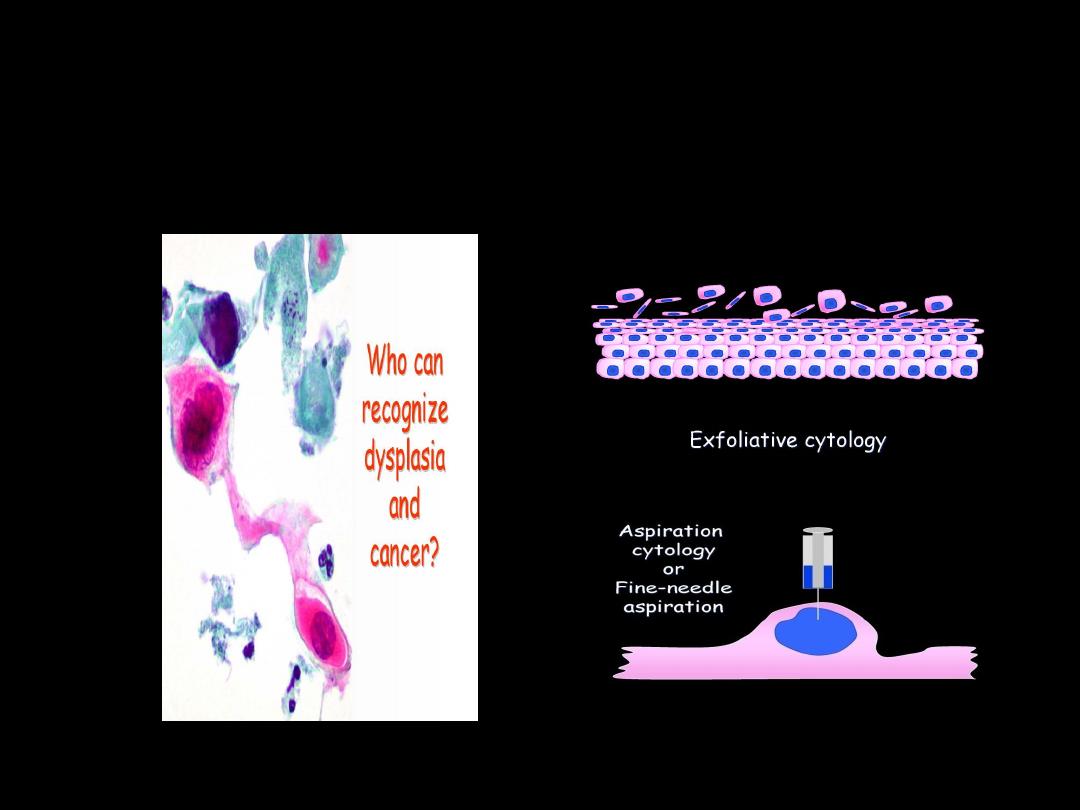
Cytopathology
Dr. Nada Al-ALwan
(Prof. of Pathology)
Prof. Nada Alwan
Prof. Nada Alwan

Prof. Nada Alwan
Prof. Nada Alwan

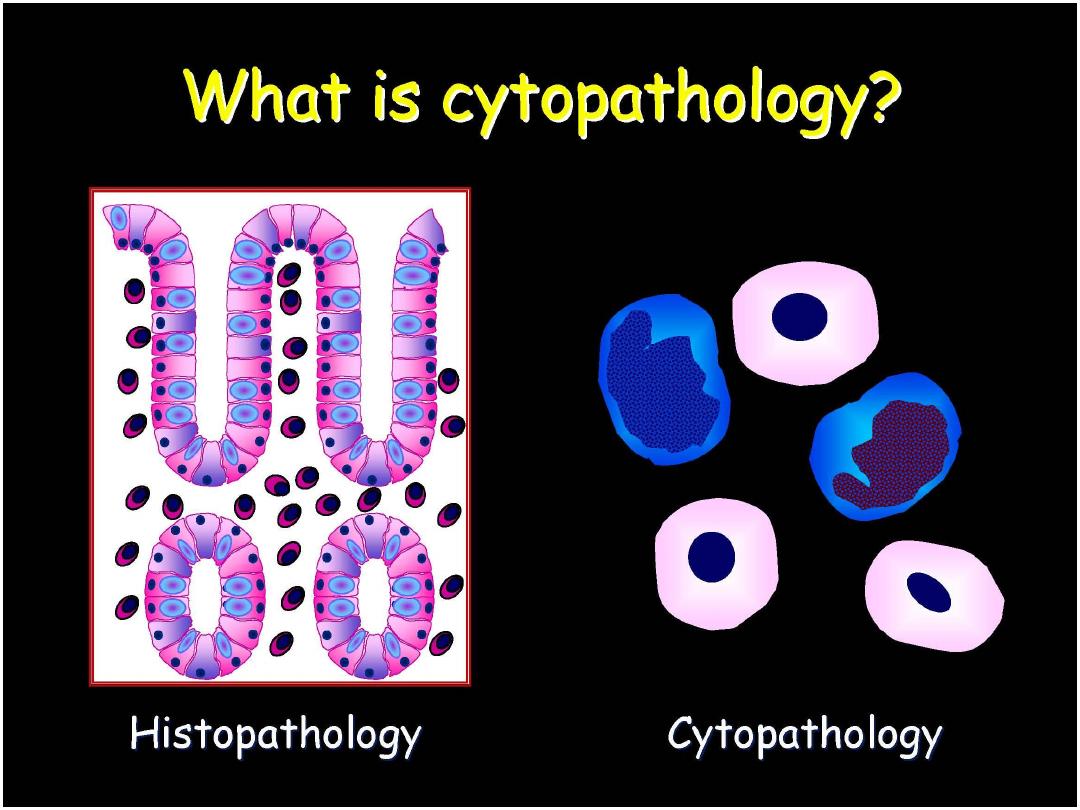
Histopathology Cytopathology
1. Deals with the form and the
structure of the tissue.
2. Evaluation with a tissue biopsy.
3. More invasive traumatic procedure
is needed; utilizing surgical
instrumentation such as foreceps,
scissors, etc..)
4. Needles if used should have a
large gauge (i.e., Tru-cut needles
measuring 14, 16 ) .
5. Diagnosis obtained after days.
6. Basic stain is H&E
7. Paraffin blocks are needed
8. Difficult to identify specific
causative inflammatory pathogen
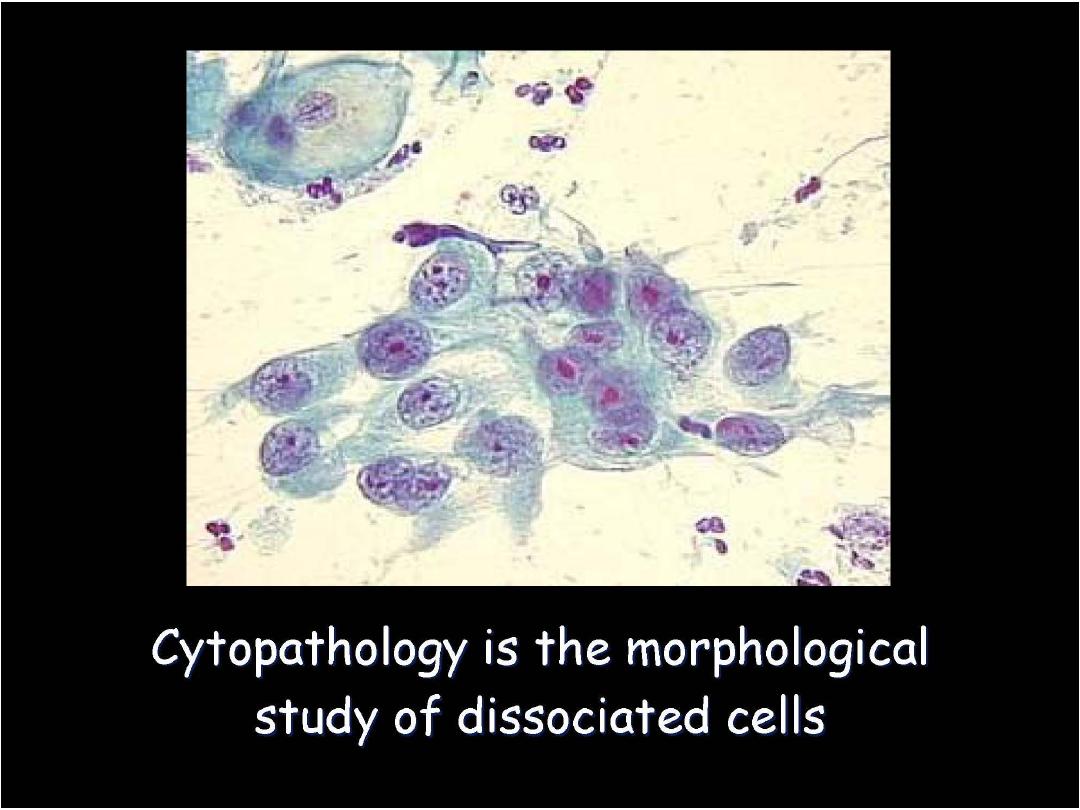
1. Deals with the structural changes
within the nucleus and cytoplasm
of individual cells
2. Evaluation requires cells only.
3. Inexpensive simple means of
diagnosis which allows frequent
repetition of cellular sampling
(since it causes no tissue injury).
4. Fine needles with 22, 23 or 24
gauge are usually preferred.
5. Rapid diagnosis that could be
obtained within minutes.
6. Basic stain is Pap stain (however
H&E could be used as well)
7. Mainly slides are needed
8. Smears permit better evaluation of
the nature of the inflammatory
process. Fungi and parasites are
usually easier to be diagnosed.
