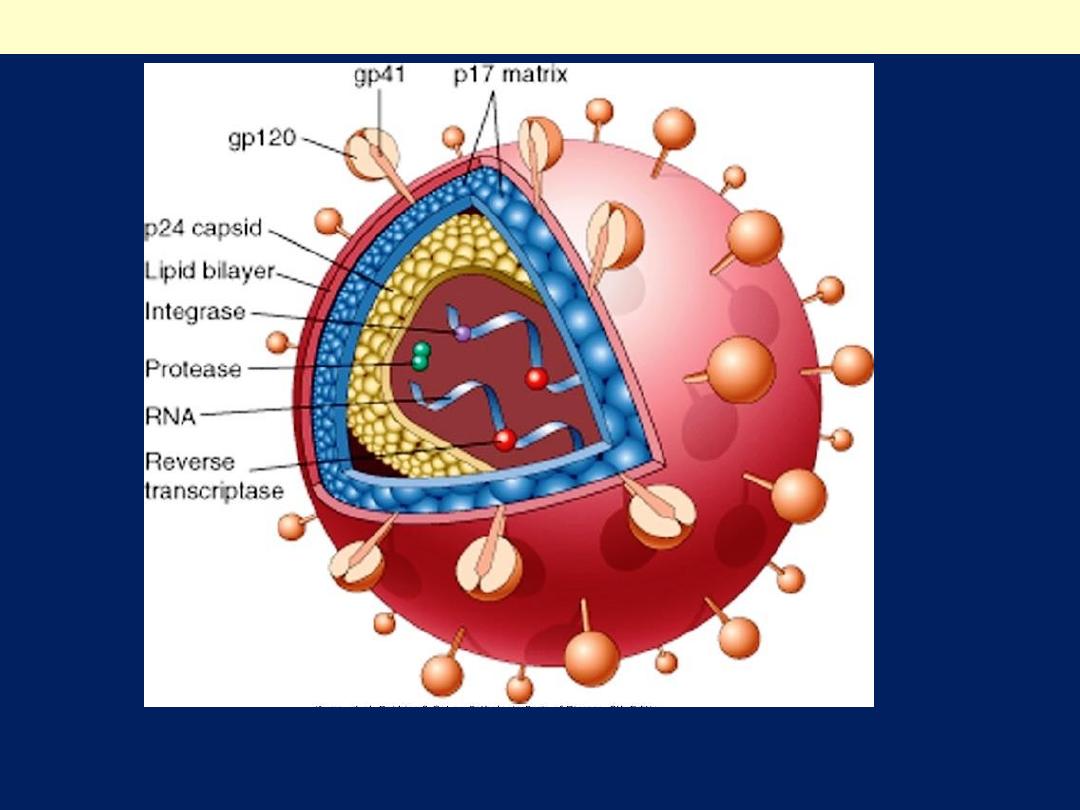
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-1
The viral particle is covered by a lipid bilayer derived from the host cell and
studded with viral glycoproteins gp41 and gp 120
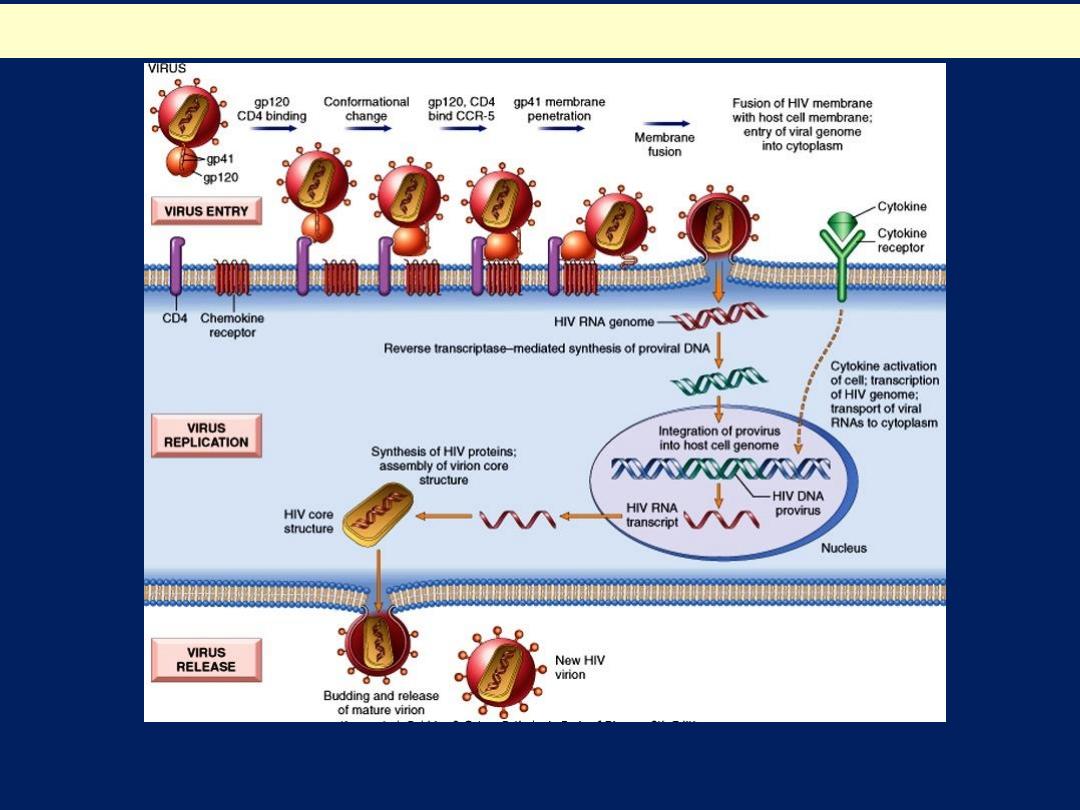
Life Cycle and Pathogenesis of HIV-1 infection
