into a form in which it can be made into thin
microscopic sections. The usual way this is done is with paraffin. Tissues embedded in paraffin, which
is similar in density to tissue, can be sectioned at anywhere from 3 to 10 microns, usually 6-8 routinely.
The technique of getting fixed tissue into paraffin is called tissue processing.
Next
Tissue processing
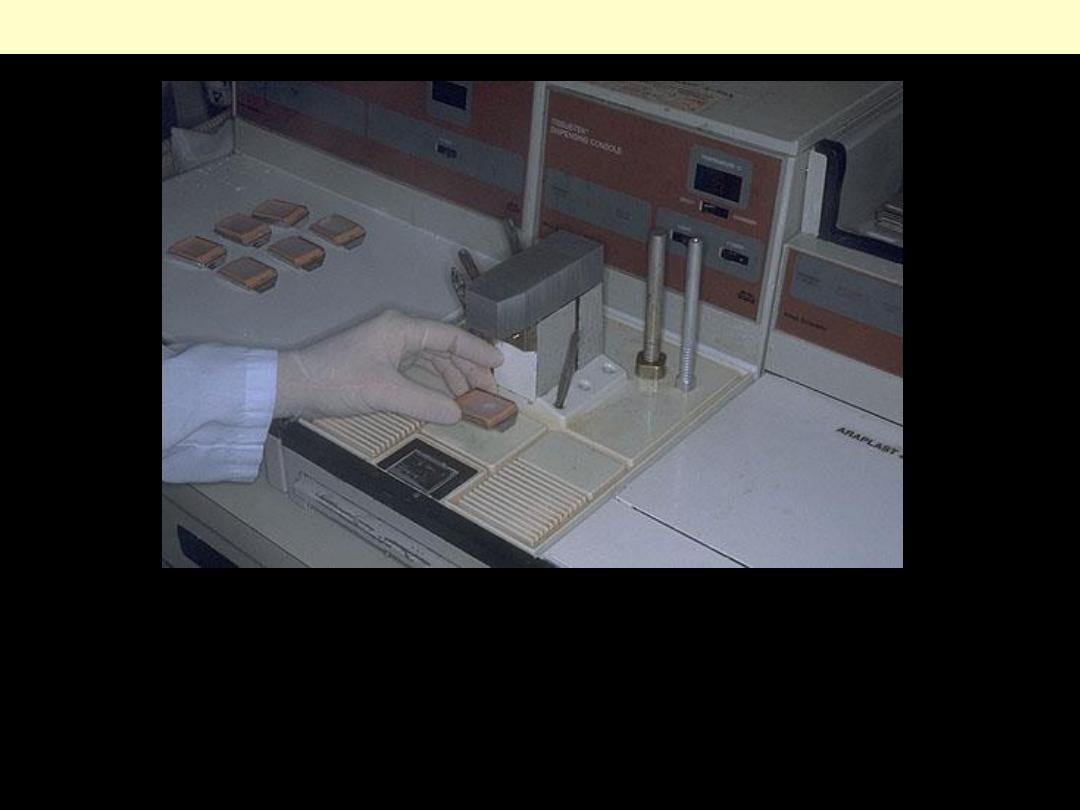
Tissues that come off the tissue processor are still in the cassettes and must be manually put into the
blocks by a technician who must pick the tissues out of the cassette and pour molten paraffin over
them. This "embedding" process is very important, because the tissues must be aligned, or oriented,
properly in the block of paraffin.
Next
Tissue embedding

Once the tissues have been
embedded, they must be cut into
sections that can be placed on a
slide. This is done with a
microtome. The microtome is
nothing more than a knife with a
mechanism for advancing a
paraffin block standard distances
across it.