Prof. Nada Alwan
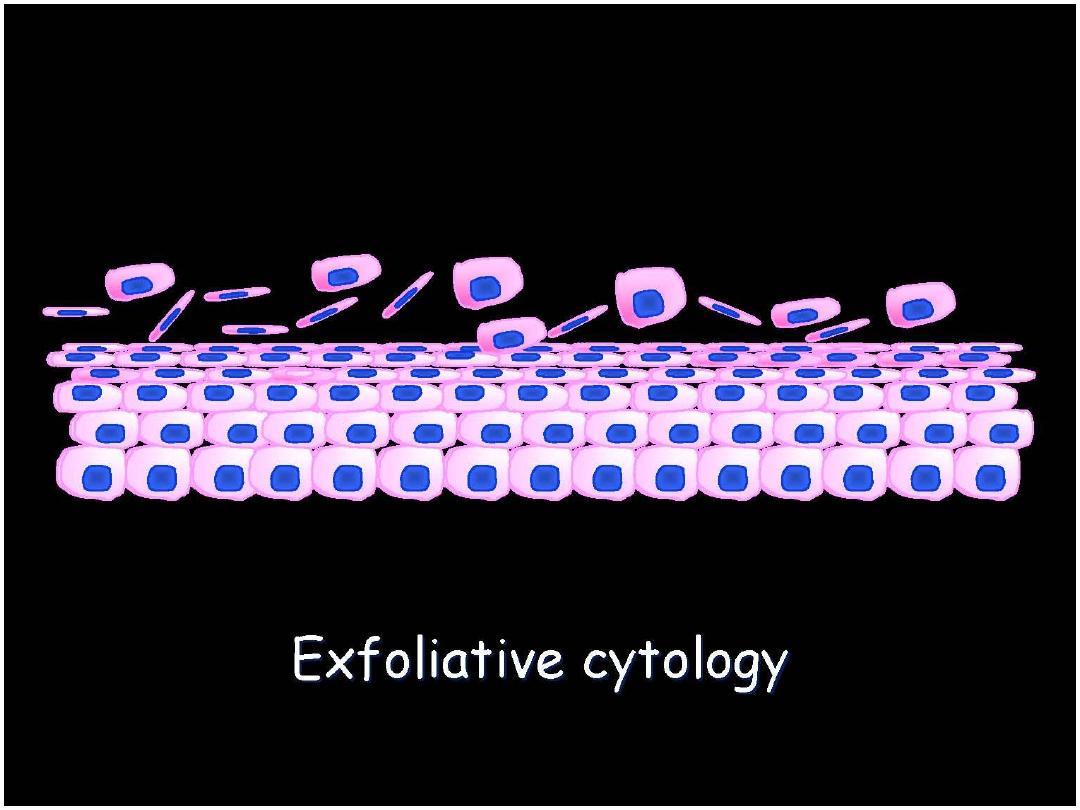
Prof. Nada Alwan

Prof. Nada Alwan
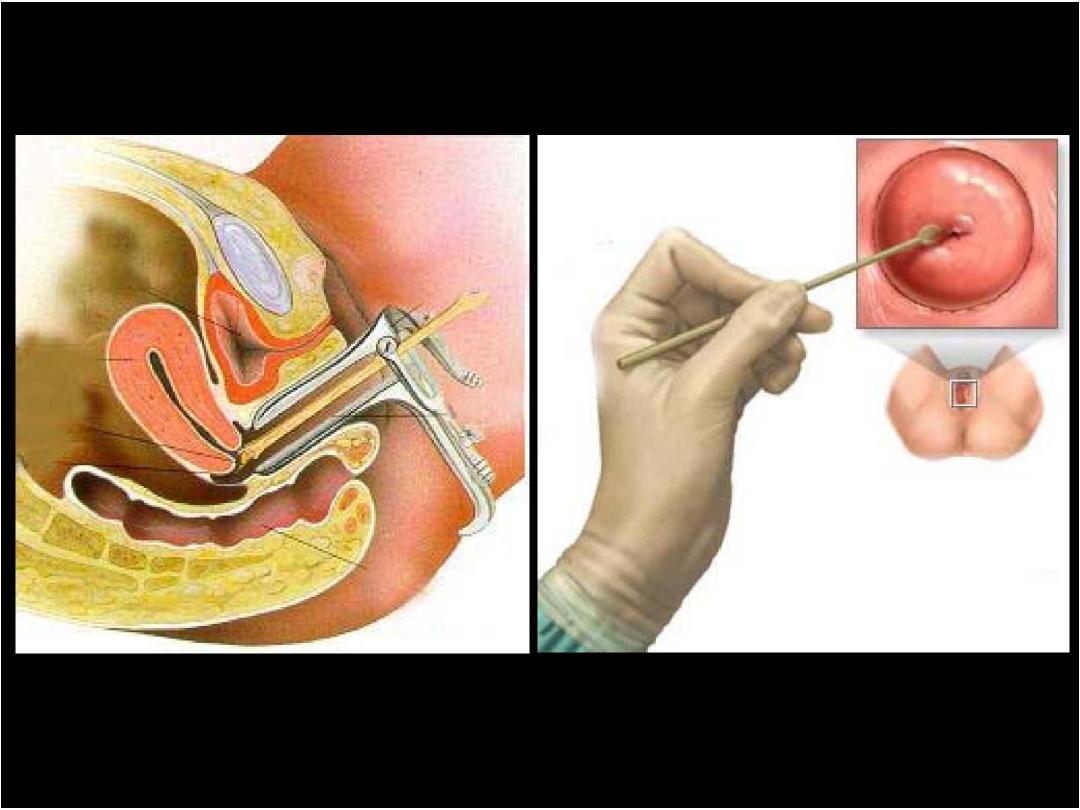
Prof. Nada Alwan
Pap Smear
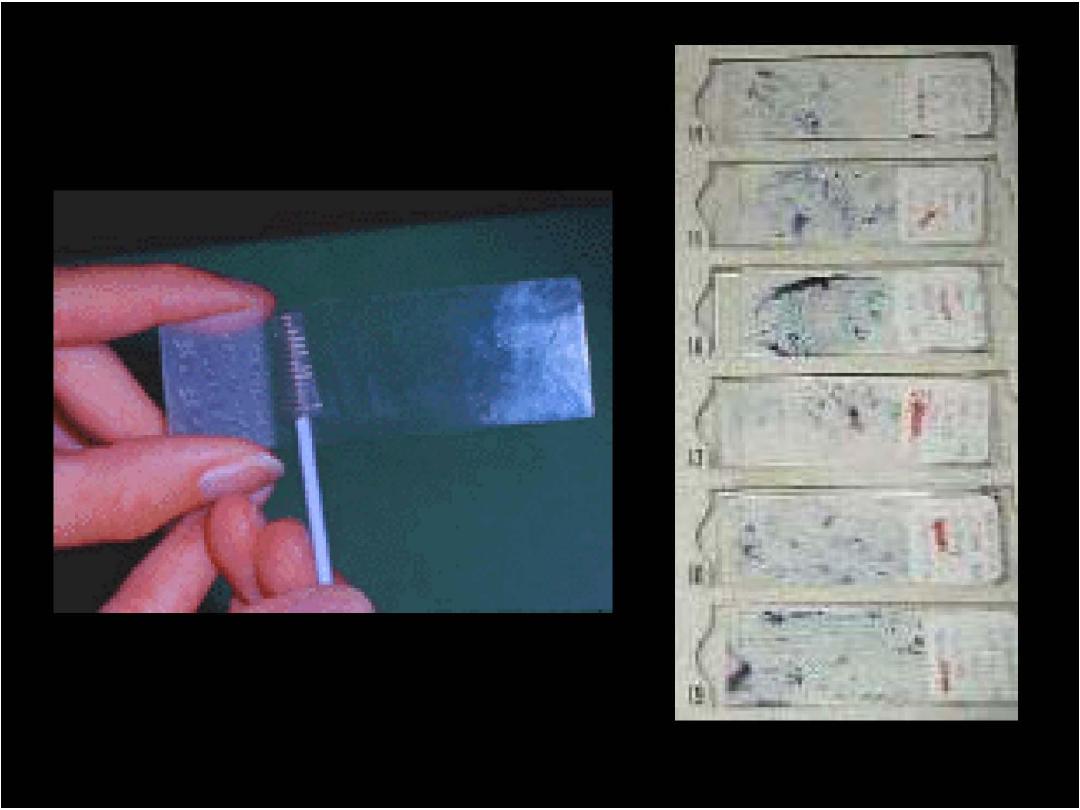
Prof. Nada Alwan
Prof. Nada Alwa
n
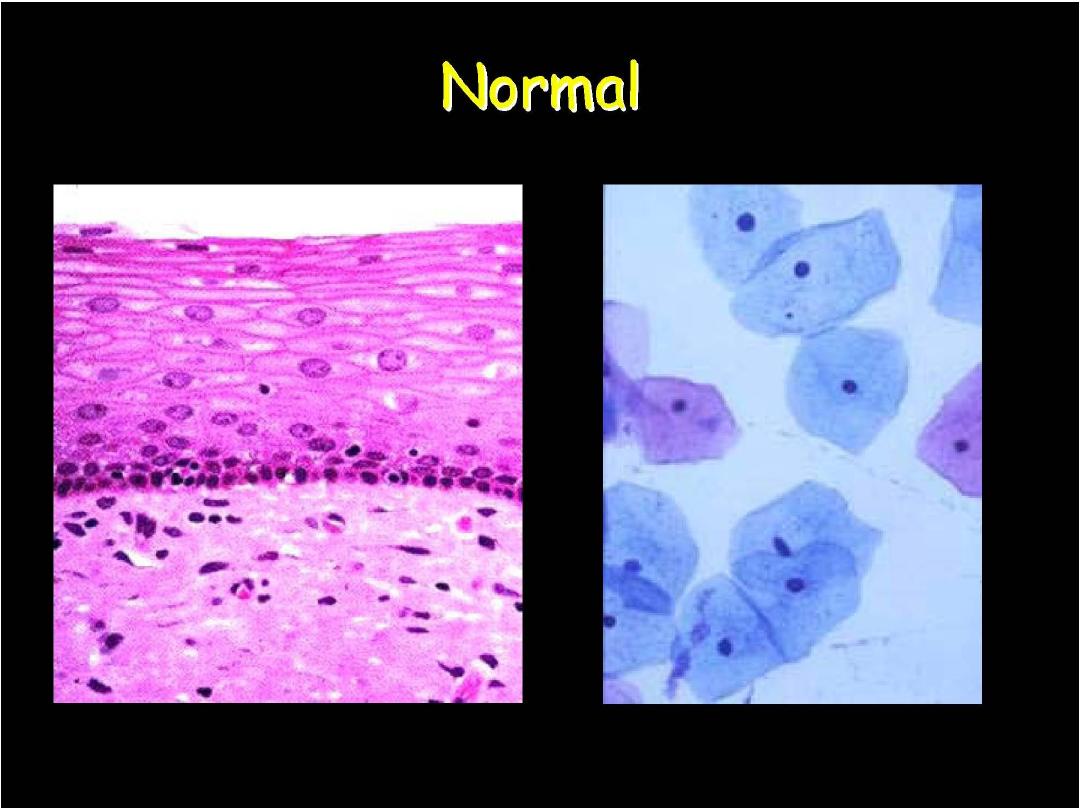
Cervix cytology-normal
superficial cells
parabasal cells
immature sq. cells
endocervical cells en face
endocervical cells-profile

Prof. Nada Alwan