The life cycle of HIV consists of infection of cells, integration of the provirus into the host
cell genome, activation of viral replication, and production and release of infectious virus
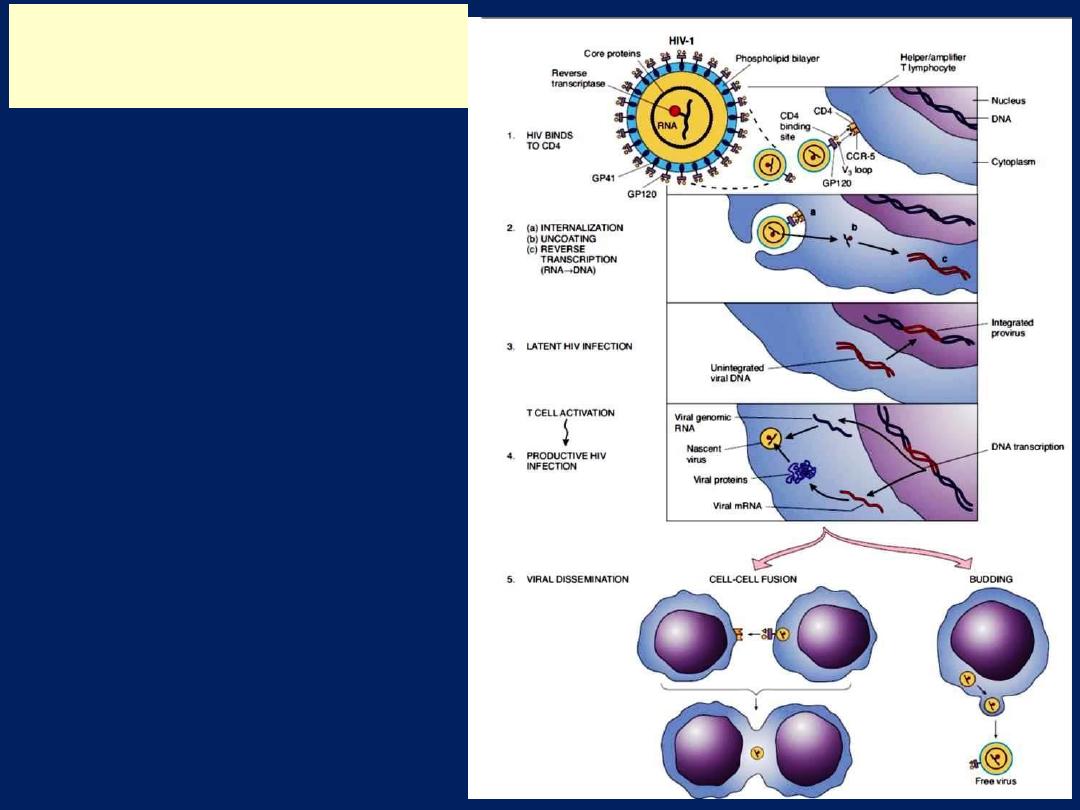
The life cycle of HIV
consists of infection of
cells, integration of the
provirus into the host
cell genome, activation
of viral replication, and