Next
Sectioning
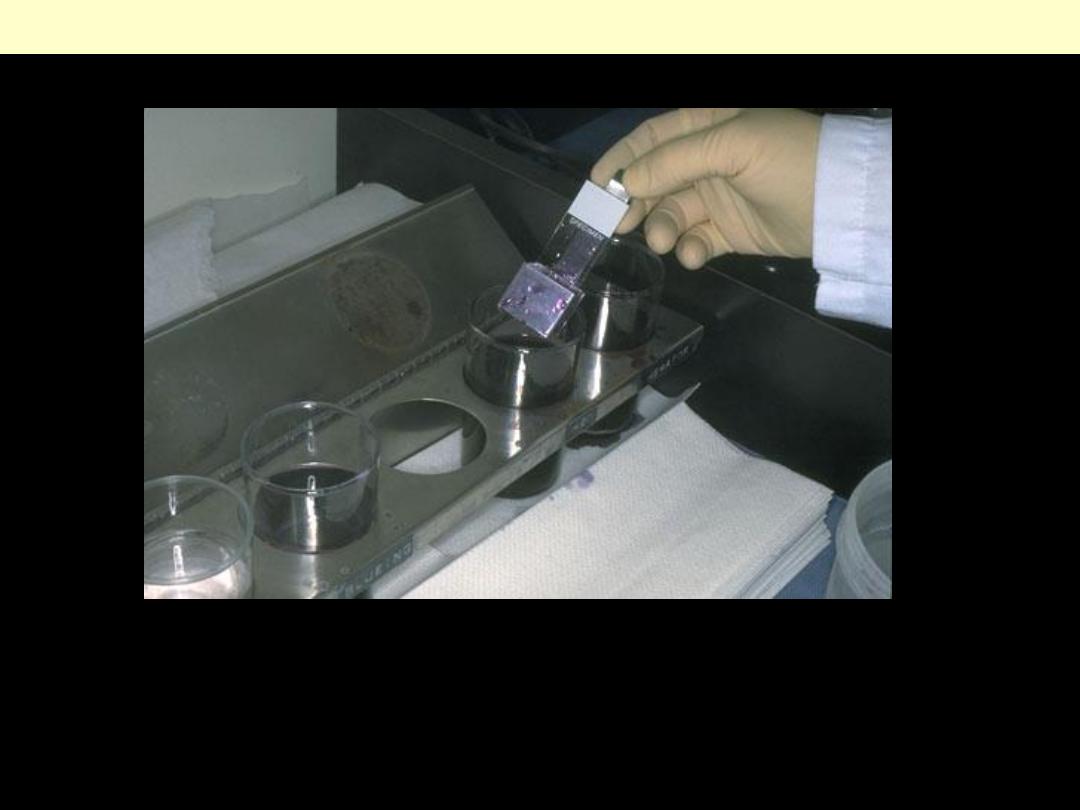
The staining process makes use of a variety of dyes that have been chosen for their ability to stain
various cellular components of tissue. The routine stain is that of hematoxylin and eosion (H and E).
Other stains are referred to as "special stains" because they are employed in specific situations
according to the diagnostic need.
Next
Staining
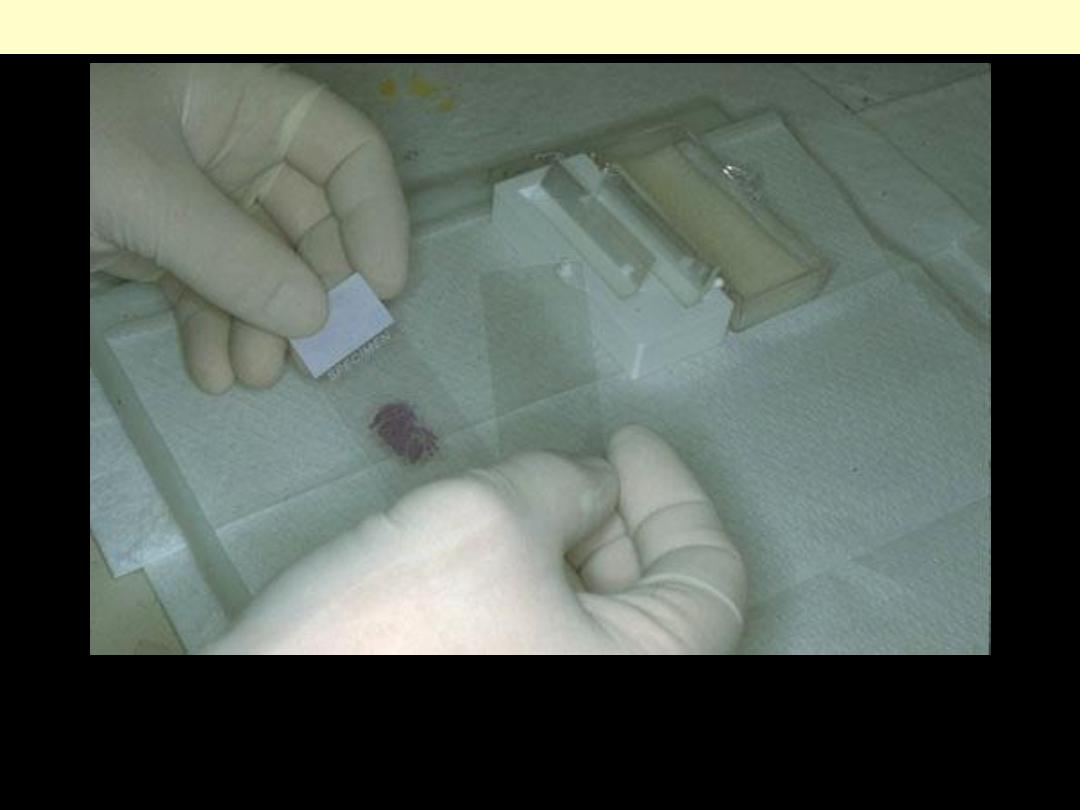
The stained section on the slide must be covered with a thin piece plastic or glass to protect the tissue
from being scratched, to provide better optical quality for viewing under the microscope, and to
preserve the tissue section for years to come.
Coverslipping