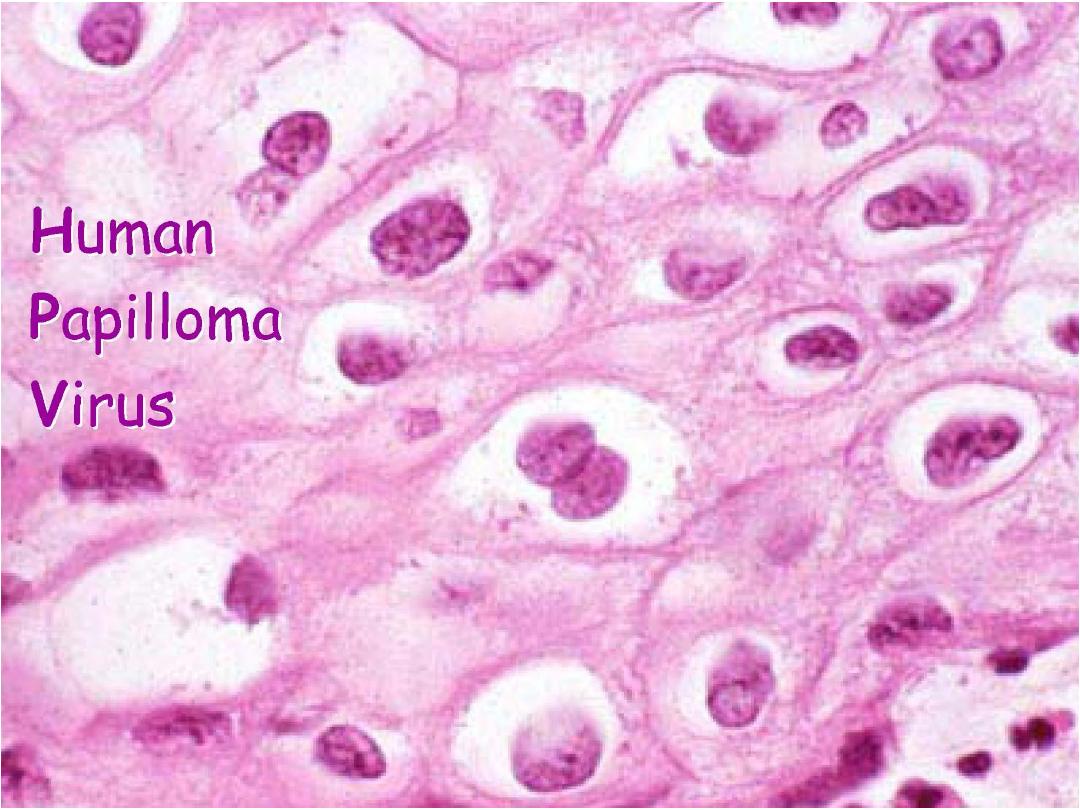
:Human Papilloma Virus

Prof. Nada Alwan
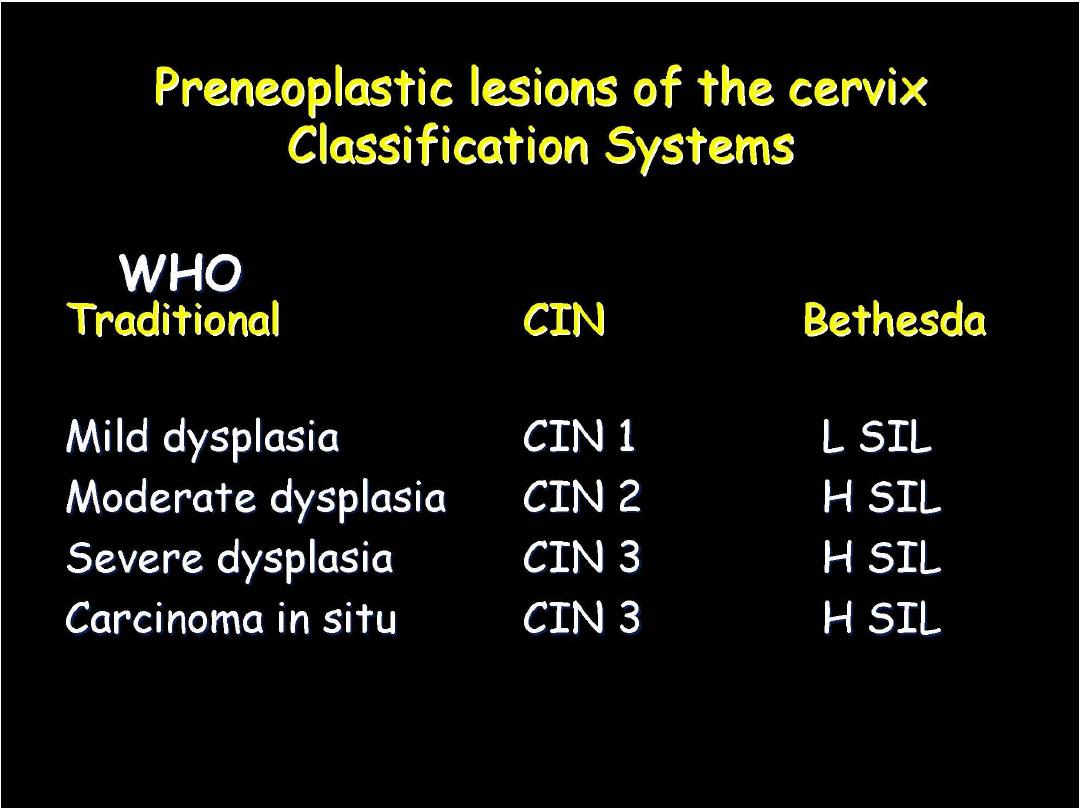
Prof. Nada Alwan
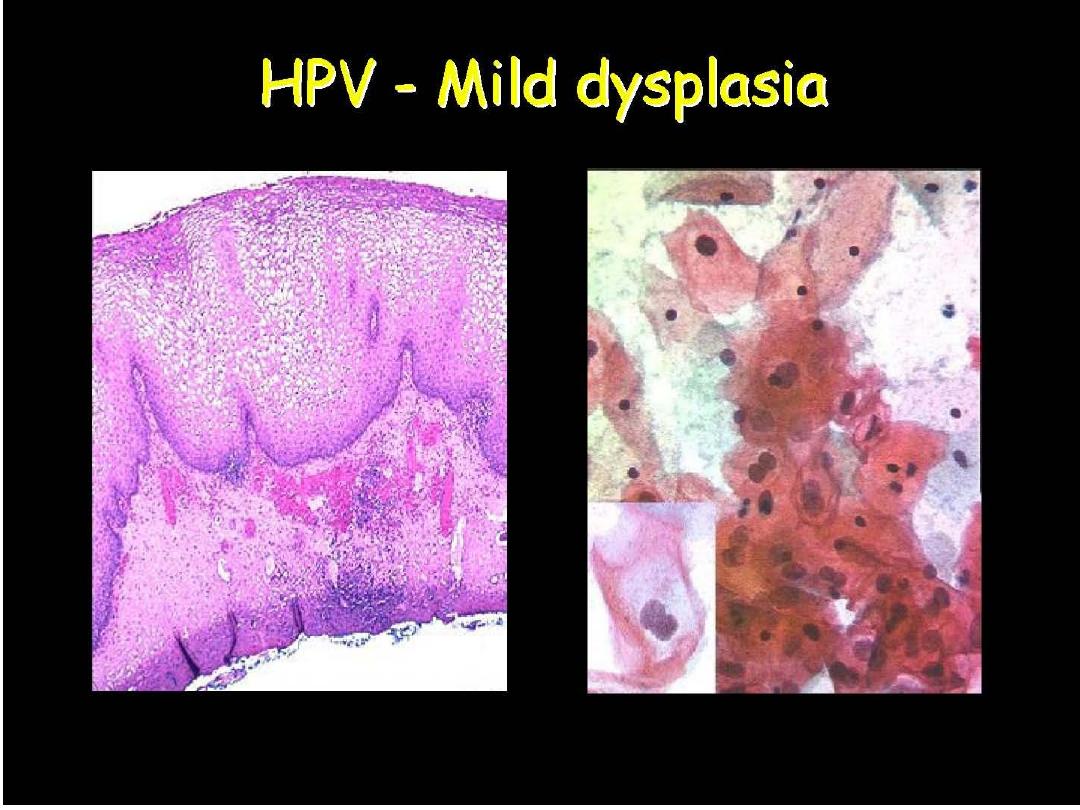
Prof. Nada Alwan
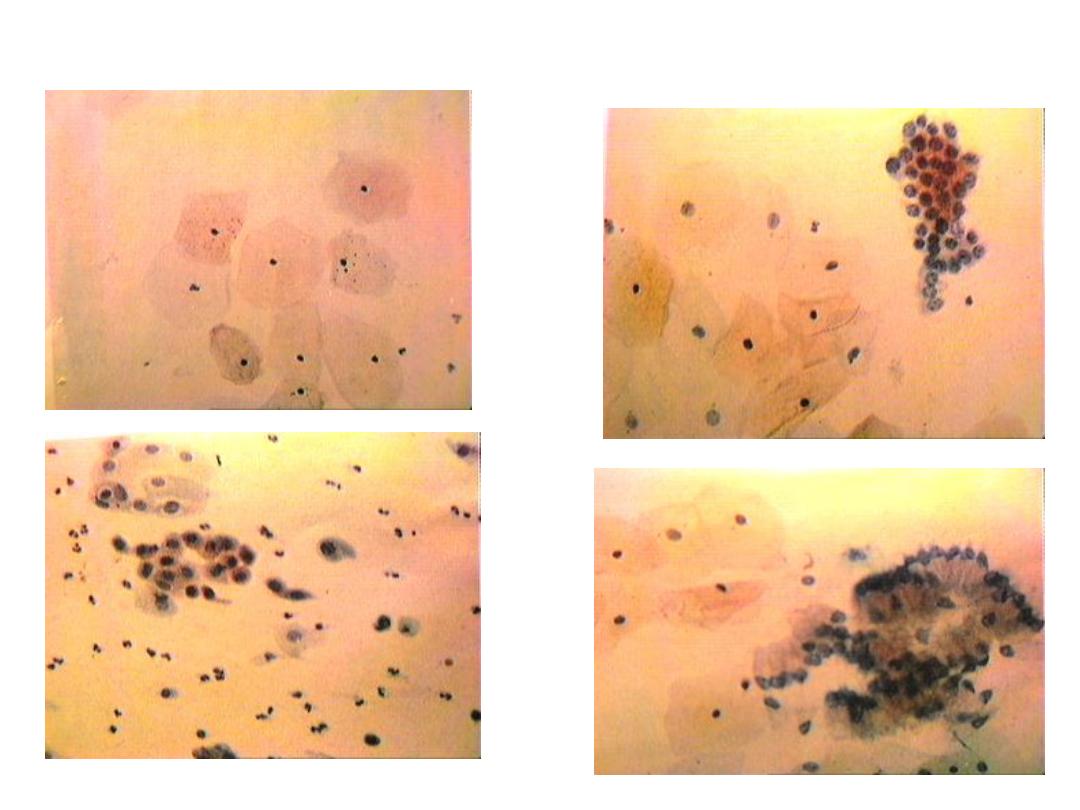
CIN I or LSIL
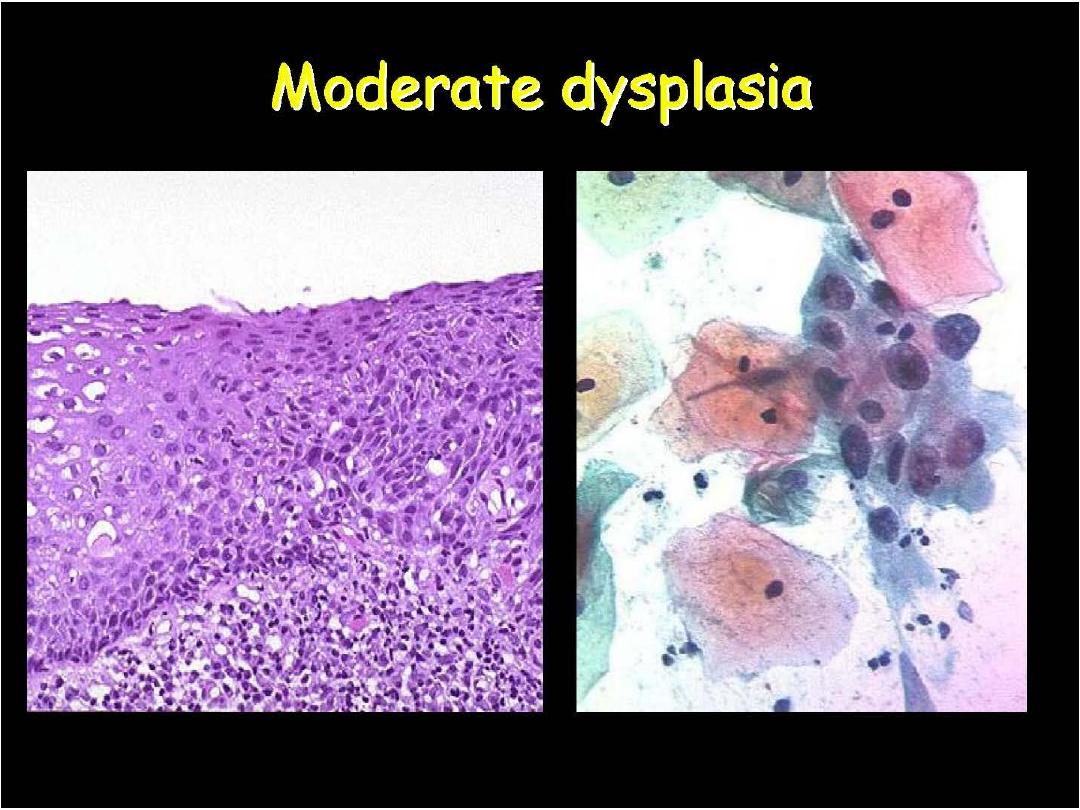
Prof. Nada Alwan
CIN II or HSIL
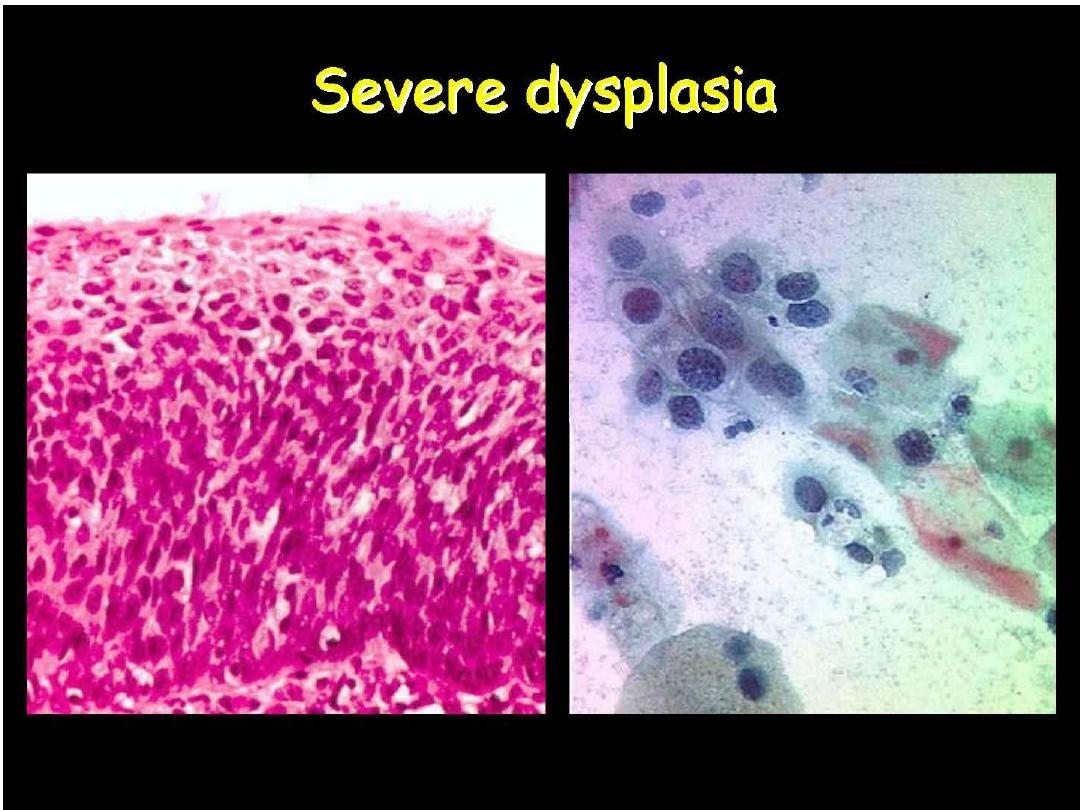
Prof. Nada Alwan
CIN III or HSIL
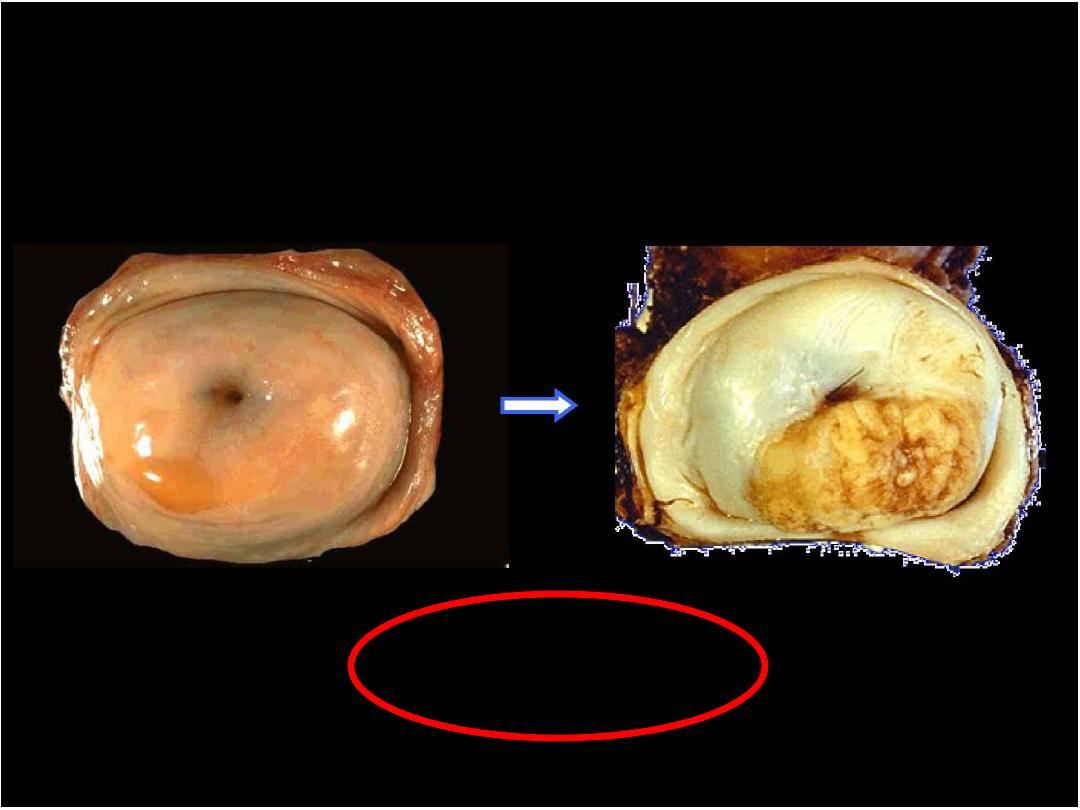