production and release
of infectious virus
Life Cycle and Pathogenesis
of HIV-1 infection
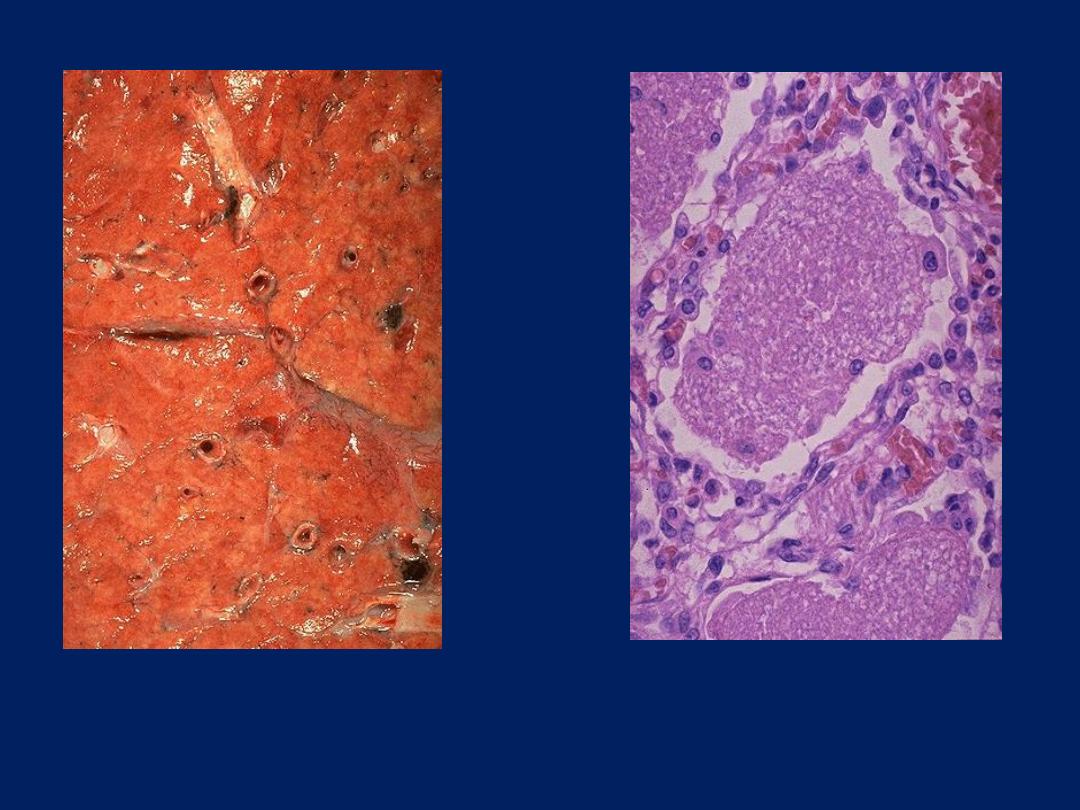
The appearance of Pneumocystis
carinii grossly in lung is shown here.
Note that this is an extensive
pneumonia.
At low magnification, note the
appearance of Pneumocystis carinii
in lung with exudate in nearly every
alveolus.
AIDS: Opportunistic infections
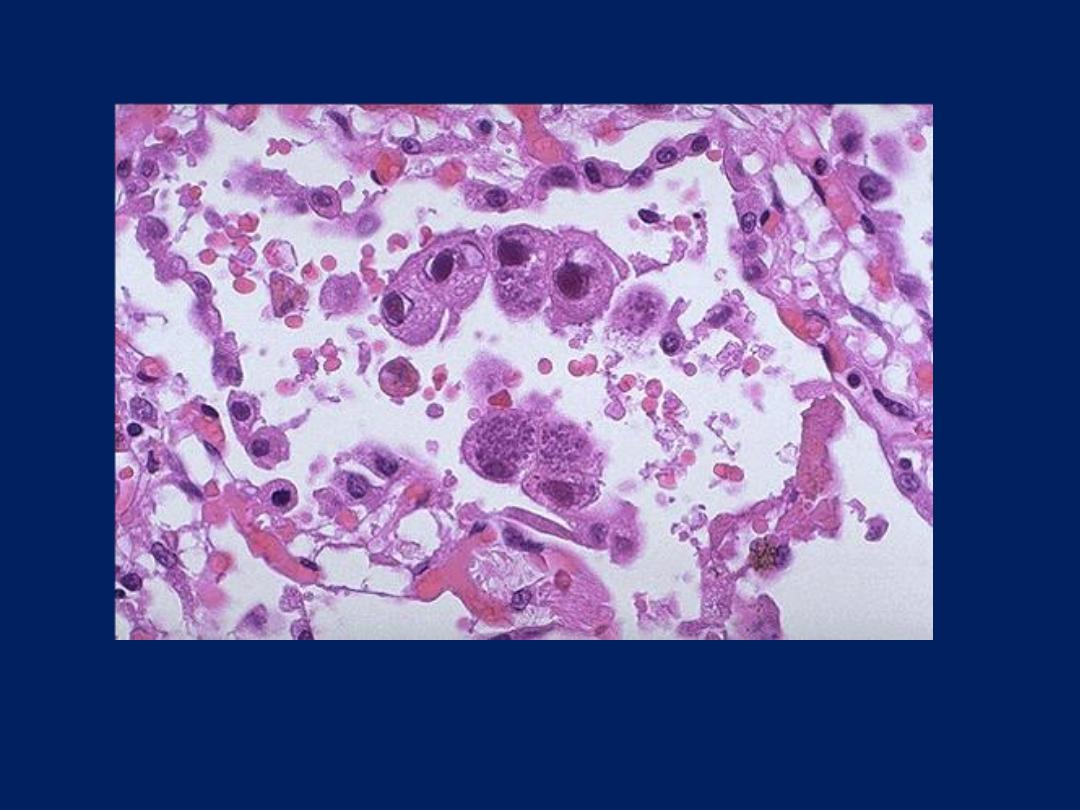
CMV can often produce a pneumonia. Here are CMV inclusions
in lung.
AIDS: Opportunistic infections
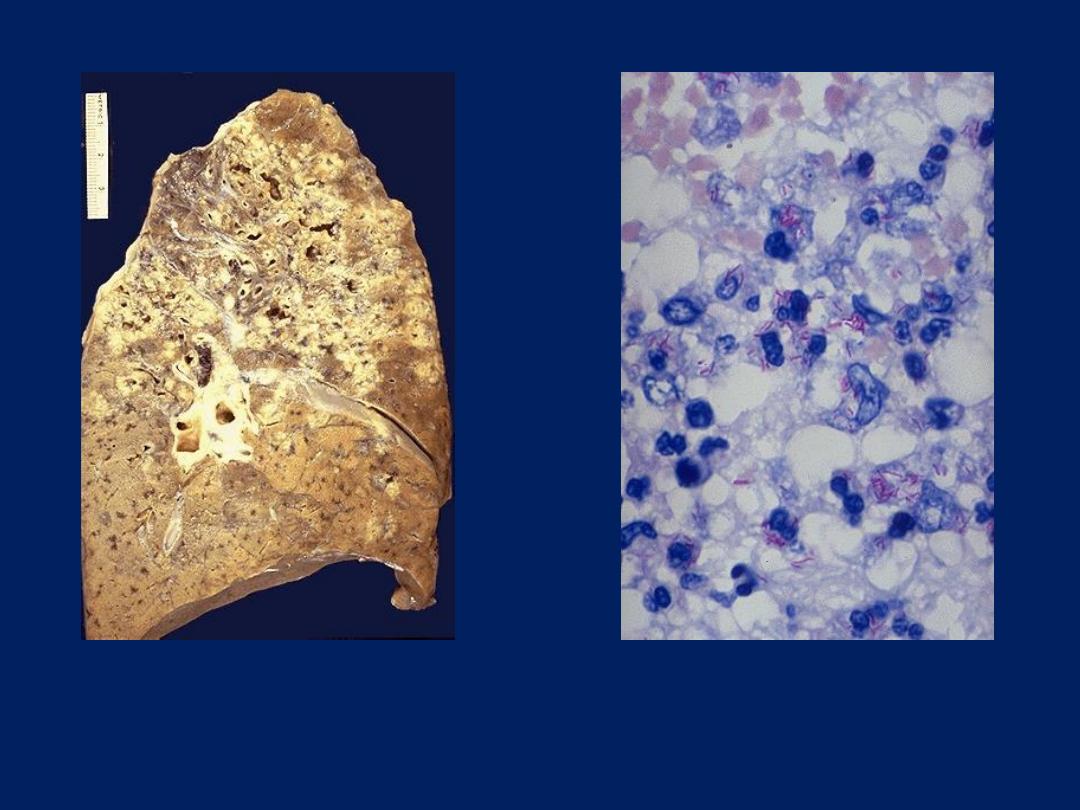
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection of lung is shown here with