Prof. Nada Alwan
Human Papilloma Virus
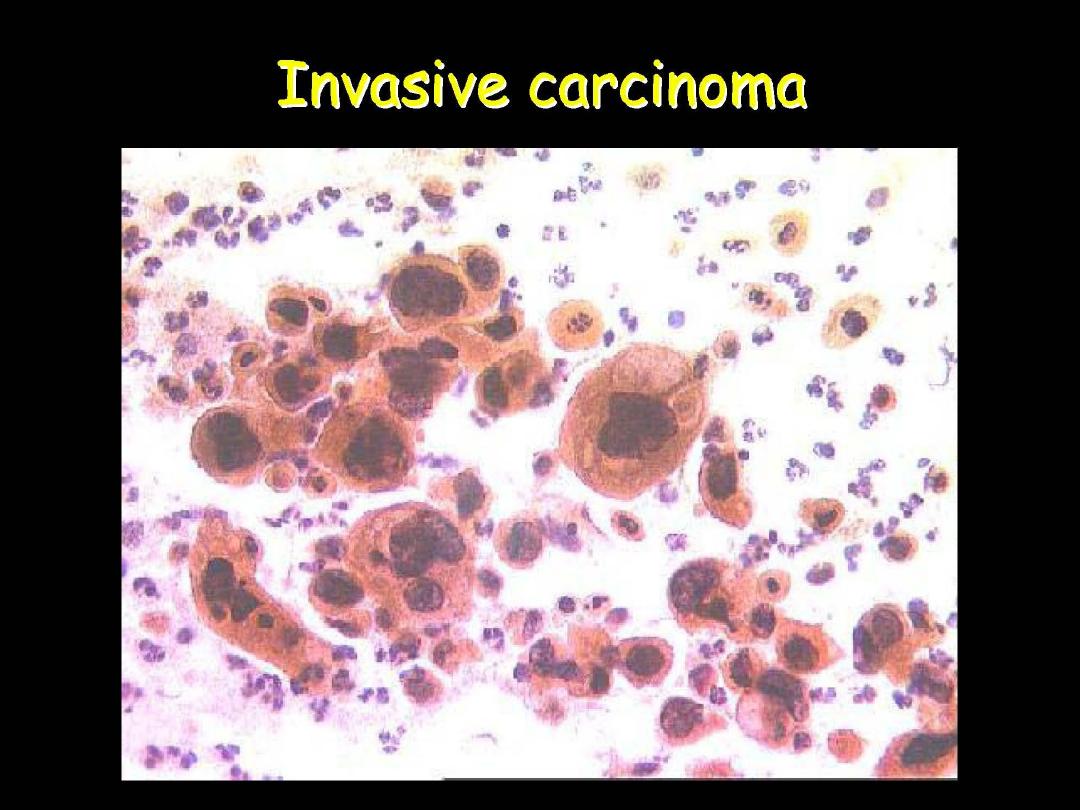
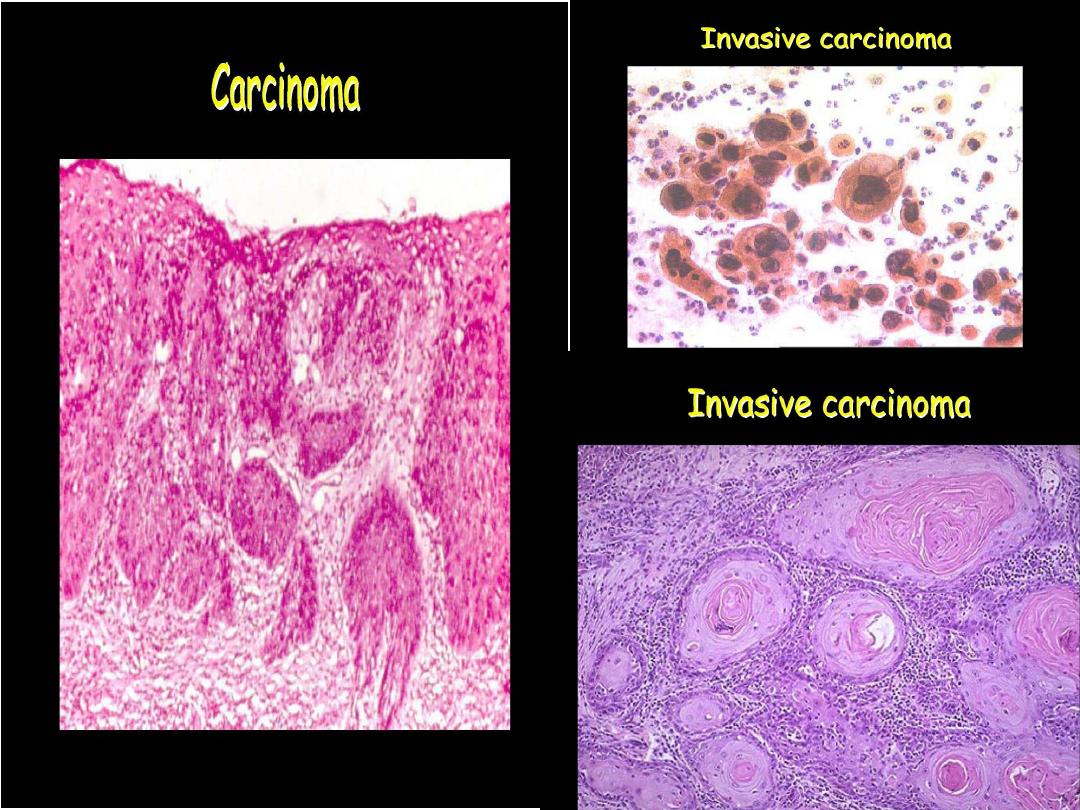
Prof. Nada Alwan
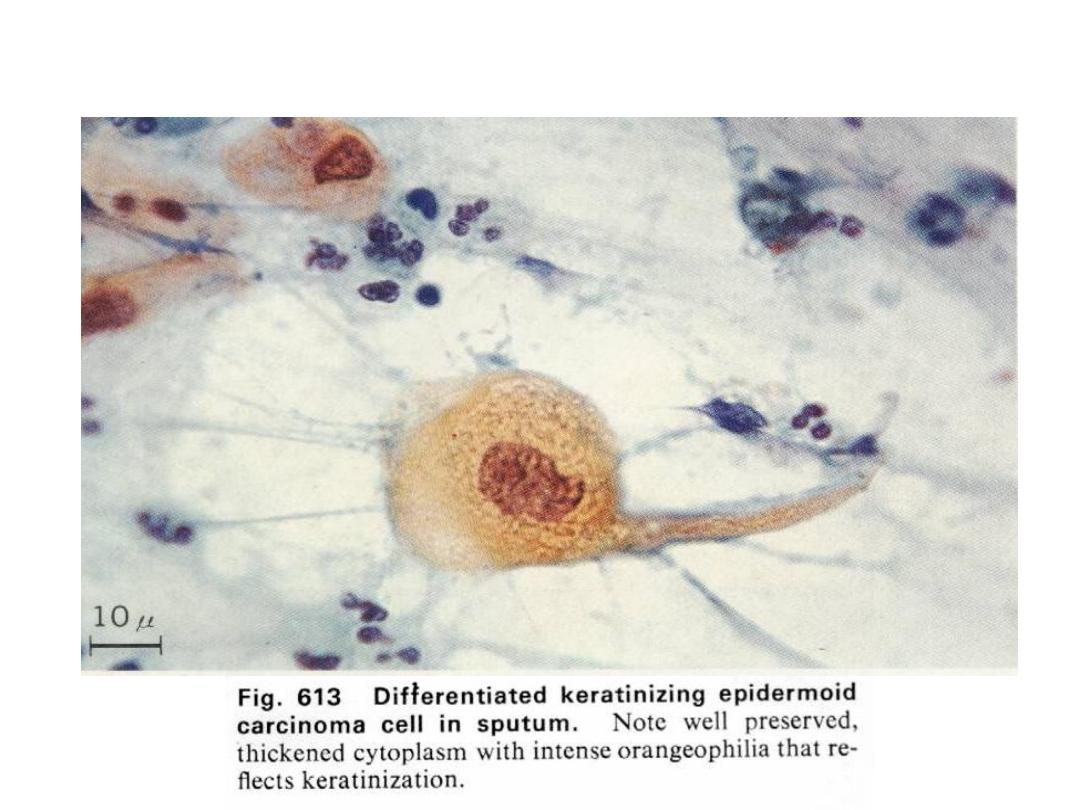
SPUTUM CYTOLOGY: EXFOLIATIVE
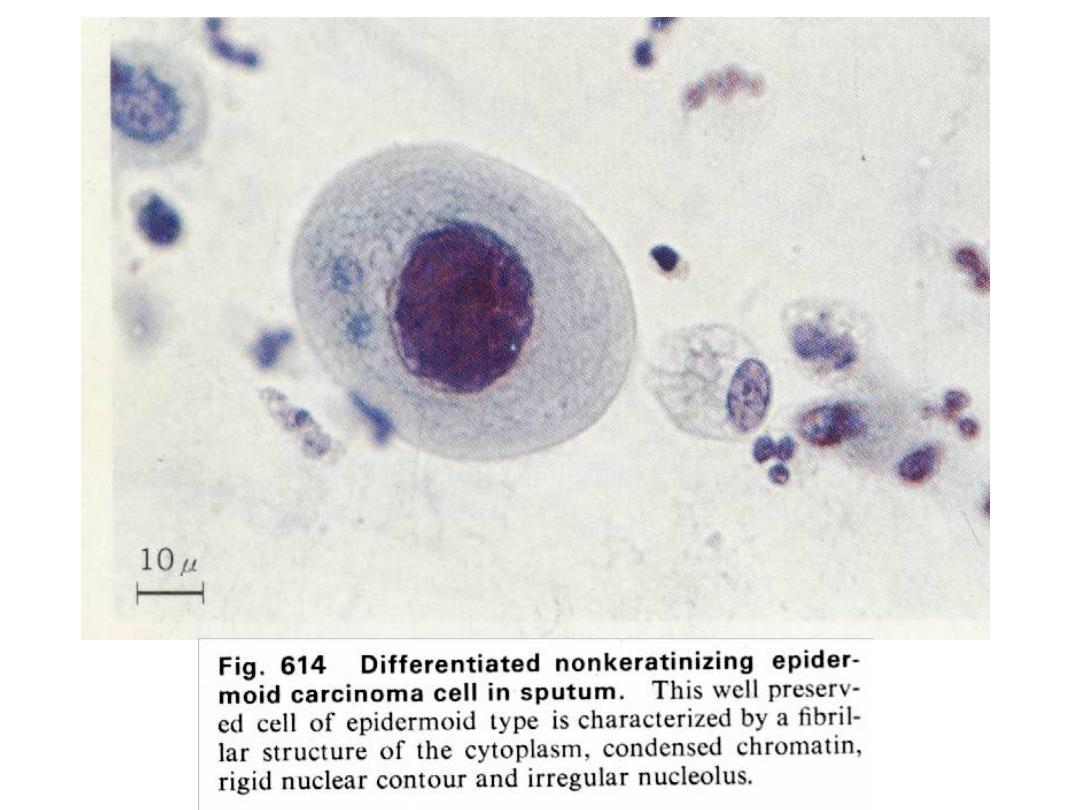
SQUAMOUS CELL CARCINOMA
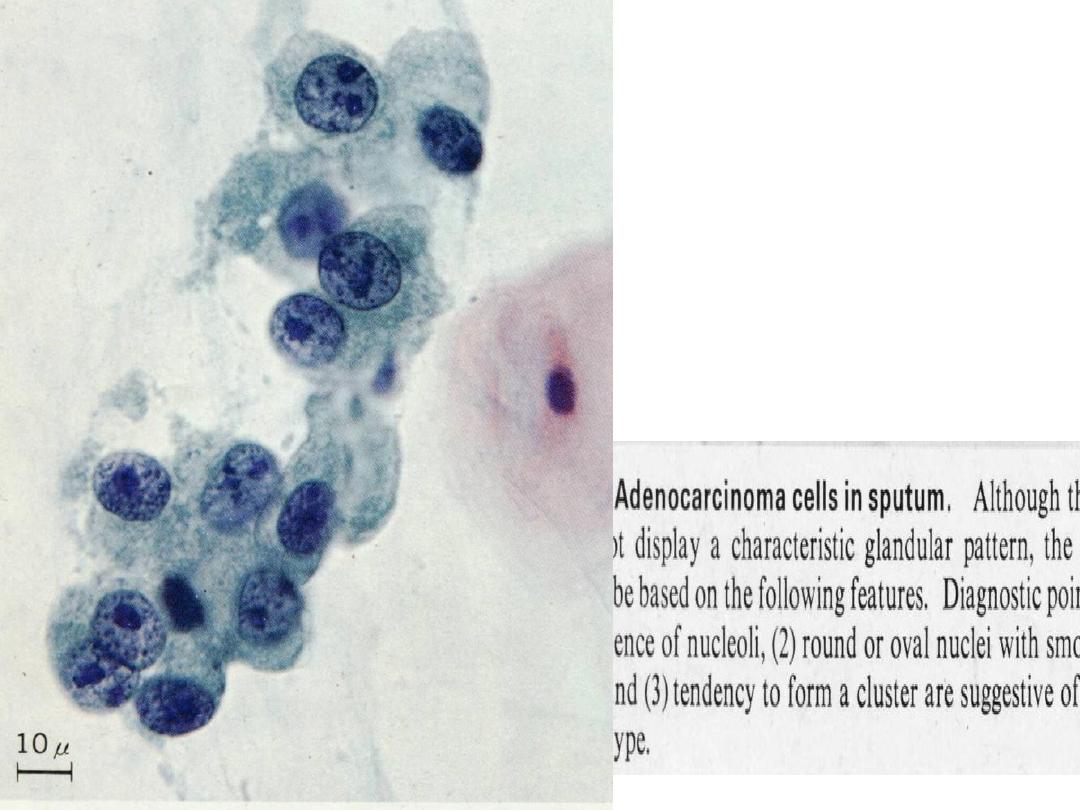
ADENOCARCINOMA
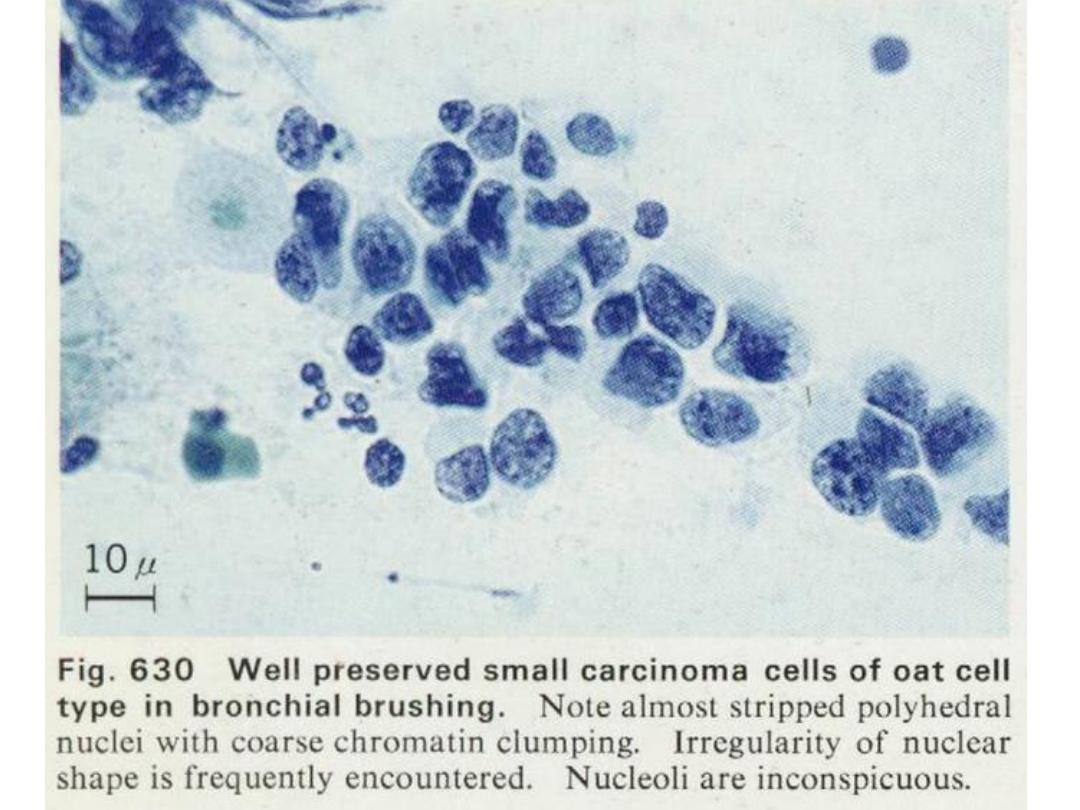
SMALL CELL CARCINOMA
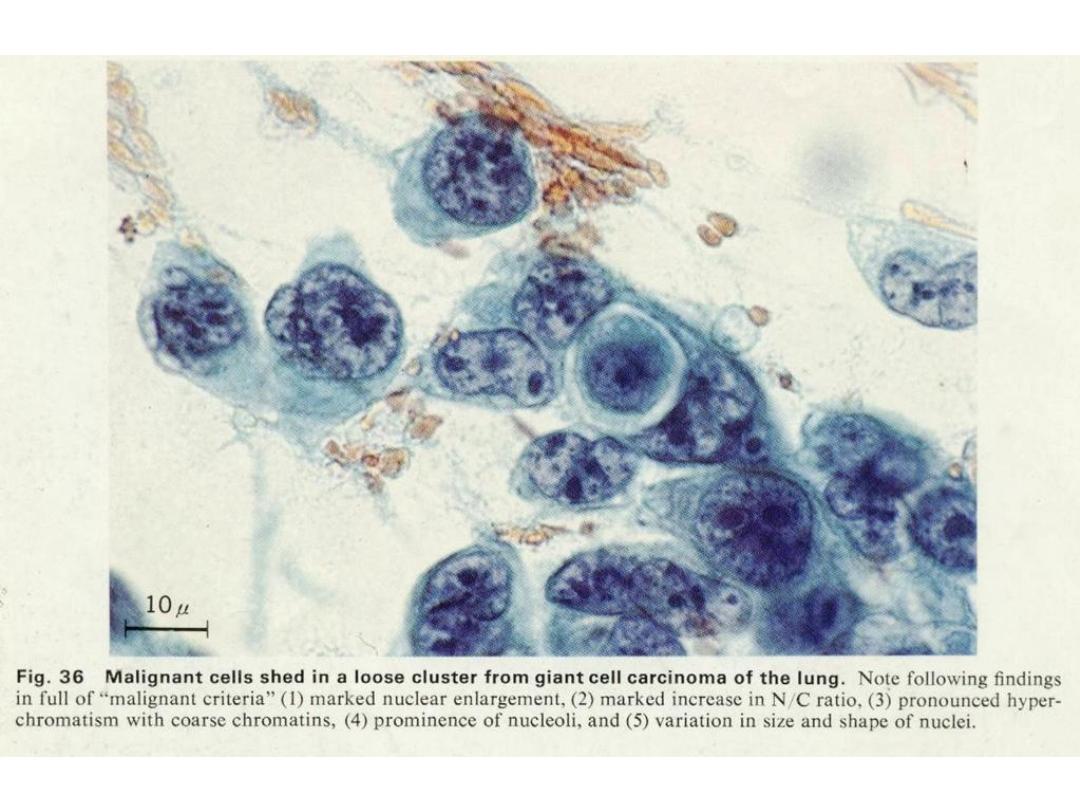
LARGE CELL CARCINOMA
Prof. Nada Alwan
Prof. Nada Alwan

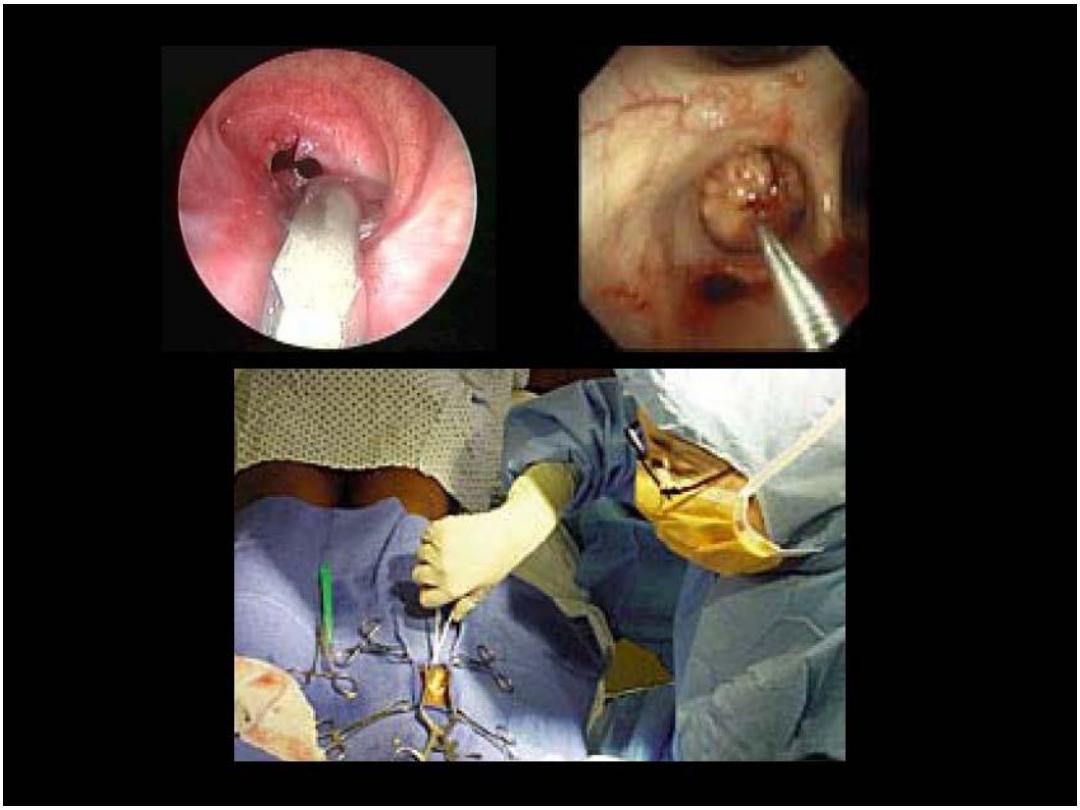
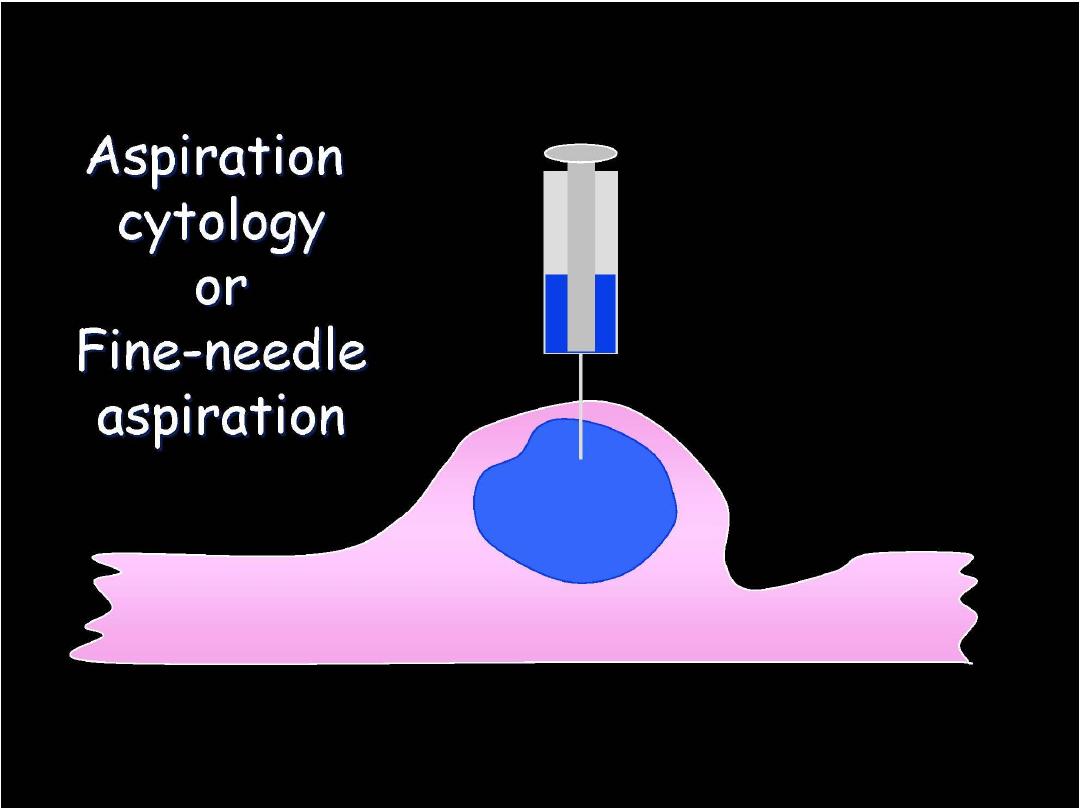
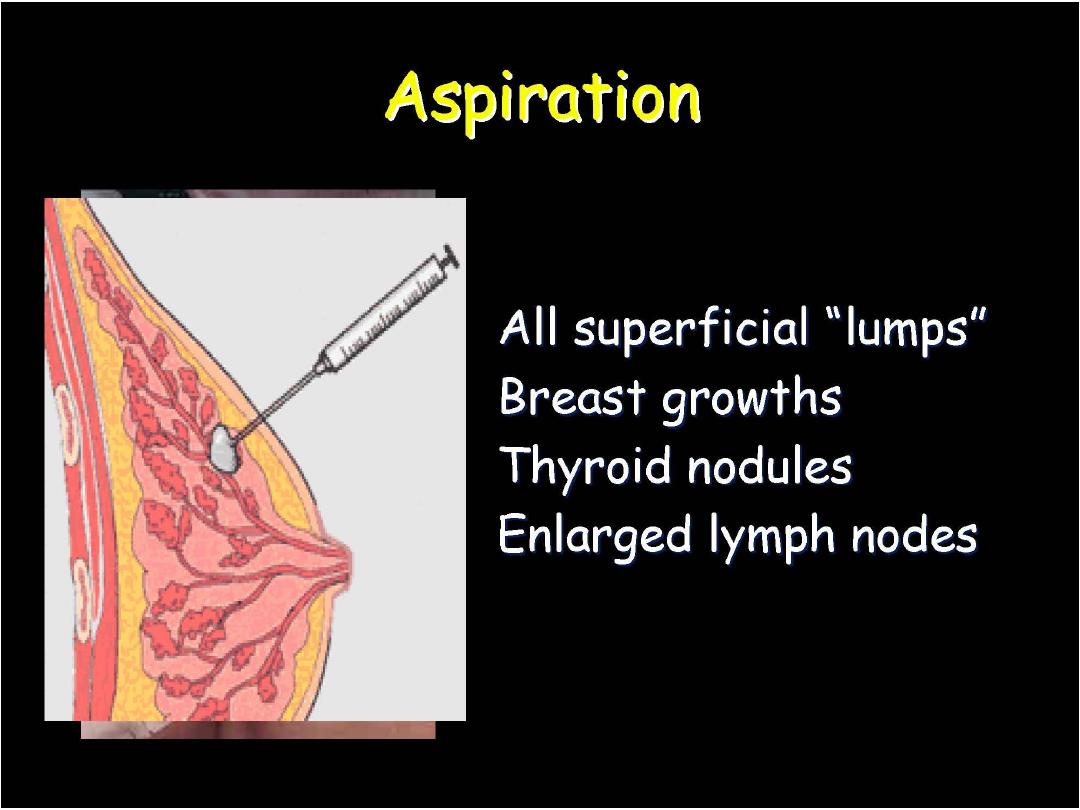
Fine Needle aspiration Cytology
In general, the definitive diagnosis of any mass can be
established by:
Open biopsy,
Tissue core needle (Tru-cut) biopsy,
Fine needle aspiration biopsy.
Compared to FNA, Tru-cut biopsy is a more traumatic