numerous red rods seen with acid
fast staining.
Mycobacterium tuberculosis
infection of lung, with upper lung
field granulomatous and cavitary
disease.
AIDS: Opportunistic infections
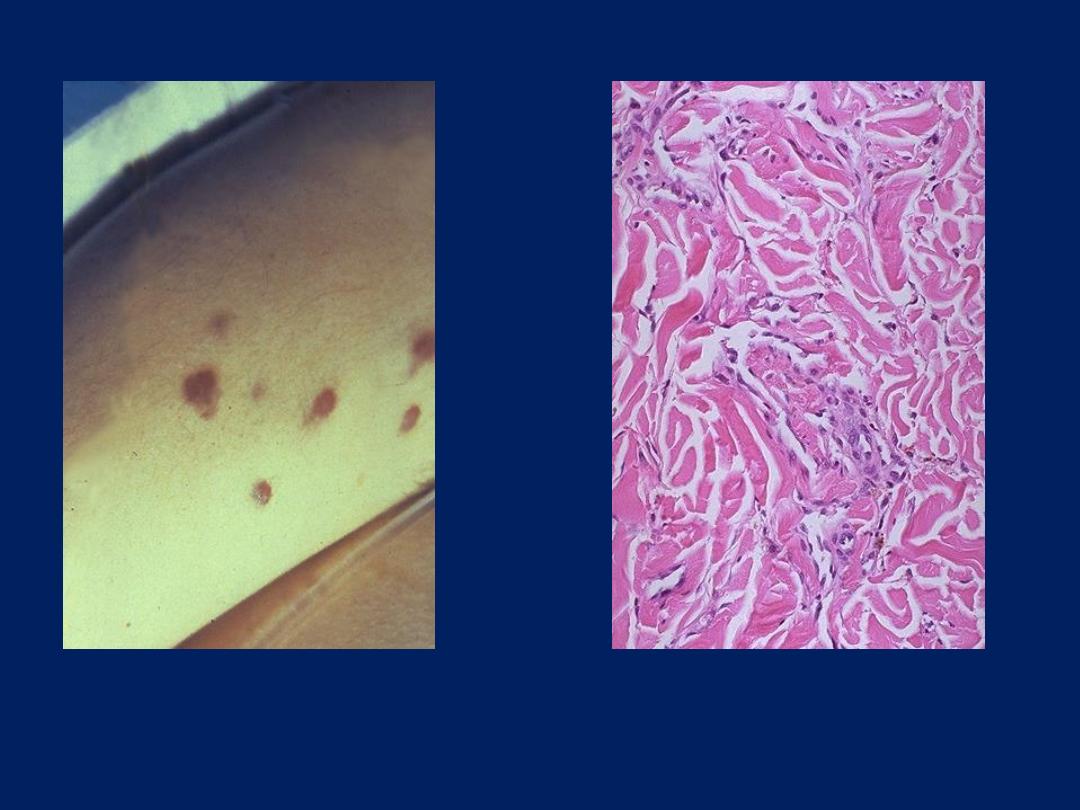
Kaposi's sarcoma microscopically
produces slit-like vascular spaces
in the dermis of the skin.