procedure which should be performed under local
anaesthesia. It requires more time and special
equipment that are more expensive. Pain, discomfort
and bleeding are common complications.
Prof. Nada Alwan

Fine Needle aspiration Cytology
FNAC, on the other hand, provides many
advantages to the surgeons:
It is an
easy, reliable, cost effective diagnostic
technique which can give
rapid results
.
The procedure could be performed in an office
setting
without anaesthesia
. It is usually
not
more
painful
than a venipuncture and can be
repeated
immediately if the acquired material
is inadequate.
Prof. Nada Alwan

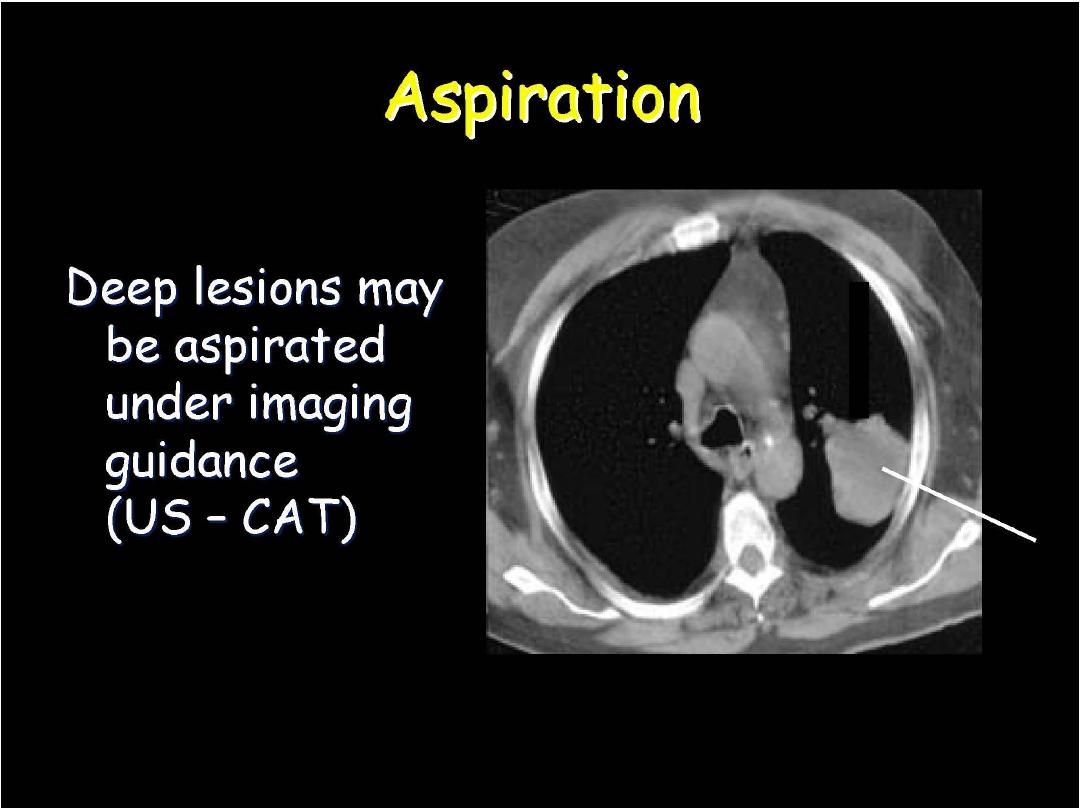
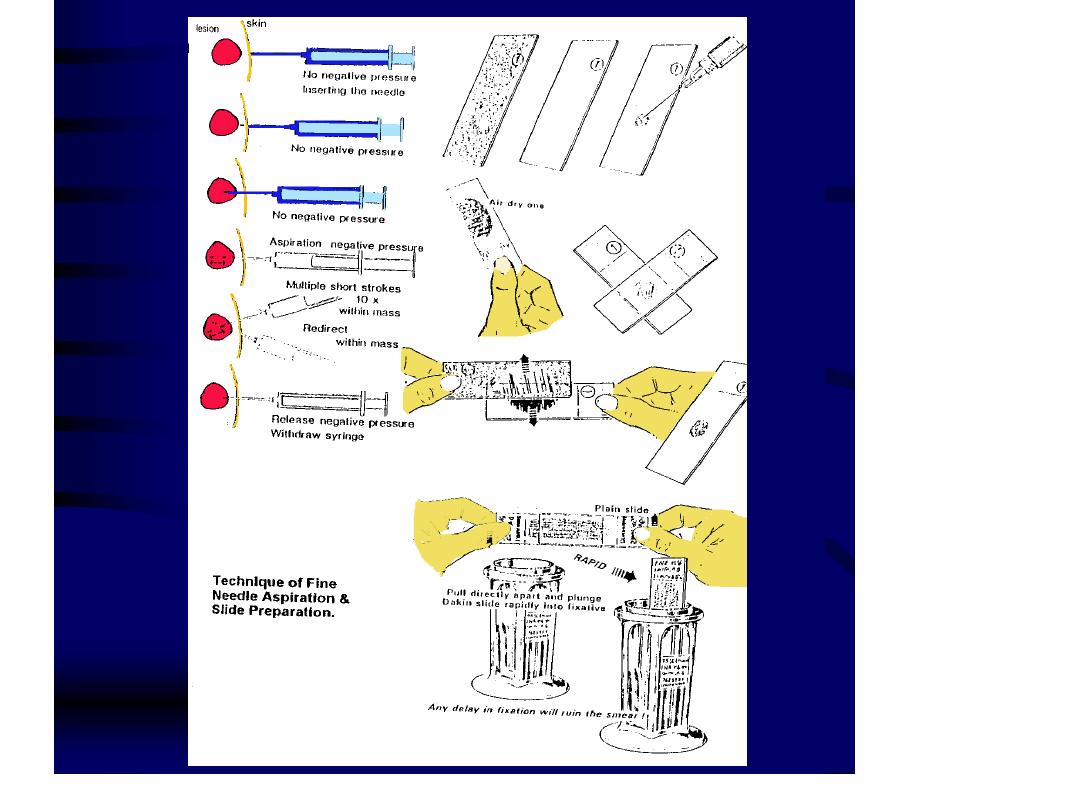
Equipments and Procedure of FNAC:
When reduced to its simplest terms, FNA
consists of:
- Using a needle and syringe to remove
material from a mass.
- Smearing it on a glass slide.
- Applying a routine stain.
- Examining it under the microscope.
Prof. Nada Alwan
Prof. Nada Alwan
n
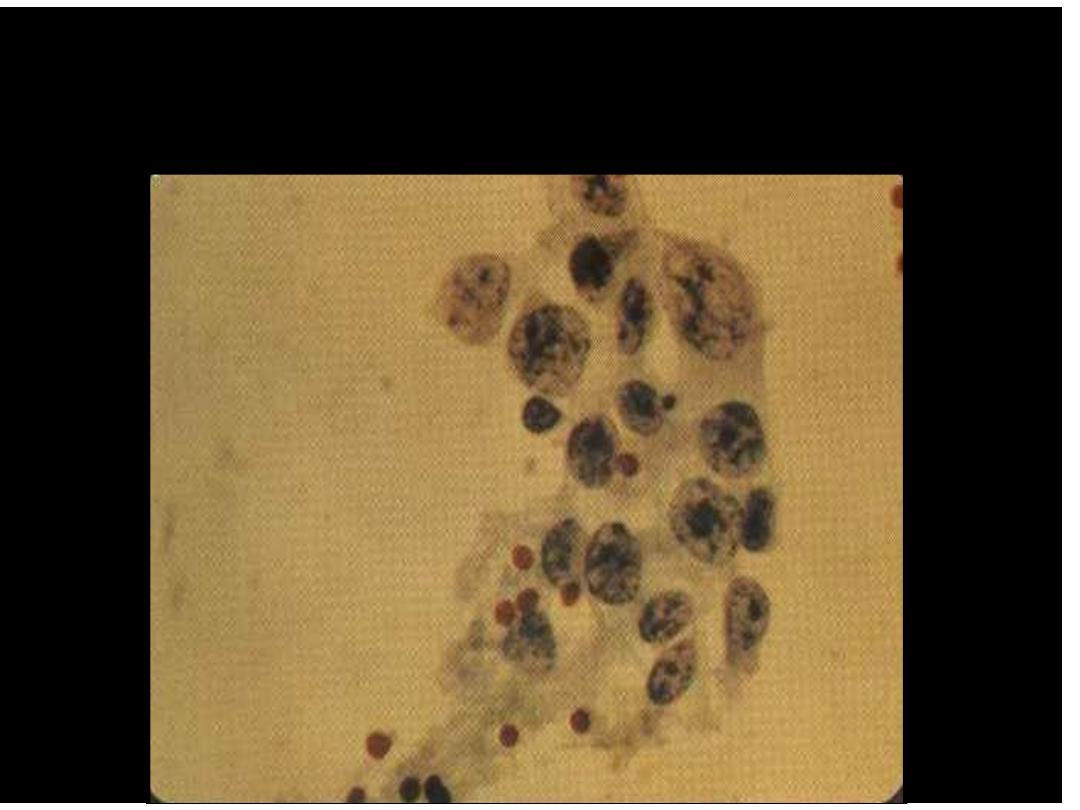
Malignant Mammary Epithelial Cells
Prof. Nada Alwan

Indications for Cytopathology
1. Differentiation between
benign and
malignant lesions
2. Diagnosis of
the type of Malignancy
3. Diagnosis of
premalignant diseases
4. Detection of
inflammation and certain
types of pathogenic agents
5. Study of
hormonal patterns
6. Monitoring of
response to therapy
and
Follow-up of
irradiation
7. Study of
tumour markers
Prof. Nada Alwan
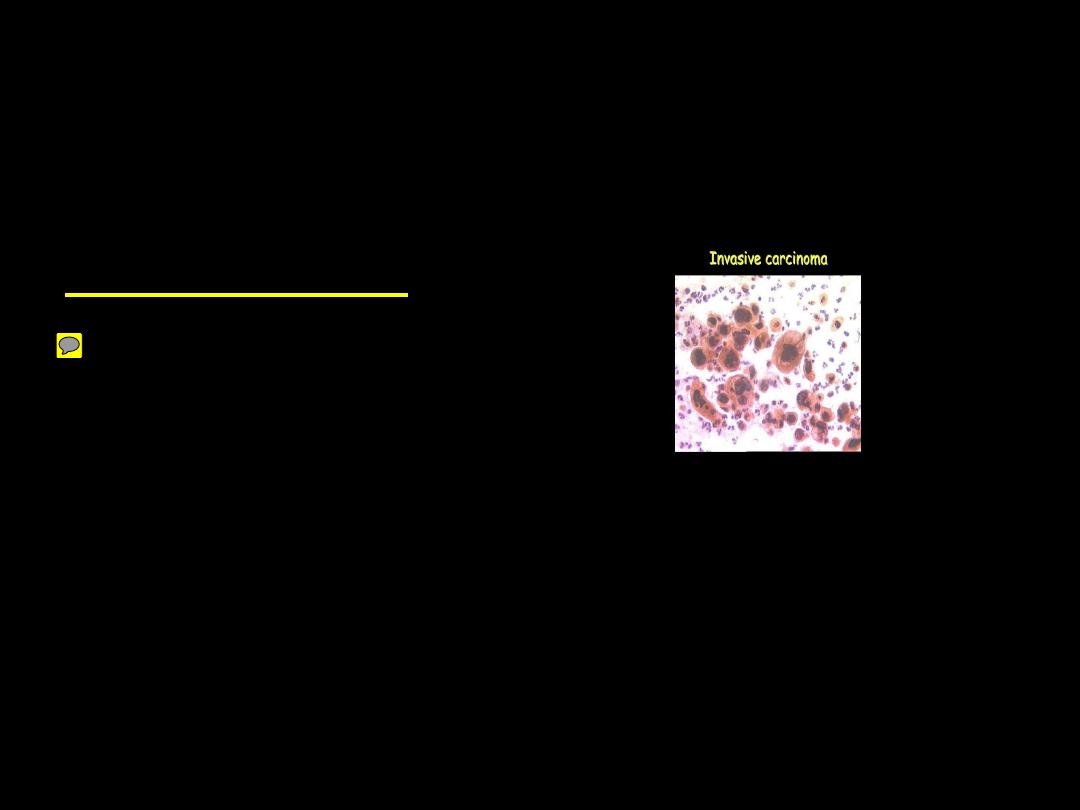
Criteria of Malignancy
How can we detect the presence of malignant cells
cytologically?
Nuclear Changes
Nuclear Hypertrophy
Nuclear Size Variation
Nuclear Shape Variation
Hyperchromatism and Chromatin Irregularity
Multinucleation
Irregularity of Nuclear Membrane
Irregular and Prominent Nucleoli
Prof. Nada Alwan
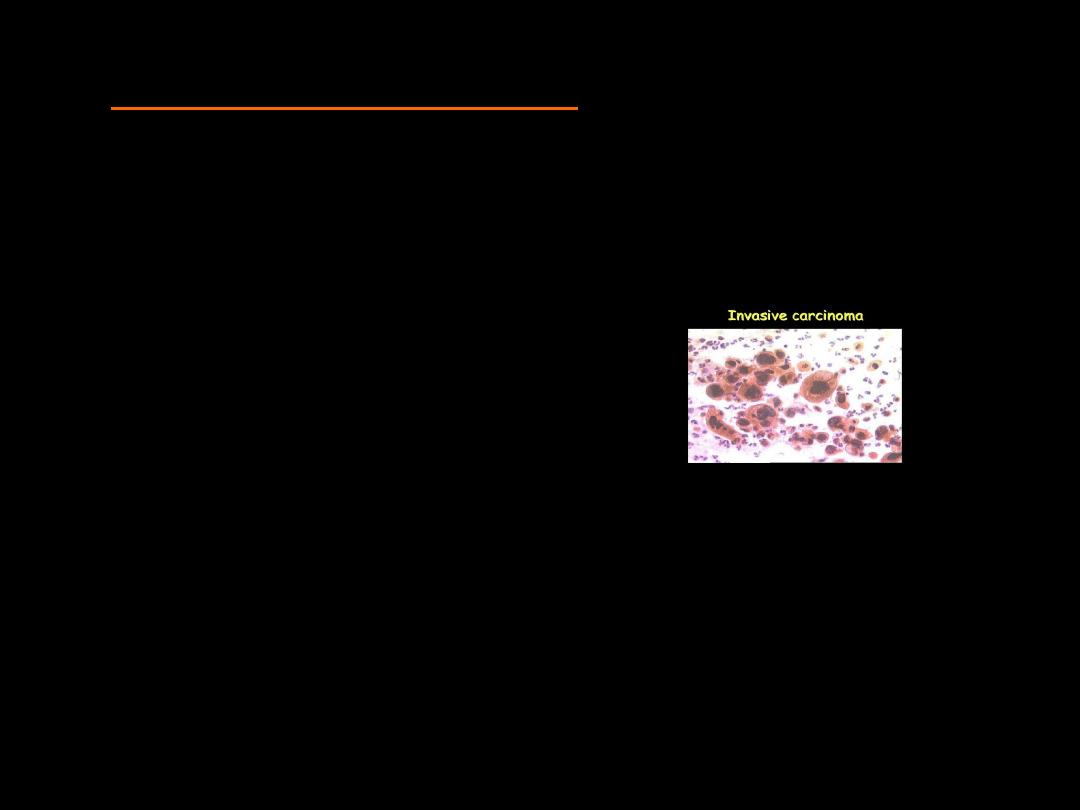
in Malignant Cells
Cytoplasmic Changes
Scantiness
of Cytoplasm
Cytoplasmic
Boundries
(
sharp & distinct in Squamous cell
ca & indistibnct in undifferentiated ca)
Variation in
Size
Variation in
Shape
Cytoplasmic
Staining
( deep orange in keratinizing
squamous ca or basophoilic in immature poorly differentiated
ca)
Cytoplasmic
Inclusions
(melanin pigments in melanoma)
Cytoplasmic & Nuclear membrane relationship
Prof. Nada Alwan

Changes in Cells as a Group in Malignancy
Cellular Phagocytosis or Cannibalism
(indicating
rapid growth of cells within a narrow cavity)
Lack of Cellular Adhesion
(due to abnormalities in
desmosomes)
Abnormal Mitosis
Bloody Background
(fresh blood is meaningless, but
when RBCs are ingested by histeocytes or blood obtained
without trauma)
Foreign Cellular Structures
(ex. psammoma Bodies)
Degeneration and Inflammation
(Tumour Diathesis)
Prof. Nada Alwa
n