Kaposi's sarcoma typically
produces one or more reddish
purple nodules on the skin.
AIDS: Secondary Neoplasms
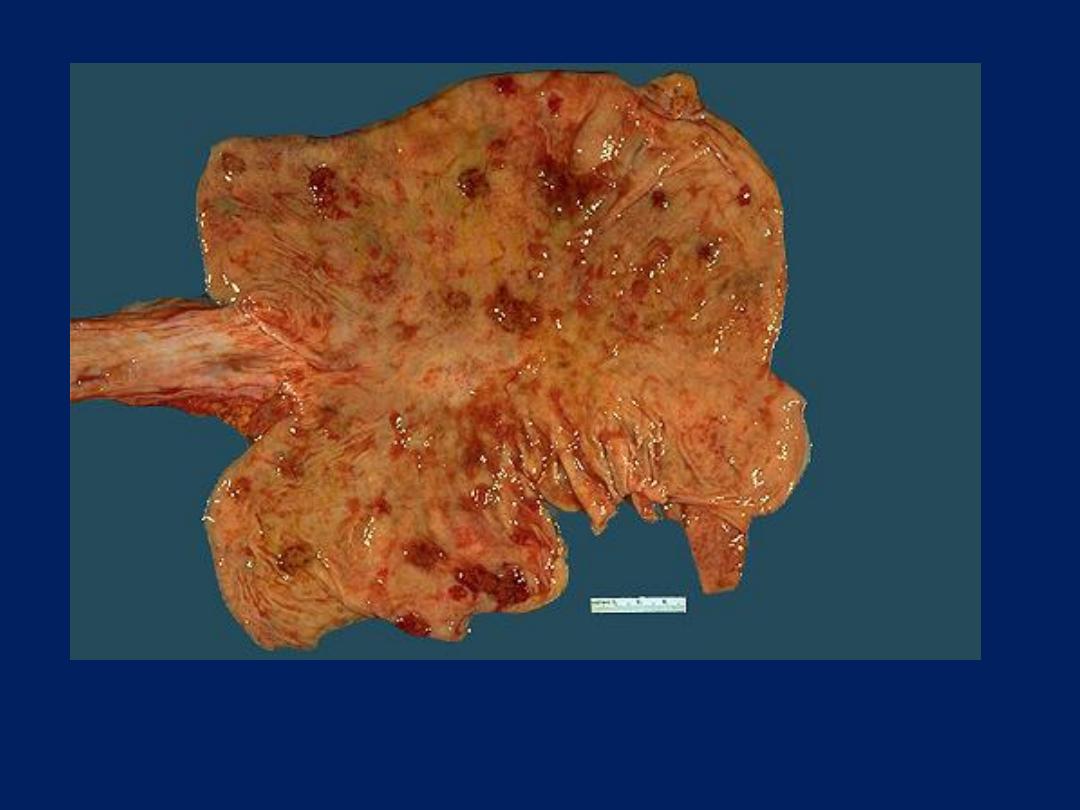
Visceral involvement with Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS is common.
Here are multiple reddish nodules seen over the gastric mucosa.
AIDS: Secondary Neoplasms
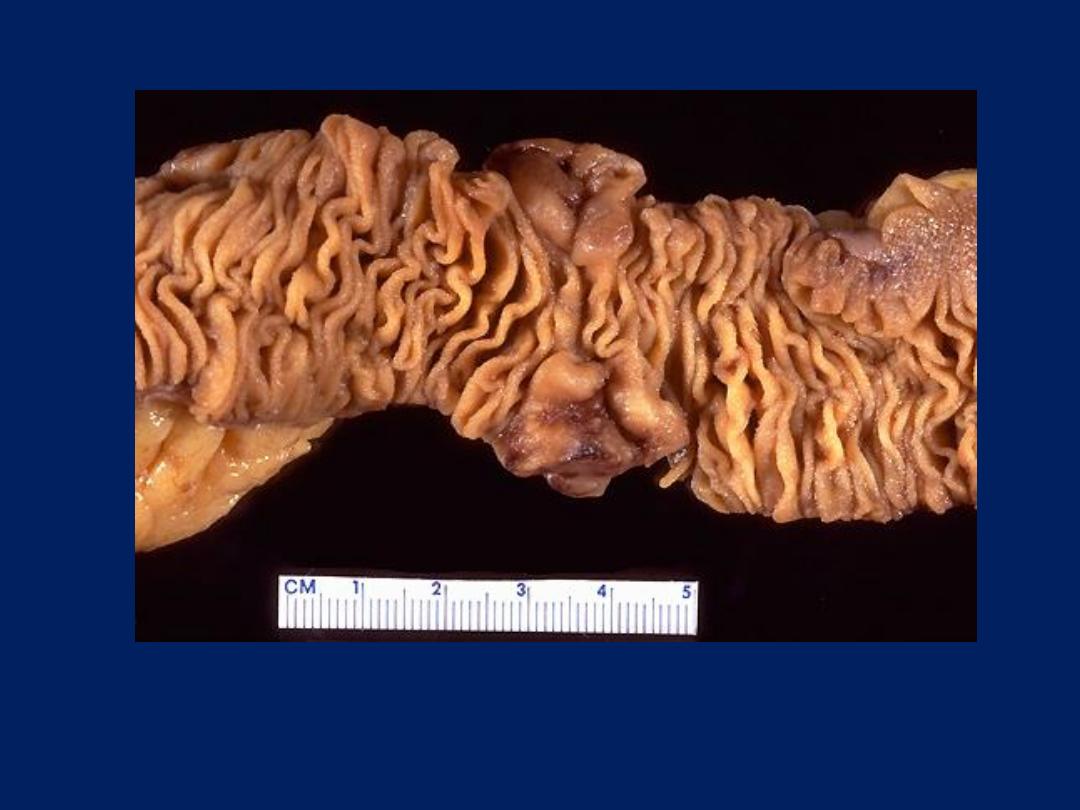
Malignant lymphoma is typically extranodal in AIDS. Seen here in
small intestine are two mass lesions on the mucosal surface.
AIDS: Secondary Neoplasms
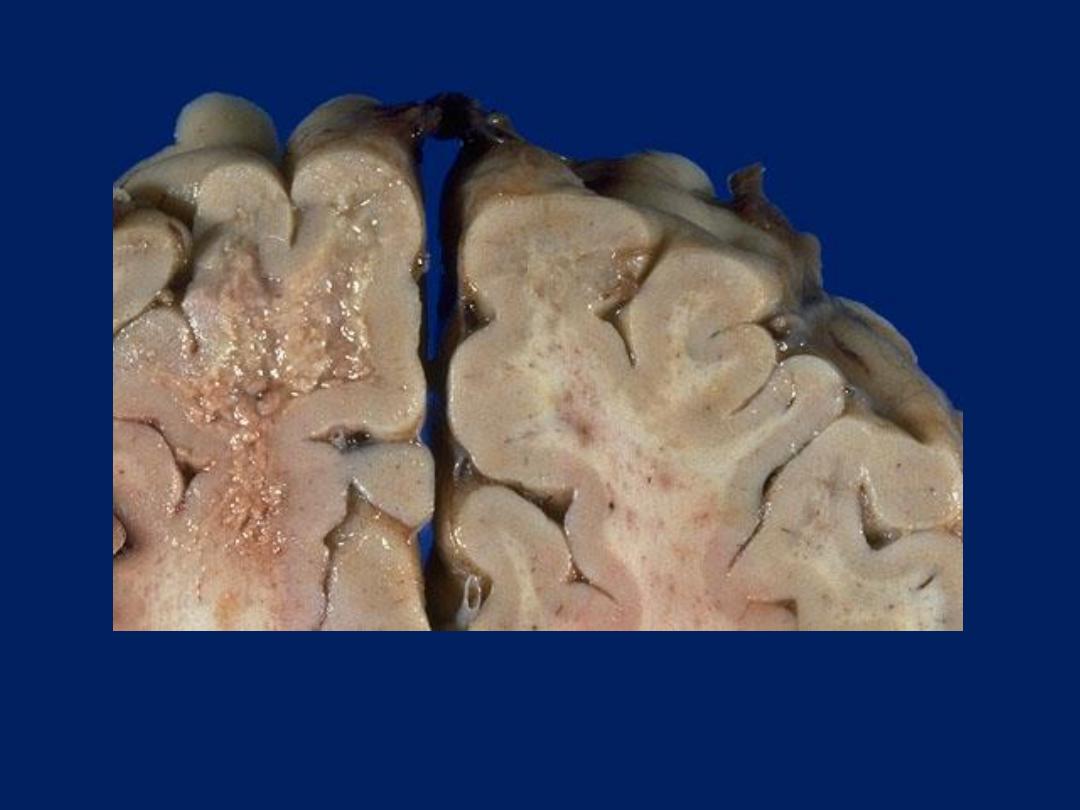
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) appears grossly as
irregular areas of granularity in white matter which bear some
resemblance to the plaques of demyelination with multiple sclerosis.
AIDS: CNS Involvement
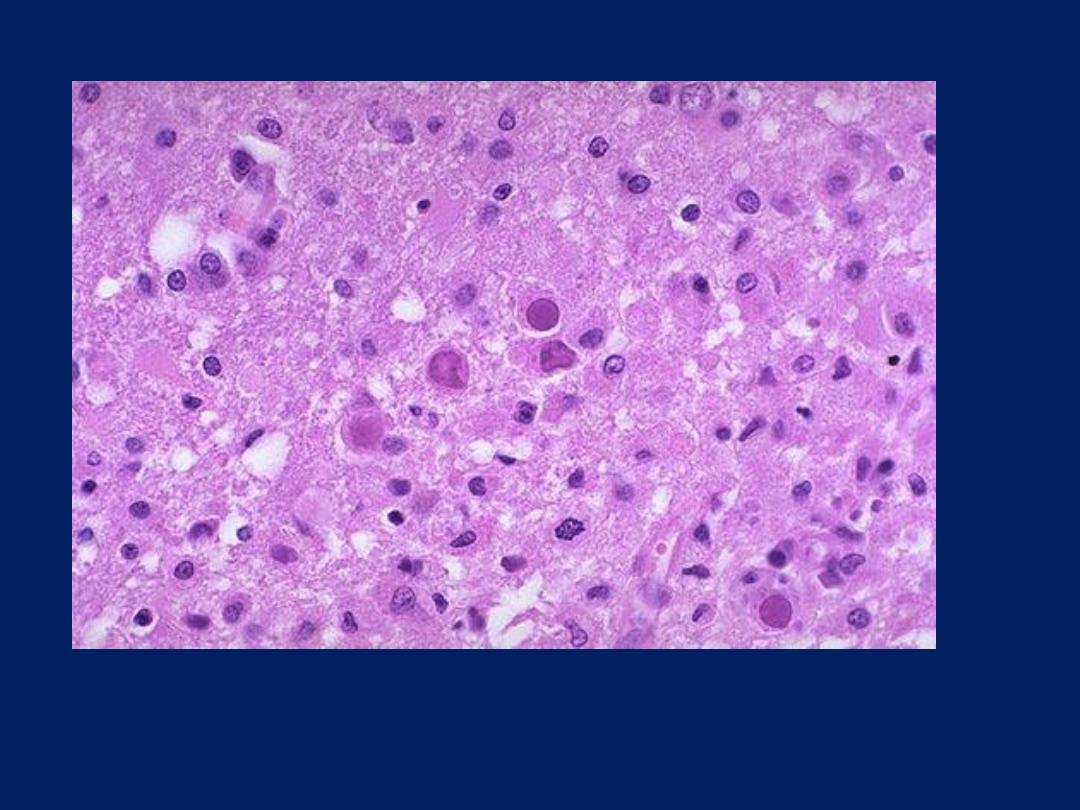
Microscopically: PML lesions appear with perivascular monocytes,
astrocytosis with bizarre or enlarged astrocytes and central lipid-laden
macrophages.
AIDS: CNS Involvement
